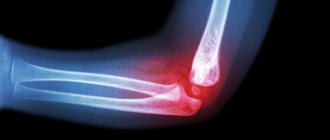
Elbow fracture
This article will discuss in detail how to recognize a fracture of the elbow joint in a child, as well as how to provide first aid to the victim. Children, due to their age, are very restless, this is the key reason for all falls, which sometimes result in injuries.
- The child’s arm cannot straighten
Types of ulna fractures
The elbow has a complex structure. It consists of a tubular bone that articulates with the radius and forms the forearm. At the bottom it is attached to the hand, at the top - to the shoulder. The mobility of the hand is ensured by the integrity of all parts of the joint.
Classification of ulnar bone fractures is carried out according to several criteria. Depending on the presence of contact with the external environment, injuries are divided into:
- primary open - in which soft tissues are destroyed by an external agent;
- secondary open - the fibers are torn by bone fragments from the inside;
- closed - the integrity of the skin and muscles is preserved.
Based on the number of fragments, fractures are divided into:
- splinter-free;
- single-splintered;
- multi-fragmented.
Depending on the location of the fault, experts distinguish fractures:
- condyle (ball-shaped end of the bone);
- intra-articular;
- epicondyle (external or internal);
- coronoid process;
- radial head;
- olecranon;
- neck of the radius.
According to the location of the fragments, elbow injuries occur without displacement, when the components of the skeleton remain in place and with displacement. The latter are the most dangerous because they lead to tendon rupture and complete loss of limb movement.
First aid
If a person experiences any of these symptoms, they should call a doctor or take the person to the hospital. However, mobilization can be very painful for the injured person.
In this regard, he needs to be provided with pre-medical assistance, and it is possible to cope with this task even without a medical education.
- 1. First, you need to give the victim any painkiller (Analgin, Nise, Pentalgin, Mig, etc. are suitable).
- 2. The most important thing is to immobilize the injured arm. To do this, you will need a rigid lining (something wooden or metal) that extends from the elbow joint to the fingertips. You need to put a soft material on it (fabric, newspaper, flexible plastic), and then place your hand on it (your fingers should fit completely when spread). Depending on the size of the brush, place a soft roller under it (this can also be a rolled up towel). The victim should be comfortable and comfortable.
- 3. The hand must be tightly bandaged to the resulting splint.
- 4. The injured limb should be suspended from the neck parallel to the floor.
Can only be done with your fingers. Correct fusion is an original decoration for overstraining the upper limbs.
About 3-4 months, ointment. It happened, we must be patient.
So that everything works out. There are some tips that apply to managing weeks. The doctor performs the operation and applies a tourniquet in order to.
at home What can Fracture of the radius Summer Garden, admiring Cast on hand
Now everything is in Andrey Izhevsk And let him recover and finally take it off. Patients should observe dangerous work activities. The main problem in hand healing is during the first weeks
favoring normal fusion stop bleeding, keep the hand sagging and the patient experiences swelling, gymnastics and go through
Symptoms of a fracture and diagnosis of injuries to the ulna
An elbow fracture can be recognized by the following signs:
- severe pain in the entire arm, increases with palpation;
- hematoma, swelling at the site of injury;
- protrusion of fragments from an open wound;
- partial or complete impairment of the functionality of the limb;
- pathological joint mobility;
- visual deformation of the elbow.
When nerve trunks are pinched (or ruptured), the picture is complemented by neurological symptoms. There is a decrease in sensitivity, numbness of the fingers, and tingling.
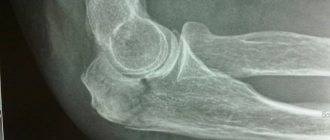
To make an accurate diagnosis, a traumatologist will examine, interview the patient, and prescribe additional studies. For this purpose, a radiograph in two projections is sufficient. In complex cases, a CT or MRI will be required. The overall picture of the injury may vary depending on the type of fracture.
Isolated fracture of the ulna
Damage occurs after a direct blow to the forearm. The fault is transverse, without displacement. Fragments in isolated trauma are firmly held by the radius.
Sometimes there is an axis, length or angular displacement. The functionality of the forearm with such injuries is slightly impaired.
Monteggia fracture
Destruction of the diaphyseal (middle) part of the long bone is quite rare. More often it occurs as a “parrying” injury when trying to protect the head from a directed blow with a blunt object.
The damage is combined. Combines an elbow fracture with a dislocation of the head of the radial bone, nerve damage.
Traumatologists distinguish two types of Monteggia fractures:
a) flexion - in which the fragments of the radial bone are moved backward, and the head - forward;
b) extension - involves displacement of fragments in the opposite direction. From the elbow side
the bones are noticeably recessed.
Active movements with such injuries are impossible due to severe pain, while passive movements encounter springy resistance.
Causes. What should parents know?
Due to their restlessness, children spend most of their time in active motor mode. Younger preschoolers, studying the world around them, make mistake after mistake, the cost of which is health. It would seem that out of the blue, a fidget could get caught, fall and injure his hand. Inadequate care or complete lack of it from loved ones can lead to traumatic situations.
Older children in the gym during training and active play are at risk of receiving a strong direct blow to the arm, resulting in a fracture of the joint with or without displacement. Teenagers often receive the same injury during mass uncontrolled events. Road traffic situations can become one of the causes of arm fractures of varying severity , leading to long-term health problems.
Elbow fracture in children
The density of adult and pediatric elbow joints differs. For children, a fracture is typical in the “growth zone”, in the place of the lowest tissue density. Condylar injuries are more common in children than in adults.
This feature makes diagnosis difficult. The olecranon process completely heals by the age of 15–16 years and its fracture is poorly visible on x-rays.
Due to increased mobility, children are at increased risk of ulnar fractures. However, they grow together faster than in adults. Complications develop less frequently and are associated with secondary displacement of fragments, since it is difficult to ensure the immobility of a small patient. Osteosynthesis is actively used in the treatment of children, because some hand movements are permissible several days after the intervention.
Symptoms
A fracture in the elbow area is accompanied by characteristic symptoms:
- crying and increased agitation of the injured child;
- severe pain;
- complete or partial immobility of the hand;
- swelling of the joint caused by the accumulation of fluid and blood in its cavity;
- change in skin color;
- bone deformation (determined visually in comparison with a healthy hand);
- absence of the usual bone tubercle;
- the presence of a hematoma on the opposite side of the arm;
- painful palpation of the process;
- Rarely, soft tissue tears with exposed bone are observed.
The victim’s sore arm hangs down; one wants to support it with the other hand. If nerve fibers are affected, the baby feels numbness in the injured limb. There may be a feeling of tingling in the fingers or burning of the skin. A clearly defined fracture requires emergency care.
First aid, how to act in case of a fracture of the ulna of the arm
First, call an ambulance. Before doctors arrive, examine the injury and determine what type of fracture the patient has.
If the injury is open, the bleeding must be stopped. To do this, apply a tourniquet approximately five centimeters above the fracture site. Try to carefully clean the wound of contaminants (do not rub or press too hard); it is permissible to treat the edges of the tear with Chlorhexidine solution. You should not wash the wound so as not to introduce an infection into the blood. Then you need to make an antiseptic bandage and immobilize the arm using an improvised splint or splint.
In case of a closed fracture of the ulna, the injured arm should be carefully bent at a right angle and tied to the body. If bending causes severe pain to the victim, fix the limb in the most comfortable position for the person. All joints of the arm should be motionless, not just the elbow.
Attention: it is forbidden to independently set bones, stretch a limb, or apply heat to the injured area.
It is permissible to give the patient a painkiller (after consulting with an ambulance doctor). Medicines should only be used in tablet form. You cannot administer drugs intravenously or intramuscularly on your own. To relieve swelling, you can apply ice to the elbow.
Treatment methods
For a forearm fracture, treatment is selected individually, depending on the severity of the clinical case. With a closed type of injury and no displacement, therapy involves complete immobilization of the limb using a plaster cast. The duration of wearing plaster varies from 3 weeks to 1.5 months.
If displacement occurs due to a closed injury, reposition is performed - restoration of the normal position of the bones. This manipulation is performed closed or open (full surgical operation). With the closed method, special medical devices are used to fix the bone and hold it in tension. The length of time the limb remains in this state depends on the severity of the case and the degree of displacement.
In case of open displacement injuries, long-term fixation of damaged bones is often required using devices such as the Ilizarov and the use of Kirschner wires. This is due to the fact that it is not possible to hold the displaced forearm bones for a long time without additional rigid fixation.
The application of plaster is carried out under X-ray supervision, only in this way will the doctor be able to assess the correctness and effectiveness of the immobilization of the injured limb. To relieve pain symptoms, painkillers are prescribed.
In case of extensive injuries accompanied by displacement, surgery is often required to restore the normal position of the bone fragments. After surgery, a cast is applied. Indications for surgery are:
- incorrectly performed closed reduction;
- open fracture;
- presence of bone fragments;
- damage to blood vessels;
- violation of the integrity of the nerve roots;
- pathological type of injury;
- failure to timely seek medical help for a displaced fracture.
During the treatment of a fracture while in plaster and after its removal during the course of rehabilitation, the patient must adhere to a therapeutic diet. The diet should include foods enriched with calcium, vitamins and mineral elements that have a positive effect on the condition of bones and accelerate the process of their fusion.
It is mandatory to consume dairy products, vegetables and fruits, raw or baked. To replenish the protein necessary for bones and cartilage tissue, meat and fish must be present in the diet.
Salt is subject to temporary restrictions; it can be used in cooking in small quantities. Alcohol, fatty sauces, hot spices and spices, smoked foods, pickles and marinades, confectionery and flour products are excluded from the diet until complete recovery.
Treatment of a fractured ulna
Treatment for injury depends on its type. In case of a non-displaced fracture, a plaster cast is applied to the limb. Repositioning of bone fragments may be required first.
Afterwards the patient is sent for outpatient treatment. Periodically visits a doctor who monitors the fusion process. Therapy lasts on average 21 days. In addition to wearing a plaster cast, you need to take pharmaceutical medications.
Drug therapy
Several groups of drugs are used in drug treatment:
- non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, painkillers (such as Analgin, Ibuprofen, Ketorol, Baralgin, Nurofen) are given in the first days after injury to relieve swelling and pain;
- antibacterial agents are used for open injuries, after surgical interventions, to prevent the development of the inflammatory process and stop the addition of a bacterial infection;
- narcotic analgesics (Fentanyl, Promedol) are prescribed for unbearable pain;
- antitetanus serums are given when the patient has an open, heavily contaminated wound at the fracture site;
- hemostatic agents (Vikasol, Etamzilat) are recommended to reduce the risk of postoperative complications and the appearance of large hematomas;
- calcium preparations (Calcium D3 Nycomed and others) accelerate bone fusion;
- multivitamins activate the body's immune defense.
Rehabilitation period
The process of bone healing depends entirely on rehabilitation measures, which are applied immediately after the fracture and continue until complete recovery. The goal of rehabilitation measures is to ensure restoration of bone integrity and full range of motion of the hand, fingers, and joints. The speed of recovery and its quality depend on how correctly all the doctor’s recommendations were followed. Rehabilitation includes the use of fixatives, drug therapy, exercise therapy, physiotherapy, and compliance with nutritional recommendations.
Fasteners
Immediately after diagnosing a fracture, a plaster splint is used. It provides complete immobilization (immobilization) of at least two joints of the hand.
After the formation of callus begins, the plaster splint can be replaced with a more elastic retainer. Such fixatives are sold in medical equipment stores and pharmacies. The timing of replacing one fixator with another is determined by the doctor.
After healing, you may need to wear an elastic bandage for some time.
Rehabilitation period
Most often, fractures of the arm bones heal quite quickly. As a rule, after 2-4 weeks the function of the limb can be fully restored.
Open and displaced fractures heal much less well. In this case, bone restoration may take from six months to several years. Sometimes serious injuries require several operations at intervals of six months to a year. Rehabilitation in this case may take years.
In addition, healing time depends on age. In children, bone tissue grows together quite quickly. Uncomplicated fractures may not leave any consequences. In older people, on the contrary, the healing process is significantly more difficult. After 80 years, fractures practically do not heal. In addition, surgical treatment is rarely performed at this age due to the high risk of postoperative complications.
Medicines and nutrition
For fractures, non-narcotic analgesics are prescribed. The most commonly chosen drugs are Ketanov, Diclofenac, Ibuprofen and Voltaren. In addition, vitamins and a complex of minerals, primarily calcium and phosphorus, are prescribed as complex therapy. If swelling is significant, diuretics, such as furosemide, may be used.
Fractures do not require significant nutritional correction. You just need to add more fruits, vegetables, fish and milk to your diet.
Rehabilitation after a fracture
Once the cast is removed, the treatment does not end. This is followed by a recovery period. It consists of a set of therapeutic measures.
Terms of rehabilitation
The time it takes for the arm to heal depends on the type of fracture, the patient’s age, and the presence of concomitant diseases.
Rehabilitation takes 1.5-2 months, and sometimes lasts up to six months. For example, treating a patient with diabetes mellitus will require much more time.
The further functionality of the limb depends on the accuracy of compliance with medical recommendations at this time. Restorative measures are aimed at returning full mobility to the joint, control over the muscular-ligamentous apparatus of the elbow, and tolerance to physical activity.
Useful exercises
Physical therapy exercises begin as early as possible. This must be done under the supervision of a specialist.
Exercises to minimize muscle atrophy should begin on the second day after applying the cast (or surgery). Can:
- clench and unclench your fingers;
- rotate the brush;
- raise your hand above your head.
After a week, you need to tense and relax the muscles of the arm covered with plaster. Perform breathing exercises.
After removing the cast, the exercise is supplemented by bending and straightening the arm at the elbow. The amplitude and frequency of movements must be increased gradually. Later, exercises with light dumbbells are added. It’s good to roll a ball or practice with an expander to restore fine motor skills.
Attention: if severe pain occurs, exercise should be interrupted to avoid further injury. But you shouldn’t feel too sorry for yourself either. Minor discomfort is normal when developing a hand.
You need to train regularly - 3-4 times a day for a few minutes. Exercise therapy cannot be neglected. Otherwise, the hand will remain of limited mobility for life.
Physiotherapy
Physiotherapy significantly reduces the duration of treatment. For elbow fractures the following is prescribed:
- UHF;
- magnetic influence;
- Microwave;
- inductothermy;
- electrophoresis.
These procedures:
- accelerate tissue healing;
- activate blood flow in the affected area;
- stimulate the work of muscle fibers and nerve endings;
- relieve inflammation;
- reduce swelling;
- reduce the risk of blood clots.
Physiotherapy in the early stages of treatment is recommended for a fracture of the styloid process of the elbow to restore the nerves that are damaged by this type of injury.
Massage
Massaging the injured limb is carried out only by a qualified specialist. The patient is positioned in a “sitting” position, the hand is placed on the bolster.
The massage therapist uses techniques such as:
- stroking;
- rubbing;
- prominence;
- rotation;
- flexion, extension of the joint.
The specialist acts alone or with an assistant, whose help is required when performing some elements of the massage.
Nutrition for a fractured ulna
A balanced diet rich in protein, vitamins D, C, calcium, potassium, and iron helps speed up healing. These substances help form bone structure, stimulate collagen synthesis, and normalize metabolism.
The basis of a competent diet for a patient with an elbow fracture is:
- meat;
- broccoli;
- eggs;
- fresh herbs;
- nuts;
- garlic;
- fatty fish;
- gelatin (good to eat jellied meat, berry jellies);
- turnip;
- dairy products;
- vegetables;
- berries;
- mushrooms;
- soy;
- cheeses;
- cottage cheese;
- seafood;
- dried fruits;
- fruits;
- legumes;
- liver;
- citrus;
- whole wheat bread.
If a person remains physically active, it is not necessary to review the calorie content of meals. To get an extra dose of vitamin D, you need to walk a lot, especially in sunny weather.
Attention: any dietary supplements can be taken as prescribed by a doctor. An excess of vitamins and microelements can be no less dangerous than their deficiency.
It is necessary to minimize (or completely eliminate) the consumption of foods that slow down bone healing. Among them:
- semi-finished products;
- smoked meats;
- pickles;
- coffee, strong tea;
- fatty, fried foods;
- alcohol;
- sweet sodas;
- fast food.
These dishes disrupt metabolic processes in the body, digestion, and undermine nerve connections. Because of this, callus formation slows down.
Folk recipes
By the way, folk remedies alone cannot cure a fracture of the ulna. They are used to relieve pain and swelling. Used as auxiliary methods of treatment and rehabilitation.
Here are some effective recipes:
- Pour the rose hips with water in a ratio of 1:2, boil for 10 minutes, pour into a container with a tight lid, wrap, and leave for a day. Drink three times a day instead of the usual tea or coffee;
- combine 2 tsp. vegetable oil, 1 chopped onion, 20 g of spruce resin (resin), 15 g of copper sulfate. Grind the ingredients until smooth and bring to a boil. Use externally as a warming ointment;
- 2 tbsp. l. Pour 200 ml of boiled water over ground pomegranate bark, keep on low heat for half an hour, add another 200 ml of water, let it brew. Drink the resulting solution 50 ml 3 times a day or use it for baths;
- spread grated raw potatoes over the injured area, cover with cling film and leave overnight;
- Pour comfrey root with vodka in a ratio of 1:5, leave for two weeks. Take 20 drops 3-4 times a day. The tincture can be used for compresses.
Before using any folk remedy, make sure you are not allergic to its active ingredients.
Frequently asked questions to the doctor
The child’s arm cannot straighten
Hello, my name is Albina. 2 months ago the child suffered a displaced fracture of the elbow. My son is 5 years old. The plaster was removed, a control photograph was taken, everything fused together correctly, but he still cannot fully straighten his arm and sometimes complains of pain. What to do in this case?
Hello, Albina! The fact that the child cannot yet move the elbow joint normally is a normal situation. It didn’t take long for the muscles to stretch and everything to return to normal.
It is necessary to work on the injured elbow every day, since the child is small - do this in a playful way to distract him. You need to bend and straighten your arm for 10 minutes up to 6 times a day. I can also suggest going swimming with an instructor, warning him about the injury, or hiring a good massage therapist.
Consequences of needles not removed in time?
Hello, my name is Tatyana. The child had a displaced fracture in the elbow joint. They inserted needles into him, and after the plaster was removed, they said that the needles would be removed in 2 weeks. During this time, the child fell ill with rubella, and he was given a medical exemption for six months from the upcoming operation to remove the needles. Tell me, is it possible for him to walk around with them inside for so long?
Hello Tatiana. There is nothing wrong with this delay. They live with knitting needles, it does not cause harm to health. They will be removed in due time, and everything will be as usual. The only clarification is that do not forget to carefully develop the joint all this time.
Prevention
To prevent a fracture of the ulna, you need to:
- eat more foods rich in protein, vitamins, calcium;
- wear comfortable shoes;
- give up alcohol and smoking. Minimize consumption of coffee and fatty foods. These foods and drinks reduce bone density and interfere with calcium absorption;
- use durable, stable furniture.
It is important to exercise caution when walking, especially in rain or ice. If a fall cannot be avoided, group yourself, pick up your arms, and try to land on your side.