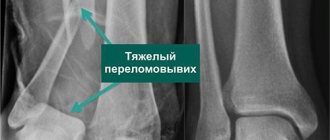
According to statistics, 54% of fractures and fracture-dislocations of the ankle joint occur at a young age, when it is important for a person to maintain working capacity. These injuries are classified as severe injuries to the musculoskeletal system. Even with high-quality treatment, they lead to disability in 3-12% of cases. Therefore, restoring the functions of the ankle joint requires a careful approach, individual for each patient.
The situation is similar with injuries to the ligamentous apparatus. The ankle is often injured in athletes and young, active people. In 30-50% of them, late diagnosis or poor-quality treatment leads to chronic instability of the ankle joint. It interferes with leading an active lifestyle, and over time even leads to disability.
Early diagnosis and quality treatment help reduce the risk of disability. Moreover, ligament injuries, sprains and fractures are much easier to treat initially, immediately after the injury. At the same time, the chances of restoring ankle function are much higher. And the treatment and rehabilitation itself is less invasive and takes less time.
Therefore, after an injury, it is better to immediately contact a good clinic, where they use the most effective diagnostic and treatment algorithms.
How to restore ankle function after injury
How doctors will treat depends on the severity of the injury and the nature of the damage to the joint. After all, ligament tears are much easier to treat than, for example, displaced fractures or fracture-dislocations. Specialists decide on treatment tactics only after examining the patient, having a complete understanding of his condition and the severity of the injury.
Several methods are used to restore the functions of the ankle joint:
- Conservative treatment. Effective for minor injuries that are not accompanied by fractures, dislocations and complete rupture of ligaments. The functions of the ankle are restored with the help of rest, fixation with an elastic bandage, painkillers and anti-inflammatory drugs, physiotherapy and exercise therapy.
- Plaster immobilization. Used in the treatment of fractures in which there is no displacement of the bone fragment and instability of the ankle. Plaster is also applied for fresh ruptures and tears of the ligaments (no later than two to three months after the injury). Plaster immobilization is also used after osteosynthesis and skeletal traction as a final treatment method.
- Closed reduction with further plaster immobilization. Used for closed displaced fractures. It is not recommended for use in cases of concomitant ankle subluxations due to the high risk of unsatisfactory treatment outcome.
- Open reduction with fixation with immersion structures. All open and some closed fractures are treated in this way. In some cases, after surgery, the joint is additionally fixed with plaster.
- Skeletal traction and transosseous compression osteosynthesis. Used to treat complex and chronic fractures in the ankle joint. It is carried out using special external fixation devices.
- Surgery. It is performed for chronic ligament injuries, post-traumatic osteoporosis, severe fractures and fracture-dislocations. Allows you to restore ankle function even when it is impossible to do this in other ways.
Ankle immobilization
For complete ruptures and significant tears of the ligaments, plaster immobilization or external fixation devices are used. However, they are effective only in the early stages, before a person has developed instability of the ankle joint. For old injuries that are more than 2-3 months old, these methods do not give the expected result.
If a person’s ligament rupture is not detected in time or he does not receive quality treatment, he develops ankle instability. In this case, no immobilization will help restore the function of the joint. And in order to return to work, it is necessary to undergo surgery.
Ankle inward
Sitting on the floor, the leg being worked out is extended and closer to the door, the healthy leg is bent at the knee. Wrap one end of an elastic band or expander around the toe of your sore leg, and secure the other end to a door or any stationary object at the level of your ankle. Gently tip the toe inward, stretching the elastic. Return to the starting position. 2 sets of 15 reps.
Non-surgical treatment of fractures
Conservative treatment is possible only when there is no displacement of bone fragments and the ankle joint remains stable. In this case, the patient is given a plaster cast for 1-2 months or asked to wear a boot for rehabilitation walking.
Despite the availability and low-traumatic nature of plaster immobilization, it has a number of disadvantages:
- limits the mobility of the lower limb and complicates rehabilitation;
- disrupts peripheral circulation;
- causes irreversible changes in the neuromuscular system of the leg and foot.
In order to partially neutralize the harm of long-term immobilization, from the second or third day after applying the cast, a person begins to engage in therapeutic exercises. Exercise therapy helps relieve swelling, improve blood circulation in the ankle area, and strengthen the muscles of the foot, lower leg and thigh. And this speeds up recovery and prevents the development of post-traumatic osteoporosis.
After the cast is removed, rehabilitation continues for several more months. During this period, the patient is prescribed massage, physiotherapy, physical therapy, etc. The main goal of these procedures is to strengthen muscles and ligaments, improve metabolic processes in tissues, normalize blood circulation and restore the functions of the injured joint.
Contraindications
Although physical activity is essential for recovery from a broken ankle, it is not for everyone.
The following pathological conditions are contraindications to exercise therapy:
- Inflammatory and purulent processes in the body;
- Diseases in the acute stage;
- Pregnancy;
- Unstable compound fracture;
- Mental illnesses;
- Malignant formations;
- Bleeding from all locations.
Closed reduction with further plaster immobilization
This is a common treatment method used primarily for ankle fractures. Its essence lies in the manual reposition of bone fragments and subsequent fixation of the ankle with a plaster cast. This method is accessible and low-traumatic, but has its drawbacks.
Long-term plaster immobilization disrupts trophism and impairs blood circulation in the tissues of the limb, causing irreversible changes in the nerves and muscles of the lower leg, foot, and ankle joint. It does not provide sufficiently stable fixation and does not guarantee complete immobility of the fragments. All this can lead to improper bone fusion and the formation of a false joint.
In case of concomitant dislocations and subluxations of the ankle, it is recommended not to use closed reduction. The reason is the high risk of unsatisfactory treatment results.
The most common of them:
- postoperative contractures;
- false joints;
- severe deforming arthrosis.
Therefore, many specialists prefer a different approach to the treatment of displaced fractures. For patients of working age, they recommend open reduction with fixation of bone fragments with metal structures. And for patients in the older age group, reposition under image intensifier control and fixation with Kirschner wires.
Important Tips
Physical therapy will be more beneficial if you take care of auxiliary recovery techniques. Let's consider the main ones:
- Go for a massage to a specialist or do it yourself twice a day. Stroke, squeeze, knead and shake your leg. Repeat each technique 10 times, but do it in such a way that it does not hurt.
- Before going to bed, run a warm bath on the injured limb. In the water, move your feet in different directions.
- Go for magnetic therapy, ozokerite and electrophoresis.
- Move more, but within your capabilities. During movements, your foot should bend at different angles. Therefore, it would be optimal to walk up the stairs and exercise your legs on an exercise bike (or on the pedals of a sewing machine).
- Take vitamins and calcium.
Open reduction with internal fixation
The method is used to treat complex fractures when manual reposition of fragments and holding them in the desired position with the help of plaster is impossible. To compare bone fragments and securely fix them, submersible elements and structures are used:
- tie bolts;
- screws;
- bolts with clamp terminals;
- Kirschner wires;
- bolts with flexible rod;
- lavsan ribbons and so on.
Open reduction ensures immediate accurate comparison of fragments and their reliable fixation. After surgery, early weight-bearing ability of the limb is often preserved, which allows it to be loaded soon after surgery. Nevertheless, many experts are confident that none of the methods of open reduction can ensure complete immobility of bone fragments. Therefore, after surgery, patients require additional plaster immobilization.
Operative comparison and fixation of fragments has other disadvantages:
- Injury to soft tissue at the surgical site.
- Risk of developing infectious complications.
- The likelihood of secondary displacement of fragments due to failure of fixators.
- High incidence of pseudarthrosis.
In some cases, closed fractures are best treated by skeletal traction or transosseous osteosynthesis. These methods exclude the intervention of a traumatologist in the natural healing process. Regeneration is accelerated because the doctor does not remove the hematoma and does not damage the muscles, blood vessels, or periosteum. And the opposition of fragments and stretching of soft tissues additionally stimulates regenerative processes.
Transosseous osteosynthesis
Today, osteosynthesis is carried out using hinge-distraction devices and skeletal traction devices. The technique allows you to reliably fix bone fragments, which creates ideal conditions for their fusion.
The main advantage of transosseous osteosynthesis is that it does not require open surgery. The disadvantage is that it does not always allow bone fragments to be compared. Therefore, transosseous osteosynthesis can be combined with surgery. First, the fragments are connected surgically, and why the bones are additionally fixed with an external fixation device.
Reconstructive surgeries
Reconstructive surgeries are used to treat chronic ligament tears that are accompanied by ankle instability. The integrity of the ligaments is restored surgically, after which the joint is fixed with an Ilizarov apparatus. If the injury is less than 5 months old, surgery is often performed by arthroscopy. But old ruptures require open reconstruction.
The integrity of the ligaments can be restored:
- local tissues;
- allotissues;
- synthetic endoprostheses.
Plastic surgery with local tissue is associated with additional trauma to the donor site, so it is rarely performed. To restore ligaments, synthetic tissue or allotendon is often used.
Endoprosthetics and arthrodesis
Surgeries on the ankle joint are performed mainly for severe post-traumatic osteoporosis, which is accompanied by severe pain and limited mobility of the ankle.
Young patients often undergo endoprosthesis replacement - replacement of a joint with an artificial endoprosthesis. This operation allows you to completely restore the function of the ankle. When endoprosthesis replacement is not possible (old age, severe concomitant diseases), the patient undergoes arthrodesis - immobilization of the joint. This operation is resorted to as a last resort.
Let's summarize:
- Torn ligaments and ankle fractures often occur at a young age. They are difficult to treat and often lead to disability.
- Fresh injuries are much easier to treat. The sooner a person receives medical help, the higher the chances that joint function will be restored.
- To treat injuries, different methods are used, ranging from conservative treatment to surgical treatment.
- The choice of treatment method depends on many factors. The severity and duration of the injury, ankle instability, the degree of post-traumatic osteoporosis, etc. play a role.
- Surgery is a radical method of treatment. As a rule, surgery is performed when it is impossible to restore the function of the joint in other ways.
Ankle out
Sitting on the floor, the leg being worked out is extended and further from the door, the healthy leg is bent at the knee.
Wrap one end of an elastic band or expander around the toe of your sore leg, and secure the other end to a door or any stationary object at the level of your ankle. Gently tip the toe outward, stretching the elastic. Return to the starting position. 2 sets of 15 reps. When you can stand on your injured leg without pain, begin the following exercises.