- Carpal tunnel syndrome
- Stages
- Fresh damage
- Benefits of Arthroscopy
- Old partial damage
- Recovery after surgery
- Is treatment possible without surgery?
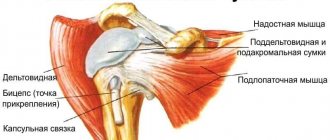
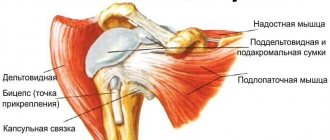
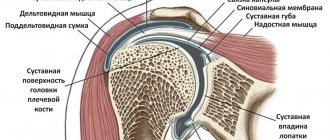
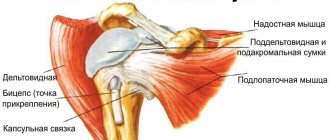
The supraspinatus muscle is part of the rotator cuff. This is a group of muscles that provide rotational movements in the joint and maintain its stability. The supraspinatus muscle stabilizes the confluence of the scapula, thereby forming the point of rotation of the shoulder. If it is damaged, lifting the shoulder joint and maintaining it in abduction becomes impossible.
Carpal tunnel syndrome
Tunnel syndrome
With long-term existence of rotator cuff tunnel syndrome, degeneration of the supraspinatus muscle occurs. Subsequently, its tendon is damaged. To prevent pathological changes, decompression of muscle tissue is required.
Symptoms of this condition:
- chronic pain;
- violation of active movements in the shoulder joint.
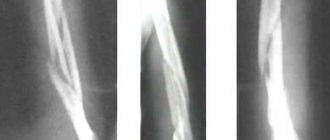
X-rays and MRI show an increased size of the acromial end of the clavicle and a degenerative change in the supraspinatus muscle of the shoulder. Treatment for this disease is only surgical. It should be performed as early as possible to avoid significant damage to the tendon.
Forecast
As a rule, a favorable prognosis for eliminating the above ailment depends on the approach of the patient himself. Since tendinitis of the shoulder joint is a common and dangerous pathology, treatment procedures should be started early. That is, as soon as you notice any signs of the disease, you must immediately see a doctor, since even minor discomfort can be fraught with serious complications. Moreover, it is necessary to strictly adhere to the drawn up treatment plan, regularly perform therapeutic exercises, take prescribed medications and do restorative massage.
Unfortunately, if you are inattentive to your own health and the disease progresses to an advanced stage, you risk getting an atrophied and completely devoid of mobility joint.
By contacting our medical center, patients can count on an individual approach to the problem, the use of innovative equipment of European quality, selection of the most effective methods for eliminating supraspinatus tendinitis and affordable prices for services.
Stages
At stage 1 (compression stage) of rotator cuff injury, the patient experiences pain when trying to perform full movements in the shoulder joint. The glenohumeral rhythm is maintained. At rest there is no pain or it is mild. There is no pronounced hypotrophy in the supraspinatus fossa of the scapula.
At this stage there are still no significant destructive changes in the supraspinatus muscle. However, X-rays already show pathological changes in the distal end of the clavicle and the acromial clavicular joint. On MRI you can see compression of the supraspinatus muscle in the canal, its funnel-shaped deformation.
At stage 2 (degeneration stage), the strength of the supraspinatus muscle decreases. As a result, there is no adequate stabilization of the humeral head. Dysfunction of the initial stage of arm abduction is noted. The head of the humerus moves upward. Main complaints from the patient:
Shoulder head
Shoulder head
- inability to fully perform active abduction movements in the shoulder;
- pain at rest, worsening with exercise.
Objectively, there is a violation of the glenohumeral ri). MRI reveals signs of hypotrophy of the supraspinatus muscle. It is compressed by the distal portion of the clavicle. With prolonged untreated syndrome, degenerative processes in the surrounding soft tissues progress.
At stage 3 (anatomical damage stage), pseudoparalysis of the shoulder joint syndrome occurs. Active movements are possible, but they are insignificant in amplitude and are provided mainly by the scapula. External rotation of the shoulder becomes impossible with minimal resistance. Deforming arthrosis of the acromial clavicular joint often develops.
Preventive actions
As you know, it is better to prevent pathology than to treat it for a long time.
Thus, in order to exclude pathological processes in this area, the following useful recommendations should be followed:
- Regularly perform physical exercises aimed at increasing the strength of ligaments and muscles;
- Warm up before any physical activity;
- It is necessary to ensure optimal load;
- Increasing the intensity of loads should occur smoothly.
It is also recommended to visit a specialist as a preventive measure. The success of the treatment measures is influenced, first of all, by strict adherence to the doctor’s instructions.
Fresh damage
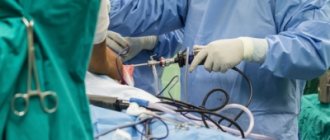
Treatment results are best for a rupture of the supraspinatus muscle of the shoulder that has occurred recently. In this case, the operation of choice is subacromial decompression of the joint. The disease is accompanied by chronic pain syndrome, which is associated with inflammation of the supraspinatus muscle of the shoulder. Treatment can be carried out arthroscopically. This is a minimally invasive operation with a short recovery period and low surgical risks.
Arthroscopic subacromial decompression is performed with the patient lying on the healthy side. The doctor examines the cartilage of the articular surfaces, assesses the condition of the biceps tendon, synovium, and rotator cuff muscles. If degenerative changes are detected, the doctor treats the superficial areas with cutters.
Then the doctor performs an inspection of the subacromial space and excises the subacromial bursa (joint capsule). The entire coracoacromial ligament is removed. Up to 1 cm of the anterioinferior section of the acromion is removed.
To identify and treat possible tears in muscle tissue and areas of fibrosis, the outer surface of the rotator cuff is examined. The distance from the attachment of the rotator cuff to the greater tubercle of the humerus to the distant edge of the acromion is measured. It should be 3 mm or more. In this case, there will be enough space for the tendon, and movements in the shoulder will become painless.
After surgery, the drains are removed after 12 hours. Shoulder immobilization lasts up to 2 weeks. It is advisable to begin restoration measures already on the second day. First, passive movements are carried out, then active ones. As a rule, as a result of successful decompression, the pain syndrome goes away. Therefore, the normal range of motion in the joint is restored without pain.
In the future, gymnastics is indicated to restore the muscles of the shoulder girdle. Full restoration of shoulder function occurs 2 months after surgery.
Symptoms
Patients consult a doctor complaining of severe shoulder pain. Discomfort occurs with certain movements: when reaching out and raising an arm, lifting a light or heavy object. In the case of throwing movements, the pain intensifies and has an acute form. Often patients indicate discomfort at night, for example, when turning towards the affected area during sleep.
As the disease actively spreads, the pain becomes intense and manifests itself even with light movements without the active participation of the shoulder joint. For example, during a handshake, trying to take a small object.
Gradually, stiffness in movement and limited joint mobility appear. Depending on the form of tendinitis of the shoulder joint, the symptom is defined as a crunch.
In the later stages, the patient regularly experiences regular pain, even at rest. Irradiation is observed along the anterior and outer surface of the shoulder. On palpation, pain occurs in the area of the intertubercular groove, the anterior edge of the acromion. Movements are constrained.
Shoulder tendonitis symptoms and treatment are as follows:
- Localized pain. However, unlike osteochondrosis, it manifests itself when performing certain movements. It can be aching, dull, sharp, depending on the stage of its progression;
- On palpation, the pain and inflammatory reaction intensify due to the penetration of bacteria. The density of tendon tissue decreases, which is determined by the thickening of the joint capsule;
- The affected area has swelling with redness of the skin;
- The presence of purulent masses in severe forms of the disease;
- Stiffness of movements.
You can suspect problems with the shoulder joint by the presence of a characteristic creaking sound in the shoulder. Gradually, the patient cannot lift even a small load. The arm does not rise above 90 degrees and does not go behind the back. Depending on the form of the disease, symptoms may vary.
Benefits of Arthroscopy
Benefits of Arthroscopy
- less blood loss;
- smaller incisions and better aesthetic effect;
- patient recovery takes less time;
- less postoperative pain;
- the duration of the operation is reduced;
- its labor intensity has been reduced.
As a rule, pain caused by compression of the supraspinatus tendon goes away immediately after decompression.
Old partial damage
Long-term partial damage to the tendon of the supraspinatus muscle of the shoulder can lead to a long-term limitation of the range of motion in the shoulder joint and the inability to perform full abduction of the upper limb. Treatment requires surgery.
Partial damage to the rotator cuff results in an increase in the length of the supraspinatus tendon over time. As a result, it becomes functionally inferior. The person cannot actively abduct the shoulder, although the amount of passive movement (performed by the therapist's hands) is usually maintained. The more the tendon is changed, the more pronounced the limitation in abduction of the limb.
If the tendon of the supraspinatus muscle of the shoulder is damaged, treatment is carried out using different methods:
- medial movement of the muscle to eliminate functional deficiency;
- osteotomy of the greater tuberosity and distal movement until physiological tension of the supraspinatus muscle is created in the state of shoulder abduction;
- lower wedge-shaped resection of the acromial process of the scapula, excision of the acromiocoracoid ligament to increase the subacromial space and eliminate pain (the ability to actively abduct the shoulder is not restored).
If a tear of the supraspinatus muscle of the shoulder occurs, treatment should be carried out as early as possible. It will be much more effective if, by the time of the operation, significant degenerative changes in the tissues and lengthening of the tendon have not yet occurred.
Recovery after surgery
Recovery after surgery
- complete restoration of function of the shoulder joint;
- reduction of periods of incapacity for work;
- elimination of pain syndrome;
- eliminating muscle spasms;
- increasing muscle strength;
- eliminating stiffness.
After surgery, external immobilization of the shoulder is indicated. For different surgical interventions, the timing of immobilization is different. They can be from 2 days to 1 month. During this period the following are shown:
- isometric muscle tension of the forearm and shoulder;
- movements in the elbow and wrist joint.
Exercises are needed primarily to normalize blood circulation in the limb, which ensures full regenerative processes and helps eliminate swelling. Exercises are performed an average of 10 times during the day, 10 repetitions each.
Almost all patients experience impaired active shoulder abduction after removal of the immobilizing bandage. It is due to a number of factors, primarily:
- long-term lack of stress on the muscles;
- decrease in their tone and contractility;
- hypotrophy (decrease in volume) of muscles.
Further rehabilitation procedures are aimed at strengthening the muscles of the shoulder girdle and normalizing the function of the joint. For this purpose, physical therapy and physiotherapy are carried out.
Diagnostics
In the treatment of tendonitis, it is important to timely and correctly diagnose the pathology. To confirm one form or another, a number of tests are prescribed after examining the patient. The disease can be determined through the following examination options:
- Magnetic resonance imaging;
- Ultrasound of the joint;
- X-rays.
To detect metabolic disorders in the body, as well as determine other negative effects, a biochemical blood test is performed. Such tests are carried out at the Yusupov Hospital clinic. After visiting the consultation, the patient can immediately carry out all the necessary tests on site using the new equipment. Quick diagnosis allows you to immediately apply a treatment method and prevent the spread of pathology throughout the body.
Is treatment possible without surgery?
It has been established that injuries to the supraspinatus tendon practically do not regenerate. Therefore, most patients require surgical treatment. It is successful in 85% of cases. However, quite often relapses occur, limiting the patient’s ability to work and requiring repeated operations.
If the supraspinatus muscle of the shoulder joint is damaged, treatment can be conservative if we are talking about stage 1 of the pathological process. Functional rest, physical therapy, and physiotherapy are indicated.
Platelet-rich plasma is used to repair the tendon. Platelets secrete several anabolic and trophic factors that promote damage healing. These cells contain growth factors: