To make an appointment with a doctor
Calling a pediatrician to your home
Our doctors
Our prices
February 11, 2021
Author of the article: Bogatov Viktor Borisovich
Highest qualification category. Doctor of Medical Sciences, Professor of the Department of Traumatology and Orthopedics, First Moscow Medical University. I.M. Sechenov.
Experience: 21 years
+ Make an appointment
A dislocated elbow joint often causes fear in children and a panic attack in parents. An unpleasant hand injury does not threaten the baby’s life, but requires surgical treatment under the supervision of a traumatologist, rheumatologist or surgeon. Let's figure out what you should know about injuries to the elbow capsules and the accompanying therapy.
Possible causes of injury
The main cause of elbow dislocation in a child is a closed injury of the upper limb. In most situations, it is provoked by an unsuccessful fall of the baby onto an outstretched arm. This is explained by the unstable coordination of human movements at the age of 2-5 years. Children who attend physical education clubs are at risk. Using sports equipment at a young age can result in sprains, dislocations or fractures.
The reason for the violation of the integrity of the tissues in the ulnar bursa may be excessive tension of the ligaments as a result of their overstrain. As an example, consider a child attempting to lift an excessively heavy object. Children experience similar hand overloads from the actions of parents who pull tired or capricious sons and daughters along with them.
The most dangerous cause of injury remains road accidents, which result in open injuries to the upper extremities of injured pedestrians, drivers and vehicle passengers. In this case, dislocation of the elbow joint in children requires immediate treatment.
Kinds
To choose treatment tactics, it is important to correctly classify the pathology. First of all, the doctor distinguishes between open and closed dislocations. In the first case, the injury occurs when struck by a bent elbow, and in the second case, when falling on an outstretched arm.
The severity is influenced by the area where the injury occurred. The joint is completely displaced if the blow is targeted to the elbow. Partial displacement or subluxation occurs when there is an indirect blow to the elbow area.
Depending on which direction the elbow is bent, the dislocation is divided into:
- rear. The radial head can be felt because the joint is flexed 140° in the opposite direction. This type is often diagnosed due to the immature strength of the child’s bones;
- front. The heads of the radius and ulna are displaced, and the elbow itself flexes anatomically correctly;
- side. Bone protrusions are exposed and ligaments are torn. More difficult to tolerate.
Symptoms of dislocation
Damage to the joint capsules occurs due to the low strength of the bones of a growing child’s body. The most common type of injury to the upper extremities at the age of 2-7 years is a pulling dislocation of the radius.
Signs of a dislocated elbow joint in a child are typical:
- swelling occurs at the site of injury, quickly spreading to adjacent tissues;
- the patient’s body temperature rises and chills begin;
- pain syndrome occurs, which intensifies with hand movements or palpation;
- The sensitivity of the fingers of the upper limb decreases (with increasing numbness).
Deformation of the joint capsule is clearly visible during visual examination of an injured patient. Complex injuries are often accompanied by a violation of the integrity of the blood vessels, which makes it impossible to feel the pulse on the child’s wrist.
Carrying out diagnostics for the disease
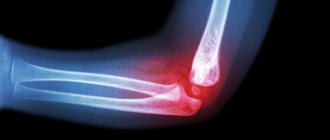
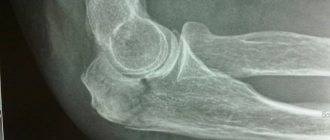
If a child experiences pain in the elbow area, parents should contact a medical facility where the child will be diagnosed and given first aid. Diagnosis of a dislocation in a child is carried out by palpation of the damaged area. After this, the little patient is sent for radiography. Thanks to the use of hardware examination, the degree and, in addition, the localization of joint injury are determined, that is, the diagnosis is clarified. Thus, treatment for a dislocation is prescribed only after a preliminary diagnosis is confirmed by a thorough examination.
Seeing a doctor
The baby’s parents will not be able to cure damage to the joint capsule on their own. If children detect symptoms of a dislocated elbow joint, adults should seek qualified help by taking the injured person to the hospital or inviting an emergency medical team to your home (if there are associated injuries).
Until doctors arrive, parents should ensure that the child's injured limb is immobilized. It is acceptable to apply a cold compress (wet towel) or ice. Taking analgesics or using anesthetics is not recommended, since without diagnostic procedures it is impossible to determine the extent of damage and possible contraindications to certain groups of drugs.
In a clinical setting, treatment of dislocations is carried out by a traumatologist, rheumatologist or surgeon. Doctors carry out the necessary diagnostic measures, develop a treatment strategy and determine the period for which the injured limb will be immobilized.
The ambulance team of JSC "Medicine" (academician Roitberg's clinic) will deliver a small patient with a dislocation to the clinic for diagnostic and therapeutic measures. The team is on call 24 hours a day.
Rehabilitation of dislocations in children
The rehabilitation program for children with congenital hip dislocation is divided into 4 periods:
- The preparatory period involves the appointment of individual physical therapy sessions, which are general strengthening and help stabilize the hip joint;
- Postoperative period. After the operation, a plaster cast is applied to the leg, which covers the belt and healthy thigh. Three days after surgical treatment, physiotherapy is prescribed, the purpose of which is to eliminate pain and inflammation. At the same time, breathing and therapeutic exercises are carried out, which includes exercises that stimulate the cardiovascular system, increase the tone and reactivity of the body;
- The next period of rehabilitation begins from the moment the plaster cast is removed, instead of which a “boot” is applied to prevent the rotation of the limb. To unload the joint, a system of blocks with loads of different weights is installed. During this period, it is important to ensure that all movements are careful and smooth, so passive gymnastics is prescribed, after which they begin to develop their own movements in the hip joint;
- The final period begins 9-10 months after surgical treatment. It coincides with the removal of metal fasteners that were installed previously. Rehabilitation activities are aimed at learning to walk. First, additional means are used (walkers, canes, etc.) without support on the sore leg, then partial support is allowed and, at the end of rehabilitation, full support without the use of additional means.
Possible complications
The most common complication of injuries to the joint capsules of the upper extremities is fibrosis. Overgrowth of connective tissue occurs as a result of untimely treatment of a dislocation, a shortened period of immobilization, or significant damage to muscles and tendons.
A dislocation of the elbow joint, accompanied by symptoms of other arm injuries in a child, requires the fastest possible surgical intervention. Thus, an open fracture of the radius of the forearm in combination with damage to the articular tissues can provoke contracture. Restrictions in arm mobility after the child’s recovery can only be avoided if timely medical care is received.
Reduction of the elbow joint in our clinic
In our medical center, we not only treat dislocations, but also monitor the entire process of tissue fusion and develop rehabilitation measures to prevent complications. The rehabilitation program is compiled individually for each child, taking into account his mobility and the severity of the injury. Immediately after removing the plaster, to normalize blood circulation, the traumatologist refers you to physical therapy, offering several procedures to choose from. If negative consequences are identified, for example, nerve plexuses are damaged, then the clinic will provide a full range of services and a neurologist will join the treatment process.
Treatment of dislocations
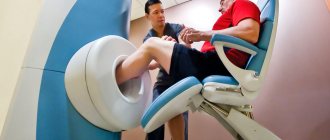
Diagnosis of damage is carried out by a traumatologist or rheumatologist using radiography, ultrasound, and computed tomography. If the child has no other injuries, the dislocation is reduced under general anesthesia: the joint is stretched, its head is directed into the articular cavity. A splint is applied to the injured arm; the immobilization period is 10–15 days. After removal of the fixing bandage, rehabilitation therapy begins for 3–4 weeks.
Complex dislocations accompanied by fractures require plaster immobilization of the injured limb. The child may require treatment from a neurologist (for nerve damage) or a surgeon (surgical intervention for ruptured tendons, arteries, blood vessels, muscles).
Our clinic provides a full range of diagnostic and treatment procedures for dislocations in children. The clinic is equipped with all the necessary equipment, and its own hospital allows patients to be placed in comfortable rooms for the period of therapy.
Congenital dislocations in children
This group includes dislocations that are the result of various congenital disorders. An example is dysplasia (underdevelopment) of the articular cavity of the femoral head. The most common congenital dislocations of the hip joint are detected, and less often - the knee joint and patella. You can notice a dislocation in a newborn child by the asymmetry of the folds on the inner surface of the thighs, a decrease in the amplitude of limb abduction, etc. If the child begins to walk, then with a dislocation, lameness, a specific “duck” gait, etc. may be observed. Attentive parents may notice different limb lengths. With congenital dislocation of the patella, pain, immobility of the knee joint, inflammatory manifestations, and hemarthrosis develop. The child has difficulty moving and often falls.
Treatment of congenital dislocation should be as early as possible. The best results can be obtained if specialized care begins before 3 months of age. Treatment can be carried out at a later date, but its effectiveness will be less. At the initial stages, conservative methods are used - reduction, splinting and plaster casts). If these measures are ineffective, as well as if the injury is long overdue, surgical treatment is used.
To prevent congenital dislocations, you must follow a few simple rules:
- It is mandatory to conduct an orthopedic examination of the newborn;
- Avoid tight swaddling;
- Do not put the child on his feet until he begins to stand;
- Do not forcefully straighten your legs.
Prevention of dislocations
Prevention of dislocations is based on the formation of a balanced menu for the child’s nutrition. A sufficient amount of minerals and vitamins in food will provide the baby’s joints and bones with sufficient strength to painlessly endure falls that are inevitable during childhood activities.
Parents should also take care of the physical development of their growing sons and daughters. Swimming, running, and playing with a ball help improve children's coordination and strengthen skeletal bones and muscle tissue. Moms and dads should remember that babies’ bodies cannot bear the same stress as adults.
Make an appointment
You can make an appointment with the children's specialists of JSC "Medicine" (clinic of Academician Roitberg) through the website. The interactive form allows you to select the general specialization of the doctor or the name and surname of a specific employee of the pediatric department.
The clinic covers all areas that can help in the treatment of dislocations: traumatology, surgery, neurology, pediatrics and others. Clinic administrators are ready to accept requests for appointments by telephone; calls are processed around the clock.
Research methods
For this, the following diagnostic methods are used:
- Carrying out radiography.
- Performing an ultrasound examination.
- Carrying out an arteriogram and electromyography.
- Performing heart rate monitoring.
The doctor may additionally refer this category of patients to a neurologist for examination. This specialist determines the degree of mobility of the injured arm.