A highly effective operation eliminates disability and makes it possible to restore normal strength, rhythm, coordination, and stability of movements of the upper limb, which has been confirmed by numerous clinical studies. Thanks to shoulder arthroplasty, flexion and extension of the corresponding part of the musculoskeletal system, abduction and adduction, and internal and external rotation become available. Moreover, what is especially important, movements in all planes are carried out painlessly and in full.
X-ray after shoulder replacement
If previously a person had to endure a lot of work and suffering, for example, to put his hand behind his head or back, move it to the side, lift it up or hold even the lightest object, then after installing the endoprosthesis, you can really forget about all these difficulties. However, it is not enough to solely replace the joint; the patient needs to work hard on his recovery afterwards in order to definitely get an excellent positive effect from the surgical procedure.
Scar after reverse shoulder arthroplasty
The maximum return of motor potential is facilitated by rehabilitation after shoulder arthroplasty, which plays a role no less significant than the operation itself. Only after qualitatively going through the entire path of postoperative rehabilitation can a person count on a favorable prognosis - restoration of the functionality of the operated area by 95% -100%. Of course, provided that the prosthetics were performed without flaws - at the highest professional level.
As for the quality of the procedure itself, you will be provided with it if you are operated on in a good orthopedic clinic abroad, where the entire surgical process is worked out and refined to the smallest detail. Therefore, it is fundamentally important to ensure that endoprosthetics, which is ideal in every sense of the word, is not done in vain, and to continuously develop a new shoulder joint in accordance with all the rules and regulations. Postoperative treatment is carried out in stages according to a specially designed scheme, it takes at least 3 months.
Parting words for the patient: a must read
The restorative regime is observed regardless of whether total replacement of all working elements of the joint, partial, superficial or revision implantation was used. The generally accepted rehabilitation program after shoulder arthroplasty begins from the first day. With each passing day, week and month, by diligently following medical recommendations, you will notice significant changes in replenishing lost mobility functions. And all thanks to the fact that numerous muscles that control the endoprosthesis began to return to normal.
You must understand that the implanted device begins to operate after the muscle tissues of the arm are put in order, primarily those that “launch” the locomotor mechanism of a given joint, and there are quite a lot of them. The humeroscapular segment is formed by muscles such as:
- deltoid in the clavicular, acromial, spinous part - responsible for flexion, abduction and extension of the shoulder;
- latissimus and teres major – provide internal rotation;
- supraspinatus, infraspinatus, subscapularis – cause external rotation.
To improve the listed muscle groups that have undergone significant degeneration due to joint disease, you will need to perform a special set of physical therapy over periods and go to physiotherapeutic procedures. All activities must take place under the close supervision of a therapeutic exercises methodologist, rehabilitation specialist, physiotherapist and orthopedic doctor!
From a lying position, lift your arm behind your head using your healthy arm.
At the very beginning, exercise therapy exercises are prescribed as a passive type with assistance, that is, when you use your healthy hand to help the endoprosthetic limb perform one or another task. If it is difficult for you to do this, a specialist or your close relative will first take care of the correct execution of the required loads.
Movements of the hand in a tilt, first of small and then of greater amplitude.
Please also take into account the fact that shoulder replacement does not exclude postoperative complications. Consequences can develop at any of the rehabilitation stages; they manifest themselves mainly in the form of:
- local infectious abscess;
- instability (loosening) of the implant;
- paraprosthetic dislocation;
- pulmonary pneumonia;
- rigidity, contracture of the shoulder girdle;
- formation of blood clots in deep veins;
- chronic pain syndrome.
Negative reactions occur infrequently, as a rule, with an inadequately planned and applied system of treatment and rehabilitation measures, prolonged stay in a state of low mobility, as well as with forced physical activity. To prevent the above-mentioned unfavorable phenomena, even in the hospital after shoulder joint replacement, their competent prevention is ensured:
- administration of antibiotics, antiseptic treatment of the surgical wound against the activation of infection;
- therapy with antithrombosis drugs against the formation of blood clots in blood vessels;
- optimal immobilization of the limb using a bandage with a wedge-shaped pillow installed in the armpit, a bandage or an orthosis for the successful regeneration of soft structures and repair of bone tissue;
- prescription from the first hours of breathing exercises for pulmonary congestion and the development of pneumonia;
- the use of highly effective training strictly in stages that load the arm in doses and do not threaten the integrity of the artificial structure;
- the use of physiotherapy procedures that help improve the trophism of periarticular tissues, stimulate blood circulation, eliminate hematomas, relieve swelling and painful signs, get rid of muscle hypotonicity, etc.
The rehabilitation cycle is much easier than after joint prosthetics of the legs, since it does not involve such difficulties when walking, taking a sitting position, etc. But in any case, it is necessary to work on the replaced shoulder joint, its muscular-ligamentous system, because these are the functional zones are the first to be responsible for motor performance and stabilization of the upper limbs in general. And the hands, as you know, are the main organ of labor. Moreover, they play an important role in controlling the regulation of body balance in an upright position.
Be prepared for long and continuous work if you want your prosthetic arm to return to healthy performance. Believe me, there is no other way! Rehabilitation after such a complex reconstructive surgery as shoulder replacement is extremely necessary. It is of utmost importance to follow the schedule of physical activity recommended by your doctor, while remembering the principle of consistency and gradualness. And if you notice any abnormalities that are not normal (increased pain, thickening and redness of the skin on the shoulder, increased temperature, etc.), immediately notify the doctor about it!
Early recovery phase
Starting from the first day and until approximately the end of the second week, physical rehabilitation of the renewed shoulder joint after endoprosthetics is facilitated. This means that at least during this period of time a very careful and gentle development of the hand is carried out, since the bones, tendons, ligaments, and muscles are still in the process of initial regeneration. First, as mentioned earlier, you will need to help perform certain movements with the operated limb using the opposite hand. The bulk of the classes involve performing simple movements with the forearm, wrist, and fingers.
Squeezing a ball or any suitable object with a brush.
At about 3-4 days, passive mechanotherapy starts. Classes are conducted on a specialized automatic simulator in which the problematic limb is fixed. Charging occurs according to a given program, established taking into account the permissible range of motion in the glenohumeral joint, the prescribed tempo and load time. The training device allows you to use built-in programs for abduction/adduction, internal and external rotation. It also has a built-in deep oscillation feature. This method consists of local impact on injured areas with electrostatic impulses, which promotes:
- deep trophostimulation;
- activation of tissue metabolism and blood supply;
- pain relief and elimination of swelling;
- increasing the elasticity of ligamentous-muscular structures;
- improving mobility of the problem area.
It is worth noting that this is not the only physiotherapeutic tactic that has a similar therapeutic effect. The patient is also prescribed to attend electromyostimulation procedures, laser therapy, UHF or other methods of physical treatment, which have approximately the same effect.
Scar after superficial surgery.
Early rehabilitation, shoulder arthroplasty always causes pain in the postoperative period; after a noticeable reduction in pain, it includes simple stretching exercises. As a rule, they are performed on a special system equipped with a suspension cable. Therapeutic stretching in the initial period must be performed exclusively under the supervision of a physical therapy trainer.
Indications for shoulder arthroplasty
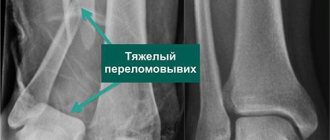
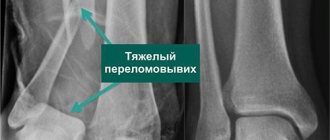
Surgery to replace the shoulder joint with a prosthesis is necessary if it is destroyed. Most often this occurs due to injury (for example, falls from a height) or diseases: arthrosis, arthritis, polyarthritis, osteonecrosis and others. Less common are benign or malignant tumors of the bones or soft tissues around the joint, as well as congenital articular dysplasia. Sometimes doctors have to perform surgery due to improperly healed fractures or necrosis.
In all these cases, the mobility of the shoulder joint is impaired. You cannot move your arm normally without pain and discomfort, carry heavy objects or play sports - this limits you physically. There is a high probability that the doctor will prescribe endoprosthetics for you, since drug treatment is ineffective here.
Late stage of recovery
Depending on the patient’s condition, after a two- or three-week period, they proceed to the implementation of a late recovery program, which is based on more intensive exercises. At the previous stage, you have already achieved partial correction of the functions of your hand and prepared it for productive training. Training in the basic techniques of active development of the shoulder joint is recommended if, we repeat, prosthetics were performed 2-3 weeks ago.
Stand sideways to the wall and move your arm to the side.
You will be offered a set of active physical exercises, performed at first with a small load, but it will gradually need to be increased. All movements should be smooth and slow. Auxiliary training equipment includes an elastic expander band, a gymnastic stick, a horizontal bar, weighting equipment and other sports rehabilitation devices.
Stand with your back to the wall and press your elbow into the wall. Repeat 5-10 times.
Wearing a shoulder brace or fixing bandage is completely canceled after 3-4 weeks. Courses of traditional shoulder and shoulder girdle massage, hydromassage, aqua gymnastics are also prescribed, and swimming in the pool is additionally recommended.
Under no circumstances should you prescribe any type of training for yourself at any stage without first consulting with a competent specialist and without receiving detailed recommendations from him on how to perform them. Unreasonable movements and an illiterate approach almost always become the cause of premature failure of the endoprosthesis, in particular its dislocation and subluxation. Then you will have to stop rehabilitation early, and most likely undergo shoulder replacement surgery again.
Working with an expander.
The late rehabilitation stage, if counted from the day of implantation, ends after 12-13 weeks. It is during these periods that the final firm fixation of the prosthesis and full motor capabilities of the upper limb are achieved in accordance with physiological standards. However, in the future it is recommended to continue to engage in exercise therapy at least 3 times a week in order to prevent weakening of the musculoskeletal corset. Caution, unhurriedness, softness and smoothness of movements in the shoulder during sports activities are the basic requirements that remain unchanged throughout life.
results
No complications were observed in the subjects during or after the operation.
All subjects completed the one-year prospective study on time.
At the first stage of the prospective study, conducted 2.5 months after surgery, subjects from group B had statistically significant higher scores on the VAS scale (7.5 ± 0.1) (P < 0.01), FF (133 ± 21.1) (P < 0.01) , ABD (66.7 ± 14.5) (error < 0.05), ER2 (63.5 ± 15.4) (P < 0.05) than in subjects from the group, A on the VAS scale (9.1 ± 0.2), FF (120.7 ± 20.6), ABD ( 60.1 ± 14), ER2 (56 ± 14).
After 6 months, a prospective study gave the following results: in patients from group B, FF scores were still significantly different (158.1 ± 9.4) (P < 0.01), ABD (86.9 ± 5.3) (P < 0.01), ER2 (83 ± 7.7 ) (P < 0.05), while patients from group A had the following indicators: FF (151.7 ± 12.5), ABD (82.3 ± 7.6), ER2 (79.1 ± 7.4). There were no statistically significant differences in VAS scores between group B (0.5 ± 0.1) and group A (0.6 ± 0.1) (P > 0.05).
At the third stage of the prospective study (after 12 months), no statistically significant differences in parameters were detected in both groups. In group B, the VAS scale scores are as follows: (0.2 ± 0.1) (P > 0.05), FF (165.2 ± (P > 0.05), ABD (90 ± 2.5) (P > 0.05), ER2 (86 ± 4) (P > 0.05), while in group A the values on the VAS scale are as follows: (0.2 ± 0.2), FF (158 ± 10.1), ABD (88 ± 1.8), ER2 (85 ± 4.2).
In group B, the VAS scale scores are as follows: (0.2 ± 0.1) (P > 0.05), FF (165.2 ± (P > 0.05), ABD (90 ± 2.5) (P > 0.05), ER2 (86 ± 4) (P > 0.05), while in group A the values on the VAS scale are as follows: (0.2 ± 0.2), FF (158 ± 10.1), ABD (88 ± 1.8), ER2 (85 ± 4.2).
Figures 1, 2 and 3 show a summary of the results of range of motion restoration in both groups of patients.
Rice. 1 — Results on the degree of arm abduction in group A (ABD) and in group B (ABD + PPM) at 2.5 months, 6 and 12 months.
Rice. 2 — Results on the degree of forward flexion of the arm in group A (FFL) and in group B (FFL + PPM) at 2.5, 6 and 12 months.
Rice. 3 — results on the degree of excess rotation during arm abduction in group A (ER2) and in group B (ER2 + PPM) at 2.5, 6 and 12 months.
Key recommendations after recovery
It is unacceptable to overload the artificial joint with prolonged loads, perform intense swings and rotations, make sharp and strong pushing movements with the hand, lift and carry heavy objects, especially on the shoulder. You also need to learn to anticipate and avoid traumatic situations. If we talk about sports training that is safe and even useful, you should prefer the following sports:
- swimming;
- Nordic walking;
- calm running;
- cycling with moderate load.
The next serious point that concerns everyone who has an implant instead of their original shoulder joint: if you have any infectious disease (colds, caries, pyelonephritis, etc.), immediately contact a doctor of the appropriate specialization! Be sure to inform that you have undergone shoulder replacement surgery in the past, and you will be given emergency antibiotic therapy (use or injections of an antibiotic). Why does the patient need immediate help?
- Any pathogenic microflora that has developed in a particular organ can quickly move along with the blood flow to the periarticular areas where the implant is placed.
- Infection of nearby structures with bacteria, infections, viral antigens causes a purulent-inflammatory focus localized, as you might guess, in a completely inappropriate place.
- If adequate measures are not taken in a timely manner to eliminate the pathogenesis, the strength of the prosthesis will be impaired, the device will become loose and will no longer be able to function normally.
- Such a complication is too difficult to treat and often cannot be treated at all, which makes it necessary to remove the implant. The next replacement is possible only after thorough eradication of the pathogen and excellent regeneration of damaged tissues.
The patient must also come to the attending physician for routine examinations every 5 weeks for six months. Then, visits to the hospital for the purpose of a medical examination, hardware and instrumental diagnostics of the operated shoulder and laboratory tests are scheduled once a year.
- Hardware methods in the long term are intended to monitor the correct position, seating depth, and integrity of the prosthetic structure. They are based on the use of radiography methods.
- Using special protractors, palpation and movement testing, motor potential is periodically assessed in all physiological directions of the area under study.
- The purpose of laboratory research is primarily to determine the indicators of calcium-phosphorus metabolism in the human body in order to have a reliable idea of the condition of the bones and the quality of bone tissue mineralization processes. As is known, the endoprosthesis is immersed precisely in the articular bones, and even the slightest destruction, deformation, or cracks create a critical situation associated with loosening and destabilization of the components of the analogue joint.
If signs of osteoporosis are detected, medications that improve the density of bone structures are prescribed, as well as constant maintenance (preventive) therapy, carried out in courses at certain intervals. The biological materials tested for determining osteoporosis are blood and urine. It is possible to perform X-ray densitometry.
The earlier signs of osteoporosis are detected, the greater the chance of surviving a normal number of years with the new joint. So don't skip essential doctor visits and important annual tests.
For which injuries is arthroscopy performed?
Injuries for which arthroscopy is performed are listed below:
- Closed joint injuries;
- Rotator cuff injury;
- Avulsion of the labrum;
- Chronic shoulder dislocations;
- A blow, bruise to the shoulder joint, etc., after which movement in the joint is disrupted or becomes completely impossible;
- Suspicion of damage to the ligaments and tendons of the joint.
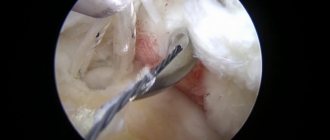
The above and other injuries and damage to the shoulder joint are indications for arthroscopy . Arthroscopy in this case allows you to establish the exact location of the injury, determine its significance and significance, and also take the necessary treatment measures that will be aimed at restoring the function of the joint.