The elbow joint is an important anatomical formation that unites the bones of the shoulder and forearm. If it functions with disturbances, then difficulties arise in performing the simplest movements. A person experiences discomfort while eating, combing, lifting weights, or grasping any object. When the elbow joint moves, the bones of the forearm, wrist, and phalanges simultaneously move and rotate in space. Only due to the normal functioning of the joint we can perform complex movements with the hand.
Fracture without displacement
When the bones that form it are fractured, the functions of the entire arm are limited. Obstacles arise when trying to perform any basic movement, for example, turning the hand upward. Complete restoration of the functions of the elbow is possible only when the bones and their fragments are placed in an anatomical position, ensuring their rapid fusion. The leading method for diagnosing all elbow fractures is radiography. The treatment method depends on the location and severity of the injury, and the age of the patient. If conservative treatment (plaster application) does not have an effect, the patient is prepared for surgery.
A little anatomy
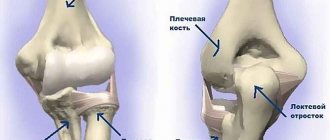
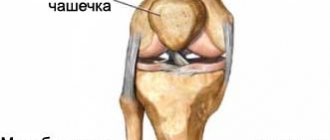
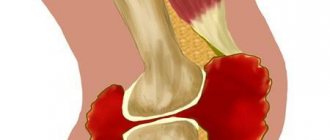
The elbow joint is formed by the ulna, humerus, and radius bones. The elbow is formed by two joints. When the bones of the shoulder and forearm join, the first is formed; Thanks to him, the elbow bends and extends. The second articulation is formed by the ulna and the smooth head of the radius. During movement in the joint, the ulna rotates around the radius. The main functions of this joint:
- supination, or turning the hand with the palm up;
- pronation, or turning it palm down.
The lower third of the humerus has a complex shape. Its central section, slightly above the elbow, is divided into two parts that support the condyles. They can be detected by palpating the soft tissues located to the right and left of the elbow joint. In the area with the condyles there is a certain number of projections and grooves in which the ends of the bones are located. In these anatomical structures they articulate and move relative to the shoulder bone.
The bone surfaces are lined with durable and at the same time elastic hyaline cartilage. It is white, smooth, slippery, and protects against damage to the bones, which often and monotonously shift in the elbow joint. Smooth and painless movements are provided by cartilage tissue. Unlike other anatomical elements of the body, they are practically not supplied with blood. Synovial fluid serves as a source for them:
- molecular oxygen;
- nutrients and biologically active substances.
In most cases, cartilage is damaged during a fracture. For its further functioning, a jewelry reposition (comparison, alignment) of fragments is needed.
The main goal of treatment for any fracture is to restore the articular surfaces. If complete regeneration of cartilage tissue does not occur, then the risk of irreversible complications increases significantly.
Traumatologists treat so-called post-traumatic arthrosis of the elbow - a degenerative-dystrophic pathology that provokes ankylosis (complete or partial joint immobility). Fractures of the heads of the radial bones of the elbow joints are very dangerous. Blood circulation in this part of the elbow is completely disrupted. With nutrient deficiency, there is a high probability of irreversible destruction of the bone head.
Causes
During a fall, people instinctively put their arms forward, which places a large load on the elbow, causing a violation of the integrity of the bone. This is the most common cause, but fractures also occur as a result of:
- in case of a strong blow to the joint area with a foreign object;
- in case of road accidents and various accidents;
- in athletes (when the main load is on the arms, as in tennis and volleyball);
- when trying to catch a heavy object falling at high speed;
- in case of accidents at work.
Children and older people are most susceptible to fractures of the elbow, since their bones and ligaments are quite fragile. People with osteoporosis are also at risk.
Clinical picture
During a fracture, acute pain occurs. One of the leading symptoms of injury is a crunching sound, reminiscent of the cracking of dry branches being broken. Pain is usually localized on the back of the joint. The following signs are also characteristic of the injury:
- pain radiates to the shoulder and forearm;
- a few minutes after the injury, swelling begins to form, the intensity of which quickly increases;
- the skin in the area of injury is cool, pale, sometimes bluish;
- a hematoma forms a little later. First, pinpoint hemorrhages occur due to ruptured large vessels. Gradually, blood pours into the subcutaneous tissue and an extensive hematoma appears on the front surface of the elbow;
- with an open fracture, the skin is damaged, and bone fragments and sharp edges of tubular bones may protrude from the wound;
- the victim is unable to move the injured arm - bend and straighten the elbow, and rotate the hand.
When injured, the elbow becomes deformed.
Usually the elbow is deformed. Often the pain is so severe that the patient may lose consciousness. Upon palpation, the doctor detects large fragments and assesses the severity of the injury. The symptoms of a crack in the elbow joint are not so pronounced. A large hematoma forms, the area of damage swells, but movement is not limited. The victim holds the injured hand with the healthy one to reduce the intensity of the pain.
Nutrition
After a fracture, you will have to eat in such a way as to replenish the microelements used by organisms as building material for the regeneration of bone tissue. Basic products should be protein and high in collagen.
Meat contains a lot of collagen, especially turkey and duck, salmon family fish, oysters and shrimp. It is useful to eat vegetables: cabbage of all varieties, tomatoes, sweet peppers, herbs and peas. Fruits rich in vitamin C will help the joint recover faster.
Healthy fats are a must. They can be found in eggs, nuts, flaxseed oil and pumpkin seed oil.
If the patient is overweight, you will have to go on a diet, since excess kilograms put pressure on the joints.
An elbow fracture (especially if children are victims of the situation) is a fairly complex injury that can lead to complications. But modern medicine can easily correct such damage, so for a successful recovery the patient only needs to follow the doctor’s recommendations.
Types of elbow fractures and treatment methods
The elbow joint is a stable anatomical formation due to the presence of elastic ligaments located on both sides of the joint. Traumatologists very rarely diagnose elbow dislocations due to its strong ligamentous-tendon system. Stability is also provided by strong biceps and triceps muscles that cross the joints. A person is able to bend the elbow due to the secure attachment of the biceps to the radius. And the triceps, which is attached to the process of the elbow, is responsible for extension. As a result of such a complex anatomical structure, victims experience a variety of fractures.
Types of fractures of the elbow joint.
A blow or fall can cause cracks in the elbow joint. They can be single or multiple, and according to their location to the bone axial line - linear, oblique, spiral-shaped. When there are cracks in the bone, the joint retains its supporting function. If they are not accompanied by a fracture, then wearing a plaster cast is sufficient for a complete recovery.
Fractures of the lower humerus
A fracture that does not affect the articular surfaces is called extra-articular. Once diagnosed, the prognosis for full recovery is favorable. Extra-articular injuries are detected slightly above the elbow, usually in the area of the epicondyles. Even applying a plaster cast does not immobilize the joint well, so surgery is performed immediately. The doctor compares the fragments in anatomical position and secures them with metal plates and screws. The shape of surgical devices follows the curves of the bones. This ensures stable fixation and rapid healing of the fracture. An operation performed using this technique allows the victim to begin developing movements earlier.
A common injury to the elbow is avulsion of the medial epicondyle, accompanied by its fracture, due to excessive traction of the collateral ligaments. A bone fragment is detached, entering the joint cavity and completely blocking movement. An attempt to bend or straighten the elbow leads to severe, piercing pain. An open operation with fixation of the bone fragment to the avulsion site is indicated. Sometimes it is possible to restore the articulation using a conservative method, but only if the fragment is located near the place where it was torn off.
If an intra-articular fracture is diagnosed, the prognosis for complete recovery is worse. The goals of therapy are high-quality alignment of fragments and restoration of cartilaginous surfaces. The most commonly diagnosed injuries are:
- Fractures of the humerus in the area of their capitate eminences. The fragments move inside the joints, limiting their functioning. Injury often occurs from a fall with emphasis on an outstretched arm or from a dislocation. Surgical therapy is indicated for patients. Large fragments are secured with screws in the correct position. Small fragments that cannot be reduced are removed;
Fracture of the capitate eminence.
- transcondylar and intercondylar injuries. These are the most commonly diagnosed types of fractures, usually caused by a strong blow to the elbow. The bone structures supporting the epicondyles are destroyed, which causes a change in the ratio of the bones. Such injuries are characterized by serious damage to cartilage tissue, the restoration of which is a difficult task. After repositioning the articular elements, they are secured with screws and plates until they are completely fused. This will not be a limitation for the gradual development of the joint.
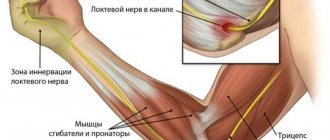
During diagnosis, the condition of the blood vessels and the degree of hemorrhage in the joints are assessed. During the operation, the surgeon also has to restore the damaged nerves. If this stage is neglected, severe complications will develop. Disruption of innervation will provoke loss of sensitivity in the hand, and a significant decrease in the range of motion in the elbow is also possible.
Fracture of the proximal ulna
With such injuries, the damage is usually localized in the upper thirds of the ulna bones. A fracture of the olecranon occurs (Montaggi fracture-dislocation).
If a fragment is displaced due to triceps traction, then only surgical treatment is performed. The surgeon restores cartilage and bone tissue, and then fixes the fragments with knitting needles and wire. The pins are removed approximately six months after assessing the condition of the elbow. And the plates are removed later - after 1-2 years.
Due to the close location of the olecranon process to the skin, the operation does not last long and is not difficult. But there are exceptions - comminuted fractures with damage to the coronoid processes. They are secured with special surgical metal structures.
Fracture of the neck and head of the radius
When a person breaks his arm at the elbow joint, he loses the ability to rotate the radius. This leads to a decrease in the functional activity of the forearm. The victim also cannot turn the hand or grasp any object. Sometimes bone fragments are displaced into the joint cavities, blocking movement. A dangerous complication of injury is damage by bone fragments to the blood vessels responsible for the trophism of the radius. If the fragments are slightly displaced, the operation is not performed. The functions of the elbow are restored when a plaster cast is applied. If the fragments blocked the articulation, then they are internally fixed with screws and plates. In case of a comminuted fracture, the patient is indicated for endoprosthetics of the bone head.
The bones that form the elbow joint are located close to the surface of the skin, so open fractures are often diagnosed. With such injuries, several elements located inside the joint are damaged at once. For an open fracture, surgery is performed. Damaged, contaminated tissue at the site of the skin break is excised, and then the bones are secured with external fixation devices. Once the wounds have healed, the device is removed. Now the bones are attached with plates and screws, which are removed after the functions of the arm are fully restored. This method of surgery reduces the likelihood of infection of the joint cavities with pathogenic bacteria.
The effectiveness of therapy depends on timely seeking medical help. The victim’s hand should be secured with a bandage in the form of a scarf, a cold compress should be applied to the area of swelling for 10-15 minutes every hour, and a tablet of Nurofen, Diclofenac, Nise or Ketorol should be given. The person should be taken to an emergency room as quickly as possible for evaluation and treatment.
Exercise therapy for quick recovery after injury
In the process of restoring the function of the upper limb after a fracture of the radius, thermal procedures play an important role. Physiotherapists at the Yusupov Hospital carry out warming in a variety of ways (paraffin or ozokerite applications). Massage is added to the complex of gymnastic exercises. The following procedures are used to treat a radius fracture:
- ultra-high frequency electromagnetic field (during the procedure, the tissues of the affected limb begin to heat up, the patient feels warmth, regeneration accelerates, pain weakens);
- low frequency electromagnetic field – reduces swelling, eases discomfort and pain;
- ultraviolet irradiation helps to increase the synthesis of vitamin D, which is necessary for the absorption of calcium from food in the digestive tract;
- Calcium electrophoresis on the area of injury helps accelerate the formation of callus and facilitates the restoration of damaged bone tissue.
You can undergo a recovery course after a fracture of the radius at an affordable price in a rehabilitation clinic. The contact center is open 24 hours a day, 7 days a week. Call the Yusupov Hospital and make an appointment.
Endoprosthetics
This technique is one of the most complex and at the same time effective. With its help, you can restore your limbs to their former mobility. Its essence is to replace a damaged part of the skeleton that cannot be restored or treated with an endoprosthesis made of neutral materials. Indications for this procedure are:
- Arthrosis and arthritis;
- Comminuted fractures;
- Ankylosing spondylitis;
- Dystrophic and atrophic processes;
- Dysplasia;
- False joint.
The prosthesis is implanted through an incision on the extensor side, fixed with cement or cementless and sutured. The rehabilitation period is 2-3 months, but movements of the replaced part are allowed within a month after suturing.
Reposition
Schematic representation of the procedure.
For fractures and dislocations, when it is impossible to set or restore the bone, reposition is performed. The operation is an internal restoration of the structure of the joint. To do this, an incision is made along the back surface of the extensor part of the arm, exposing the bones and their joints. Transverse channels are made on the fragment and on the inner surface. All components are assembled in their original position, a spoke is placed along it, which is secured with screws in the made channels. Tendon fibers, which are taken from the lateral sections of the triceps, wire, and other materials, can also be used as fastening. Fasteners are selected depending on the location of the fracture. The attachment process is called “osteosynthesis”. If the tendons were damaged during crushing, their restoration is carried out simultaneously with reposition.
When to start developing a joint?
The period when rehabilitation of the joint begins begins almost immediately after the removal of the plaster. The main thing here is to act without haste, since after an elbow fracture, excessive activity can only damage weakened muscles. As a rule, rehabilitation after an elbow fracture in the form of physical therapy, physiotherapy and water exercises takes from three to eight weeks - the duration depends on the nature of the joint injury. Properly carried out, the course allows you to restore the working function of the elbow joint by 100 percent.
Arthroplasty
Similar effects are often carried out at the joints of the ends of bones. They represent the modeling of the joint to natural forms. If the patient complies with all the requirements of the rehabilitation medicine doctor, then the probability of a positive outcome is almost 100%.
The result of the operation on x-ray.
Indications are fibrous and bone ankylosis. With this deviation, the joint partially or completely loses mobility due to pathological changes. The causes of destruction are often arthritis, trauma, and arthrosis. With multiple fragmentations of the elements included in the connection, reconstruction becomes impossible. In this case, the fragments are removed, and the missing part is filled with artificial or the patient’s own tissues.
The elbow joint is able to move normally and function only if all its components have natural sizes and shapes. The technique is aimed at performing precisely this task. Today they produce ready-made plates that cover the surface of the affected joint. They are made from medical alloys or polymers. Special pastes and mixtures are also used to coat the compound. These products penetrate into the pores and gaps and harden there.
Diagnostics
An elbow fracture is diagnosed by a traumatologist. He asks about what is bothering the patient now and how the injury occurred. The doctor then examines the affected limb and joint. Determines the volume of possible movements during flexion-extension and rotation. The doctor evaluates the presence of deformation and must also ensure the integrity of the blood vessels and nerves.
To confirm the diagnosis, the following diagnostic methods are used:
- x-ray of the joint in frontal and lateral projection;
- targeted radiography from various angles;
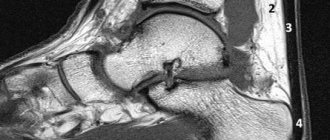
- if necessary, for a better overview of the affected joint, MRI, CT and ultrasound are performed; they are prescribed for complex injuries with damage to soft periarticular tissues and articular processes;
- a consultation with a vascular surgeon and neurologist is carried out in case of damage to blood vessels and nerves;
- if arterial rupture is suspected, arteriography with contrast is performed.
In a situation where surgical intervention is proposed, the patient undergoes the necessary laboratory tests.
Rehabilitation
It is very important to approach rehabilitation competently.
The correct sets of exercises and massages must be repeated until complete recovery. The load is increased very slowly to avoid complications.
Massage
The massage used for an elbow fracture is no different from the massage performed for other types of injuries. Massage elements such as stroking, rubbing, kneading, flexion and extension of the joint, and rotation are used. It is performed in a sitting position by a specialist.
In this case, an assistant may be present who holds the patient's hand in a suspended position, which is necessary when performing some techniques. Massage helps in the treatment of all joint diseases, provided it is carried out correctly. During recovery, massage is required.
Symptoms
Elbow injuries can lead to the following symptoms of an elbow fracture:
- Sharp pain at the time of injury;
- Sharp pain from touching the damaged area;
- Swelling and hematomas in the joint area;
- Protrusion of fragments under the skin, visible to the naked eye;
- Partial loss of limb functionality;
- Movements uncharacteristic for the hand, mobility of a pathological nature;
- An accumulation of blood in a joint, called hemarthrosis.
It is possible to maintain the position of all fragments and prevent inevitable surgery for a displaced elbow fracture through the correct application of plaster. It may be possible to achieve only partial preservation of limb function. All extension and other movements can become extremely painful.
In some cases, the damage can be felt by palpation. If nerve trunks are pinched or damaged, neurological symptoms may appear. Complaints of lack of sensitivity, tingling and numbness of the hand in the damaged area are possible.
First aid
It is important to provide first aid to a victim with an injury to the elbow joint before transporting him to the emergency room, so as not to aggravate the damage on the road.
It includes the following activities:
- If the victim breaks his elbow, it is necessary to carefully fix the arm, avoiding damage. To do this, you need to make a supporting bandage or use a splint. It is necessary to securely fix the limb to the body. It is applied, immobilizing the shoulder, wrist joints and hand. Before this, several layers of fabric are placed under the elbow.
- If there is an open wound at the site of injury, it must be washed and treated.
- If it is impossible to bend the arm at the joint, the patient is laid down and fixed to the body in a lying position. It must not be bent with force.
- It is necessary to regularly feel the pulse. When it disappears, the hand is carefully released from the bandage and straightened to restore blood circulation. Then after some time the hand is fixed again.
- After these manipulations, you need to take the victim to the emergency room or call an ambulance.
IMPORTANT Painkillers should be given to a patient with a broken arm at the elbow, only as a last resort, otherwise the clinical picture will be blurred. This will make it difficult for the doctor to make a diagnosis.