Gonarthrosis (osteoarthrosis, deforming arthrosis of the knee joint) is a degenerative disease that affects the hyaline cartilage covering the condyles of the tibia, femur and patella.
In the later stages of gonarthrosis, the entire joint is involved in the process; the joint space narrows, the underlying part of the bone becomes denser, and bone growths (spikes, osteophytes) appear. The disease usually occurs in patients over 50 years of age and is more common in women.
In some cases (after injuries, in athletes, as a result of certain diseases), gonarthrosis can develop at a young age. The main manifestations of gonarthrosis are pain that increases with movement, limitation of movement and synovitis (fluid accumulation) in the joint.
Gonarthrosis develops gradually over many years. If treatment is not started in time, the pathological process will end with the destruction of cartilage, exposure of bones and complete destruction of the joint. Timely prevention plays an essential role.
General information about the disease and pathogenesis
Gonarthrosis is a type of arthrosis, a joint lesion that occurs in older people or in young people who endure heavy physical activity.
When the joint capsule cannot cope with the increasing load on it, microdamages occur, in the place of which osteophytes grow, leading to a narrowing of the joint space. The disease most often affects large and mobile joints, which bear significant load while walking or running. Example – knee and hip joints, lower back. Gonarthrosis and a healthy joint, comparison
Arthrosis is a common pathology of the musculoskeletal system. More than half of the cases of the disease are associated with damage to the knee joints. Pathological processes in the articular cavity are associated with the following phenomena:
- Due to the disruption of metabolic processes in the cartilage associated with the functioning of the circulatory system, a parallel disturbance of osmotic pressure occurs. An example is that when you squeeze the knee during movement, synovial lubricant is released, and when it relaxes, it is absorbed. When walking, the cartilage plate is constantly nourished, helping to maintain its integrity. If this process is disrupted for some reason, premature or age-related wear of the joint capsule occurs.
- Next, the structure of collagen fibers is disrupted, which causes a loss of shock absorption properties. Against the background of this pathological process, the metabolic function of cartilage cells is disrupted, which significantly slows down the regeneration of cartilage tissue. As a result, the cartilage structure becomes thinner, loses stability and elasticity.
- Against the background of emerging pathological processes, irritation of the synovial membrane subsequently occurs, which leads to the appearance of a chronic inflammatory process. Against the background of long-term inflammation, osteophytes begin to grow, which provokes a decrease in joint mobility.
- Subsequently, there is a gradual destruction of the cartilage with its complete erasure, against the background of which there is a narrowing of the joint space and an increased growth of osteophytes.
Professional athletes and people who work mostly standing all day are more susceptible to this pathology.
Bilateral gonarthrosis can be primary or secondary due to its occurrence. The primary form is not associated with exposure to adverse external factors. In such a situation, bilateral gonarthrosis develops independently, as an age-related degenerative-dystrophic process. Secondary bilateral gonarthrosis of the knee joint is the result of previous bone injuries, substance disorders, cartilage injuries and infections.
Provoking factors
Gonarthrosis is more common in the presence of such unfavorable factors in the patient’s life:
- Metabolic disorders associated with endocrine pathologies (diabetes, obesity, thyroid problems).
- Systemic circulatory disorders, including capillary fragility and varicose veins.
- Increased body weight, which creates additional stress on the knee joints.
- Previous injuries, including torn ligaments, fractures and cracks in bones.
- Previously suffered inflammatory diseases of the joints - arthritis, rheumatism. Typically, arthrosis is already a consequence of inflammatory pathologies in this case.
- Chronic overload of joints associated with excessive loads. Typically, this phenomenon affects athletes involved in running sports - marathon runners and sprinters.
- The presence of serious hormonal disorders.
- A history of chronic knee injuries that do not go away for a long time.
- Heredity.
- The presence of congenital anomalies in the structure of the knee joint.
Persons with bilateral damage to the knee joints respond more severely to therapy, since in this case the possibility of proper movement is seriously impaired.
General signs of gonarthrosis
Arthrosis has a number of classic signs that occur when any joint is affected:
- Feeling stiff and stiff when waking up early.
- The stiffness goes away within an hour of waking up.
- No signs of inflammatory process.
- Discomfort or pain occurs in the knees with the corresponding type of load - climbing stairs or running.
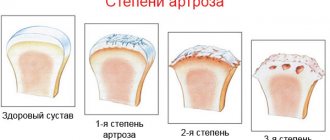
You should also consider the signs of bilateral gonarthrosis, depending on the stage of development. A total of three degrees of the disease are classified.
Symptoms of bilateral gonarthrosis of the 1st degree
The disease develops at first without obvious signs and is almost imperceptible. Most patients rarely notice signs of stage 1 disease. If symptoms appear, they are minor. Occasionally, joint pain appears alternately during physical activity. At the initial stage, the appearance of signs of severe stiffness is not typical.
Usually discomfort occurs when walking for a long time or climbing stairs. If you sit down to rest, the discomfort disappears. In rare cases, patients note slight stiffness in the knees after sleep, which goes away within a few minutes when the person walks.
Gonarthrosis in the picture
A characteristic sign indicating the development of arthrosis is the presence of starting pain, which appears when taking the first steps after waking up. Less commonly, slight swelling is observed, indicating the development of an inflammatory process in the knee joints. Since there is no obvious deformation yet, the swelling goes away on its own. It is impossible to cure bilateral gonarthrosis, since both legs are affected, but in the initial stages of development, degeneration can be slowed down if the pathology is noticed in a timely manner.
Signs of bilateral gonarthrosis of the 2nd degree
At this stage, the manifestations become obvious and painful, so the person already pays attention to them. The pain becomes bright and pronounced, often occurring not only during stress, but also at rest. Discomfort is most often localized in the area of the anterior and posterior thighs. In the morning, there is obvious stiffness and limited range of motion in the joints, so it is difficult to bend the leg. A characteristic crunch also appears. At this stage, most patients consult a doctor for treatment.
It is important to pay attention to pain. If the joint is affected, then with active inflammation there is an accumulation of fluid in the knee area, which is why the first and second legs begin to bend poorly due to discomfort. The swelling resembles a ball in shape, most often they vary in size. When making complex movements (turning the leg to the side or a sharp lunge), pain is observed that is similar in nature to a pain and aching sensation. If bilateral gonarthrosis occurs, it is necessary to improve mobility with the help of drug correction and exercises.
Gonarthrosis 3 degrees
Grade 3 gonarthrosis of the knee joint is a terminal stage and leads to a severe pathological course. Movement is very difficult due to severe stiffness and inflammation in the knees. Since the cartilage is almost completely worn away, there is a strong proliferation of osteophytes and a significant narrowing of the joint space. The lower limbs are also often affected, making it impossible for a person to walk normally. There is severe inflammation, so advanced deforming gonarthrosis leads to severe pain.
Gonarthrosis stage 3
It is possible that a large cartilaginous fragment may appear in the articular cavity at the third stage, called an articular mouse, as a result of which severe pain appears, against the background of which there is an inability to move the limb. There is an almost complete blockade of the joint. If the articular mouse slips back, then the excruciating pain disappears. This form of the disease is treated with surgery.
Characteristic symptoms
At stage 2 of the disease, the vessels in the affected area are already so worn out that the cartilage tissue receives a minimal amount of nutrition and oxygen. This is why the following symptoms appear:
- severe pain after a long rest (start-up pain);
- pain after prolonged stress on the knee (after prolonged standing or long walking);
- drying out of the lower leg muscles on the affected leg due to the fact that the patient instinctively transfers the main load to the healthy leg when walking;
- swelling of the knee without deformation of the joint.
The characteristic distinctive symptoms of exactly 2 degrees of gonarthrosis are: the first signs of deformation of the knees, damage to both knee joints is possible.
Knee deformity due to gonarthrosis
Diagnostic test
To make an accurate diagnosis, it is necessary to conduct a comprehensive study. If arthrosis is suspected, the patient should consult an orthopedic traumatologist. The doctor must conduct a visual examination, listen to the patient’s complaints and send him for instrumental diagnostics.
Different research methods have different effectiveness, depending on the stage of development of bilateral knee lesions:
- X-ray examination. This is a basic research diagnostic method. On an x-ray, you can easily see pathological changes at stages 2-3, indicating the development of arthrosis of the knees. X-rays show growth of osteophytes and narrowing of the joint space, which indicates gonarthrosis. If the patient has just begun a destructive process in cartilage, the X-ray machine may not notice minimal changes.
- CT scan. Allows you to identify knee arthrosis at the initial stage of development. This is an improved type of diagnostics of bones and joints. A CT image is a three-dimensional model of an x-ray image.
- Ultrasound diagnostics. This type of study allows us to identify arthrosis at the initial stage and inflammatory processes in tissues, which can also be affected as complications.
- MRI. This study is prescribed if other concomitant diseases are suspected - arthritis, spondyloarthrosis. When performing magnetic resonance imaging, attention should be paid to the presence of inflammatory processes in the periarticular tissues.
It is equally important to carry out laboratory diagnostics in the form of urine and blood tests in order to identify possible concomitant pathologies in the body. What studies are prescribed:
- General blood analysis. Pay attention if the analysis shows an increase in the sedimentation rate of erythrocytes, leukocytes and lymphocytes.
- Blood chemistry. The results of kidney tests - urea and uric acid - are carefully examined in order to exclude a diagnosis such as gouty arthritis.
- General urine analysis. To determine hidden inflammatory processes in the genitourinary tract.
Based on the data obtained, a final diagnosis is made, after which a treatment regimen is prescribed. Therapy methods are selected depending on the stage of development of the disease.
Treatment of bilateral knee joint gonarthrosis
Depending on the stage of development of the disease, treatment tactics are chosen. At the initial stages, complex conservative therapy is indicated, including the use of medications and physiotherapeutic procedures. If the joints are almost completely worn out, they are replaced surgically and endoprosthetics are performed. In the presence of stages 1 and 2 of the disease, complex conservative therapy with the prescription of medications is indicated.
What medications are prescribed for symptomatic treatment of pain:
- Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. These medications are the first-line pharmacological group of choice, as they have a number of advantages over other drugs - they act quickly, rarely cause side effects during short course use, and are easy to use (it is enough to give an injection or take a tablet 1-2 times a day). People with kidney, heart, and stomach diseases should take NSAIDs with caution. Examples of medications: Diclofenac solution for injection, Ibuprofen tablets.
- Corticosteroids. They can be used in combination with NSAIDs if there is severe pain and inflammation, or used in the form of intra-articular blockades. GCS is prescribed only if the use of non-steroidal painkillers does not help relieve severe pain during exacerbation. Individuals with diabetes, obesity, and hypertension should use corticosteroids with caution. Examples of medicinal names are Hydrocortisone, Kenalog, Diprospan.
- Anesthetics. This type of medication is not taken as a separate drug for the symptomatic treatment of gonarthrosis, but these drugs are always included in the blockade with GCS. Anesthetics have a powerful but short-term anesthetic effect, therefore they complement the work of the drugs included in the intra-articular blockade. During the injection procedure, the needle with the medicine is inserted at an angle, which makes it possible to fully penetrate the joint without touching the soft tissue. The course of treatment is short, it is enough to give 1-2 injections and the pain goes away quickly.
- Muscle relaxants. Often with arthrosis there is a violation of muscle conduction. Some muscles lose tone due to limited movement, which can cause severe spasms at the slightest load. Muscle relaxants reduce nerve conduction, thereby relaxing the pathological spasm.
Additionally, external agents are prescribed - ointments, gels, homeopathic mixtures. When the exacerbation period passes, the patient needs to attend physiotherapeutic procedures.
For preventive purposes, the following medications are prescribed:
- Chondroprotectors. These medications are used for preventive purposes. At the initial stages, chondroprotectors can help eliminate mild discomfort and stiffness that appear against the background of the growth of osteophytes. Regular use of chondroprotectors allows you to slow down the growth of bone masses in the joints. In medical practice, the most effective chondroprotectors are used, which consist of a combination of glucosamine and chondroitin. A specialist may prescribe injections that need to be performed once a day for at least 2-3 months without a break. An example of an effective medication is Rumalon (injected contents are extracts from fish cartilage), Chondrosat, Mucosat. Detailed information on use is contained in the instructions.
- Calcium and vitamin D3 preparations. Persons suffering from diseases of the musculoskeletal system are many times more likely to develop calcium-phosphorus metabolism disorders than a completely healthy person. To eliminate the risk of developing osteoporosis, it is necessary to periodically take calcium and vitamin D3 supplements several times a year. Calcium is the main building material for bones, but without cholecalciferol its normal absorption is impossible. It is especially important to take calcium supplements in the elderly, since their risk of fractures in the presence of bilateral gonarthrosis is significantly increased. An example of medications is Aquadetrim, Kalcemin, Detrimax.
- B vitamins. These drugs are prescribed as part of complex treatment, as they have a general strengthening and tonic effect. In the presence of degenerative-dystrophic diseases of the joints, vitamin complexes support the immune system and improve well-being. Examples of funds are Milgamma, Neurorubin.
Non-drug treatments
One of the most important stages in the recovery of the body after an exacerbation of gonarthrosis of the knees is exercise therapy, physiotherapeutic procedures, and visiting a massage room. Osteoarthritis of the joints often provokes stiffness and decreased range of motion, which leads to an unfavorable prognosis if you do not engage in gymnastics. To develop mobility of the knee joint, you need to do hip flexion and extension every day. This simple action will help develop normal motor range. If there is swelling in the knees, it is better to do the exercises while lying on your back.
Development of grade 3 gonarthrosis
Physiotherapy is an effective set of procedures aimed at eliminating stiffness and chronic pain. The mechanism of action of treatment methods is based on the effect on joints, soft tissues and ligaments through magnetic or current radiation. The device emits a certain frequency, which has a beneficial effect on joints in the presence of arthrosis. To enhance the effect, drugs are prescribed that have anti-inflammatory, restorative and analgesic effects. These may be mixtures of corticosteroids, vitamins, NSAIDs or muscle relaxants. The number and frequency of procedures used depends on the doctor’s orders. Typically, the number of scheduled sessions is determined in advance.
Massage also effectively helps in the treatment of arthrosis of the knee joints. The essence of the method is to relax the tight muscles surrounding the knee. You cannot do massages during an exacerbation. This therapy is indicated during the recovery period, when the pain has passed and remission is observed. Also, with the help of massage, local blood flow improves, which has a positive effect on well-being. The patient begins to move more easily, as the feeling of stiffness subsides.
Exercises for gonarthrosis of the 2nd degree of the knee joint
During the main course of therapy, patients are prescribed to attend exercise therapy classes in groups under the guidance of an instructor. During further rehabilitation after treatment of grade 2 gonarthrosis of the knee joint, gymnastics are performed at home. It is important not to overload the knee with excessive loads, so it is better to choose the following as the most optimal exercises:
| position – lying on your back, legs straightened | Smoothly raise your legs to a height of 20 cm, hold for 10-15 seconds and lower. Repeat 25 times; |
| the well-known “Air bike” | You need to simulate driving at 30-50 revolutions; |
| position – lying on your stomach, legs straightened | Bend your knee and try to touch your buttock. Repeat 25 times; |
| position – sitting on the floor, legs straightened | Without bending your knees, bend forward, trying to touch your forehead to your feet. Repeat 15-20 times; |
| sitting on a chair | Raise the affected leg, without bending the knee, to the maximum possible height, hold for a few seconds, and return to the starting position. |
Prevention
There are no specific preventive measures to prevent knee arthrosis. General precautions include adequate exercise, avoiding overexertion, proper nutrition, and drinking plenty of water. It is important to protect yourself from stress and avoid prolonged sitting or standing in one place. It is also required to wear orthopedic shoes, which relieve stress on the feet, knees, lower back and hip joints. Women are contraindicated from wearing high heels.
Methods that complement drug therapy
Physiotherapeutic procedures
Patients are shown mild methods of treatment, such as: laser treatment, magnetic therapy, EHF therapy. These procedures help improve the supply of nutrition to cartilage tissue.
Massage
It is necessary to improve blood circulation (and at the same time the supply of nutrients and oxygen to cartilage cells) and, judging by reviews of the treatment of grade 2 gonarthrosis of the knee joint, helps relieve pain spasms and has a beneficial effect on the general condition of the whole body.
Orthopedic treatment
It is based on wearing special devices that reduce the load on the knee joint. This could include knee pads, wrapping the pathological area with an elastic bandage, or wearing orthopedic shoes and arch supports.
Diet
It involves reducing the consumption of salt, which retains fluid in the body, which contributes to the appearance of edema. For obese patients, a low-calorie diet is required to combat excess weight. This is necessary to reduce stress on the joint.