Fractures of the ankle joint are among the most common injuries and account for 20-22% of all injuries to skeletal bones. These fractures are not much inferior to fractures of the distal end of the forearm, accounting for 40-60% of all fractures of the lower leg bones, which rank second among injuries to limb segments.
Ankle fractures are the most common injury primarily among the working population. The frequency of injury and long-term disability of these patients cause great economic damage to the country, which can be further aggravated by unfavorable social conditions - poor condition of the streets, especially in winter, very poor cleaning, untimely and incorrect provision of first aid, defects in treatment, etc.
Possible causes of fracture
In 90% of cases, the joint is damaged as a result of indirect rather than direct exposure to traumatic force. For example, when the forefoot continues to move while the hindfoot is fixed. This happens when you fall while running or walking.
A displaced fracture can be caused by falling from a ladder, ice skating, roller skating, or doing extreme sports: alpine skiing, skydiving. In any case, you should not endure acute pain, but immediately contact the emergency room to differentiate a possible fracture from a dislocation or sprain, since chronic fractures without appropriate treatment lead to serious complications.
First aid for an ankle fracture
An ankle fracture is almost indistinguishable from a sprain. Moreover, they often come together. Therefore, you should not waste precious time on assumptions, but it is better to call an ambulance or take the victim to the emergency room.
Before the medical team arrives, the following is allowed:
- fix the injured limb in a stationary position;
- stop bleeding and disinfect the wound (with an open fracture);
- it is advisable to remove the person’s shoes, and it is better to cut them first;
- give the person pain medication;
- apply cold to the damaged area.
A displaced ankle fracture is the most dangerous, so trying to set the bones yourself is strictly prohibited! If there are doubts about the correct application of the splint, it is better to leave everything as is, after first making sure that there is no external bleeding.
Types of ankle fractures
An ankle fracture is a complex injury due to the complex structure of the ankle. The nature of the damage depends on the position of the foot in which the injury was received: in a state of pronation (flexion) or supination (resting on the toe). In the event of a traumatic blow to a pronated foot, the outer side of the ankle is damaged, and to a supinated foot, the inner side is damaged.
According to the type of displacement, ankle fractures are classified as follows:
- External rotation - occurs under the influence of twisting force (in a spiral), in this case the inner ankle is damaged and the joint moves outward or backward; this type of injury often occurs in road accidents;
- Abduction-eversion - the foot is pronated and turned outward at the ankle joint; the fibula breaks due to strong abduction to the side;
- Adduction-eversion - the foot is supinated and turned inward at the ankle, the heel bone is tucked in; this often happens when you twist your leg;
- Pott's fracture - the foot is supinated and turns outward at the ankle joint; the back of the ankle breaks transversely.
When falling from a height, a vertical fracture of the ankle occurs with the foot dislocated upward and forward. Fractures with displacement and damage to the talus are classified as severe forms of fracture.
According to the severity of the damage, they are distinguished:
- Closed fracture, when the bones do not damage the soft tissues;
- An open fracture, when the integrity of the skin is broken, an open wound appears and bone tissue comes out. This is fraught with the development of an inflammatory process.
Closed (simple) fractures are diagnosed more often. They are divided into displaced and non-displaced fractures. When displaced, rotation and deformation of the joint and foot occur. All types of fractures have common symptoms.
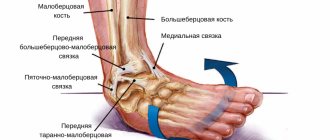
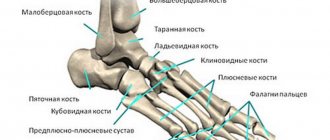
How the ankle works
An ankle fracture, contrary to its name, is not a joint injury in the literal sense. The bones that form this complex mechanism break. In structure, it resembles a trident, formed by the ends of the tibia and fibula along the edges and the talus in the middle. Inside this bone fork there is an articular capsule, and outside it is surrounded by cords of muscles and ligaments. Taken together, all this ensures flexibility and safety of the articular apparatus.
The weakest link in this robust system is the end of the tibia and fibula, also known as the ankle bones. These bony tubercles in the lower part of the leg are easy to see and feel. Especially the lateral (outer) one, which is protected only by a thin layer of skin with a fine network of blood vessels. It's no surprise that an ankle fracture is the most common type of ankle injury.
Symptoms of an ankle fracture
The main symptoms of an ankle fracture are as follows:
- Severe pain, sharp and burning in open forms and dull, aching in a closed fracture, which increases when trying to move the foot;
- The rapid appearance of edema, which gradually increases and takes on a pronounced character;
- Noticeable deformity in the ankle area;
- Limitation of range of motion in the joint;
- Inability to axial load (inability to stand on the leg with emphasis on it);
- In some cases - the presence of a hematoma (hemorrhage), an increase in local and general body temperature.
Ankle fracture
Surgical treatment is indicated for patients with an unstable fracture, patients who want to return to sports as soon as possible, and patients for whom conservative treatment has failed.
Patients should be aware that the choice of surgical treatment must be carefully considered.
There are several options for surgical treatment, each of which is selected based on the individual characteristics of the patient and the nature of the fracture.
The operation is best performed when the swelling of the soft tissues in the area of the fracture is significantly reduced. Therefore, surgery is often performed a week or more after the injury. Intervention in conditions of severe edema increases the risk of developing problems with postoperative wound healing and infectious complications. The period of time when surgery must be performed usually lasts 2 weeks; after this period, active processes of fracture consolidation begin, which further complicate the surgical intervention.
Fracture of the outer malleolus
The operation is characterized by very favorable results in terms of pain relief and return to full daily activities.
It consists of repositioning the fragments (restoring the anatomy) and fixing the fibula with a plate and screws.
The operation is usually performed under general anesthesia and using a single access to the outer surface of the ankle joint. Patients usually spend the first night after surgery in the clinic.
A – X-ray of a fracture of the lateral malleolus. B – Postoperative radiograph after anatomical reduction and stabilization of the fracture with a plate and screws
Inner ankle fracture
The operation is characterized by very favorable results in terms of pain relief and return to full daily activities.
It consists of repositioning the fragments (restoring the anatomy) and fixing the inner malleolus with one or two screws or, occasionally, a plate.
The operation is usually performed under general anesthesia and using a single access to the inner surface of the ankle joint. Patients usually spend the first night after surgery in the clinic.
A – X-ray shows an isolated fracture of the medial malleolus (white circle). B – X-ray after stabilization of the fracture with two screws
Fracture of the posterior edge of the tibia (posterior malleolus)
The operation consists of repositioning the fragments (restoring the anatomy) and fixing the posterior edge of the tibia with screws and a plate.
The operation is usually performed under general anesthesia and using a single approach in the posterior aspect of the ankle joint. Patients usually spend the first night after surgery in the clinic.
Bimalleolar fracture
The operation is characterized by very favorable results in terms of pain relief and return to full daily activities.
It consists of fixing the outer ankle with a plate and screws, and the inner ankle with one or two screws (or occasionally a plate).
The operation is usually performed under general anesthesia and using two approaches in the area of the outer and inner surface of the ankle joint. Patients usually spend the first night after surgery in the clinic.
Trimalleolar fracture
The operation is characterized by fairly good results in terms of pain relief and return to full daily activity, however, due to the nature of the fracture, the risk of developing post-traumatic osteoarthritis is higher here, even despite a flawlessly performed surgical intervention.
The operation involves fixing the outer malleolus with a plate and screws, the inner malleolus with screws (or occasionally a plate), and the posterior edge of the tibia with a plate and screws.
The operation is usually performed under general anesthesia and using two approaches in the area of the back and inner surface of the ankle joint. Patients usually spend at least the first night after surgery in the clinic.
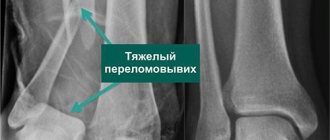
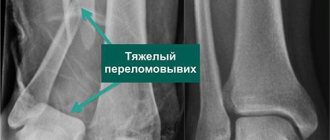
A – Lateral radiograph of a normal ankle joint. B – X-ray of a trimalleolar fracture. C – X-ray after surgical stabilization of a trimalleolar fracture with plates and screws
Fractures and dislocations
The operation is characterized by fairly good results in terms of pain relief and return to full daily activity, however, due to the nature of the fracture, the risk of developing post-traumatic osteoarthritis is higher here, even despite a flawlessly performed surgical intervention.
The specifics of the operation are determined by the nature of the particular fracture.
The operation is usually performed under general anesthesia and using two approaches in the area of the back and inner surface of the ankle joint. Patients usually spend at least the first night after surgery in the clinic.
A – X-ray of a normal ankle joint. B – X-ray of an open fracture-dislocation of the ankle joint with contamination of the wound. In such cases, there is a high risk of developing osteomyelitis and post-traumatic osteoarthritis of the ankle joint. Note also that this patient has severe damage to the tibiofibular syndesmosis (see below)
Damage to the tibiofibular syndemosis
These are high-energy injuries that damage some or all of the tibiofibular ligaments. Information on the anatomy of the tibiofibular syndesmosis can be found here.
The fibula and tibia are connected to each other by ligaments called the tibiofibular syndesmosis. As a result of injury, either partial or complete rupture of this ligamentous complex can occur, resulting in instability of the ankle joint.
Injuries to the tibiofibular syndesmosis can be isolated ligamentous injuries or combined with fractures in the ankle joint.
Surgical restoration of the tibiofibular syndesmosis is characterized by very favorable results in terms of pain relief and return to full daily activity.
This operation consists of repositioning fractures (restoring anatomy), if any, and stabilizing the tibiofibular syndesmosis itself.
More than one access is usually used during the operation. The operation is performed under general anesthesia and patients usually spend the first night after surgery in the clinic.
Radiographs A and B show a bimalleolar fracture with rupture of the tibiofibular syndesmosis, which led to dislocation and severe instability of the ankle joint. On postoperative radiographs C and D: anatomical reduction of fractures was performed, rigid fixation was performed, the anatomy of the ankle joint was completely restored
Diagnosis and treatment
First aid
First of all, you need to provide complete rest to the injured limb, if possible, apply a splint, fixing both the foot and lower leg. If the pain is severe, you can give the victim some kind of painkiller and then take him to a medical facility.
Diagnostics
To establish an accurate diagnosis, radiography is performed, which is done in two projections, anterior and lateral. Additionally, CT and MRI methods can be used.
Treatment
In order to align the parts of the broken bone, the surgeon reduces the fracture site under local anesthesia. After this procedure, a plaster cast is applied to the fracture site. If it is not possible to correct the dislocation and keep the parts of the bones aligned with plaster, then surgery is performed.
During the operation, individual bone fragments resulting from a fracture are fastened together using special fixation plates and implants. In the future, complete immobilization (immobility) of the limb is necessary for successful fusion of bones and prevention of repeated displacements. The period of wearing a plaster cast or splint lasts 1-3 months, depending on the complexity of the fracture. Simultaneously with surgical manipulations, comprehensive rehabilitation is prescribed, which is carried out until complete recovery.
On the subject: Pain in the ankle joint: what to do?
Surgery
If non-surgical treatments don't work or the ankle is too unstable, your doctor may recommend ankle fracture surgery followed by rehabilitation. After surgery, it is important to walk your leg and perform all prescribed procedures in order to reduce rehabilitation time.
Features of the operation: if the fragments are not in their place, the bone fragments must be moved surgically. The fragments had to be returned to their normal position and held together with special screws and metal plates attached to the outer surface of the bone. Surgery may include a bone graft to allow the new bone to actively heal. It is secured with screws and a metal plate. This may reduce the risk of arthritis and speed the return of movement.
general description
Damage to the ankle joint is one of the most serious injuries. The joint itself has a complex structure. It is formed by the articular surfaces of three bones (talus, tibia and fibula), tendons and ligaments. This joint is one of the strongest in the body, as it bears the main load during walking and running.
An ankle sprain or fracture may be associated with damage to various anatomical structures, but the clinical picture will not differ significantly
In most cases, a sprain or fracture of the foot causes temporary, long-term disability, and full recovery of function may take more than six months.
Ankle fracture
A fracture is a pathology in which there is a violation of the integrity of the bone. It is customary to distinguish two types of fractures - open and closed. Closed fractures are easier, with them there is rarely significant displacement of bone fragments, and recovery and rehabilitation are faster.
An open fracture is characterized by the fact that, simultaneously with bone damage, a violation of the integrity of the soft tissue occurs. In this case, bone fragments may stick out. A fairly common occurrence with an open fracture is bleeding. It develops due to the fact that the arteries pass in close proximity to the bone. When a fracture occurs, bone fragments can damage the arteries, or they rupture under the influence of mechanical forces.
When an ankle fracture occurs, damage to the head of the fibula most often occurs. This bone is the thinnest of all the components of the ankle, therefore, less external force is required for it to break.
Quite often, ankle fractures are accompanied by ruptures of the ligamentous apparatus, which requires reconstructive surgical interventions. The purpose of such operations is to restore the integrity of the tendons. If such treatment is not carried out, the joint will not function fully.
Ankle sprain
An ankle sprain is less dangerous, but also causes dysfunction of the joint. Depending on the severity of the damage, the clinical picture of a sprain can vary significantly. For mild injuries, symptoms will be mild or almost absent.
It is worth noting that a sprain of the ligamentous apparatus of the ankle joint is much more common than a fracture. This is due to the fact that the ligamentous apparatus is more susceptible to mechanical damage than bones.
Violation of the integrity of the ligaments due to ruptures requires surgical intervention to restore their integrity
Mine blast injury
Minimal damage: 1st degree burn. Maximum damage: separation of the phalanges of the fingers.
| Treatment rules | |
| There is a golden rule in traumatology: any injury - bruise, sprain or fracture - must be treated with cold for the first two days in order to relieve swelling and avoid the development of a hematoma. And then - dry heat. So if you return from the emergency room without a cast, apply a heating pad with ice or a plastic bottle with cold water to the affected area for the first few days. And after two days, wrap the affected area in a blanket and apply a warm heating pad once a day. As an aid to the resorption of hematomas, doctors, as a rule, recommend products that increase blood circulation (ointments, gels). And for sprains, bruises and fractures, you should never use warming ointments that give a burning effect. They increase swelling, and the hematoma can fester | |
Symptoms: the noble desire to please family and friends with fireworks leads to the fact that the “ammunition” explodes in the hands, and it becomes impossible not to recognize the symptoms of this injury. At best, the skin on your hands becomes red and blisters. At worst, the “exploder” is left without part of his finger.
Treatment: in case of a burn, place your hand under cold water. After this, cover the affected area with an anti-burn drug (panthenol or any analogue). If there is no medicine at hand, you need to send someone to the pharmacy and at the same time call an ambulance.
A burn of even 15% of the body may be an indication for hospitalization if there is a danger of tissue infection. For example, if the burn has eaten into the burn, particles of firecrackers remain. Additionally, if a large blister develops, it will need to be opened at the hospital.
If the phalanx of a finger is torn off, the first thing you need to do is find the lost part as quickly as possible.
Article on the topic
Bruise, sprain or fracture? How to give first aid correctly
If possible, put it in ice, bandage the injured finger and get to the hospital as soon as possible.
In our country they know how to sew fingers well and efficiently. After this operation, mobility returns to the sewn part over time. Yes, you won’t play the violin, but eating with a spoon and writing with a pen is fine.
How to avoid: An accident is usually caused by two factors. The first is cheap Chinese pyrotechnics. The second is the state of strong alcoholic intoxication of the “shooter”, from which the reaction slows down and everything explodes inexplicably.
Tailbone injury
Minimal damage: bruise. Maximum damage: coccyx fracture.
| The most New Year's injury | |
| It’s hard to imagine, but one of the most common New Year’s injuries is usually one that a person inflicts on himself: he shoots himself in the eye with a champagne cork. Funny, but true! On New Year's Day, the ambulance service is replenished with a special ophthalmological team. What is the danger of such a shot? At best, it’s a hematoma, which is popularly called a “black eye.” At worst - retinal detachment, scratches and wounds on the eyeball. You should sound the alarm and immediately seek medical help if there is any visual impairment: blurred, hazy “picture”, partial loss of vision. | |
Symptoms: as a rule, after joyfully jumping over springboards on sleds or ice skates, pain appears in the tailbone area - from aching to unbearable. You can relieve pain with potent analgesics, but only for a very short time. On average, on the fifth day of suffering, the patient goes to the doctor to understand what is hurting there.
How to distinguish: bruise or fracture? In my many years of practice, I have only encountered a fractured coccyx twice. It can be broken by athletes or participants in road accidents. Most often, winter skiers come with bruises of varying severity. The final diagnosis is made based on X-ray results.
Treatment: in case of bruise there is no special treatment. Try to sit less; cold is recommended for the first two days after injury, then dry heat. In the case of a fracture, everything is worse: the tailbone cannot be set and fused - the damaged part is usually removed. The operation is very painful. Long rehabilitation period. How to avoid: do not jump over jumps on ice skates and do not let children do it.