Last Updated on 09/13/2018 by Perelomanet
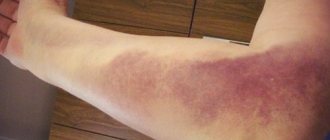
One of the most common injuries to the lower extremities is bruises. This is a closed type injury, in which soft tissues are damaged, but without changing their structure. With bruises, not only the skin, subcutaneous fatty tissue and muscles can be injured, but also nerves with blood vessels, in such cases hemorrhage begins and a bruise occurs. Often, with bruises, not the entire limb is damaged, but only part of it: thighs, legs, knees, toes. Typically, such injuries do not require medical attention, but if the leg is severely bruised, especially the knees, feet and fingers, it is better to visit a traumatologist, since the lack of adequate treatment can lead to dysfunction of the joints and chronic pain.
In this article you will learn everything about this injury, as well as what to do if you bruise your leg first and how to treat it yourself.
Causes
A severe bruise of the leg can be caused by a simple fall at home or on the streets, it can be caused by a blow to the leg with a blunt object, and it can also be the result of sports, occupational injuries and road traffic accidents. The risk group is children and people doing heavy physical work. We list the main causes of such injury:
- Damage to the foot and ankle may be preceded by heavy objects falling on them;
- the shin can be damaged from a direct blow to it;
- the femoral part is injured during a direct blow to it, during a fall, during sports activities or a traffic accident;
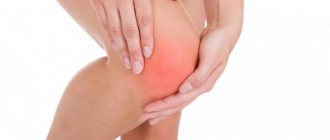
- The knee joint can be damaged during a fall or when it is hit during training or household activities;
- The hip joint can be bruised by a direct blow to it or from a side fall.
Symptoms
Symptoms of a bruise will be:
- severe pain appears at the site of injury, which can severely limit a person’s mobility;
- swelling of the affected area, which may increase over time;
- bruising may appear in cases where blood vessels are damaged;
- hemarthrosis occurs when a knee injury occurs when blood accumulates inside the joint;
- the functions of bruised joints are limited;
- difficult to move;
- in case of severe injuries, pain may occur in the periosteum, it can peel off, even causing bone damage.
Damage may appear differently depending on the extent of the injury and the general condition of the patient.
Symptoms
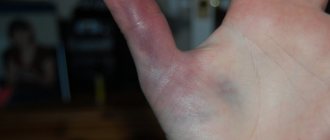
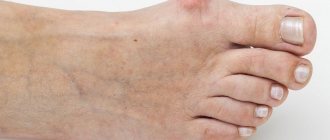
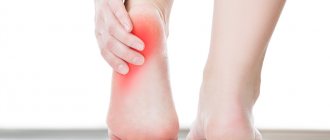
The following signs are characteristic of a foot bruise:
- pain;
- swelling;
- skin redness;
- scratches and abrasions;
- fluctuation - detachment of subcutaneous fat or periosteum with subsequent filling of the resulting void with blood or lymph;
- local hyperemia - heating of the skin in the area of the bruise due to increased blood flow;
- hemorrhage contributing to the formation of a hematoma.
When a foot is bruised, the pain syndrome remains even if it is immobile. The first symptoms: hematoma and swelling appear immediately after injury. Their cause is subcutaneous hemorrhage and accumulation of lymph.
Degrees of injury
The classification of damage by severity is as follows:
- easy first degree. Minor injuries affect only the skin. There are abrasions and scratches on it. In this case, there is no need to treat the bruise with special means; the body fully recovers from the injury in 3-4 days;
- at the 2nd stage, swelling occurs after a bruise due to rupture of muscle fibers, a hematoma may appear, the general condition of the victim worsens, and acute pain is felt. With this degree of damage, a visit to the emergency room is required;
- in the third degree of injury, muscles and tendons are damaged and complications may occur (dislocations, ligament rupture). The most dangerous injuries are in the knee area;
- the most severe is the 4th degree, in which the bruised limb will cease to function due to changes that have occurred in it.
In order to choose the right treatment tactics, you should initially determine the extent of the injury.
In case of 3-4 degrees of damage, you should definitely seek medical help.
In other cases, you can eliminate the consequences of a bruise on your own.
More information about the consequences of an untreated bruise can be found in a detailed article at this link: https://otekoved.ru/nogi/opuhla-noga-posle-ushiba.
Consequences of leg injuries
Trauma is mechanical damage to tissue due to various external factors. Acute leg injuries can be very diverse and depend on the location (injuries of the hip, knee, leg, foot), degree and type of damage (bruises, sprains and tears, dislocations, fractures). Also, there are leg injuries due to constant heavy overload. Such injuries most often occur in people who undergo heavy physical activity (for example, professional athletes).
Types of Injuries
Bruises are closed tissue damage in which their structure is not significantly damaged. Appears as a result of a blow with a blunt object or a fall.
Sprains and tears. In fact, both a sprain and a rupture are a rupture, only on different scales of damage. When stretched, individual collagen fibers or microscopic connections break. A rupture is considered to be a direct rupture of the entire ligament. This type of injury occurs when there is a sudden movement of the joint, much more than the joint can withstand.
Dislocation is a disruption of the connection of the articular surfaces of bones, both with and without disruption of the integrity of the articular capsule. They arise due to mechanical stress, or due to destruction processes in the joint (arthrosis, arthritis).
Bone fractures can be closed or open. It occurs due to heavy loads on the bone, collisions, or sudden falls. Symptoms of a fracture: pain, deformation of the limb, movement of the bone in the wrong place, rapid swelling, hematoma, crunching, disruption of the limb. With an open fracture, the bone can be seen with the naked eye.
Causes of leg injury
The main causes of leg injuries:
- Repetitive movements (during vigorous walking, running);
- Sharp sudden load on a muscle, tendon, bone;
- Overload;
- Concomitant diseases (arthrosis, arthritis, bursitis, inflammatory processes).
Consequences of leg injuries
Consequences of sprains and tears. After sprains, provided the regimen is followed, there are practically no complications. After a rupture, there can be many consequences: chronic pain and inflammation (due to the appearance of nodules at the site of fusion), numbness and tingling due to nerve damage.
After a fracture, there may be various complications: nerve damage, improper bone healing, tissue infection, muscle atrophy due to long-term immobility, circulatory disorders in the fracture area.
Consequences of bruises. In most cases, bruises go away without consequences. Complications after a bruise can be: violation of the integrity of large vessels, tumors, compactions, which can cause pain when moving.
The consequences of dislocations can be circulatory disorders, violations of the integrity of the joint, and normal dislocations.
Treatment
Treatment of a fracture. Depending on the severity of the fracture, treatment is chosen: conservative or surgical intervention.
Treatment of dislocation: closed or open (surgical) reduction of dislocation, strengthening of the capsule, bone grafting, muscle and tendon grafting, use of grafts.
Treatment of bruises. Immediately after injury, cool the injury site and rest. In case of complications, surgical intervention is possible.
Treatment of sprains and tears. With conservative treatment, everything depends on the severity of the injury - rigid (plaster) or non-rigid immobilization of the rupture site is recommended. During surgical treatment, the torn ligament is stitched with lavsan and fixed to the place of attachment.
During the rehabilitation process, physiotherapy, exercise therapy, and massage are recommended for all types of injuries.
For any injury, you should not delay treatment; you should always pay attention and respond to even the slightest changes and inconveniences. Following your doctor's instructions will help you regain maximum function in your leg.
First aid
Since a bruise of the lower limb is a fairly common injury that can be received on the street, at home, at work or in the gym, every person must know how first aid is provided for such injuries. The sequence of actions will be as follows:
- the victim must be seated, and the injured limb must be placed on a pillow and provided with rest;
- if there are skin damage (wounds, abrasions), they need to be disinfected;
- if the leg is swollen, you need to carefully apply a non-pressure bandage;
- A cold compress should be applied to the injured area. This could be a water bottle, an ice pack, or anything from the freezer. In order not to freeze the skin, the compress is applied through a towel for 10-20 minutes, the procedure can be repeated after half an hour;
- if the bruise is severe and the victim feels acute pain, it is necessary to give a painkiller.
With 1-2 degrees of injury, the above actions are enough to relieve swelling and relieve pain, but if the uncomfortable symptoms do not go away and the swelling increases, you should definitely contact a traumatologist.
On the first day after injury, you should not rub your legs or apply heating compresses or ointments, and you should also limit physical activity.
First aid
A foot injury requires immediate medical attention. However, before being examined by a doctor, the victim needs to provide first aid through several simple steps:
- Ensure absolute rest of the affected limb.
- Apply a fixing bandage, avoiding pinching of the vessels.
- Apply cold to the damaged area. It is best to use ice wrapped in cloth for this purpose. A cold compress helps to constrict blood vessels and reduces the risk of hematoma and swelling. It is applied for 15-20 minutes, after which it is removed and a five-minute break is taken.
Attention!
If a fracture is suspected, it is necessary to apply a splint and ensure complete immobility of the affected leg.
Swollen foot: what to do
If swelling appears after a bruise, you should promptly consult a doctor who will prescribe a course of treatment with drugs that remove fluid. Before being examined by a specialist, it is important to ensure that the injured limb is immobile, fixed in an elevated state, and then not to step on it until complete recovery.
What to do if the integrity of the skin is damaged
The damaged area of the skin of the foot is treated with any antiseptic: brilliant green, alcohol, iodine or chlorhexidine. In order to prevent bleeding, an antiseptic bandage is applied to the wound.
What is prohibited to do
Before being examined by a doctor, it is prohibited to take medications (especially painkillers), as this will lead to a distortion of the clinical picture.
Note!
If you suspect dislocations or fractures, you should not try to set them yourself, or transport the victim without fixing the injured limb.
When to see a doctor
Self-treatment of a foot bruise is possible only with minor damage (grade I), expressed by the appearance of scratches and abrasions. In all other cases, the victim requires qualified medical care.
My leg is swollen - what to do?
The most common problems after bruises are the legs with swelling, which causes the victim not only pain, but also inconvenience.
In the first three days, treatment will consist of applying cold compresses, but over time, to eliminate the compaction, you can resort to hot baths and lotions, which additionally promote the resorption of the hematoma.
You can also rub non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs into the leg - Voltaren emulgel, Ibuprofen ointment, Heparin gel, Proxevasin. They need to be applied to the affected area several times a day. Compresses with Dimexide, Menovazin or Romazulan will help reduce swelling. Dolobene and Troxevasin can simultaneously eliminate swelling, pain and inflammation.
For severe bruises, a specialist may prescribe physical procedures such as ultra-high-frequency therapy, electrophoresis, and magnetic therapy.
In the following cases, a bruise and its consequences can only be cured surgically:
- when the bruise festeres;
- if the nerve roots are damaged;
- when intra-articular hemorrhage occurs;
- in case of ligament ruptures and their separation from the place of attachment.
Diagnostic measures
To determine the nature of the bruise, the specialist first examines, performs palpation, and then sends the patient for radiography, where they take a picture of the foot in two projections. After confirming the diagnosis, the traumatologist may prescribe a consultation with an orthopedist or neurologist.
The difference between a fracture and a bruise
You can distinguish a soft tissue bruise in the foot from a fracture by the following signs:
- Violation of bone integrity
- With a fracture - yes.
- With a bruise - no.
- Violation of skin integrity
- In case of a fracture – observed with an open injury.
- If there is a bruise, it is absent.
- Presence of pain syndrome.
- When fractured, it does not decrease.
- If there is a bruise, it will subside after a while.
- Physical activity
- In case of a fracture, it is impossible.
- In case of bruise, it is preserved.
At the moment of fracture, a crunching sound is clearly heard, indicating a violation of the integrity of the bone.
Important!
A fracture of the bones of the foot requires the mandatory application of a plaster cast, but with a bruise there is no need for this.
Treatment at home
Treatment at home for an injured leg involves limiting physical activity in general and resting the leg in particular; in addition, you can use alternative medicine methods, which in practice have shown to be effective for mild bruises. We list the most common and effective means:
- if you need to relieve swelling, you can make a vodka compress. Gauze is dipped in vodka and applied to the affected area for a couple of minutes;
- onions help relieve pain. The onion head is rubbed on a coarse grater, the resulting gruel is wrapped in gauze, and when the material is completely saturated with juice, it is applied to the injured surface for 3 hours. The procedure can be carried out in the morning and before bedtime;
- To improve peripheral blood circulation and quickly resolve the hematoma, you can use a vinegar-garlic mixture. This paste should be rubbed with light massage movements into the affected area;
- Aloe will help eliminate inflammation and reduce swelling. It can be used in several ways: firstly, take a leaf, cut it lengthwise and apply the cut to the bruised area, secondly, squeeze aloe juice from the leaf and make a compress from it;
- After eliminating the swelling, you can speed up the healing process by using salt baths. To prepare them, you can use table or sea salt. Dissolve half a pack of salt in a bowl of warm water. The water should be warm, since hot water can increase blood flow and make the hematoma even larger. The bath should be done for no more than an hour, every day until the functions of the damaged limb are completely restored.
Treatment of bruises of the lower extremities with the right systematic approach will not take much time, but even a mild injury should not be ignored in order to prevent consequences that can subsequently adversely affect the quality of your life.
3. “Overworking” injuries
Leg injury, ankle injury, foot injury or toe injury can occur not only due to sudden exposure to some factors, but also when an activity is repeated too often and for a long time. “Overworking” injuries can be:
- Bursitis
is an inflammation of the bursa (the mucous membrane of the bursa in the joint area). Bunions cause swelling and tenderness in the back of the heel and ankle. The pain usually gets worse when you wear shoes or do any physical activity on your feet. And during rest, the pain decreases. - Achilles tendonitis
(tendopathy) is an inflammation of the tissue in the area of the Achilles tendon, which connects the calf muscles and the heel bone; - Microcracks in the bone;
- Plantar fasciitis
is an inflammation of the plantar fascia, a broad, flat ligament on the bottom of the foot that runs from the front of the heel to the base of the toes and helps support the arch of the foot; - Metatarsalgia
is pain in the foot in the front part (metatarsal part of the foot).
About our clinic Chistye Prudy metro station Medintercom page!