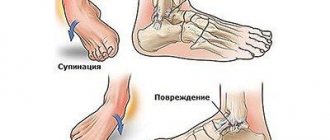
Anatomy of the foot
The foot is the last section of the lower limb and consists of:
- Tarsus – back side. Includes seven bones, which are arranged in two rows: calcaneus, talus, navicular, three wedge-shaped, cuboid.
- Metatarsus – plantar part. It is formed by five tubular bones having a base, a head and a body. They are connected into a single whole using joints.
- Fingers. Four of them have three phalanges, one has two.
The following joints are located in this area:
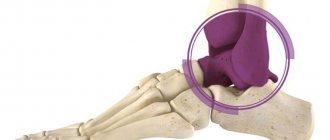
- ankle (located at the base of the foot, shaped like a block),
- subtalar,
- wedge-scaphoid,
- metatarsophalangeal.
There are two muscle groups here:
- shins - form the arches of the feet,
- plantar - provide movement of the fingers, serve to support bones.
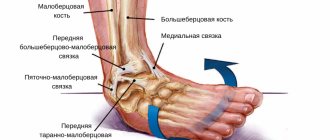
To connect them to the bones there are tendons and ligaments.
Due to the structural features of the foot, it supports the weight of a person and allows the body to move freely in space.
Features of damage
Over the past year, only 10% of patients went to the emergency room with a foot injury. Such a small percentage is due to the anatomical features of the structure of the foot. The bones that make up the lower part of the leg are small and located very close to each other.
The causes of a fracture can be indirect injuries:
- Jumping from a swing or any height;
- When walking, twisting of the leg;
- A heavy object falling on your leg.
Since the bones in the foot are closely connected, a fracture of any of them leads to deformation and changes in the functionality of the entire lower part of the leg.
In adolescents and older people, a foot fracture can be caused by flat feet and improper support on the limb. If not treated promptly, the injury causes arthrosis, and the person loses the ability to move the foot normally for life.
People whose lives are connected with sports, women over 45 years of age and the elderly are at risk. Women experience hormonal changes after menopause. The body stops absorbing calcium and fluoride in normal amounts. Bone tissue loses strength, becomes fragile and vulnerable. Any mechanical impact on the foot causes a fracture.
Children suffer mainly due to active games. A child gets injured while jumping from a swing or any structure. The foot can also be damaged if a heavy object falls on it. Men whose activities are related to construction work are more likely to go to medical institutions with such injuries.
Types of fractures
The following types of fractures of the 5th metatarsal bone are distinguished:
- separation of the head or base tuberosity,
- injury to the wide part of the base of the bone (Jones fracture),
- diaphyseal,
- fracture of the neck or distal metaphysis.
Depending on the displacement of the bones, a fracture may be:
- oblique,
- transverse,
- wedge-shaped
- T-shaped.
Based on the degree of damage to the skin, injuries are determined:
- open,
- closed.
Anatomical features of the lower leg
To understand the nature of the injury, it is necessary to understand the structural features of the foot. The foot consists of 26 small bones, which are connected by joints and ligaments. Anatomically, the foot is divided into three sections:
- Tarsus;
- Metatarsus;
- Phalanges of the fingers.
A fracture of each section causes individual symptoms and requires specific treatment.
There are general symptoms that should alert the victim and encourage him to contact a specialist:
- Pain that increases when you try to step on your foot;
- The foot loses its functionality and does not move;
- The skin on the lower part of the leg turned blue and cold. Swelling has appeared.
According to the mechanism of injury, foot fractures are of two types:
- Open - when a wound forms over the broken bones. This type of fracture is dangerous due to bleeding and a high probability of infection in the tissue;
- Closed - the bone is broken, but the soft tissues are not damaged.
First aid for injury
If a limb is injured in the foot area, you must immediately call a doctor. Before doctors arrive, the injured person needs to be given first aid correctly. To do this you need:
- Immobilize the affected leg as much as possible.
- Apply cold to the injured area. Ice is applied for no more than 20-30 minutes, the interval between compresses should be one and a half hours. Otherwise, frostbite and tissue necrosis may occur.
- Apply a bandage. The elastic bandage should not be wound too tightly so as not to pinch the blood vessels.
- Raise the limb higher than the body and fix it: this measure helps reduce swelling and dull pain.
If possible, the patient should be taken to the emergency room independently, without waiting for doctors.
Technical features of installing and removing fasteners
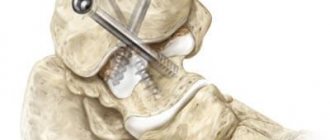
If the structure with an external location is installed correctly, removing the spokes after a fracture is not difficult - the spokes are simply removed. If the fixation is intraosseous, inside the joint, using nails and screws, then a full-fledged operation is required.
Fixation with knitting needles is used to connect the joints of the limbs and fingers. It can be performed externally, when the end of the needle rises above the surface, or internally, when the entire structure is under the skin. The technique is used as a temporary measure. In some cases, if patellar fractures, clavicular or elbow injuries are fixed, stable fixation and a longer time for fusion are required.
When a hand is broken, osteosynthesis techniques are used - metal structures, knitting needles and an Ilizarov apparatus is installed. They are removed only after complete healing.
Using plates you can fix any bone. This is a convenient and reliable method. Today, many variants of such plates are used, varying in size, shape, and functionality. The plate is used for fractures of the tibia and ankle, when there is a need to fix bone fragments. Its removal occurs as planned. The time of the operation is determined by the doctor.
Intraosseous rods (pins) are used to fix tubular bones - for example, in case of a fracture of the collarbone or leg. Such operations are performed quickly and are characterized by minimal trauma. After fixation, loading is allowed in just a few days.
Removal of the structure is carried out in half an hour if the installation was carried out correctly. If there is damage to the threads or screws, it becomes necessary to drill out the elements.
Treatment
Treatment for a fracture of the 5th metatarsal bone depends on the nature and severity of the injury. If there is no displacement, fragments, or open wounds, then the damage heals quickly. Acute pain is relieved with painkillers in the form of tablets, ointments and gels for external use. Until the bone heals, you should limit physical activity on the affected leg. For this purpose, the limb is immobilized with a plaster cast, and the person can move with the help of crutches. After receiving the results of the control x-ray and making sure that the bone has fused, the patient is allowed to step on the injured leg. To reduce the load, it is recommended to use special orthopedic insoles.
In the event that there are fractures with displacement of bone fragments or the integrity of the skin is compromised, mandatory surgical intervention is indicated.
Operation
It is carried out when parts of the bone are displaced relative to each other by more than half their width. During the operation, they are positioned in the desired position, fixed with special fasteners, and then the needles are inserted. After the manipulation is completed, a suture is placed on the surgical incision (plaster is not used). The victim has the ability to move independently with support on his heel for one month.
Plaster boot
It is a tight plaster cast that is applied from the ankle to the toes. It ensures the immobility of the broken bone, prevents further divergence by the fragment, and protects the limb from accidental blows and bruises. The cast is worn continuously for 4-6 weeks.
Foot orthosis for metatarsal fractures
A foot brace or orthosis is used for a minor fracture (without displacement or rupture of soft tissue). It is more aesthetic, allows you to immobilize the foot, reducing the load on this part of the body. It is unacceptable to use such fixing devices when there are several fractures of the metatarsal bones.
Closed reduction of a calcaneal fracture with fixation in an external fixation device.
It is often used as an intermediate method of fracture fixation in cases of significant soft tissue damage at the planned surgical site.
It can also be used as a final method of fixation, especially in cases where the surgeon knows the technique of installing the device with Ilizarov apparatus modules.
External fixation often allows one to achieve good reposition without significant damage to soft tissues; after swelling subsides and wounds heal, a transition to internal fixation is possible.
Rehabilitation
Recovery after a fracture of the metatarsal bone of the foot, which lasts a month and a half, involves procedures aimed at developing the limb and returning its functionality. Rehabilitation measures begin immediately after the plaster is removed. Exercise therapy and massage are shown as the main ones.
Exercise therapy
Therapeutic exercise helps to develop damaged joints, strengthens the entire musculoskeletal system, prevents muscle atrophy and prevents fluid stagnation and tissue swelling.
To effectively develop the foot, it is recommended to perform the following set of exercises:
- flexion and extension of fingers,
- turning the feet alternately in different directions,
- pulling the feet towards you and back,
- rolling from heel to toe,
- circular movements of the feet,
- grasping and moving small objects,
- rolling the ball on the floor.
All techniques must be performed 10-15 times each, movements are performed slowly, with strict adherence to all safety rules. This will help prevent the risk of re-injury. It is recommended to conduct the first classes in a physical therapy room under the direct supervision of an instructor.
Errors and complications in the treatment of complex fractures of the ankle joint
R.Z. SALIKHOV, I.O. PANKOV, Yu.A. PLAKSEICHUK, V.V. SOLOVIEV
Republican Clinical Hospital of the Ministry of Health of the Republic of Tatarstan, 420064, Kazan, st. Orenburgsky Trakt, 138
Salikhov Ramil Zaudatovich - senior researcher of the scientific department, traumatologist-orthopedist, tel. +7-917-285-28-28, e-mail
Pankov Igor Olegovich - Doctor of Medical Sciences, Professor, Chief Researcher of the Research Department, Head of the Clinic of Traumatology and Orthopedics, tel., e-mail: [email protected]
Plakseychuk Yuri Antonovich - Candidate of Medical Sciences , leading employee of the scientific department, head of the orthopedics department No. 1, tel. +7-917-269-60-01, e-mail
Soloviev Vladislav Vsevolodovich - research fellow of the scientific department, traumatologist-orthopedist, tel. +7-927-672-42-99, e-mail
Errors and complications in the treatment of 116 patients with consequences of injuries to the ankle joint that required repeated surgical treatment were analyzed. The share of errors and complications that arose at the stage of primary diagnosis and treatment was 59.5%. Complications related to the severity of the injury itself amounted to 37.1%; “due to the patient’s fault” 3.4% of complications occurred. The disappointing data obtained highlight the need to improve the training of orthopedic traumatologists and the implementation of standards of care.
Key words : ankle fractures, post-traumatic arthrosis of the ankle joint.
R. _ Z. _ SALIKHOV , I. _ O. _ PANKOV , Y. _ A. _ PLAKSEYCHUK , V. _ V. _ SOLOVYEV
Republican Clinical Hospital of the Ministry of Healthcare of the Republic of Tatarstan, 138 Orenburgskiy Trakt, Kazan, Russian Federation, 420064
Errors and complications in the treatment of complex ankle fractures
Salikhov RZ - Senior Researcher of the Scientific Department, traumatologist-orthopedist, tel. +7-917-285-28-28, e-mail
Pankov IO - D. Med. Sc., Professor, Chief Researcher of Scientific-Research Department, Head of the Clinic of Traumatology and Orthopedics, tel., e-mail: [email protected]
Plakseychuk Yu.A. — Cand. Med. Sc., Leading Researcher of the Scientific Department, Head of the Orthopedic Department No. 1, tel. +7-917-269-60-01, e-mail: [email protected]
Solovyev VV - Researcher of the Scientific Department, orthopedic surgeon, tel. +7-927-672-42-99, e-mail: [email protected]
Errors and complications in the treatment of 116 patients with ankle fractures were analyzed, which required iterated operative treatment. The rate of mistakes and complications encountered at primary diagnosis and treatment was 59.5%. Complications associated with the type of fracture constituted 37.1%. The failure of the patient to adhere to doctors recommendations was revealed in 3.7% of cases. These unsuccessful results highlight the importance of orthopedic surgeons training and the need to follow all necessary procedures.
Key words: ankle fracture, posttraumatic osteoarthritis of ankle.
The frequency of fractures of the ankle joint is 13-20% of all skeletal bone fractures and 30-60% of shin bone fractures, occupying one of the first places in frequency among all injuries of the musculoskeletal system [1, 2]. The frequency of complications and unsatisfactory treatment outcomes is high and reaches 30% or more, depending on the type and type of fractures and the severity of associated tissue damage [3-6].
The purpose of the study is to develop recommendations to reduce unsatisfactory treatment outcomes for patients with complex fractures of the ankle joint.
The objectives of the study are to analyze errors and complications in the treatment of patients with consequences of injuries to the ankle joint.
Materials and methods
Based on anamnesis, physical examination data and radiological research methods (x-ray, computed tomography), errors and complications that led to unsatisfactory treatment results for patients with complex injuries of the ankle joint and required surgical treatment were analyzed and structured. The data of 116 patients who were admitted for surgical treatment in 2003-2013 were studied. Of these, there were 55 men and 61 women. There were 109 patients of working age. The duration of injury ranged from 4 months to 12 years.
The reasons for hospitalization for surgical treatment were: secondary displacement of ankle fragments, relapses of diastasis in the tibiofibular joint, delayed consolidation and pseudarthrosis of ankle fractures, pseudarthrosis and avascular necrosis of the talus, post-traumatic arthrosis and contractures of the ankle joint. All patients underwent appropriate surgical treatment, which included reconstructive operations (transosseous osteosynthesis, corrective osteotomies with restoration of congruence of articular surfaces, arthroscopy of the ankle joint) and stabilizing operations (arthrodesis of the supratalar joint, supra- and subtalar arthrodesis). Errors and complications in the management and treatment of patients with complex injuries to the ankle joint were divided into those that arose at the diagnostic stage, during the treatment process, directly related to the severity of the injury itself, and also into complications “due to the fault of the patients themselves.”
Results and its discussion
The distribution of patients by nosological categories and types of surgical interventions required is presented in Table. 1.
Table 1.
Nosological categories and types of surgical interventions required
| Type of nosological category | Type of surgery | Number of patients |
| Incorrectly healing ankle fractures, damage to the tibiofibular syndesmosis | Closed repair of damage to the tibiofibular syndesmosis | 24 |
| Incorrectly healed fractures of the distal leg bones, damage to the tibiofibular syndesmosis | Corrective osteotomies | 37 |
| Post-traumatic arthrosis of the supratalar joint stage I-II | Ankle arthroscopy | 11 |
| Post-traumatic arthrosis of the supratalar joint stage III-IV | Arthrodesis of the supratalar joint | 18 |
| Post-traumatic arthrosis of the supra- and subtalar joints stage III-IV | Arthrodesis of the supra- and subtalar joints | 22 |
| Pseudarthrosis and avascular necrosis of the talus | Arthrodesis of the supra- and subtalar joints | 4 |
| Total nosological categories | 116 |
Errors and complications that arose at the diagnostic stage included incorrect interpretation of clinical and radiological data - 11 patients, undiagnosed injuries to the distal tibiofibular syndesmosis - 3 patients. There were 14 patients in total, which accounted for 12.1% of the total. To avoid these errors, it is necessary to pay attention to the features of the mechanism of injury, taking into account that all types of complex fractures of the distal articular end of the tibia bones, where suprasyndesmotic or transsyndesmotic fractures of the fibula occur, are accompanied by partial or complete damage to the tibiofibular ligaments; with subsyndesmotic fractures of the fibula, damage to the tibia syndesmosis, as a rule, is not observed (classification by K. Webber, 1966). It is necessary to perform a full clinical and radiological examination (including comparative radiographs of both ankle joints with placement “on syndesmosis” or X-ray computed tomography in doubtful cases).
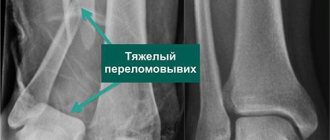
In Fig. Figure 1 shows radiographs of a patient with a healed fracture of the lateral malleolus, damage to the distal tibiofibular syndesmosis, and outward subluxation of the foot (compared to the uninjured side).
Picture 1.
X-ray of a patient with consequences of damage to the left ankle joint (healed fracture of the lateral malleolus, damage to the distal tibiofibular syndesmosis, subluxation of the left foot outward compared to the uninjured side)
Errors during medical manipulations and surgical procedures: incomplete and inaccurate reduction of the fracture (residual displacement of ankle fragments and incongruity in the supratalar joint), inadequate fixation of fractures - 37 patients, incomplete elimination of tears in the tibiofibular syndesmosis - 10 patients, relapses of displacement of ankle fragments and excessive diastasis in tibiofibular joint - 5 patients, long-term fixation of the foot in a hypercorrection position - 3 patients (in such cases, there is a mutual convergence of muscle attachment points, a weakening of their tone with the subsequent development of combined flatfoot). A total of 55 patients, which accounted for 47.4% of the total. When treating patients with injuries to the ankle joint, one should be guided by the principles of complete restoration of congruence of the articular surfaces, reliable fixation of fragments, and careful implementation of management protocols.
In Fig. Figure 2 shows radiographs of a patient with severe damage to the distal articular part of the leg. The displacement of the fragments was not eliminated, an inadequate method of fixation of the fragments was chosen, and, as a result, the patient developed grade 4 post-traumatic arthrosis. and a sharp impairment in the ability to support the limb.
Figure 2.
Radiographs of a patient with severe damage to the distal articular part of the leg; the displacement of the fragments was not eliminated, an inadequate method of fixation of the fragments was chosen, and, as a result, the patient developed post-traumatic arthrosis of the 4th degree. and a sharp impairment in the ability to support the limb
Complications related to the severity of the injury were identified in 43 patients, which amounted to 37.1% of the total. Severe damage to the capsular-ligamentous apparatus of the ankle joint, extensive destruction of the articular surface of the tibia and talus can cause the development of persistent contractures and deforming arthrosis of the supratalar joint and joints of the foot, even after restoration of congruence of the articular surfaces. Such patients, as a rule, require several courses of rehabilitation treatment and timely referral for repeated surgical treatment. With the development of post-traumatic arthrosis of the 1st–2nd stage. Arthroscopy of the ankle joint can be performed; in case of grade 3–4 arthrosis, formation of a false joint and/or avascular necrotalar bone, arthrodesis remains the operation of choice. Arthroscopy of the ankle joint allows you to clarify the diagnosis, eliminate anterior impingement syndrome, remove loose intra-articular bodies, and increase range of motion. Arthrodesis of the supratalar or supra- and subtalar joints eliminates pain and restores the ability to support the limb.
In Fig. Figures 3 and 4 show radiographs of a patient with severe damage to the distal articular part of the leg. The displacement of the fragments was eliminated, and PCOS was performed using an external fixation device. After 5 years, the patient came to the clinic due to severe pain syndrome, and the development of post-traumatic arthrosis of the 4th degree was diagnosed.
Figure 3.
Radiographs of a patient with severe damage to the distal articular part of the leg. Displacement of fragments was eliminated, PCOS was performed using an external fixation device
Figure 4.
Radiographs of the patient after 5 years. Post-traumatic arthrosis of the 4th degree has developed
Complications due to the “fault of the patients themselves” are conditionally subjective in nature, and they are associated with non-compliance with the prescribed regimen on the part of patients.
Complications of this category: untimely referral of patients for medical help, accidental falls on the operated limb, too early loading of the limb, which can lead to secondary displacement of fragments, fractures of fixators requiring repeated corrective interventions, unjustifiably late loading and function of the limb, which, as a rule, lead to the development of persistent joint contractures and so-called stress osteoporosis, requiring long-term rehabilitation treatment, ignoring full rehabilitation treatment on the part of patients, which leads to significant functional disorders, often leading to permanent disability. We included 4 patients in this group, which accounted for 3.4% of the total.
conclusions
Complex fractures of the ankle joint area are severe intra-articular injuries to the bones of the extremities. The features of this category of fractures include: multiple nature of the damage, a frequent combination of fracture and dislocation with damage to the capsular-ligamentous apparatus of the joint; significant violations of congruence in the ankle joint; a wide variety of types and types of damage; often - difficulties in ensuring reposition and adequate stable fixation of fragments during the period of consolidation; the development of complications in the form of deforming arthrosis and persistent contractures of the ankle and foot joints, combined post-traumatic flatfoot, avascular necrosis of the talus during its fractures, requiring a long period of rehabilitation and often repeated, including reconstructive operations. Among patients with consequences of severe injuries to the ankle joint, a high proportion of errors and complications that arose at the stage of diagnosis and treatment was revealed - 59.5%, which requires improved training of orthopedic traumatologists providing emergency traumatological and orthopedic care, and a wider introduction of diagnostic methods (X-ray computed tomography, magnetic resonance imaging), providing specialized departments of traumatology and orthopedics with power equipment, instruments and modern metal structures.
LITERATURE
1. Oganesyan O.V. Restoring the shape and function of the ankle joint / O.V. Oganesyan, S.V. Ivannikov, A.V. Korshunov // M.: BINOM: Laboratory of Knowledge: Medicine, 2003. - 120 p.
2. Sobhani S. Epidemiology of Ankle and Foot Overuse Injuries in Sports: A Systematic Review / S. Sobhani, R. Dekker, K. Postema, PU Dijkstra // Scand. J. Med. Sci Sports. - 2012. - 12. - P. 32-43.
3. Samoday V.G. Errors and complications in the treatment of ankle fractures / V.G. Samoday, A.N. Letnikov // Materials of the international congress “Modern technologies in traumatology and orthopedics: errors and complications - prevention, treatment.” - M., 2004. - P. 141-142.
4. Khoroshkov S.N. Surgical treatment of patients with adverse consequences in the ankle joint / S.N. Khoroshkov, G.I. Chemyanov, N.G. Doronin, A.Yu. Kostyakov // Abstracts of reports of the I scientific-practical conference “Current issues of orthopedics. Achievements. Prospects." - M., 2012. - P. 130-131.
5. Smith MV Lower Extremity-Specific Measures of Disability and Outcomes in Orthopedic Surgery / MV Smith, SE Klein, JC Clohisy, GR Baca // J. Bone Jt. Surg. - 2012. - 94(A). - No. 5. - P. 468-477.
6. Ovaska MT Risk Factors for Deep Surgical Site Infection Following Operative Treatment of Ankle Fractures / MT Ovaska, TJ Makinen, R. Madanat, K. Huotari // J. Bone Jt. Surg. - 2013. - 95(A). - No. 4. - P. 348-353.
REFERENCES
1. Oganesyan OV, Ivannikov SV, Korshunov AV Vosstanovlenie formy i funktsii golenostopnogo sustava. Moscow: BINOM: Laboratoriya znaniy: Meditsina, 2003. 120 p.
2. Sobhani S. et al. Epidemiology of Ankle and Foot Overuse Injuries in Sports: A Systematic Review. Scand. J. Med. Sci Sports, 2012, 12, pp. 32-43.
3. Samoday VG, Letnikov AN Oshibki i oslozhneniya pri lechenii perelomov lodyzhek. Materialy mezhdunarodnogo kongressa “Modern tekhnologii v travmatologii i ortopedii: oshibki i oslozhneniya - profilaktika, lechenie.” Moscow, 2004. Pp. 141-142.
4. Khoroshkov SN et al. Operativnoe lechenie patsientov s neblagopriyatnymi posledstviyami v oblasti golenostopnogo sustava. Tezisy dokladov I scientifically-prakticheskoy konferentsii “Aktual'nye voprosy ortopedii. Dostizheniya. Perspektivy.” Moscow, 2012. Pp. 130-131.
5. Smith MV et al. Lower Extremity-Specific Measures of Disability and Outcomes in Orthopedic Surgery. J. Bone Jt. Surg., 2012, 94(A), no. 5, pp. 468-477.
6. Ovaska MT et al. Risk Factors for Deep Surgical Site Infection Following Operative Treatment of Ankle Fractures. J. Bone Jt. Surg., 2013, 95(A), no. 4, pp. 348-353.
Possible complications after injury
With a favorable prognosis, as well as a correctly selected regimen of therapy and rehabilitation after injury, the fracture heals within several months. Upon completion of the recovery period, the person can return to a normal, physically active life.
Failure to comply with the above conditions may result in serious consequences. These are:
- constant pain in the foot,
- arthrosis,
- limb deformity,
- drooping longitudinal and transverse arches (flat feet),
- formation of bone spurs,
- deterioration of foot mobility.
To reduce the risk of complications, you need to be able to competently provide first aid to the victim, and then clearly and strictly follow all the recommendations of the attending physician regarding treatment and rehabilitation.
Injury to wedge-shaped and cuboid links
Fractures of the wedge-shaped and cuboidal links of the leg skeleton are caused by a fall of gravity on the back of the leg. The injury is complex and usually occurs in combination with other ankle injuries.
Symptoms
When damaged, a person exhibits symptoms:
- Painful symptom when trying to turn the foot left and right during palpation;
- Swelling on the inside of the foot;
- Bruise.
The injury is detected using an x-ray. If the fracture is not visible in the photograph, but the symptoms indicate that the leg is damaged, then the person is given a plaster cast for 2 weeks. After 14 days, a repeat image is taken, and if the bones are broken, the formation of a callus is recorded. Based on this, the doctor makes a diagnosis of a simple fracture.