Elbow bruises are common in street, sports, and household injuries. This is a closed mechanical injury to soft tissue without visible disruption of the integrity of the skin. It usually appears when struck by a blunt object or a fall and is accompanied by rupture of small vessels, hemorrhage into soft tissues, as well as damage to ligaments, muscles, and the neurovascular bundle.40
With bruises, damage can occur not only to soft tissues, but also to the bones of the joint. Such injury in some cases is complicated by synovitis, bursitis and other pathologies.40
Causes of injury
Before diagnosing the problem, determining effective treatment, reducing rehabilitation time and forming competent prevention of the development of complications, the orthopedic surgeon will take into account the causes. Diagnostic manipulation requires an understanding of the anatomy of the affected area, which consists of 3 joints, 4 muscle groups, several nerves and 2 sets of ligaments.
Among the common reasons when a bruise of the elbow joint is diagnosed are:
- increased loads , mistakes during sports (skiing and swimming, golf and boxing, gymnastics and weightlifting, tennis, football, etc.);
- extreme events , travel in the mountains, caves;
- negligence while staying in a water park or other entertainment complex with rides, swings, swimming pools;
- solving everyday problems , carelessness when performing actions that are directly related to the profession, work;
- accidental falls on the street , for example, during icy conditions;
- swimming in prohibited places;
- high-altitude work , facade repairs, when safety precautions are partially complied with;
- experiments with parkour , high-speed overcoming of obstacles;
- blows with blunt objects, fights;
- transport accidents ;
- unsuccessful trips on a bicycle, scooter, skateboard, hoverboard;
- falling from a small height (from steps, curbs, fences, garage roofs, etc.).
There are a huge number of reasons when an adult or child hurts their elbow. But even an accurate independent determination of this fact will not help to quickly solve the problem without medical advice. Self-medication in most cases leads to prolonged therapy, often the development of complications, and deterioration of well-being. It is better to immediately abandon the idea of waiting until it goes away on its own or using medications recommended by the pharmacy worker.
Only a doctor, having collected an anamnesis and examined the affected area, can advise what to do next. It is good if the patient, at the first appointment, tells in detail about the cause and circumstances under which the elbow was injured. This will make it much easier for a medical specialist to recreate the picture of what is happening and, taking into account the age and concomitant chronic diseases of a particular patient, to select effective therapy.
The clinical picture of closed elbow injuries is varied and depends on the causes of the problem. In the first stages of symptoms, painful discomfort of varying intensity most often occurs. Unpleasant sensations can be mild, aching, pressing, tingling, pulsating, with a burning effect inside. The severity of the symptoms depends on the resulting disorders, including hemorrhages, sprains, as well as on the measures taken by the victim in the first minutes after the incident.
Symptoms of a bruised elbow may include:
- small or large swelling in the bruised area;
- increased skin temperature around the elbow joint;
- the occurrence of painful sensations when trying to bend or straighten the elbow;
- bruises, which signal the opening of bleeding in the muscles and subcutaneous fat;
- decreased motor activity of the hand due to a pinched nerve.
At risk:
- children of all age groups, teenagers;
- elderly people (over 60 years old);
- people with pathologies of the visual, vestibular, and musculoskeletal systems;
- athletes (football players, hockey players, tennis players, volleyball players, skiers and other participants in competitions where physical activity is required);
- extreme sports enthusiasts (climbers, parkourists, racers);
- workers of enterprises (factories, mines, factories), where compliance with safety regulations plays a vital role.
An injury in the form of a bruise does not have any specific symptoms, so it would be possible to determine the type of injury at home, prescribe effective treatment and reduce the risks of worsening the situation. Therefore, experiments are not appropriate. Especially if the problem is diagnosed in a child, the elbow is re-injured, and there is a sharp pain that is almost impossible to endure.
Causes of severe pain from a bruised elbow
Severe pain is an important signal for an emergency response. It is necessary to seek medical support as soon as possible, preferably from an experienced orthopedic surgeon.
A severe symptom may appear immediately after an injury, a blow with a blunt object, or a fall from a height. Often acute pain occurs some time after the incident. It happens that initially there is almost nothing to worry about, but signs of a problem appear after 1-2 days, sometimes after 5 days.
When the elbow hurts severely after a bruise, a doctor’s consultation is not planned, effective and safe medications are not used, serious complications may develop, for example:
- Bursitis. This is an inflammatory process, the localization of which concerns the mucous bursae in the joint area.
- Hemarthrosis. This is a hemorrhage into the joint cavity resulting from vascular ruptures.
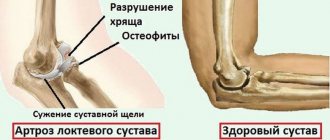
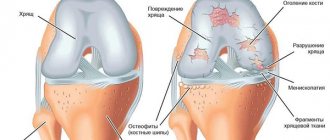
This is not a complete list of possible causes of severe pain. In any case, with complications or severe cases, tissue nutrition is disrupted. In the future, this often leads to deforming osteoarthritis (pathological damage to articular cartilage) and limited joint mobility.
Anatomical features
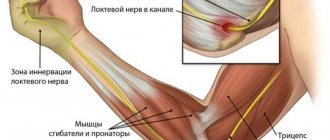
The elbow joint is represented by a movable connection of three bones: the ulna and radius (which make up the forearm) with the humerus.
The elbow joint has a complex anatomical structure
The joint connects three bones to form three simple joints that are enclosed in one capsule. Therefore, according to its structure, it belongs to complex joints.
The simple joints that form the elbow are:
| Joint | Description |
| Humeral-ulnar | Movably connects the humerus and ulna bones |
| Brachioradial | Connects the humerus to the radius |
| Proximal radioulnar | Connects two bones of the forearm in the ulnar region: the radius and ulna |
Thanks to these joints, the following types of movements are possible:
- flexion and extension of the limb around the frontal axis;
- rotation of the radius around a vertical axis (inward and outward movement).
Three bones with three joints combine to form one complex elbow joint to form the joint capsule.
The joint capsule or bursa is one of the most important elements of any joint, ensuring their tightness. It consists of dense fibers, including the ligamentous apparatus and tendons of adjacent muscles.
Functions of the joint capsule:
- ensuring the tightness of the articular cavity and the strength of its walls;
- secretion of synovial fluid - a kind of lubricant necessary for the normal functioning of the joint, which is carried out by providing nutrition, hydration and minimizing friction of the articular surfaces.
The articular capsule of the elbow joint is strengthened by the auxiliary ligamentous apparatus, which includes two ligaments - the radial and ulnar collateral.
Blood supply and innervation
The joint receives the necessary nutrition from arterial blood, which passes through the articular network of the elbow. The articular network is formed from two larger arteries - the superior and inferior ulnar collateral, which, in turn, originate from the large brachial artery.
Nutrition also comes from the branches of the ulnar, deep brachial and posterior interosseous arteries. Venous outflow occurs through the arteries of the same name. In the elbow area there are lymph nodes from which lymph flows into the deep lymphatic vessels.
The elbow is innervated by branches of three large nerve fibers: the median, radial and ulnar nerves.
Diagnosis of bruises
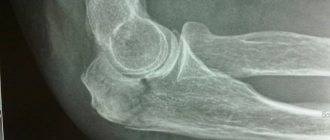
An elbow bruise is identified by the symptoms, a visual medical examination and an x-ray. But these are not all the manipulations through which an orthopedic surgeon will be able to correctly identify the problem and choose the best solution. An appointment with a specialist always begins with an introduction. If the situation is not critical, the doctor will write down personal data and ask about complaints, reasons, and circumstances under which the injury occurred. An anamnesis is being collected. Information about the presence of chronic diseases and disorders of the musculoskeletal system is clarified.
To diagnose when a woman seriously hurt her elbow at home or a man was injured at work, the doctor:
- visually examine the affected area, pay attention to hyperemia (redness), swelling;
- perform palpation, carefully feel the injured area;
- check the level of joint mobility;
- will take into account the degree at which the elbow bends without pain (the optimal indicator is more than 30 degrees);
- If necessary, prescribe x-rays and ultrasound diagnostics.
All these methods make it possible to determine the degree of damage to the elbow joint, make an accurate diagnosis, prescribe complex and effective therapy, and carry out proper prevention of the development of complications.
First information, scientific materials on the topic
- "Emergency Medical Care", ed. J.E. Tintinally, Rl. Kroma, E. Ruiz, Translation from English by Dr. med. Sciences V.I. Kandrora, Doctor of Medical Sciences M.V.Neverova, Dr. med. Sciences A. V. Suchkova, Ph.D. A. V. Nizovoy, Yu. L. Amchenkova; edited by Doctor of Medical Sciences V. T. Ivashkina, Doctor of Medical Sciences P. G. Bryusova; Moscow "Medicine" 2001.
- Joint diseases. Guide for doctors. Mazurov V., 2008.
- Emergency medical care, ed. J. E. Tintinally, R. L. Crome, E. Ruiz. – M.: Medicine, 2001.
- Traumatology. National leadership. Ed. acad. RAMS G. P. Kotelnikova, acad. RAS and RAMS S. P. Mironova, 2008.
- Traumatology and orthopedics. Management. Kornilov N.F., St. Petersburg, 2006.
- X-ray method in the diagnosis of joint diseases. Svetlova M. S. RMJ “Medical Review” No. 27 dated 12/02/2014. https://www.rmj.ru/articles/nevrologiya/Rentgenologicheskiy_metod_v_diagnostike_zabolevaniy_sustavov/
First aid for elbow bruises
The main goal of first aid is to minimize the aggressive influence of inflammatory processes occurring in cartilage. To do this, first of all, you should ensure immobility of the bruised elbow joint. This can be done by placing a splint on it, which needs to be wrapped in soft cloth. For severe pain, it is recommended to take analgin or ibuprofen.
Next, apply a towel soaked in cold water, a bottle with it, or a piece of ice to the affected area. This will reduce pain, relieve swelling and slow down internal bleeding. Then you need to worry about reducing blood flow to the elbow, for which you need to place it on a hill.
Before visiting a doctor, in order to avoid worsening the situation, it is prohibited:
- massage the affected area;
- bend and straighten your arm;
- lift heavy objects with a bruised limb;
- lubricate damaged skin with warming ointments;
- apply warm bandages.
How to relieve pain and swelling in the elbow joint
When the elbow hurts after a bruise, various therapeutic methods are used, including drugs for local application. Doctors often recommend creams, ointments, and balms with anti-inflammatory and analgesic effects, which can be easily purchased at any pharmacy.
Immediately after the injury, release the limb from the load, immobilize it and relax the muscles. This will dull the pain. You can apply a cool compress, a heating pad with cold water, or a chilled steel spoon to relieve swelling in a bruised elbow.
If it is not possible to see a doctor urgently, and the pain is quite severe, you can use a painkiller, for example, Ibuprofen. Remember that self-medication in most cases is fraught with negative consequences. It is better to contact a specialist who will accurately determine the problem and develop an individual scheme for effective therapy. Now you know how to treat a bruised elbow.
Effective ointments for elbow bruises
External treatment is one of the main ones for bruises. In this case, creams, gels, balms and all kinds of liquid preparations are used, including oils with analgesic and anti-inflammatory effects. Ointments are especially popular. They are applied to intact areas of the skin (places where there are no open wounds) and often demonstrate a resolving, decongestant effect.
Considering the composition, the main action of all ointments is divided into:
- non-steroidal (Ketoprofen, Diclofenac);
- warming (with pepper, bee venom, essential oils);
- homeopathic;
- absorbable (with bodyaga, troxerutin).
Combination products are common, which contain several active ingredients, often of plant origin.
Treatment of elbow bruise
Treatment of the patient begins with a puncture (puncture) of the bruised elbow joint. This procedure is carried out when there is fluid in the joint cavity, which is pumped out at this time. It can also be used to determine whether internal bleeding has occurred or not. Without this, it is impossible to prescribe competent treatment for the elbow.
If no blood is found in the joint, doctors prescribe the patient anti-inflammatory drugs to eliminate inflammation and relieve swelling. This may be diclofenac or indomethacin, which are available in the form of ointments, tablets or injection solutions. In such cases, ointments for external use are mainly recommended.
In the treatment of a severe elbow bruise, magnetic therapy and UHF therapy (exposure to the problem area of high-frequency electromagnetic waves) have proven themselves well. They help relieve inflammation and reduce swelling. Additionally, the patient is prescribed exercise therapy, which is recommended to be done daily and begin a week after the injury.
Complications
Often, an elbow bruise can be complicated by hemarthrosis - an outpouring of blood into the joint cavity.
To minimize the development of complications, it is necessary to consult a doctor promptly
As a result of the fact that the articular cavity is tightly and hermetically closed on all sides by the walls of the articular cavity (articular surfaces), the gushing blood does not find a way out, compresses the feeding vessels, and impairs blood supply. Without timely assistance, this process can lead to the destruction of articular cartilage at the bend of the arm and the formation of deforming arthrosis.
An extremely unfavorable outcome of hemarthrosis is the formation of contracture.
The accumulated blood triggers the formation of adhesions in the joint, which ultimately leads to a complete lack of movement in the elbow, i.e. contracture, the joint ceases to perform its function.
Treatment of hemarthrosis
In the presence of hemarthrosis, a puncture of the joint is performed with aspiration of blood, removal of blood clots, and possibly the introduction of injectable hormonal drugs - glucocorticoids - into the cavity.
Hormones are administered to reduce the inflammatory response. However, recently evidence has emerged indicating that intra-articular administration of hormones is not always justified, since they have an adverse effect on articular cartilage.
The issue of hormone administration is decided by the doctor individually, depending on the degree of hemarthrosis and the condition of the joint. The first few days after injury, the limb is fixed using a special bandage.
Treatment with folk remedies
Sometimes bruises of the elbow joint in adults and children are treated with traditional medicine recipes. But it is important to do this after consultation and only on the recommendation of a doctor. Not all advice from the Internet is safe and useful. Be careful.
The most popular folk remedies that are relevant when you are concerned about the question of what to do if you have a bruised elbow are:
- white cabbage leaves;
- plantain leaves;
- natural honey;
- milk;
- onion;
- vinegar, vegetable oil;
- Oak bark;
- pharmaceutical dry chamomile;
- raw potatoes;
- flax seeds;
- aloe leaves;
- St. John's wort;
- burdock root;
- young hop cones;
- laundry soap;
- pine resin;
- lard.
In folk medicine, there are a huge number of substances that have a healing effect on tissue when an elbow is bruised from a fall or hit with a blunt object. But blindly believing all the recommendations of folk connoisseurs and healers is stupid. Treatment should be selected only by a competent doctor, who forms his recommendations based on the patient’s diagnostic results. This takes into account the age of the victim and the possibility of developing an allergic reaction to a particular substance.
Physiotherapeutic procedures
Often, in combination with medications, the doctor prescribes a course of physiotherapeutic procedures. The number and duration depend on the severity of the damage to the elbow joint. These measures are needed to restore and normalize the functioning of the injured limb. Often recommended:
- paraffin therapy;
- laser and magnet treatment;
- electrophoresis;
- wave treatment, as well as balneotherapy.
You may need massage and health exercises to help with rehabilitation. Such procedures, thought out to the smallest detail, normalize blood circulation and improve motor function. The list of safe exercises is different for each patient. The doctor will not prescribe training if the symptoms of the pathology are pronounced, because carelessness and incorrect movements can lead to a deterioration in health.
Now that you have bruised your elbow, you know what to do. Make an appointment now to eliminate risks and in no case make things worse for yourself.
Severity of elbow bruises
In trauma, the level of damage may vary significantly depending on the situation. The main point is the strength and duration of the damaging factor.
With short-term and mild exposure, minimal pathological changes occur, while with short-term and strong exposure they can be quite disabling. The duration and strength of the trauma factor directly complement each other.
- First degree . Characterized by superficial damage. The skin is mainly affected. Scratches, abrasions, and minor bruises appear on them. They go away on their own, without the participation of a doctor.
- The second degree is accompanied by uncomplicated ruptures of the lower layers of skin and upper layers of muscle. From the ruptured vessels, blood flows into the surrounding tissues, where it accumulates, forming subcutaneous hematomas. There may be a concussion of the elbow joint with disruption of its function.
- Third degree . Multiple ruptures of muscles and ligaments. Massive subcutaneous and intramuscular bleeding. Necrosis of muscle tissue.
Rehabilitation
For successful rehabilitation, you can move the fingers of your bruised hand and roll balls over your palm. This way, it will be possible to speed up the release of fluid accumulated in the joint cavity. Recovery should be gradual, without pain, and it can take 2 weeks or a month or more. It is not allowed to massage the problem area during this period.
An elbow bruise is a really serious problem that can temporarily change your previous lifestyle. But, following all the proposed recommendations, rehabilitation after such an injury will pass quickly and without complications. Take care of your health!
| First aid for bruises | To the list of articles | Shoulder bruise |
Types of damage
There are several types of bruises:
- minor (with minimal or no symptoms);
- mild (with symptoms such as pain immediately after injury, a small hematoma, with rapid healing without consequences for the joint);
- severe (extensive tissue damage around the joint, prolonged healing with possible complications).
Bruises can be multiple or single.
By localization they are divided into:
- combined (involving periarticular tissues - tendons, muscles);
- isolated (damage to only the skin or muscles, nerves).