This degenerative-dystrophic disease, as a rule, occurs in women after 40 years of age, but men can also suffer, especially those prone to excess weight, prone to frequent hypothermia, involved in active sports or due to injury.
Among all arthrosis, gonarthrosis of the knee joint is the most common.
There is an opinion that the cause of gonarthrosis is the deposition of salts in the joint. This opinion is absolutely incorrect and the deposition of salts is rather a secondary process and is the cause of painful sensations during the development of the disease and is localized in the places of attachment of tendons and ligaments. Prevention plays an important role in preventing the disease.
Anatomy of the knee joint
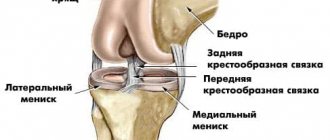
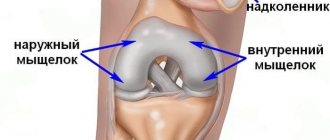
The knee joint consists of two surfaces, which are formed by the tibia and femur. The front of the knee joint is protected by the patella, which moves between the condyles of the femur. The fibula does not participate in the formation of the knee joint and essentially does not bear any functional load, due to which it is often used for the reconstruction of other bone elements in the body.
All articular surfaces: the tibia, femur and the inner surface of the patella are lined with hyaline cartilage, which is very smooth in texture, has a high degree of strength and elasticity, the thickness of this dense and elastic structure reaches 5-6 mm. Cartilage absorbs shock during physical activity, prevents friction and softens impacts.
Orthopedics and traumatology services at CELT
The administration of CELT JSC regularly updates the price list posted on the clinic’s website. However, in order to avoid possible misunderstandings, we ask you to clarify the cost of services by phone: +7
| Service name | Price in rubles |
| Appointment with a surgical doctor (primary, for complex programs) | 3 000 |
| X-ray of bones and joints of the limbs | 2 200 |
| MSCT of the knee joint | 7 500 |
| MRI of the knee joint (1 joint) | 7 000 |
All services
Make an appointment through the application or by calling +7 +7 We work every day:
- Monday—Friday: 8.00—20.00
- Saturday: 8.00–18.00
- Sunday is a day off
The nearest metro and MCC stations to the clinic:
- Highway of Enthusiasts or Perovo
- Partisan
- Enthusiast Highway
Driving directions
In its development, arthrosis of the knee joint goes through the following stages:
- First stage of gonarthrosis
– does not cause significant suffering to the patient, is characterized by intermittent aching or tightening pain, especially after heavy physical exercise or direct load on the knee joint. The so-called “starting pain” symptom appears, when the patient stands up abruptly, painful sensations arise that gradually pass, but if increased stress is placed on the limb, the pain resumes. May manifest as slight swelling, which goes away on its own. Rarely, but it occurs, synovitis - fluid accumulates in the joint capsule of the knee, due to which the knee area becomes spherical and swollen, movements in the limb are limited. At this stage there is no deformation of the joint yet.
- Second stage
– the patient begins to be bothered by prolonged and quite severe pain on the front and inside of the joint, even with light loads, but after a long rest they usually go away. When the joint moves, a crunching sound is heard; if the patient tries to bend the limb as much as possible, sharp pain appears. A limited amplitude in the movement of the joint is revealed, and deformation begins to appear. Synovitis occurs frequently, lasts longer, and occurs with a large accumulation of fluid in the joint.
- Third stage
– causes significant suffering to the patient, the painful sensations are constant and disturb not only while walking, but also during rest and even at night, preventing sleep. The joint is already significantly deformed, the position of the limb becomes X or O-shaped. A waddling gait appears, and often, due to significant deformation, a person cannot not only bend, but completely straighten his leg, as a result of which he has to use a cane or even crutches to walk.
What symptoms will indicate the disease?
Dystrophic changes in the knee joint provoke deformation of the limb.
During the development of the disease, people complain of the following symptoms:
- stiffness of movements in the morning gives way to their complete absence;
- severe pain occurs in the knee when bending the lower limb;
- swelling appears;
- the muscles surrounding the knee joint atrophy;
- Varus deformity of the leg occurs.
Pathology of gonarthrosis of the knee joint
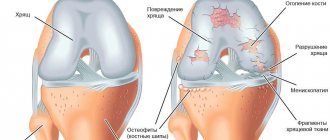
- At the initial, first stage of gonarthrosis, due to the development of a pathological process in the vessels supplying blood to the hyaline cartilage intraosseously, the articular surfaces gradually lose their inherent characteristics. They begin to dry out, lose their smooth texture, cracks appear, which disrupts the sliding of the articular surfaces, they begin to cling to each other, increasing the defects on the surface. Hyaline cartilage degenerates, losing its shock-absorbing function due to constant microtrauma.
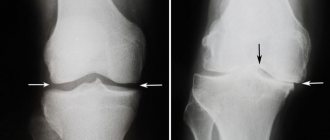
- At the second stage of gonarthrosis, degenerative-dystrophic manifestations increase: the joint space narrows, the articular surfaces flatten, adapting to increasing loads. The part of the bone adjacent to the hyaline cartilage of the joint becomes denser, and along the edges of it osteophytes appear, in the form of an overgrowth of bone tissue shaped like spines. The knee joint capsule also undergoes changes, losing its elasticity. The fluid inside the joint becomes thicker and more viscous, changing its nutrition and lubrication properties, which further impairs the function of the joint. Due to malnutrition, the condition of hyaline cartilage worsens, it begins to disintegrate, and in some places disappears completely. As a result of increased friction, degeneration of the knee joint progressively increases, which leads to the third stage of gonarthrosis.
- At the third stage of gonarthrosis, a pronounced limitation in the range of motion in the joint occurs. The surfaces are significantly deformed, hyaline cartilage is virtually absent, and the bones seem to be pressed into each other.
Prevention
There are no specific preventive measures to prevent knee arthrosis. General precautions include adequate exercise, avoiding overexertion, proper nutrition, and drinking plenty of water. It is important to protect yourself from stress and avoid prolonged sitting or standing in one place. It is also required to wear orthopedic shoes, which relieve stress on the feet, knees, lower back and hip joints. Women are contraindicated from wearing high heels.
Reasons for the development of gonarthrosis
Essentially, it is impossible to determine any single cause of gonarthrosis. Basically, its occurrence is due to a combination of a number of reasons and many internal and external factors.
In 20-30% of cases, gonarthrosis is provoked by traumatic injuries to the knee joints or their components (ligaments, tendons, menisci), as well as fractures of the femur or tibia. The disease usually manifests itself 3-5 years after the injury. But there have been cases of development of gonarthrosis in the early period (2-3 months).
In some patients, gonarthrosis can be triggered by high physical activity. Often, the disease can be triggered by active physical activity, especially after 40 years of age, when people begin to actively exercise to maintain health and realize the need to lead a healthy lifestyle. The greatest load on the joints comes from running, jumping and squats.
Excess weight can also lead to gonarthrosis, especially in combination with varicose veins of the lower extremities. The load on the knee joints increases, and microtraumas or even severe injuries to the menisci or ligaments of the joint occur. In this case, healing is much more difficult, because It is impossible to quickly lose excess weight in order to ease the load on the joint.
The development of gonarthrosis can be provoked by various types of arthritis (gouty, psoriatic, rheumatoid, reactive or ankylosing spondylitis), some neurological pathologies (spinal column injuries, traumatic brain injuries and other diseases that occur with impaired innervation of the lower extremities), as well as hereditary diseases, causing weakness of connective tissue.
Preventive actions
To avoid the development of gonarthrosis, doctors recommend that patients not exhaust themselves with excessive physical activity and lifting heavy objects. In addition, it is important to monitor your body weight. If a person has extra pounds, it is better to get rid of them. Excess weight creates additional stress on the entire musculoskeletal system, including the knee joints. An active lifestyle is also important in the prevention of gonarthrosis. It is recommended to spend more time in the fresh air, take walks, and ride a bike. Swimming lessons, as well as attending massage sessions at least once a year, would also be useful. In addition, it is important for people to monitor their diet by including enough foods that contain vitamins and minerals.
Diagnosis of gonarthrosis
To diagnose a patient with gonarthrosis, a combination of collecting complaints, examination, and X-ray examinations is necessary.
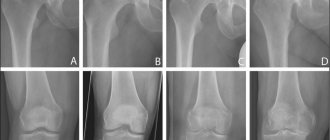
An X-ray image of a joint today is the simplest and most easily accessible research method, with the help of which it is possible to diagnose the patient with a sufficient degree of accuracy, observe the development of the process over time, and determine the tactics of further treatment. Among other things, an x-ray allows you to make a differentiated diagnosis, for example, to exclude a tumor process in the bone tissue of the thigh or lower leg or an inflammatory one. Also, to diagnose gonarthrosis, computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging are used, which can show changes not only in bone structures, but also in soft tissues.
In old age, everyone has certain signs of gonarthrosis, so a diagnosis can be made only after a complete collection of anamnestic data, complaints and visual examination, as well as instrumental research methods.
Stages and their clinical manifestations
It is customary to distinguish three stages of development of this disease, which are manifested by different symptoms and dysfunction of the knee joint:
Stage I gonarthrosis
This stage includes clinical manifestations characteristic of the onset of the disease.
As a rule, this is a dull pain localized inside the knee joint and occurs after a long walk. From time to time the knee joints swell, but there is no visual deformation.
Stage II gonarthrosis
This stage is characterized by an increase in existing clinical manifestations:
- the pain becomes prolonged and becomes more pronounced;
- when you move your knee, you can clearly hear a crunch in the joint;
- in the morning there is stiffness in the joints;
- there is a slight limitation in extension and flexion of the joint;
- the size of the joint increases.
Stage III gonarthrosis
At this stage, all the symptoms are fully manifested:
- pain bothers you constantly - both during exercise and at rest;
- restrictions on joint extension and flexion are clearly expressed;
- gait is disturbed;
- the knee joint is noticeably enlarged and deformed.
Gonarthrosis 3 degrees
IV stage of gonarthrosis
Grade 4 gonarthrosis is one of the stages of the disease, which is characterized by the development of degenerative processes in the knee joint.
Gonarthrosis 4 degrees
Treatment of gonarthrosis of the knee joint
When the first signs of a knee joint disease appear, you should consult an orthopedic doctor as soon as possible. At the initial stage of the process, the doctor prescribes drug therapy and complete rest of the affected limb.
After the acute period has subsided, it is possible to prescribe:
- exercise therapy course,
- massage,
- as well as physiotherapeutic procedures (electrophoresis with analgesics, UHF therapy, magnetic or laser therapy, phonophoresis with steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, mud treatment, etc.)
At the next stage of treatment, the doctor may prescribe drug therapy, which involves taking chondroprotectors that stimulate metabolic processes in the joint. Sometimes intra-articular injections with hormone-containing drugs are required. If the patient has the opportunity to receive sanatorium-resort treatment, it is recommended to him. Often, the patient is recommended to use a cane when walking to unload the joint. You can use special orthopedic insoles or orthoses for prevention.
If the patient is diagnosed with the third stage of gonarthrosis, in which its manifestations are most pronounced (pain, impairment or complete lack of functioning of the joint), surgical treatment may be required, consisting of knee replacement. Rehabilitation measures until the joint function is completely restored usually take from 3 to 6 months, after which the patient can return to a full life.
How is the treatment carried out?
Conservative therapy
Anti-inflammatory medications quickly and effectively relieve pain.
Most doctors are convinced that stage 4 gonarthrosis of the knee joint cannot be cured using conservative treatment methods. Prescribing painkillers only makes it possible to relieve pain for 2-3 hours. With the help of medications it is not possible to restore damaged cartilage and components of the knee joint. However, in some situations they still resort to conservative therapy, prescribing the following groups of pharmaceuticals to the patient:
- Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. They make it possible to relieve the inflammatory process and get rid of pain. Ibuprofen is often used.
- Chondroprotectors. Allows the renewal of cartilage tissue. Chondroitin is mainly used.
Sometimes intra-articular injections are used, which have an immunosuppressive and anti-inflammatory effect. When the inflammatory process subsides, hyaluronic acid is injected into the joint.
Surgical intervention
During the operation, a complete joint replacement is performed.
Surgery is resorted to in most cases when the patient has stage 4 gonarthrosis. Surgery is divided into 2 types:
- Removal of growths that are localized on the joint, as well as deformed elements that prevent it from working normally. Mostly this is a minimally invasive surgical intervention, which is performed using an endoscope.
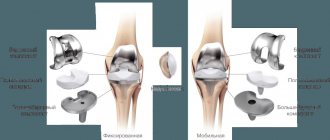
- Endoprosthetics, which is a complete or partial replacement of the knee joint with an artificial implant.
For the treatment of gonarthrosis, which is at stage 4, the following surgical methods are used:
- Arthrodesis. It represents the removal of cartilage tissue that has undergone deformation. This type of operation is used quite rarely, since it does not allow maintaining the physiological range of movements.
- Osteotomy. It involves fixing the lower limb at a different angle.
- Arthrolysis. During surgery, synovial membranes are removed to relieve stiffness.
- Arthroplasty. During the manipulation process, the surgeon forms simplified joint surfaces from the remains of the articulation.
- Endoprosthetics. It can be partial or total, and involves complete or incomplete replacement of the affected knee joint with an artificial prosthesis.
Rehabilitation after grade 4 gonarthrosis
Restorative procedures must be performed under the supervision of a rehabilitation physician.
To avoid postoperative consequences, the patient is prescribed the following medications:
- antibacterial agents;
- painkillers;
- decongestants;
- medications that improve blood circulation.
During the first 24 hours after surgery, people will need to remain on strict bed rest. On the second day, you are allowed to sit down on the bed and do simple exercises to prevent atrophy of the muscle tissue of the limb. The stitches are removed 14 days after surgery, after which the person is discharged from the hospital. It is important that the patient follows all the recommendations of the attending doctor regarding recovery throughout the entire rehabilitation period. He will need to attend physical therapy and engage in physical therapy, combining it with massage.
Physiotherapeutic procedures
For bilateral gonarthrosis, the following physiotherapeutic procedures are used:
- electrophoresis . Under the influence of a constant electric field, charged particles deliver medications (chlorine, anesthetics) to deep tissues, directly to the area of inflammation. The course of treatment is 10–14 days. The duration of one procedure is 30 minutes;
- ultraphonophoresis . Under the influence of ultrasound, drugs enter deep tissues. Combinations of painkillers and hormonal medications are usually used. The duration of the procedure is 10 minutes. The course of treatment can last from 10 days to two weeks;
- infrared radiation . Under its influence, deep tissues warm up (the temperature rises by 1–2 °C), which allows the body to launch recovery reactions. Each joint is treated for about 10 minutes, treatment duration is 7 days;
- laser irradiation . The rays activate cells responsible for restoration processes in tissues. The duration of the procedure is from 7 to 10 minutes. Treatment should last for two weeks;
- magnetotherapy . Exposure to a pulsed magnetic field makes it possible to stabilize the permeability of the cell membrane and normalize metabolic processes in tissues. The course of treatment is 7 days, session duration is 7–8 minutes;
- cryotherapy . Under the influence of low temperature, the body's protective properties are enhanced, which leads to stimulation of recovery and metabolic processes. The duration of the procedure is 10 minutes, the course of treatment is 10 days.