The hip joint is one of the most important joints of the musculoskeletal system. His injuries and illnesses are accompanied by pain and limit movement, and the solution to the problem is often surgery. A course of rehabilitation procedures, selected individually depending on the characteristics of the patient, helps to quickly return to a normal lifestyle after it. Their goal is to avoid negative consequences, eliminate the inflammatory process and pain, restore a person’s motor functions, teach how to use a prosthesis and live fully despite their health condition.
The recovery time depends on the competence of the doctors, the equipment of the rehabilitation center (handrails, ramps, crutches, etc.), the availability of the necessary equipment, and the professionalism of the staff providing assistance in the daily life of the patient.
Principles of rehabilitation
Rehabilitation after hip replacement is considered successful if the following improvements are observed after completion of the course:
- there is no pain when moving the hip joint;
- the patient returns to normal life and does not need outside help;
- the work of muscles and ligaments is normalized, articular joints move smoothly;
- correct movement patterns and coordination in individual muscle groups are restored;
- weak muscles are strengthened.
Rehabilitation consists of physiotherapy, exercise therapy, and drug treatment. With the right approach, you can achieve the following results:
- blood circulation in the lower extremities improves;
- muscle strength and range of motion in the damaged joint increases;
- pain, swelling, signs of inflammation disappear;
- the statics of the spine is normalized;
- The body's protective functions are strengthened, which reduces the risk of complications.
Methods for effective rehabilitation after hip replacement are selected by the doctor. You should not self-medicate, as this can lead to negative consequences.
Rehabilitation methods after endoprosthetics
Among the methods that help to recover after joint replacement, physical therapy plays a key role. Osteopathic treatment helps complement and enhance the effect of exercise therapy. Let's take a closer look at these methods.
Exercise therapy is the main method of recovery for patients with endoprostheses
Movement therapy plays a key role in the recovery of patients after joint replacement. The advantage of this method is that you can create a complex that includes a variety of exercises. He will take into account the patient’s capabilities at any rehabilitation stage.
That is why physical exercises after endoprosthetics play such an important role. Exercise therapy after joint replacement includes:
– dynamic exercises with self-help; – a set of relaxation exercises; – a set of active-passive exercises; – dosed isometric muscle contractions.
It is very important that the exercises are selected by a specialist after assessing the patient’s capabilities. You cannot create a set of physical exercises based on general recommendations or videos on the Internet.
At first, classes must be supervised by a specialist. And only then, when the doctor is convinced that the patient is doing everything correctly, independent training is allowed.
Physical exercise is the basis of a proper rehabilitation program for patients after joint replacement. They accelerate tissue healing processes, improve their nutrition and restore joint function.
In addition to exercises, specialists at the Quality of Life clinic use the Redcord suspension system . Exercises on it help reduce the axial load on the joint and strengthen the deep muscles, which is especially important after the installation of an endoprosthesis.
Another modern method that perfectly complements rehabilitation measures is kinesio taping . Applying tapes to the area of the operated joint relieves swelling, reduces postoperative pain, improves joint mobility and protects it from excessive stress.
Osteopathy as part of comprehensive rehabilitation
Osteopathy in the rehabilitation of such patients is effective due to the fact that it affects the cause of the development of the pathological process. In this case, the osteopathic doctor does not use any drugs - the result is achieved by activating the body’s own forces.
If the patient is bothered by postoperative pain, swelling or contracture, the doctor will use his techniques to eliminate their root cause:
— Restores normal blood circulation and lymphatic drainage; — Eliminates muscle spasm and normalizes tone; — Restores normal sensitivity; — Relieves excessive stress and improves joint mobility; — Restores the symmetry of the pelvic bones and balance throughout the body.
The doctor works with the patient’s entire body, and not just where it hurts. If there are concomitant diseases that may complicate recovery, the osteopath will definitely work on them.
For example, flat feet, poor posture or back pain can prevent the patient from developing correct movements - disrupt his gait, etc. If he has had a hip or knee replacement, the abnormal movement pattern may cause the prosthesis to become misaligned and thus reduce its lifespan.
Thus, visiting an osteopath as part of a rehabilitation program allows operated patients to reduce pain, swelling, stiffness of movement without medications, and also prevent the development of long-term complications.
Terms of rehabilitation
The average duration of the rehabilitation period is 3 months. If the pain persists, you can continue to walk using a cane. You can start active training after 8-12 months.
But even after complete recovery, you must follow some rules throughout your life:
- do not bend the joint more than 90 degrees;
- regularly perform moderate physical activity;
- do not quit training after full recovery;
- visit a doctor regularly;
- stop smoking and drinking alcohol;
- Healthy food;
- Do not take any medications or herbs without consulting your doctor.
Drug treatment
Medicines are prescribed to relieve pain, signs of inflammation, accelerate regeneration and prevent the development of complications.
Main groups of drugs and their action:
- Broad-spectrum antibiotics prevent the development of secondary bacterial infections after surgery.
- Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs - eliminate pain and manifestations of the inflammatory process.
- Vitamin complexes with calcium, chondroitin, collagen accelerate the regeneration of muscles and bone structures.
- Anticoagulants - prevent the formation of blood clots.
- Cardioprotectors - reduce the risk of developing heart failure.
- Gastroprotectors - protect the walls of the stomach and duodenum from the aggressive effects of other drugs.
- Anticholinesterase drugs - eliminate intestinal atony.
After antibacterial therapy, a course of probiotics and dental antibiotics is prescribed to restore the balance of the intestinal microflora.
Contraindications during the rehabilitation period
Self-medication and violating the basic principles of rehabilitation are strictly contraindicated - the patient must strictly follow the recommendations of the attending physician.
Each rehabilitation method has a number of its own contraindications, from pregnancy and fever to systemic blood diseases and malignant tumors. That is why, before drawing up a rehabilitation program, each patient at “Blagopoluchiya” is carefully examined by a doctor. He clarifies the presence of contraindications and only on the basis of these data selects procedures and their parameters.
Comprehensive physiotherapy
Physiotherapy is an important component of successful rehabilitation after endoprosthetics. The goals are to improve microcirculation, activate metabolic processes, increase muscle tone, and eliminate spasms.
Kinesiotherapy is a type of physical therapy, movement treatment, prescribed at an early stage of rehabilitation. Classes are held on a special simulator for the hip joint. The complex is compiled taking into account the individual characteristics of the body, the presence of certain diseases in the patient.
To achieve results, you need to practice regularly under the strict guidance of an instructor. The patient masters all exercises gradually, the loads increase gradually taking into account the body’s adaptation. During gymnastics you need to breathe correctly, this helps to cope with pain and engage deep muscles.
Contraindications: malignant neoplasms, infectious pathologies, open and closed bleeding. Gymnastics cannot be performed with high blood pressure, tachycardia, diabetes, thrombosis and thrombophlebitis.
Hydrokinesitherapy - therapeutic exercises in the pool. Allows you to avoid excessive loads on the joint capsule and the appearance of unpleasant sensations. Improves the functioning of the entire musculoskeletal system and immune system.
Effective physiotherapy after endoprosthetics:
- Cryotherapy. Forms filled with hydrogel are applied to the prosthetic site. The duration of the procedure is 15 minutes. Helps quickly get rid of pain and swelling.
- Electrical stimulation. Exposure of tissue to current of a certain frequency. Muscles contract, strengthen, and tone increases. The method activates metabolic processes and improves blood circulation in the surgical area.
- Magnetotherapy. The tissue is exposed to a high or low frequency magnetic field. The result is a decrease in pain, a decrease in signs of inflammation, a mild sedative effect, improved vascular elasticity, and accelerated tissue recovery.
- Watsu is a body-oriented technique. Combines body support, muscle traction, mobilization of cartilage tissue, joint healing, massage. Allows you to increase the range of motion of the hip joint to its natural amplitude. After the first session, mobility improves, spasms disappear, and pain decreases. Additionally, the protective and restorative functions of the body are activated, sleep improves, and emotional stress goes away.
- Orthotics. An orthosis is selected for the patient for fixation, correction of functions, and unloading of the limb during recovery after surgery.
- Laser therapy. The light beam improves the body's self-regulation. After the procedure, swelling and pain are reduced, and the immune system is activated.
Therapeutic massage is prescribed after relief of acute pain. Sessions are carried out to improve blood circulation, saturate tissues with nutrients and oxygen, and accelerate the regeneration process.
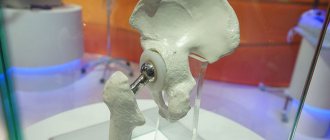
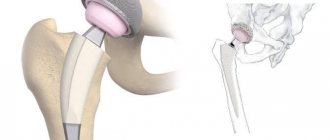
What is the essence of the operation
During surgery, the patient has all or part of the affected joint replaced with an implant or endoprosthesis.
The first attempt to replace a diseased joint with an artificial one was made in 1890 by the German surgeon Themistocles Gluck - he replaced the diseased knee joint with ivory.
Today, we have accumulated extensive experience in installing endoprostheses. The hip joint is most often replaced - more than 500 thousand such operations are performed annually in the world. In second place is the knee joint, in third place is the shoulder joint.
Modern endoprostheses are made from high-strength materials that combine well with the tissues of the human body and do not cause allergies. They are attached to the bone using special medical cement or a screw.
This operation is quite traumatic for the patient - it can last from 40 minutes to 3.5 hours and is performed under general anesthesia. But despite this, in some cases it remains the only method of treatment.
Indications and contraindications for endoprosthetics
Joint replacement is performed when their function and structure are so impaired that the patient cannot move normally or has severe pain. It is often indicated for the following diseases and conditions:
- Coxarthrosis; - Gonarthrosis; — Bekhterev's disease; - Rheumatoid arthritis; — Osteoporosis; - Gout; — Congenital developmental anomalies (hip dysplasia); — Deformation of joints as a result of injury; - False joints; — Tumors; — Aseptic necrosis; — Fracture of the femoral neck.
When deciding on the need for endoprosthetics, the stage of the disease, the intensity of pain, the degree of limitation of joint function, the effectiveness of conservative treatment, the need for additional means of support for the patient, the degree of reduction in physical activity and the inability to treat with other surgical methods are taken into account.
Despite advances in drug therapy, the number of patients with indications for arthroplasty is growing. This is facilitated by predisposing factors that aggravate the course of the underlying disease and accelerate the wear and tear of the joints.
Here are the main ones:
– obesity; – excessive physical activity; – injuries and microtraumas; - sedentary lifestyle; – flat feet; – incorrect posture; – metabolic pathology; – osteochondrosis; – adhesive disease; – diseases of internal organs; – frequent infections; – food with insufficient content of vitamins and microelements.
If patients have joint diseases and under the influence of these factors, the risk of needing surgery for them increases significantly. But even this can guarantee complete restoration of joint function, relief from pain, return to work capacity and everyday independence only if there is adequate rehabilitation.
There are also absolute and relative contraindications to the operation.
Absolute contraindications: – the patient’s inability to move independently (this will hinder his recovery after surgery); – chronic diseases of the cardiovascular system in the stage of decompensation (defects, heart failure, rhythm and conduction disorders, etc.); – respiratory failure of 2–3 degrees; – anemia of 2–3 degrees, poor blood clotting; – uncontrolled diabetes mellitus; – previous sepsis; – presence of a chronic focus of inflammation; – restriction of muscle movements of the right or left half of the body (hemiparesis) on the side where the operation is planned; – low bone density (osteopenia); – severe mental disorders; – bone tuberculosis; – thrombosis.
Relative contraindications: – exacerbation of chronic diseases that are in the stage of compensation; - liver failure; – 3rd degree obesity.
Obesity is an aggravating factor for those patients who require lower limb joint replacement.
Excess weight can greatly overload the endoprosthesis and shorten its service life. But at the same time, reducing pain after joint replacement and increasing the patient’s activity will contribute to his weight loss.
Early period
It begins after surgery, lasts 3 weeks, and takes place in the hospital. Consists of two stages. Gentle - inflammation is observed in the area of the surgical intervention for 1-7 days. On days 7-15, the wound heals, this is called the tonic stage.
The patient is transferred from the operating room to intensive care. Heart rate, blood pressure, and breathing are constantly monitored. Antibacterial therapy is started and anticoagulants are administered.
What happens during this period:
- swelling decreases;
- blood circulation in the area of intervention is restored;
- postoperative sutures heal;
- the patient learns to sit and then get out of bed;
- The task of the medical staff is to prevent the occurrence of bedsores, thrombosis, pleurisy, and pneumonia.
What the patient needs to know:
- 2 hours after recovering from anesthesia, you must definitely go to the toilet; if you cannot do it yourself, the nurse will insert a catheter;
- for the first 3-4 nights you should not sleep on your side or stomach;
- You can start walking with crutches or a walker after 2-3 days, but only with an accompanying person;
- you can turn over on your side in a day, on your stomach in a week, while you need to spread your legs slightly to the sides, you cannot perform the movements yourself, only with the help of a nurse;
- you can sit down on the third day;
- Do not bend over or use a spoon to change shoes;
- stay in one position for no more than 20 minutes;
- Do not make sudden movements of the hip joint;
- for the hospital, choose shoes without backs;
- the operated leg can be bent at an angle of no more than 90 degrees;
- place a pillow between your knees, do not cross your legs;
- to sit up in bed, you need to lean on your hands;
- perform simple exercises to prevent congestion;
- When walking, do not lean on the operated leg.
Gymnastics for the early period:
- Move, bend and straighten the toes on both feet.
- Press down on the bed with your heels.
- Perform swings, circular movements with your arms, raise and lower your shoulders.
- Tighten the muscles of your healthy leg.
- Rotate and slightly bend the ankle of the operated leg.
- Slide your foot along the bed, bend your leg, pull it towards you.
- Move your legs away from each other one by one.
- Alternately, straighten your legs a few centimeters above the surface of the bed.
- Additionally, perform breathing diaphragmatic exercises.
Perform the first 5 exercises 6 repetitions every 10 minutes. After 2-3 hours, add exercises from the second part of the complex, do 10 repetitions. Perform all movements slowly and smoothly, inhale while tensing the muscles.
When the doctor allows you to get up and walk, you need to do other exercises:
- With emphasis on the headboard, lift your legs one at a time, bent at the knee.
- With emphasis on one leg, take the other one to the side and lift it slightly. Then change the supporting leg.
- The starting position is the same as in the previous exercise, but the leg is taken back. You need to feel how the hip joint works.
You should not lie in bed for a long time after surgery. This will lead to muscle contractures and other negative consequences. Before exercise therapy and training, you should not take painkillers.
Late period
At this stage, rehabilitation after hip replacement takes place in the physical therapy room. You need to visit him immediately after discharge from the hospital. The goal is to restore the functionality of the limb, improve posture and the ligamentous-muscular center.
Stages and their duration:
- Early. It begins 2 weeks after the intervention and ends 2 months after the operation. At this stage, fusion of bone structures and the prosthesis occurs.
- Late. Terms - 60-90 days. Internal bone structures begin to recover.
In addition to physical therapy, from day 22 it is necessary to take walks. Walk with emphasis on a cane 3-4 times a day for 3-10 minutes, gradually increase the duration to 20 minutes. You can give up crutches and walkers when there are no problems with balance or self-doubt. This will take 1-2 months, depending on the method of fixing the prosthesis. Walking with a cane is necessary until the lameness disappears completely.
Exercise therapy for the late period, you will need a ball, an elastic gymnastic tape.
Exercises with tape:
- Secure one end of the tape to the door, the other to the shin. The back is straight, holding onto the support, stretch your leg forward.
- The starting position is the same. But raise your straight leg up.
- Do not change the starting position. Move your leg to the side.
Do all exercises smoothly 10 times.
Basic exercise therapy complex:
- Place the ball between your knees and squeeze rhythmically.
- While lying on your stomach, reach your buttocks with your heels.
- Starting position - lying on your back, knees bent, feet resting on the floor. Raise your pelvis, hold at the top point for a count of 5. Slowly return to the starting position.
- Lying on your back, alternately bend your legs, do not lift your feet off the floor.
- Lie on your stomach, slowly raise your straight leg, tensing the muscles of your buttocks. At the top point, fix the position for a count of 5. Return to the starting position and perform the exercise with the second leg.
- While sitting on a bed or chair, perform the “bicycle” exercise.
Do each exercise 6-10 times. Perform 2-3 approaches per day.
Plan of rehabilitation measures depending on the terms of rehabilitation (End)
According to official data, osteoarthritis occupies a leading place in prevalence among diseases of the musculoskeletal system. In the Russian Federation, 3 million 700 thousand patients with osteoarthritis are registered. According to the Moscow Department of Health, the overall incidence of osteoarthritis is 8863 patients per 100 thousand population [1, 2]. Acquired pathological changes in joints are a pressing problem in orthopedics; conservative therapy using medications, physiotherapeutic and kinesiotherapeutic methods is not always effective, which is an indication for surgical treatment of this category of patients.
Endoprosthetics of large joints of the lower extremities is an effective method of treating severe degenerative-dystrophic diseases of the joints [3-5]. The experience of domestic and foreign specialists reliably confirms that total hip and knee replacement is the most promising operation that improves the quality of life of patients, as it relieves them of pain and restores the ability to support the injured limb. An increase in the range of motion in the joints returns patients to an active lifestyle, thereby improving social and domestic rehabilitation [6–14]. The duration of the effect is about 10 years, and the re-operation rate is 0.2-2.0% [15].
Every year in Moscow, more than 8 thousand endoprosthetics of large joints of the lower extremities are performed; the ratio of hip replacement to knee replacement is 4:1. For comparison: in the USA - 420 thousand operations, in Germany - 200 thousand [16].
Currently, more than 100 modifications of endoprostheses of the hip and knee joints are known, depending on the method of fastening there are cemented (fixed with bone cement), cementless (the bone of the joint grows into the surface of the endoprosthesis) and hybrid (the cup is attached without bone cement, and the leg with cement ) endoprostheses. Moreover, about 80% of cases account for cementless endoprosthetics, and 20% - for cemented and hybrid endoprosthetics. Cementless primary total arthroplasty is used at a younger age, since cemented arthroplasty has a shorter period of effectiveness. Modern combinations of endoprostheses are made of metal, plastic and ceramics. Currently, minimally invasive surgeries for hip and knee replacement are used. The issues of surgical technology, hospital equipment, and financing of hip and knee replacement programs have largely been resolved. However, total endoprosthetics does not completely solve many problems associated with diseases of the musculoskeletal system, since patients continue to experience pain and decrease muscle strength; despite the increase in the range of motion in the joints, some patients move with support; the biomechanics of walking remains impaired, and the indicators of statodynamic function do not achieve the desired result.
The implementation of rehabilitation measures in full after endoprosthetics of large joints in specialized centers is an important and mandatory part of the postoperative management of patients [3, 17].
Rehabilitation treatment is based on the principles of continuity, phasing, continuity and complexity. The technology of patient management involves the participation in the rehabilitation process of doctors of various specialties: neurologist, traumatologist-orthopedist, therapist, physical therapy doctor, physiotherapist, chiropractor, reflexologist, etc. This approach allows for rehabilitation measures to be carried out using pathogenetically based methods, taking into account the rehabilitation potential the patient and his further prognosis for recovery. An individual rehabilitation program is drawn up for each patient.
In patients who have undergone endoprosthetics of lower limb joints, early postoperative (up to 1.5 months after surgery), intermediate (from 1.5 to 3.5 months after surgery) and late rehabilitation or adaptation (from 3.5 to 10 months) are distinguished. after surgery), periods (stages). At the first and second stages, repeated rehabilitation courses are conducted in specialized centers. The third stage of rehabilitation includes treatment of patients in an outpatient clinic system or a sanatorium-resort institution.
The goals of rehabilitation of patients who have undergone hip and knee replacement, from the perspective of the International Classification of Functioning, Disability and Health (ICF; 2001) are:
1) restoration of the function of the operated joint (at the level of damage according to the ICF);
2) improving the ability to move and self-care (at the ICF activity level);
3) increased social and professional activity, improved quality of life (at the level of participation according to the ICF).
The technology of rehabilitation measures includes drug therapy, motor regimen, dosed walking, physical exercise, adherence to the correct load on the limbs, massage, physiotherapeutic procedures, acupuncture, classes with an occupational therapist and psychologist.
The risk of postoperative complications ranges from 4.8 to 10% [18]. Complications arise mainly from the cardiovascular and respiratory systems, and the gastrointestinal tract. During this period, measures to activate peripheral circulation and prevent postoperative blood loss become especially important. The high morbidity of surgical intervention is accompanied by the risk of blood loss, which amounts to 2.4% after primary arthroplasty of large joints [19]. Disturbances in the hemostasis system in the postoperative period are corrected with antifibrinolytic drugs. In case of total arthroplasty, the use of plasma argon coagulation is relevant, which significantly reduces intraoperative and postoperative blood loss [20].
In the early postoperative period, issues of preventing postoperative complications, preventing trophic disorders, bedsores, and reducing soft tissue swelling are resolved, since during this period the postoperative wound heals and sutures are removed [21].
No less important in lower limb arthroplasty are measures to prevent deep venous thrombosis; lethal outcomes with this pathology are up to 5% [22]. Deep vein thrombosis of the lower extremities and the development of pulmonary embolism are among the most serious complications after surgery in orthopedics, especially after endoprosthetics.
The development of thromboembolism is facilitated by hypercoagulation, venous congestion, bed rest for more than 4 days, prolonged immobilization, and surgical interventions. Since most patients have a complicated somatic history, the main methods of preventing venous thromboembolic complications are used: a comprehensive examination, drug preparation of the patient, mechanical methods. For drug therapy, direct (heparin) anticoagulants and thrombin inhibitors, indirect oral anticoagulants, and drugs that improve the rheological properties of blood are used. Non-pharmacological methods of prevention include the use of compression stockings [22].
In the early postoperative period, kinesiotherapy methods include training in sitting down (no more than 30 minutes on a small pillow), sitting, moving with the help of crutches without load on the operated leg up to 100 m along the corridor, isometric gymnastics lying on the back, stomach, healthy side to strengthen the abductors and stretching of the adductor muscles of the thigh (exercises are performed with aids), manual massage of the leg, gluteal region, passive mechanotherapy using devices. To avoid dislocation of the head of the endoprosthesis due to muscle weakness due to surgical trauma, exercises related to internal rotation and adduction of the lower limb are contraindicated; full axial load is not assigned to the operated leg. In this way, restoration of muscle tone and range of motion in the joint is achieved, and a gradual transition to full support on the operated limb occurs in the intermediate recovery period.
When implanting an endoprosthesis with bone cement, the operated limb can be loaded from the first days, and by the end of the 1st month, full axial load is possible. For cementless implantation of an endoprosthesis, walking with support from crutches is prescribed from the 5-7th day after surgery, with the load gradually increasing to 50% of body weight by the end of the 3-4th week. Full load with this type of endoprosthetics is achieved by the end of the 3rd month.
In the early postoperative and intermediate periods, the influence of physical factors is used to obtain analgesic, anti-inflammatory, anti-edematous, absorbable and reparative effects. To prevent suppuration, the area of the postoperative scar and surrounding skin is exposed to ultraviolet irradiation using the ORKSH and BOP-4 devices, a course of 8-10 procedures [23]. To stimulate healing, improve reparative processes, relieve tissue swelling and reduce pain, the Polus, Cascade and Gradient devices are used in the mode of generating an alternating magnetic field and a pulsating magnetic field with a frequency of 50 Hz, magnetic induction up to 40-50 mT. For low-frequency therapy with a traveling and rotating magnetic field, Alimp, Almag and Polimag devices are used with a frequency of 10-100 Hz, magnetic induction up to 30 mT. To improve microcirculation and metabolism in the operated limb, pulse barotherapy and pneumocompression of the limbs are used (BTL-6000, Body-Drain, Extremiter devices) [24].
In the intermediate period of rehabilitation, functional multichannel muscle stimulation is added during walking with impact on the gluteus maximus and medius muscles on both sides, the quadriceps and biceps femoris muscles on the operated limb.
At the second stage of rehabilitation, hardware methods of pneumocompression and lymphatic drainage are used; the use of Pulsar, BTL-6000, Body Drain, PM-1, etc. devices has a low level of complications and is an important condition in the prevention of thromboembolic complications. The essence of the method of hardware pneumocompression is a mechanical effect on the lymphatic and venous systems of the body using compressed air supplied to special cuffs that are worn on the hips and waist. This method of exposure is used only on a healthy limb or on both limbs for 10 minutes under a pressure of 60-120 atm. Thus, intermittent pneumatic compression complements anticoagulant therapy in patients after lower extremity joint replacement as an accessible, safe and effective treatment method [25–27].
In the intermediate and late recovery periods (from 8 to 12 weeks after surgery), the stabilotraining method is used using stabilometric platforms with biofeedback, which makes it possible to train the uniform distribution of the load on both lower extremities and improve statolocomotor functions [28].
During this period, the correct walking stereotype is developed with the help of additional means of support (crutches, canes). During therapeutic gymnastics classes, breathing exercises are introduced; exercises aimed at increasing range of motion; uses isometric tension on the muscles surrounding the involved joint; swinging movements of the arms and straight legs. It is recommended to perform exercises to transfer body weight to the operated leg in order to restore the strength of its muscles, exercises for all joints of the legs to overcome the weight of the limb, and train the quadriceps femoris muscle [29].
Thus, the total recovery period ranges from 1.5 to 12 months for hip replacement and up to 6 months for knee replacement.
The main task of the late rehabilitation period is to restore support function. The motor mode is expanded, movements with additional aids (cane), and exercises to transfer body weight to the operated limb are included. Together with occupational therapists, classes are held to teach self-care skills and adaptation to everyday life.
During this rehabilitation period, physiotherapeutic methods include low-frequency magnetic therapy using Alimp, Almag and Polimag devices with a frequency of 10-100 Hz, magnetic induction up to 30 mT. The combined use of laser radiation and an alternating magnetic field is widely used (Mustang, Matrix, Polyus-101, ELBI, Gradient devices), which allows for a pronounced vasoactive effect, as a result of which blood circulation in ischemic tissues, metabolic and trophic processes in the affected area are enhanced. When using the method of electrical neurostimulation (Amplipulse, Ionoson, FMNS, Duo-400 devices), the receptor apparatus and sensitive afferent conductors are exposed to low-frequency electric currents of varying amplitude and duration of exposure, which promotes analgesic and anti-inflammatory effects, in addition, reserve functional elements are mobilized tissues, impaired functions are restored. Under the influence of darsonvalization (Iskra-1 device), anti-inflammatory, anti-edematous and antispasmodic effects are noted, and the processes of regeneration of damaged tissues are stimulated. After 6-8 weeks, four-chamber therapeutic baths and dry carbon dioxide baths (Reabox) are prescribed. Cryotherapy using the Kriotur-600 apparatus to influence the muscles adjacent to the joint area, ozokerite and mud therapy, balneotherapy, underwater shower massage, and swimming are widely used [30].
During all periods of rehabilitation treatment, corporal and auricular reflexology is used. For pain, sedation is used. When developing locomotor functions, superficial acupuncture, cauterization of local painful points, and acupressure are indicated.
Psychological support for patients after lower limb joint replacement is to maintain compliance and sustainable motivation for recovery. Psychocorrectional methods are widely used, such as psychotherapy, including cognitive-behavioral therapy, auto-training, relaxation and breathing control techniques, work with thoughts, as well as assessment of severity using scales. For psychocorrection of pain syndrome, rational psychotherapy, conscious meditation and existential techniques (the meaning of pain) are used. The combination of these methods makes it possible to fully correct higher mental functions, anxiety and depression, and social skills, which makes it possible to achieve maximum adaptation of patients in everyday life.
To analyze the effectiveness of rehabilitation of patients who have undergone endoprosthetics of large joints, a visual analogue scale is used, the strength of the muscles of the lower extremities is assessed (6-point system), the severity of the function of the affected joint and mobility are determined (6-minute walk test, ICF), stabilometry is used to determine balance .
According to the order of the Ministry of Health of the Russian Federation dated December 29, 2012 No. 1705n “On the procedure for organizing medical rehabilitation,” restorative treatment of patients after joint replacement is carried out in three stages:
Stage 1 includes two periods:
— preoperative period — 2 weeks before surgery;
— postoperative period, consisting of one stage of medical rehabilitation in the trauma department; discharge from the hospital is carried out on the 5-8th day;
The 2nd stage is carried out in the early and late rehabilitation periods in stationary conditions of rehabilitation centers;
The 3rd stage is carried out in the early and late rehabilitation periods in outpatient clinics and sanatorium-resort conditions (see table).
Plan of rehabilitation measures depending on the terms of rehabilitation
Plan for carrying out rehabilitation measures depending on the terms of rehabilitation (end)
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Information about authors
Rud
Inessa Mikhailovna ,
general practitioner
; address: Russia, 105120, Moscow, st. Zemlyanoy Val, 53 [address: 53 Zemlyanoy Val str., 107120 Moscow, Russia];
ORCID:
https://orcid.org/0000-0003-3999-8210;
eLibrary SPIN:
4493-1609;
e-mail:
Melnikova Ekaterina Aleksandrovna,
Doctor of Medical Sciences
[Ekaterina A. Melnikova,
MD, PhD];
address: Russia, 105120, Moscow, st. Zemlyanoy Val, 53 [address: 53 Zemlyanoy Val str., 107120 Moscow, Russia]; ORCID:
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-7498-1871;
eLibrary SPIN:
8558-0908;
e-mail:
Rasulova Marina Anatolyevna,
Doctor of Medical Sciences, Professor [
Marina A. Rassulova,
MD, PhD, Professor];
address: Russia, 105120, Moscow, st. Zemlyanoy Val, 53 [address: 53 Zemlyanoy Val str., 107120 Moscow, Russia]; ORCID:
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-9566-9799;
eLibrary SPIN:
9763-9952
Razumov
Alexander Nikolaevich
, Doctor of Medical Sciences, Professor, Academician of the Russian Academy of Sciences
; address: Russia, 105120, Moscow, st. Zemlyanoy Val, 53 [address: 53 Zemlyanoy Val str., 107120 Moscow, Russia];
ORCID:
https://orcid.org/0000-0001-8549-0106;
eLibrary SPIN:
8793-5173
Gorelikov Andrey Evgenievich,
orthopedic traumatologist
; address: Russia, 105120, Moscow, st. Zemlyanoy Val, 53 [address: 53 Zemlyanoy Val str., 107120 Moscow, Russia];
ORCID:
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-9269-3726;
eLibrary SPIN:
6793-6987
Functional recovery period
The longest stage lasts 3 months. During this time, subject to all rules, the femur acquires a normal anatomical shape and structure. It is better to stay in a sanatorium at this stage of recovery. Sanatorium treatment includes restorative physical education, therapeutic baths, mud applications, and exercises in the pool.
Treatment with mud and healing waters helps:
- strengthen bones, improve muscle endurance;
- get rid of scar formations;
- improve the mobility of all joints, blood circulation;
- eliminate swelling of soft tissues, pain;
- normalize the functioning of the nervous and immune systems, sleep, and mood.
At this stage, exercise equipment can be added to exercise therapy. On an exercise bike, lower the pedals so that your leg is completely straightened when moving. Pedal backwards or forwards for 15 minutes, 2 times a day. Gradually increase the time to half an hour, and the number of workouts to 3-4 per week. Walking backwards on a treadmill. Start at a speed of 1-2 km/h. Be sure to fully straighten your legs.
Is it possible to carry out rehabilitation at home?
Rehabilitation after hip replacement at home is possible. But provided that there is a specialist in the family who has the necessary knowledge.
Benefits of home rehabilitation:
- you can study at a convenient time;
- classes in a familiar, comfortable environment;
- You can combine rehabilitation with work from home.
To avoid falls, you need to conveniently lay out all the necessary things so that you do not have to reach, secure or remove carpets. The house should have good lighting. Install special handrails in the bathtub. Despite all the advantages, rehabilitation should be carried out by specialists.
Nutrition rules
Within 6 weeks after the operation, the process of fusion of the head of the prosthesis with the pelvic bone occurs. The success of this process largely depends on proper nutrition. If the diet is not followed, the risk of dislocation of the head of the prosthesis, constipation, and enterocolitis increases.
Why is a diet prescribed after surgery?
- To normalize the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract. After application of anesthesia, temporary intestinal atony develops. You can only eat semi-liquid, pureed foods. These can be soups in vegetable broth with chopped dietary meat, slimy porridges. It is forbidden to consume any fast carbohydrates, fatty, fried, spicy foods.
- To compensate for blood loss. To restore the volume of circulating blood immediately after the end of anesthesia, you must regularly drink water in small sips. During the week you need to drink more, limit the daily amount of salt. To restore hemoglobin, consume foods high in iron, ascorbic acid, and vitamin B
- Strengthen the body's protective functions. Consume more fermented milk products to improve intestinal microflora.
- Accelerate the process of bone tissue restoration. The menu should include protein products.
Proper nutrition must be maintained even after rehabilitation is completed. This will help avoid excess weight gain and increased stress on the joint. Therefore, the basis of the diet is proteins, slow carbohydrates, and healthy fats.
Diet during rehabilitation:
- Proteins are necessary for the body to build its own proteins, collagen fibers of bone tissue. Sources of healthy animal protein include dietary meat and fatty fish. You definitely need to eat jelly and jellied meat - these dishes contain gelatin, which is a protein in its pure form. Plant sources of protein include soy, peas, beans, lentils, buckwheat and oatmeal.
- Complex carbohydrates. After endoprosthetics, you must give up sweets, pastries, white bread, and pasta. The menu includes foods with healthy carbohydrates - vegetables, grains, which contain few calories, but are rich in fiber and vitamins.
- Unsaturated fatty acids. After endoprosthetics, it is useful to consume foods with Omega-3 acids, which are found in fatty fish, crab meat, shrimp and red caviar. Unsaturated acids reduce the manifestations of the inflammatory process, cleanse blood vessels of harmful cholesterol, prevent the development of obesity, and accelerate wound healing.
- Bran as a source of fiber and vitamins. There is also a lot of fiber in flax seeds, dried mushrooms, and dried fruits.
- Calcium and vitamin D are essential to reduce the risk of osteoporosis and lysis. After endoprosthetics, it is necessary to consume 1-1.2 thousand mg of calcium per day. Sources: cheese, fish, sesame, almonds, herbs, garlic, hazelnuts. Calcitriol is required for normal calcium absorption. Vitamin D is found in cod liver, mushrooms, and egg yolk.
- Iron-rich foods. Chicken, shrimp, tuna, beets, pumpkin, nuts, buckwheat porridge.
Possible risks of surgery
Thanks to the professionalism of doctors, modern techniques and equipment, most patients with endoprostheses do not feel pain, live a full life and are no different from other people.
But still, 2–8% of operated patients experience complications.
These include:
- Feeling of numbness, pain and swelling; — Infection and development of inflammation; — Loosening, displacement, dislocation of the endoprosthesis; — Postoperative contracture; — Different lengths of limbs; - Pelvic distortion; - Lower back pain; - Gait disturbance; — Fracture in the area of the endoprosthesis; — Damage to nerves (sciatic, femoral); - Massive blood loss; — Allergic reaction to an artificial joint.
Many complications are associated with muscle weakness, lack of adequate motor load on the joint, deterioration of blood supply and lymph drainage in the surrounding tissues. The patient can avoid them with the help of specially selected exercises and other methods.
There are factors that shorten the service life of the endoprosthesis:
– the patient is overweight; - diabetes; – taking glucocorticoids; – smoking; – alcohol abuse; – systemic osteoporosis; – excessive physical activity.
The patient must adjust his lifestyle so that the operation is truly justified - give up bad habits and monitor his health. Otherwise, revision (repeated) endoprosthetics surgery may be required.
The patient must also be in good physical shape. For example, after a hip or knee replacement, he will have to walk for a while on crutches, then with a cane. This requires strong arm muscles, good balance and dexterity.
Weak muscles are not able to properly support the endoprosthesis. As a result, under load and movement, it can become loose and shift. Therefore, the patient should start training before surgery:
– do special exercises to strengthen the muscles of the limb in which the joint will be replaced; – learn to walk using additional means of support if there is a joint replacement of the lower limb; – prepare your home (make handrails and steps in the bathroom for safety, install a nozzle on the toilet).
Complaining about pain in a joint is not always a reason to change it. Often a good therapeutic effect can be achieved using conservative methods.
At the Quality of Life clinic we use a comprehensive approach to treating joints. He has helped many patients regain the joy of movement without surgery. And if surgery cannot be avoided, rehabilitation in the clinic will help you recover after it.
Possible complications
In the absence of proper rehabilitation after hip replacement, negative consequences develop:
- decreased tone of injured muscles;
- formation of scars at incision sites;
- dislocation of the head of the prosthesis, inflammation of the nerve endings, fracture of the bone structures near the prosthesis.
Complications can also occur after surgery:
- bleeding in the area of suturing;
- displacement, rejection, destruction of the prosthesis;
- wound infection;
- limb asymmetry;
- pulmonary embolism;
- After the intervention, the pain does not go away for a long time.
Endoprosthetics are prescribed for hip fractures, coxarthrosis, osteonecrosis, and rheumatoid arthritis. Previously, these pathologies made a person disabled. But now, with proper treatment and compliance with rehabilitation rules, it is possible to completely restore the function and mobility of the joints.