Swelling, limited mobility of the knee joint along with subcutaneous hematomas - these symptoms are often observed after injury. A disease that is accompanied by hemorrhage into the joint cavity is called hemarthrosis. How to properly treat this disease and what rules to follow to avoid worsening?
Most often, hemarthrosis is diagnosed in winter - during icy conditions.
What are the causes of hemarthrosis
Most often, the disease results from a bruise, dislocation or subluxation, rupture of a ligament or meniscus. Trauma leads to damage to the blood vessel - blood enters the cavity. This happens, for example, when falling while skating or skateboarding, if the athlete does not use knee pads, as well as in everyday life - even when going down the stairs unsuccessfully.
Very rarely, the cause of hemarthrosis is a blood disease, such as hemophilia or hemorrhagic diathesis, as well as other coagulation pathologies.
First aid has been provided: what next?
It is not surprising that with serious injuries to the knee, the leg hurts for a long time. In addition to the medications prescribed by the doctor, you can use traditional medicine. If your knee hurts badly after an injury, and you don’t know what to do, and the prescribed remedies do not bring relief, you need to reduce the load on the injured leg, and ideally, stop walking altogether for several days. A tight bandage around your knee will help minimize joint mobility and reduce pain. In the first days after injury, you should avoid drinking large amounts of liquid to prevent swelling of the limbs. Sometimes, after such injuries, patients’ temperature may rise—in this case, it is worth using antipyretics.
If quite a lot of time has passed after the injury, joint mobility has been restored, but the knee still hurts when bending after the injury, you should contact your doctor again, who will prescribe additional physiotherapeutic procedures. This can be massage, warming up, physical therapy, which will help relieve pain symptoms and will be the last stage of rehabilitation after an injury.
Symptoms
If the volume of blood spilled into the joint capsule is small, there may be no external signs at all. A person only experiences pain and discomfort - by analogy with the treatment of arthrosis or osteoarthritis of the knee, and is also forced to limit mobility. External symptoms appear if more than 40-50 ml of blood has spilled into the cavity:
- the joint swells and increases in volume;
- bruises are noticeable;
- It becomes very painful to move your leg.
Knee swelling? Fix the limb and go to a rheumatologist-orthopedic surgeon
Complications
Pain varies but is rarely a serious problem. Movement and function of the limb may be limited, which especially hinders creative people and those whose work involves the use of motor skills (musicians, artists, seamstresses, etc.). But the most common reason why patients go to the hospital is their unaesthetic appearance.
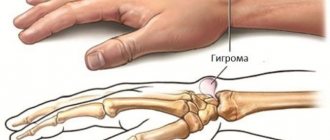
Due to the same hygroma of the shoulder joint, a decrease in functionality occurs, which jeopardizes the quality of life and comfort. It is likely to reappear spontaneously or after surgical treatment.
Read more about hygroma removal in Moscow
Subtleties of diagnosis
Often, an external examination is sufficient to diagnose hemarthrosis. The doctor will palpate and make sure that the patella is balling. Such a “floating” patella is never detected with ordinary bruises.
A puncture of the knee joint will help confirm the presence of blood in the cavity, but it is not enough to understand the nature of the damage. Therefore, patients are prescribed additional examination - MRI, CT or ultrasound.
How does blood get into the joint capsule? Expert - about the mechanism of development of hemarthrosis:
Diagnostics
The formations appear in the form of lumps or swellings, the size of which varies from a few millimeters to centimeters. These are hard, elastic buds. Movable, but fixed at the base. Sometimes there is local soreness of the surrounding tissues.
The cause of the development of hygroma of the hand joint is unknown. There are two theories: the first considers the effect of injury, and the second associates it with a disruption in the flow of fluid in the tendons and sheaths, an increase in pressure inside these sheaths, which together cause the appearance of a bag in which the liquid contents collect.
A detailed clinical examination with anamnesis is sufficient. Diagnostic biopsy is recommended only in cases of unclear diagnosis to differentiate from rare but malignant soft tissue changes. Sometimes an x-ray is needed to evaluate the condition.
Treatment tactics for hemarthrosis
First of all, it is necessary to quickly remove blood and synovial fluid from the cavity through puncture. The procedure is carried out under local anesthesia under aseptic conditions, after which special drugs are administered orally - anti-inflammatory, analgesic and hemostatic. Sometimes, as in the treatment of osteoarthritis of the knee, arthroscopy may be necessary if the damage to the internal structures is large.
If the blood volume is less than 20-30 ml, you can do without a puncture: the clots will gradually dissolve on their own. If the manipulation is carried out, the patient is given a pressure bandage, and the joint is immobilized using a plaster or splint. For a week, it is recommended to use crutches to walk so as not to rely on the affected leg. At the end of this period, as in the treatment of arthrosis, rehabilitation measures are indicated - physiotherapy, massage and exercise therapy.
The doctor will decide whether a puncture is necessary. It all depends on the volume of blood in the joint cavity
Elastic bump
An elastic and elastic lump of a clear shape, when pressed on, fluid vibrations are felt inside - one of the characteristic signs of Baker's cyst and bursitis.
Baker's cyst
A Baker's cyst is a hernia (protrusion) of the mucous bursa, which is located in the popliteal fossa (posteriorly) and communicates with the joint capsule.
Baker's cyst
Due to injuries, rheumatoid arthritis, meniscopathy (changes in the structure of meniscus tissue) and other diseases, the synovium of the knee joint produces more fluid than necessary. Under pressure, this fluid enters the intertendinous bursa behind the knee (only 50% of people have such bursae), and it increases in size.
As a result, a lump of a clear shape forms in the popliteal fossa (in the form of a crescent, a bunch of grapes, with constrictions across it, dividing the cyst into 2 parts, etc.).
While the formation is small, nothing bothers the patient, but as soon as it greatly increases in size, the person experiences a squeezing or aching pain, which intensifies when moving the leg, radiating to the thigh or lower leg.
Treatment: fluid is removed from the cone, glucocorticosteroids (Hydrocortisone) are injected into the capsule, local anti-inflammatory drugs (Indomethacin ointment) are prescribed, and a tight pressure bandage is applied.
If conservative treatment is ineffective or if the cyst is greatly enlarged, it is excised (removed).
Prepatellar bursitis
A round, clearly visible lump located in front under the knee joint is one of the symptoms of prepatellar bursitis (an inflammatory disease of the synovial bursa that protects the patella from damage).
Damage (bruises, falls) or pathological processes (arthritis, arthrosis) lead to inflammation of the synovial membrane inside the bursa, which causes fluid to accumulate in its cavity.
Aseptic inflammation (without penetration of infection into the bursa) almost does not complicate a person’s life - the lump does not hurt, can increase in size under load, and occasionally causes discomfort when bending the joint.
The septic process (inflammation caused by infection with the formation of pus) is more acute. Lump in the joint area:
- increases in size (within 2–3 days);
- turns red and becomes hot to the touch;
- It begins to hurt very much when pressed, when moving, or at rest.
The sore knee swells and swells, the person’s general temperature rises, and signs of poisoning by cell breakdown products appear (weakness, sweating, lack of appetite).
Treatment: liquid is extracted from the cone (the procedure can be repeated 2 to 4 times in a row, as it accumulates).
Glucocorticosteroids (Hydrocortisone) or antibiotics (for a purulent process) are injected internally, and a tight pressure bandage is applied (for a septic process, a drainage tube is installed until the pus is completely cleared).
Why is hemarthrosis dangerous?
If blood is not removed from the cavity in a timely manner, the disease can cause complications. Blood saturates the joint and clots form in it. Even if they resolve over time, adhesions may remain in their place - the cartilage surface is deformed and will no longer be smooth. Due to unevenness, the cartilage in certain areas will wear away - sooner or later treatment for arthrosis will be required.
And if in case of hemarthrosis the problem can be solved by puncture followed by rehabilitation, then in case of osteoarthrosis, long-term therapy will be required, for example, an annual course of intra-articular injections of Noltrex. Injections of this synthetic drug relieve pain for 9-15 months, replacing the missing synovial fluid. They must be done at regular intervals to maintain results. Today this is one of the most effective ways to combat arthrosis. If hemarthrosis is treated in time, the knee can remain healthy.
Another danger of this disease is purulent arthritis. Since pathogenic bacteria multiply especially intensively in the blood, there is a high risk of infection. That is why do not ignore a swollen knee: consult with an orthopedist and follow all the instructions for hemarthrosis that are likely to help you avoid arthrosis.
Causes of bone growth under the knee
The following are the main factors that contribute to the growth of bone tissue:
- Prolonged physical activity accompanied by strong pressure on the kneecap area (teenagers and professional athletes often face this problem).
- A pathology that is accompanied by severe pain, swelling and tension in muscle tissue.
- Genetic predisposition.
- Arthritis and arthrosis.
Pain when a growth occurs may be absent, constant or intermittent, and occur only during physical activity.
What exactly hurts in the knee?
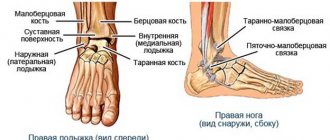
The knee joint is the most complex joint, as it bears the main load. Structure: three bones (femur, tibia and patella form a single trochlear joint, consisting of two interconnected joints: femorotibial (tibiofemoral) and femoral-patellofemoral (patellofemoral).
The patella is a flat sesamoid (additional in the joint) bone that is attached to the head of the femur, sliding in its concave groove and acting as a block. Structural features: the anterior surface of the patella is covered with periosteum, the posterior surface, connecting to the femur, is covered with hyaline cartilage. The patella is strengthened by ligaments: main and lateral – vertical (upper and lower) and horizontal (lateral – internal and external).
O transmits the force of the quadriceps femoris muscle to the musculoskeletal formations of the lower leg, ensuring extension of the lower leg at the knee joint. The surface of the joint-forming bones is covered with cartilage, which acts as a shock absorber. Additional shock absorbers that protect the joint from injury are two crescent-shaped cartilaginous menisci located between the femur and tibia. The joint is held in its correct position by ligaments, tendons and the surrounding capsule.
Structure of the knee joint
Injuries and diseases affect various joint tissues. Not all of them can get sick. Thus, cartilage tissue does not have nerve endings and therefore can be destroyed imperceptibly and painlessly. But the ligaments and synovial membrane have many nerve endings and in case of injury or inflammatory processes they immediately begin to react, which manifests itself in the form of severe pain. With significant destruction of articular cartilage, pain may be associated with the involvement of the periosteum, the outer layer of bone that has good innervation, in the process.
Treatment for bumps on knees
Various methods of treatment are used to treat bumps on the knees. The basis of therapy is the restoration of the physiological integrity of pathologically altered tissue. Therefore, if the lump appears as a result of an inflammatory reaction, then the actions of the chiropractor will be aimed at eliminating the cause of this reaction. And if the lump is formed due to deformation of cartilage or bone tissue, then when developing a course of individual treatment, the emphasis will be on techniques that allow restoring blood microcirculation and starting the regeneration process.
Treatment includes massage and osteopathy, kinesiotherapy and therapeutic exercises, reflexology and laser therapy. The course of treatment is always developed individually and depends on what disease is detected in the patient.
Do not self-diagnose or treat. Schedule a free orthopedic appointment at our chiropractic clinic. During the consultation, you will be diagnosed and treated.
Treatment of knee pain: the possibilities of modern medicine
The effectiveness of treatment of the spine and joints often depends on how promptly the patient consults a doctor. Therefore, you should not delay going to the clinic. You, of course, can use the help of the Internet - the Internet provides a huge amount of advice on the topic of a swollen knee - what to do at home. But you need to clearly understand that traditional methods can not only alleviate symptoms, but also harm and worsen your condition.
The only thing you can (and should) do on your own is to give yourself first aid - before seeing a doctor. Regardless of whether the knee is swollen inside or outside, or what type of pain bothers you, it is important to provide as much rest as possible to the leg. A cold compress for fifteen minutes will help reduce swelling and reduce pain. In case of bruises or injuries, it is recommended to immediately bandage tightly with an elastic bandage. You need to start bandaging 20 cm below the knee, and end 20 cm above. If you have severe pain, you can take a painkiller.
In the case of knee pain, traditional medicine usually offers elimination of the pain syndrome, but the cause remains, and the disease continues to develop: time is working against you. Therefore, at the first sign that your left or right knee is swollen or painful, contact a specialist - an orthopedist, surgeon, rheumatologist, neurologist.
The general treatment course includes medication, symptom relief, physiotherapy, and exercise therapy.
- Treatment begins with pain relief - with the help of anesthetics and non-steroidal drugs.
- If damage, trauma, or disorders in the structure of cartilage tissue have been diagnosed, medications from the group of chondoprotectors that improve the structure of cartilage can be prescribed.
- To restore joint functions - flexion and mobility, vitamins, steroids and external agents are prescribed.
- Physiotherapy can relieve swelling, eliminate pain, and sometimes speed up the elimination of the causes of the disease. The doctor may recommend electrophoresis, laser or magnetic therapy, cryotherapy procedures or exposure to low-frequency microcurrents.
Therapeutic exercise is carried out under the supervision of doctors. All exercises are performed in stages, the load and intensity are increased sequentially. Most of the exercises are based on knee circles, extension and flexion.
Lump on the side of the knee on the inside and outside
A painful lump on the lateral side of the knee may be due to a cystic expansion of the bone tissue of the head of the tibia. This pathology mainly affects young people leading an active lifestyle. A severe bruise with damage to the periosteum leads to the fact that the bone tissue loses its integrity. A deep crack forms on the surface. From the damaged blood vessels of the periosteum, blood begins to flow into the crack. It provokes inflammation and aseptic melting of the tissue. A cavity is formed, inside of which there is fibrous scar tissue.
With a cystic lesion of the head of the tibia, the lump on the leg on the side of the knee has a dense structure and is absolutely painless on palpation. The X-ray image shows a dark cavity. Treatment is possible only through surgery. The danger is that there is a high probability of a bone fracture in this place.
With Schlatter's disease, a lump on the outside of the knee may be associated with congenital or acquired osteochondropathy. A lump appears when there is a serious scar change in the cartilage and tendon tissue in the area of increased tuberosity of the tibia.
Other probable causes include the following diseases:
- chondromalacia of articular tissues;
- hygromas, lipomas and other types of cystic tumors;
- bursitis and tendovaginitis;
- cicatricial deformities of the lateral ligaments of the knee joint;
- exit of the head of the tibia from the joint capsule;
- oncological processes.
Do not discount the possibility of developing rheumatism, gout, idiopathic polyarthritis and other serious pathologies of a systemic nature. Self-diagnosis when a lump appears on the knee is impossible and unacceptable. Consult a doctor who, during the examination, will be able to make a preliminary diagnosis and prescribe additional examinations as necessary.
What to do: how to treat and remove a bump on the knee?
The first thing to do when a lump appears on your knee is to see an orthopedist. An experienced doctor will be able to make an accurate diagnosis. only after this will it be possible to talk about how to treat a bump on the knee with minimal risk of harm to human health.
It is important to understand that a lump is not an independent disease. This is a symptom of pathological changes affecting the bone, cartilage or soft tissue of the knee joint. Methods for treating bursitis and tenosynovitis may differ radically from methods of treating deforming osteoarthritis or Baker's cyst. Therefore, correct diagnosis is the most important step towards effective treatment.
There are several ways to remove bumps on your knees, and they include:
- surgery to remove bone growths due to deformation of the head of the femur or tibia;
- performing a puncture to remove accumulated fluid in the joint capsule or bursa;
- arthroscopic intervention for the purpose of enucleation of cystic cavity tumors (lipoma and hygroma);
- endoprosthesis replacement is an operation to replace the knee joint with severe deforming osteoarthritis.
All of these are extreme measures that will be required if timely treatment is not started. In the early stages, any pathology in which bumps develop on the knees can be treated conservatively.