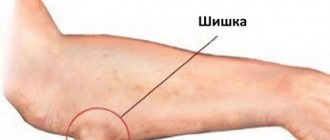
During the day, a person's elbow joints are subject to heavy loads. The elbows of people whose activities are aimed at monotonous movements of the upper limbs are especially affected. The resulting tumor on the elbow causes discomfort and provokes a number of symptoms, which, if not treated in a timely manner, lead to diseases of various directions.
First of all, a bump on the elbow has a noticeable cosmetic defect that develops psychological discomfort over time. The resulting compaction additionally causes inconvenience in the form of pain and limitation of movements. A tumor on the elbow should be treated after a competent diagnosis by a specialist who clarifies the nature of the tumors, eliminating associated clinical signs, and stopping the main focus of the pathology.
Article structure
Possible reasons
Experts say that the term “bump” does not exist in their professional field. Any neoplasm in the joint is characterized by a special hematoma that occurs against the background of violations of the integrity of the blood or lymphatic vessels. A tumor on the elbow has individual clinical manifestations depending on the nature of the formation. Doctors have identified widespread causes of the development of the pathological process:
- After the blow, a soft lump forms on the elbow joint. It may not be visible immediately after the injury. In conclusion, doctors indicate a fracture or displacement of a bone fragment.
- An elbow bruise is manifested by pain migrating to the shoulder area. The tumor is localized under the skin or deeper inside the upper limb.
- Sometimes a person develops a growth on their elbow due to an insect bite. It is better not to put off visiting the doctor. Often the lump becomes red, swollen, and painful.
- Less commonly diagnosed is the development of pathology against the background of allergic reactions to food, medicines, and hygiene products.
- A tumor of the elbow is possible due to violations of sanitation rules during drug therapy. In this case, it is quite insidious, because untimely treatment provokes a number of complications. Accumulated intercellular fluid or water can lead to an inflammatory process.
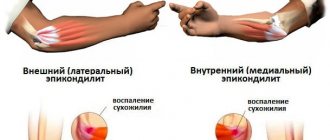
- In medicine, a disease of the elbow joint that most often affects athletes is called bursitis. It is formed due to heavy physical stress on the joints in the elbow.
A tumor on the elbow may have a malignant form of lesion. Neoplasms appear internally or externally on the right or left arm, bother the patient with intense pain, and require immediate surgical procedures.
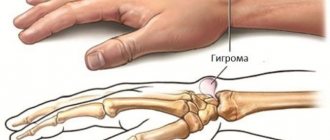
Lumps on the elbows can appear due to regular stress on the arm. A soft cyst filled with fatty tissue without pain is called a lipoma in medicine. If serous fluid forms inside, doctors diagnose hygroma of the elbow joint. The reason for the development of the pathology is long-term and systematic compression of blood vessels.
Analysis of the main reasons for the appearance of a lump on the elbow, their features
Let's look at the main causes of diseases that cause a tubercle to form in the elbow joint.
Causes of elbow bursitis
- Increased stress on the elbows: athletes (tennis players, wrestlers), miners, office workers are affected.
- A bruised elbow can cause post-traumatic bursitis.
- Direct infection of the synovial bursa through an abscess, open wound, or boil.
- Infection through the blood or lymph in the presence of carbuncles (purulent inflammation around several sebaceous glands), boils, erysipelas (an infectious disease caused by group A beta-hemolytic streptococcus, leading to redness of the skin and increased body temperature), osteomyelitis (purulent inflammation of the bone) , purulent wounds, bedsores (deaths of skin and muscles as a result of pressure on them with body weight in a stationary position).
- The risk of the disease is increased by: metabolic disorders, diabetes mellitus, reduced immunity, disorders of the immune system, taking steroid drugs (drugs based on adrenal hormones: Dexamethasone, Prednisolone, Hydrocortisone).
Risk factors for elbow bursitis
Causes of gouty arthritis
- Excess in the diet of foods containing purines: red meat, offal, fish, coffee, cocoa, tea, chocolate, legumes, beer, wine.
- Kidney failure.
- The risk increases due to high cholesterol levels, hypertension, and hereditary predisposition.
Causes of rheumatoid arthritis
The exact reasons are unknown.
Factors that increase the risk: genetic predisposition, the presence in the body of herpes viruses, Epstein-Barr, mumps, measles, hepatitis B, cytomegalovirus, T-lymphotropic virus, frequent hypothermia, stress, endocrine disorders.
Features of lumps in various pathologies (depending on the cause)
For different diseases, the tumor looks different:
| Disease | Features of the cone |
| Bursitis | Swelling and swelling, large red elastic lump It is painful, but the pain is not sharp, its severity is average, it intensifies when touching the elbow |
| Gouty arthritis | Very painful hard red lump Her skin shines from tension Very painful, most often appears at night |
| Rheumatoid arthritis | Multiple subcutaneous lumps with a diameter ranging from a few mm to 2 cm Painless and non-reddening They are not the main symptom and appear in only 20% of patients |
| Malignant neoplasm | Hardening and swelling of the soft tissue around the joint that is very painful |
Clinical picture
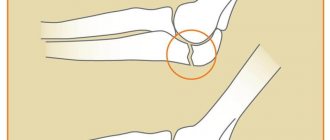
A tumor on the elbow joint is characterized by a change in its contours. Additional signs may be:
- Edema. It is formed due to the accumulation of intercellular fluid in the tissues, which subsequently disrupts its migration, increasing the size of the affected area.
- Swelling. Appears when inflammation activates in the affected area of the elbow. It often occurs with a local increase in temperature and redness of the skin tissue.
Partial or complete immobility of the joint. Patients feel discomfort from the inability to fully move their arm.
Recommended reading: How does a coccygeal cyst manifest itself?
The lump is soft and does not hurt
A soft lump on the elbow without significant symptomatic manifestations indicates the development of bursitis. Often the inflammatory process occurs after injuries in the form of a sprain, dislocation, or strong blow. Trauma promotes the accumulation of synovial fluid. There is swelling on the elbow. After a while, a lump grows under the skin, the size of a chicken egg.
When bursitis of the elbow joint occurs, increased tension and damage to tissue fragments occur. The elbow suffers due to physical activity. Frequent flexion and extension of the upper limb provoke pain attacks.
hard lump
After an accidental blow, patients notice the formation of a hard tumor in the elbow joint. Compaction sometimes signals the onset of a malignant neoplasm, which for a long period of time does not make itself felt by clinical manifestations.
- Diseases that cause pain in human elbow joints, a list of causes and symptoms
Over time, patients suffer from intense pain attacks in the elbow, which can radiate to other areas of the upper limb. A large number of vessels in the elbow provokes the migration of cancer cells through the bloodstream into healthy human organs and systems. A cancerous tumor on the elbow has specific clinical manifestations:
- general increase in body temperature;
- increased fatigue from ordinary everyday chores;
- weakness throughout the body;
- lack of appetite;
- unreasonable reduction in weight indicators;
- elbow joint deformity;
- enlarged regional lymph nodes;
- feeling of brittle bones.
It is important to note that patients diagnosed with elbow malignancy have a high incidence of spontaneous fractures. Visual examinations do not always reveal the development of the disease. To confirm the diagnosis, several instrumental diagnostic techniques are prescribed.
Features of the pathology
The term “bump” does not exist in surgery. That is, any lump that occurs in a joint is a kind of hematoma that occurs as a result of a violation of the integrity of the lymphatic or blood vessels. Such a neoplasm may not cause any discomfort or, conversely, be accompanied by pain and inflammation and interfere with normal motor activity.
The main feature of such a neoplasm is its location - due to the close proximity of the moving joint, the risk of hematoma rupture or complications increases. Therefore, therapy should be carried out as soon as the tumor is detected.
Possible causes of a lump on the elbow
If a person’s elbow is swollen, red, begins to hurt and becomes hot, then the patient most often consults a doctor to understand what it could be and what to do to alleviate the condition. But such a neoplasm may not be red, and, being inside both the right and left arm, may not cause any inconvenience - patients are in no hurry to treat such hematomas, which is why complications subsequently arise. Even if the contents of the tumor are water or intercellular fluid, over time it can become inflamed.
Bursitis
This pathology is also called “athletes’ disease.” It received its name for the formation of tumors on the joints that are subject to the greatest physical stress. The pathology develops gradually, without causing any inconvenience at first. Over time, the tumor begins to interfere with the activity of the joint, and inflammation begins to appear. Bursitis of the elbow joint is characterized by chronic exacerbations and in some cases does not manifest itself in any way other than an increase in the size of the tumor.
Malignant tumors
If the lesion is malignant, the tumor in the elbow joint can be located on the left or right arm, on the outer or inner side. The cause of this elbow lesion is a cancerous tumor, which is characterized by night pain and requires surgical treatment.
In case of malignant joint damage, conventional painkillers cannot relieve pain. Such tumors have specific characteristics:
- a sustained increase in body temperature to a subfebrile level;
- feeling of general weakness;
- chronic fatigue syndrome;
- increased fatigue;
- decreased appetite;
- gradual loss of body weight;
- paroxysmal pain resistant to painkillers;
- deformation of the outlines of the joint;
- enlargement of regional lymph nodes;
- increased fragility of bones until spontaneous fractures occur.
Note! To confirm the diagnosis, the doctor prescribes a series of tests. It is impossible to determine the malignant nature of the neoplasm by visual examination.
Lipoma and hygroma
If a patient develops a lump on the elbow joint that is soft and does not hurt, then it is most likely a lipoma. A lipoma is a benign neoplasm, which is a cyst filled with adipose tissue. This tumor does not cause any discomfort, but it does not respond to traditional treatment. and therefore its removal is carried out exclusively surgically.
Hygroma is a cystic neoplasm that is filled with serous fluid. Such a tumor is formed from the joint capsule or from the tendon. The reason for its appearance is regular exercise.
It occurs predominantly on the inside of the elbow, which interferes with the motor activity of the joint. As the cyst grows, the blood vessels are pinched, which leads to the development of pain and swelling.
Lump after impact
The appearance of a bump after a blow is one of the most common causes of the formation of neoplasms. If, after a fall or blow, the elbow joint swells, the elbow itself begins to swell and hurt, the cause is the formation of a hematoma. In this case, the hand may swell, it swells and requires prompt treatment.
Diagnostics
To correctly diagnose and prescribe effective treatment, doctors prescribe an X-ray examination. The technique allows you to identify the focus of the tumor and its effect on the surrounding tissue areas.
A tumor on the elbow is examined by tomography. The results of magnetic resonance or computed tomography determine the boundaries of the pathology. With their help, the source of damage is studied.
Additionally, doctors practice osteoscintigraphy. During the examination, a special liquid is injected into a vein, which accumulates inside malignant tumors. When X-rayed, the zones become contrasting, allowing you to accurately study the size of the bumps and the condition of the tissue areas that are located nearby.
When making a diagnosis, the doctor orders a biopsy. The accumulated fluid is collected and examined using histological techniques. In most cases, biopsy is practiced for therapy. The manipulation involves pumping out fluid from the cyst through a needle.
Experts often recommend performing an MRI or CT scan of the damaged area. Diagnostic measures confirm or exclude the malignant nature of the tumor on the elbow joint.
Treatment methods
If a lump appears on your elbow, you should immediately consult a doctor. Therapy has a complex direction, including treatment with medications, folk remedies, and physiotherapeutic manipulations.
It is important to understand that self-medication relieves unpleasant symptoms only for a short period of time. A competent treatment regimen can change the situation, relieving the patient of the pathology forever. During therapeutic measures, doctors observe how the lump on the arm behaves under the skin above the elbow. If necessary, the treatment regimen is adjusted by the attending physician.
We recommend reading: How to treat a tumor on the tailbone?
Conservative methods
If the bone in the elbow hurts due to injury or the development of bursitis, traditional methods of therapy are used. Attacks of pain subside after taking non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. In combination, doctors recommend using absorbable creams and ointments to help reduce swelling.
- Shoulder pain: causes, symptoms and diagnosis
Operation
Sometimes identified compactions in the elbow bend require surgical interventions. Doctors in most cases perform a puncture. When manipulating with a thin needle, the capsule is pierced, pumping out the accumulated liquid from it. The procedure is performed to treat small or large tumors with liquid materials. After the puncture is completed, the resulting fluid is sent to the laboratory, where histology is performed. The injured elbow is fixed with a tight bandage.
When the tumor grows rapidly, doctors resort to draining the ulnar bursa. A damaged joint requires the installation of drainage, which allows fluid to drain out. Manipulation allows you to treat the cavities of neoplasms from the inside, promptly stopping inflammatory processes.
To restore the mobility of the affected joint in a short period of time, bursectomy is practiced. The surgical procedure is characterized by removal of the joint capsule. The operation is performed closed or open, depending on the severity of the pathology. During the recovery period during pain attacks and to eliminate inflammation, the patient is prescribed NSAIDs by injection.
Traditional treatment
Alternative medicine for the formation of lumps on the elbow has a special place among treatment methods. Most patients study the recipes of folk remedies, preparing healing decoctions, tinctures, ointments, adhering to the advice of famous healers and healers. Modern medicine does not exclude treatment with traditional methods, including them in complex therapy measures.
Propolis has a miraculous effect on neoplasms. There are many recipes that allow you to forget about pain, limited mobility of the affected arm, and inflammation in a short time. For the healing liquid you need to take:
- 1 tbsp. propolis;
- 2 tbsp. water.
After mixing the ingredients well until smooth, leave the liquid in a warm place for 15-20 minutes. Then rub the product into the damaged segment on the elbow. To ensure immediate results, it is recommended to wrap your elbow with an elastic bandage and leave it until the morning. The procedure must be carried out daily before bed for at least 10 days.
It is recommended to apply compresses of ordinary salt for two weeks. A glass of salt is heated in a hot frying pan. Next, the product should be poured into a fabric bag and placed at the site of the tumor, secured with a scarf or towel for 3-4 hours.
For a therapeutic compress, which is allowed to be applied no more than 2-3 times every 7 days, you will need:
- aloe juice – 1 tablespoon;
- liquid honey – 2 tablespoons;
- alcohol – 50 grams.
After thoroughly mixing the ingredients, the resulting mixture is poured into a glass container and left in a dark, warm place for 2-3 days. Afterwards, compresses are applied at night, wrapping the pre-rubbed sore elbow fragment with polyethylene material, securing it with a warm scarf on top.
- Hygroma of the knee joint: photos, causes, symptoms and treatment
You can relieve attacks of pain and prevent the progression of inflammation with the help of cabbage leaves. The easiest way is to place the sheet on the elbow with the inside. The procedure is complicated for effectiveness with a compress of leaves soaked in sunflower oil, lubricated with a natural bee product. It is recommended to make compresses with beets or potatoes. Cabbage leaves can be replaced with burdock.
It is important to know that seemingly harmless herbal remedies can cause complications. Having decided to relieve symptoms using “old-fashioned” methods, you should consult a doctor so as not to harm your general health.
Physiotherapeutic sessions
After making sure that there are no purulent masses, doctors recommend physical therapy. Proven methods are often the main treatment. The procedures are practiced during the rehabilitation period after operations.
It is important to choose the right physiotherapeutic methods to prevent worsening of the condition. They practice X-ray therapy, radiation procedures, and UHF. Cold compresses and dry heat are effective.
Methods of treating diseases
Which methods will be used depends on the reason why the lump has formed on the elbow joint.
Treatment of bursitis
If the form of the pathology is acute, a tight bandage is applied to the elbow, and the doctor also prescribes anti-inflammatory medications (Ibuprofen, Meloxicam, Diclofenac) to take. Sometimes a therapeutic puncture of the synovial bursa is performed.
If acute bursitis is accompanied by the formation of a purulent infiltrate, then anti-inflammatory drugs are prescribed in combination with painkillers (Bupivacaine, Trimecaine). Punctures are also performed.
Sometimes they are not enough, and then surgical methods are used: the synovial bursa is opened and drained (pus is removed from the joint using a tube).
In the chronic form, only excision (removal of the affected tissue with a scalpel) of the synovial bursa is effective, since punctures do not give results - some time after removing the infiltrate, it forms again and the joint swells.
Treatment of rheumatoid arthritis and the nodules that form due to it
As a local treatment, ointments and creams with glucocorticosteroids (drugs based on adrenal hormones: Hydrocortisone, Betamethasone) are used. They allow you to relieve the inflammatory process in the nodules themselves and reduce them.
It is also necessary to treat rheumatoid arthritis itself, which consists of taking:
- anti-inflammatory drugs (non-steroidal or glucocorticosteroid);
- antirheumatic medications (Methotrexate, Sulfasalazine);
- immunosuppressants (Remicade, Enbrel, Orencia).
Treatment of gout
You can get rid of a tumor on the elbow, which is caused by gout, by relieving the exacerbation.
| To do this, the doctor will recommend taking one of the anti-inflammatory drugs | To prevent relapses it is prescribed |
| Colchicine | Low Doses Colchicine |
| Indomethacin | Medicines that interfere with the production of uric acid (for example, Allopurinol) |
| Naproxen | Medicines that accelerate the excretion of uric acid (Sulfinpyrazone, Azapropazone) |
| Phenylbutazone |
Treatment of a malignant tumor of the elbow
Depending on the stage, choose one of the following tactics:
- At the initial stage of disease development, radiation therapy (targeted exposure to high doses of radiation to destroy tumor cells). It is also used as preoperative preparation at later stages.
- At a more severe stage - removal of the cancerous tumor.
- In very advanced cases – amputation of a limb.
Anticancer drug therapy is also used to prevent metastases (the appearance of tumor cells outside the primary focus) in the lymph nodes.
Prevention
To prevent deformation in the elbow segment, many preventive measures have been developed. Experts advise starting heavy physical activity with a warm-up, warming up the joints.
If human activity involves constant stress on the elbow joint, it is necessary to use special protective equipment, bandages. It is important to learn how to distribute activities to the upper limbs so as not to provoke overstrain of muscle structures and to eliminate unwanted injuries as much as possible.
Specialist Trandafilov Eduard Antonovich Specializes in diseases of the musculoskeletal system, injuries of the knees and legs, hands, etc. Performs closed reduction of dislocations, applies immobilizing bandages, etc. Consultation with a surgeon / Max 3085 July 2020
The Ask a Doctor service offers online consultation with a surgeon on any problem that concerns you. Expert doctors provide consultations around the clock and free of charge. Ask your question and get an answer immediately!
Answers from doctors ComplainOlga Lee, July 11, 2021 Children's ENT, ENT Hello. Please send a photo. ComplainAngelina Slepova, July 11, 2021 Cardiac surgeon, Surgeon, Phlebologist Hello! Can you attach a photo of the new growth? + 1Complain Yakov Martirosyan, July 11, 2021 SurgeonComplain Max, July 11, 2020 Client Yakov, Why did this appear? After all, there were no bruises or other injuries. ComplainOlga Lee, July 11, 2021 Children's ENT, ENT The bruise or blow could be minor, and therefore not noticeable to you. Elbows and knees are often susceptible to injury. They answered you correctly - yes, you need to puncture or open it. Get well. + 1Complain Elena Prilepina, July 11, 2021 Mammologist, Surgeon, Oncologist Hello. According to the description of the problem, most likely we are talking about elbow bursitis. It is necessary to limit the load on the arm, locally on the joint 2-3 times a day for 10-14 days - ointment/gel (Nise, diclofenac, indomethacin, fastum-gel) + compress dimexide 1:6 (water) or vodka compress. Make a compress on top of the ointment without cellophane, without compress paper for 15-20 minutes. If the swelling does not decrease, you will need to contact a surgeon for a puncture. ComplainMax, July 11, 2020Client Elena, Why did this appear? After all, there were no bruises or other injuries. ComplainMax, July 11, 2020Client Elena, is Voltaren 2% suitable? Complain Elena Prilepina, July 12, 2021 Mammologist, Surgeon, Oncologist This can be not only due to injury, but also due to overload on the joint. Voltaren is also useful. Complain Yakov Martirosyan, July 11, 2021 SurgeonComplainVladislav Khmel, July 12, 2021 Surgeon Hello, the photo shows ulnar bursitis. Causes: Chronic traumatization (manual work, builders, mechanics, etc., but not always). Treatment - puncture by a surgeon or traumatologist at the clinic on Monday - application of a pressure bandage - topical diclofenac gel 3 times a day - NSAID tablet (Nise, Airtal, Meloxicam - any of your choice, 1 t 2 times a day for 5-7 days). If it is repeated, then puncture followed by the injection of Diprospan solution into the joint capsule. Be healthy! ComplainKonstantin Tishchenko, July 12, 2020 Orthopedist, TraumatologistComplainKonstantin Tishchenko, July 12, 2020 Orthopedist, Traumatologist Similar questions on the topic Bedsore7 answersFebruary 21200.00 RUR, St. PetersburgBarrett, fixed hiatal hernia5 answersFebruary 25300.00RURVeraBolti belly. Gastroenterologist. Surgeon40 answers February 23, 200.00 R.Oleg, ChelyabinskPain under the knees from behind8 answers February 24, 200.00 R.Anna, MoscowHangnail is festering1 answerFebruary 24,AntonInflamed lateral nail fold without ingrown nail1 answerFebruary 24Armen,MoscowFibrosis on the buttock8 repliesFebruary 24,300.00 R.AnastasiaWhat to do if I Didn't find the answer to your question?
If you have a similar or similar question, but you have not found the answer, get your medical consultation online.
If you want to get a more detailed consultation with a doctor and solve the problem quickly and individually, ask a paid question in a private personal message. Be healthy!
28063
If a soft lump on the elbow joint does not hurt, this is not a reason to ignore it.
It is a hematoma, which is a consequence of a violation of the integrity of the lymphatic and blood vessels.
A detected tumor can sometimes be accompanied by pain and inflammation. This leads to disruption of the motor function of the joint.
Lump on the inner bend of the elbow
Injuries, professional activities and the age factor cause the appearance of a lump on the elbow. In most cases, it has the shape of a ball with pronounced swelling and intense pain.
In medicine, this disease is called “bursitis”. Sometimes it starts for no apparent reason. The disease affects various joints, but the elbows and knees are most at risk due to constant stress throughout the day.
What causes this disease and how to treat it?
A lump on the bend of the elbow can occur due to monotonous and uncomfortable working conditions.
Causes and symptoms
The bursa (also called bursa) is a fluid-filled capsule that protects muscles, ligaments, and skin from friction with bone. Bursitis of the elbow joint develops due to inflammation. Doctors list the causes of the disease as:
- elbow injuries;
- prolonged overexertion or pressure on the joint (for example, the elbow is in a certain position for a long time);
- strong physical activity,
- gout and arthritis;
- an infection that entered the body through cuts (in very rare cases).
There are 2 forms of the disease: acute and chronic. In the acute form, inflammation develops quickly. The first and main symptom is a soft-to-touch lump that has formed on the inside of the elbow, which quickly increases in size.
The skin around the lump turns red, the pain is intense, intensifies with flexion and extension and causes significant discomfort. Body temperature rises to 37−37.2 degrees. Against this background, the following signs of intoxication occur: nausea, vomiting (in rare cases), chills.
If acute inflammation is left untreated, there is a danger of the disease becoming chronic.
In the chronic form, the lump on the elbow joint is soft, the pain becomes mild, and always occurs after exercise, especially in the area on the inner bend.
It is important to pay attention to the mobility of the limb. If the arm goes numb and the elbow does not bend/extend, then this is not bursitis.
When the bursa is inflamed, movements cause discomfort associated with pain, but they are not difficult.
Diagnosis of lumps on the bend of the elbow
To prescribe the correct treatment for a lump on the elbow, the patient must undergo an MRI or ultrasound.
The patient should not jump to conclusions that bursitis is characterized only by pain in the elbow and minor swelling. There are many disorders with similar symptoms. General condition plays a significant role.
At the first signs, you should consult a doctor. Self-medication can have unpleasant and dangerous consequences. The primary diagnosis is carried out by a therapist or surgeon who prescribes an x-ray. When treating bursitis, it is important to establish an accurate diagnosis, since other joint diseases require different treatment.
The patient must clearly describe the symptoms, duration and intensity of pain, and what could have caused the injury. For example, if it was a blow, the doctor must rule out a bruise, crack, or fracture that causes swelling.
Infectious bursitis is recommended to be treated with anti-inflammatory drugs and general-spectrum antibiotics.
The degree of joint damage affects the course of treatment. An MRI or ultrasound will show how the process affects the tissues around the elbow. Inflammation causes the accumulation of pus and a more acute picture of the disease. In this case, surgery may be necessary.
The doctor prescribes general blood and urine tests to check for signs of cancer in the body. The similarity of symptoms between bursitis and tumor is the main danger to human life. If the neoplasm is malignant, the lump will begin to harden and affect the movements of the hand.
In such cases, only surgical intervention and proper postoperative therapy will be an effective treatment method.
How to treat?
Correctly selected treatment is a guarantee of complete recovery. Under no circumstances should you try to cure the disease yourself, without first consulting a specialist. If the doctor correctly selects treatment methods, then the possibility of its repetition or becoming chronic is minimal. The following recommendations will help speed up your recovery.
Don't overexert the joint
In case of intense stress or joint injury, the hand needs complete rest. Keep movement to a minimum by immobilizing your arm as your doctor does. But this does not mean immobilization of the limb. Blood circulation should not be impaired, and the patient should not feel numbness in the limb. Bed rest is important.
Try not to overwork in the first days of illness, rest more, do a light massage and warm up your arms. Doctors recommend drinking more fluids. Tea with chamomile or mint will help reduce pain. Do not perform the activity that caused the injury.
After recovery, change the position of your elbow more often and use special shields (available at pharmacies) that reduce pressure.
Remove inflammation and cool
To reduce the amount of fluid in the synovial bursa, take pills against inflammation and pain, as prescribed by your doctor (Aspirin, Ibuprofen, etc.). Anti-inflammatory ointments for joints have a noticeable effect.
In severe cases of the disease, antibiotics may be prescribed. In addition, using cold compresses is effective. Ice is one of the most effective remedies for relieving swelling. Ice cubes should be placed in a thick cloth and pressed against the bump for 20-25 minutes.
Repeat the procedure no more than 2 times a day.
Constant movement
To fully restore the functionality of the joint, it is important to warm it up regularly. Sets of exercises for the hands will improve the condition of the joints in general and will prevent the disease in the future. But only a doctor can determine the correct load, who can also explain the technique for performing them.
Operating method
In case of accumulation of pus in the bursa, chronic disease, or when diagnosing malignant tumors, surgical intervention is required. Rehabilitation after this operation is quick, the patient immediately feels a decrease in pain and swelling. In addition, the operation guarantees the exclusion of severe damage to the joint, which in the future can affect the motor abilities of the hand.
Source: https://StopRodinkam.ru/shishki/na-sgibe-loktya.html
Development of the disease
Flexion of the elbow joint is carried out thanks to synovial fluid. It is located in the periarticular bursa (bursa) and acts as a lubricant, reducing friction and preventing various damage.
For a number of reasons, the synovial bursa can become inflamed and filled with fluid, causing the onset of a disease such as bursitis. It can have an infectious form of development, consisting of two types - specific and nonspecific.
The first type of inflammation occurs in diseases such as gonorrhea, brucellosis, and syphilis. The second is the consequences of injury or infection of an open wound, when some of the purulent contents enter the periarticular fluid. After this, the inflammatory process begins, leading to the formation of a soft compaction under the skin.
A feature of the disease is its location, since the proximity of a moving joint can affect the rupture of the hematoma and provoke complications. Therefore, if a tumor appears, you should immediately consult a doctor.
Causes
If a jelly-like lump appears on the elbow joint, it means that we are talking about bursitis. This disease is more common than cancer, which also causes a lump. A wen may also appear under the skin, hard to the touch and located on the inside of the elbow. It is not a malignant tumor and is removed surgically.
What is a soft lump on the elbow joint can only be answered by a doctor after examining the patient. It is usually the main symptom of the development of bursitis. Causes of the disease:
- Inflammatory process due to injury - sprain, dislocation, severe bruise. After the impact, the joint tissues become injured and inflamed. This leads to an increase in the volume of synovial fluid. As a result, swelling in the form of a lump forms on the elbow bend under the skin.
- Overstrain of the joint during physical activity. Occurs when the arm bends frequently and the arm remains in one position for a long time.
A hard lump that hurts on the elbow joint usually appears after a sharp and strong blow.
The compaction may be a symptom of the onset of the development of a malignant tumor, which does not manifest itself for a long time, but gradually impairs motor functions. Subsequently, the changed shape of the hand indicates a possible manifestation of oncology at the initial stage.
Associated symptoms
There are many vessels concentrated in the olecranon process, so cancer cells can quickly spread through the bloodstream into nearby tissues. When the elbow is deformed, the following signs are observed:
- persistent pain after taking painkillers;
- obvious protrusion formed under the skin;
- enlarged joint lymph nodes;
- general weakness of the body, fatigue, loss of appetite;
- elevated temperature;
- painful sensations when bending and straightening the arm.
If you do not start treatment in time, having discovered such symptoms, then in addition to the lump, the disease may also be accompanied by spontaneous fractures.
Some reasons for the growth should be considered. Symptoms of individual cases:
- The formation of purulent bursitis can be affected by injuries, infection with streptococcus, as well as advanced inflammation. The disease is accompanied by the growth of a tumor on the elbow joint, the occurrence of throbbing pain, and an increase in temperature above 40. The general condition worsens, accompanied by nausea and fever. In its advanced form, infectious bursitis is complicated by consequences - cellulitis and fistulas that form under the skin. The joints of the bones are affected, which threatens the occurrence of purulent arthritis and lymphadenitis.
- Lipoma is painless and quite mobile, which cannot be said about the formation of an inflammatory nature. It only causes inconvenience when the lump is large (about 10 cm). This is a non-malignant neoplasm.
- With joint cancer, the main difference is aching pain at night, which is not relieved by painkillers. In advanced stages, severe intoxication of the body occurs, which is accompanied by fever, lack of appetite, and increased fatigue.
With a malignant lesion, the tumor can be located on the outer or inner side of the left or right arm. For any suspicions, whatever they may be, it is necessary to undergo an examination to clarify the disease.
Prognosis for recovery
It depends on the disease that caused the lump to form:
- With bursitis, the swelling can be completely removed if you consult a doctor on time. Conservative treatment is often sufficient, but if the form is purulent, surgery is prescribed. Sometimes traumatic bursitis goes away on its own if you provide rest to the joint, but there is a high chance that it will not go away, but will develop into a chronic form that can only be cured surgically.
- With gouty arthritis, edema and swelling can be completely eliminated by relieving the exacerbation. The disease itself is completely incurable, so you will need to constantly follow all the doctor’s recommendations in order to prevent relapses of the acute form of the disease.
- In rheumatoid arthritis, rheumatoid nodules do not completely resolve. But they themselves do not bring any painful sensations.
- For malignant neoplasms of the elbow, which are very rare, the prognosis should be associated with the stage at which the disease is diagnosed and treatment is started. The sooner you take active action, the higher the chances of recovery. Only an oncologist can give accurate forecasts.
As you can see, a tumor on the elbow joint can be either harmless, which can be completely eliminated, or it can indicate many serious chronic pathologies in the body.
Diagnostics is the key to recovery
The resulting lump should be shown to the surgeon. Often a visual examination is sufficient to determine the pathology. If joint mobility is impaired, additional examinations are prescribed.
If the lump appears after an injury, then you need to undergo an x-ray to rule out fractures or bone punctures. Additionally, CT and MRI are prescribed to determine the extent of joint damage, as well as ultrasound examination to find out how much nearby tissue is affected.
A biopsy is used to detect malignancy. Currently, such a survey is the most accurate and reliable. The operation involves removing a small piece of altered tissue. It is subjected to cytological and histological examination.
Methods to combat the disease
In order for the treatment to be effective and with a positive end result, you should trust the doctor. He will determine the exact cause of the lump and prescribe appropriate therapy. Under no circumstances should you try to fix it yourself.
In the acute form of bursitis, you should provide rest to the sore arm, fixing it with a special bandage that will limit movement and prevent further damage. Under anesthesia, the doctor cleans the bursa from exudate, pus and blood, then treats the cavity with an antiseptic drug. After these manipulations, the patient is prescribed therapy.
Bursitis is treated with medications, hormonal therapy and surgery:
- Non-steroidal drugs are prescribed to relieve pain. In addition to pain relief, they prevent the further development of inflammation and remove toxic substances from the body. Additionally, ointments are prescribed to promote tumor resorption. Local drugs to relieve inflammation are used simultaneously with Dimexide. This remedy affects the permeability of cell membranes, promoting deep penetration of active substances into the joint.
- Hormonal therapy is used for chronic disease. Corticosteroids are usually taken in short courses with good results, although they have many contraindications. Such drugs can only be prescribed by a doctor.
- To eliminate infections caused by pathogenic microorganisms, antibiotics are prescribed that correspond to the pathogens identified by the culture procedure.
- In advanced stages of the disease it is necessary to resort to surgical intervention. Damaged cavities must be removed. If necessary, missing elements are replaced with implants.
During the rehabilitation period, a course of physiotherapy is prescribed in combination with physical therapy. Recently, the scalpel has been replaced with laser devices, which can reduce the rehabilitation period.
Cancerous tumor
Dealing with cancer is not as easy as dealing with bursitis. Usually you have to resort to the help of surgeons. Tissues affected by pathology are excised, preserving healthy cells. With oncological processes affecting large vessels, the disease rapidly progresses. In such cases, they resort to radical removal of tissue and even amputation of a limb.
When treating a tumor, radiation therapy is also used, affecting the area of the elbow joint with X-ray radiation and destroying cancer cells. The procedure is performed on a stationary basis. Sometimes it is used before surgery to prevent relapses.
To prevent a malignant tumor, preventive blood tests should be performed regularly. With the help of a healthy lifestyle, moderate physical activity, and the absence of heavy loads in the elbow area, a disease such as bursitis can be prevented.
Lipoma and hygroma
Lipoma is often called a wen. It is considered a benign neoplasm of adipose tissue, prone to rapid growth. The lump does not cause pain or discomfort, but drug treatment is useless. Lipoma can only be removed through surgery. To get rid of wen, two methods are used:
- classic (complete excision);
- laser.
- classic (complete excision);
- laser.
Lipomas must be removed. Increasing in size, they grow, squeezing the blood vessels. In addition, when damaged, the tissues begin to become inflamed, and abscesses form in their place.
Ulnar hygroma is a cyst filled with serous fluid. It has a benign course. Begins to develop in the joint capsule or tendon. Regular loads on the elbow contribute to the appearance of a lump on the inside of the elbow, which impairs the motor function of the joint. Gradually, the tumor grows and puts pressure on the vessels, causing throbbing pain and swelling.
Previously, treatment of hygroma was limited to crushing, that is, mechanical impact. This method is very painful and ineffective, as relapses may occur. Currently, hygroma is excised using local anesthesia. If a suspicious tumor appears on the elbow, you should not wait until pain occurs and the tumor begins to grow.
Lump on the elbow: what could it be?
A lump under the skin in the elbow area can indicate several diseases. The diagnosis is made based on the factors preceding the formation of the lump, its nature, location, and the presence of other symptoms (eg pain). Once the diagnosis is made, appropriate therapy is prescribed.
- A fatty tissue, or lipoma, is a lump under the skin. Mostly it is round and small, but there are pathologies of significant size - up to 10 cm in diameter. This lump is a benign tumor of adipose tissue.
It is mobile and does not cause pain. However, a large lipoma can compress surrounding tissues and nerve endings, causing moderate pain. Fatty deposits tend to grow and sometimes require surgical removal.
If a painless soft lump appears on the elbow and the doctor confirms the diagnosis, then the only treatment method is surgery. Conservative therapy in the presence of lipoma is absolutely ineffective.
- Atheroma is a hard lump in the form of a ball on the bend of the elbow or other part of the limb. As a rule, it is painless. Mostly atheromas form on the head, neck, back and on the inner surface of the armpits, but it is possible that they may appear on other parts of the body. In the absence of discomfort, patients rarely turn to doctors.
Infection of the tumor forces you to visit the doctor. In such a situation, severe pain occurs and an increase in size may be observed. Inflammation is sometimes accompanied by an increase in body temperature. If such a pathology is present, surgery must be performed.
- Hematoma is a consequence of injury. The blow entails rupture of small blood vessels, as a result of which blood penetrates into the soft tissue and forms a tumor-like bluish compaction. The size and shape of hematomas varies significantly (from 1-2 to 15-20 cm and more). The hematoma may be round or irregular in shape. The color of the neoplasm also varies - from reddish to black. Hematoma is very painful.
Sometimes there is a local increase in temperature, limitation of the functions of the affected limb when an arm/leg is damaged. It is the last symptom that is the main difference between a hematoma and a banal bruise. Treatment is usually carried out surgically: the hematoma is punctured, its contents are pumped out and infection is prevented.
A lump on the elbow may appear during certain medical procedures, for example, intensive lymphatic drainage. Enlarged lymph nodes are caused by excessive intensity and errors in the procedure.
- Hygroma is a lump that is most often localized in the area of the wrist joint, but can also occur on the elbow. Usually its appearance is associated with the structure of the joint on the hand. Usually, hygroma does not provoke pain, but when it increases in size, it occurs during movement. Conservative methods of treating hygroma are ineffective. Surgery is the only correct solution. It is worth noting that if a hygroma appears, then it is removed right down to the joint itself, otherwise it may form again;
- Lymphadenitis is inflammation of the lymph nodes. The latter can have different sizes, but are almost always painful. Usually this disease is secondary, that is, it occurs against the background of inflammation of other tissues and organs, for example, with a boil, phlegmon, hidradenitis, infectious processes, etc. Treatment is aimed at sanitizing the source of infection or inflammation.
- If the damage is serious enough, pain is present, a crack, bone displacement, or pinched nerve may be suspected. In such a situation, hospitalization is required. If a lump has formed, under no circumstances should various local warming agents be used. Traditionally, cold is applied to the bruise: a bottle of cold water, an ice pack, or a piece of ice wrapped in a cloth. You can use ointments like “Rescuer”.
- If after the blow the consequences are less serious, the first step is to ensure the rest of the affected limb. However, seeing a doctor should also be mandatory. He may prescribe non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. For diagnostic purposes, a puncture biopsy may be performed. Physical therapy helps speed up the healing process.
The appearance of compaction is always promoted by some reason. Usually the latter is hidden in an injury, blow or bruise, less often as a result of allergies, metabolic disorders, or infection.
Inflammation of the synovial bursa is medically called elbow bursitis. This disease is often observed in drivers and athletes.
In some cases, bursitis occurs as a secondary pathology with gout, tuberculosis or gonorrhea. Therefore, if there is pain above the elbow, you need to urgently contact a specialist to make a diagnosis. The doctor will be able to make a differential diagnosis of arthritis, since these two diseases have similar symptoms.
Treatment:
Treatment for bursitis begins with eliminating the cause of its occurrence. It should be noted that, as with any other pathologies, the earlier therapy is started, the better for the patient. At the initial stage, you can limit yourself to conservative methods, but in case of protracted and severe course of the disease, surgical intervention is required.
In addition to the bump, elbow bursitis is characterized by a local increase in temperature. In acute inflammation, severe pain is observed, and in chronic inflammation, the thickening resembles a scar.
- In case of acute inflammation of the limb, rest is required. A pressure bandage is applied to the arm and warm compresses are made if the presence of pus is excluded. Fixing bandages are also required. Treatment for bursitis after injury involves injections of hydrocortisone for pain relief.
- In case of chronic inflammation, surgical intervention is required: the soft lump is opened, cleared of inflammatory effusion, and washed with an antibiotic or antiseptic. Purulent bursitis is treated in a similar way, but first it is recommended to perform a puncture. If the procedure is ineffective, the synovial bursa is opened and the pus is removed. The doctor may also remove the lump through extirpation.
- Therapy is mainly aimed at removing the tumor. For this purpose, UHF, dry heat and other procedures, radiography and radiation therapy can be used. This treatment allows you to relieve pain, provide an anti-inflammatory effect, and quickly restore damaged tissue.
I wish you health and good health!
The materials posted on this page are informational in nature and intended for educational purposes. Site visitors should not use them as medical advice. Determining the diagnosis and choosing a treatment method remains the exclusive prerogative of your attending physician.
Source: https://allergology.ru/sustavy/shishka-na-lokte