A clavicle fracture is a change in the physiological structure of the bone. The patient, during or after a clavicle injury, experiences pain in the supraclavicular and infraclavicular areas, with disruption of the usual previously available active movements in the upper limb on the injured side. In addition, the person notices swelling and changes in the shape of the collarbone.
When examining a bone injury, a traumatologist or surgeon relies on the patient’s complaints, medical history, general examination, and the results of instrumental studies. X-ray examination has high diagnostic value. Depending on the type of fracture, the doctor will determine treatment tactics. For example, in case of a “green stick” type injury (in this case, the integrity of the periosteum is preserved), a soft fixing bandage must be applied to the child. If a clavicle fracture is accompanied by displacement of fragments, then the tactics change: reposition is used with further fixation using a plaster cast. Finally, if there is a possibility of damage to nearby nerve trunks or vascular structures, the patient needs immediate surgical treatment.
Therefore, if your collarbone hurts , you should definitely contact a traumatologist! The doctor will conduct a qualitative examination and determine the causes of pain.
Causes of clavicle fractures
Often, a clavicle fracture occurs at home, and if symptoms of a clavicle fracture , you should immediately consult a traumatologist. Clavicle injury can occur for the following reasons:
- Direct mechanical impact on the bone. Due to direct trauma (for example, a sharp or strong blow) to the collarbone area, sharp pain in the collarbone may occur - a characteristic symptom of its damage. Direct trauma causes oblique, transverse and comminuted fractures of the clavicle. Situations in which a direct injury to the collarbone occurs are completely varied: a fall of a heavy object, a collision with a protruding part of a structure at work, a fight with the use of bats or large metal objects.
- Indirect bone injury. A broken collarbone can result from a person falling on an outstretched arm, shoulder or elbow. This mechanism causes the formation of oblique and oblique-transverse fractures. Often, indirect injuries occur during difficult weather conditions (ice), as well as when a person is under the influence of drugs or alcohol.
In addition, sudden muscle contraction can be a rare cause of a clavicle fracture. Such situations are observed in patients with epilepsy: after a generalized convulsive attack, the patient notes pain under or above the collarbone, as well as symptoms of limited motor functions of the arm.
Causes of a crack in the collarbone in a newborn and an adult
One of the reasons for a fracture may be injury due to medical errors.
There are many reasons for the appearance of cracks, chips and fractures of the collarbone. As a rule, injuries are sustained as a result of mechanical impact under different life circumstances. It may also be a congenital defect due to a difficult pregnancy. As a rule, the causes of the pathological condition are:
- dislocations of the periosteum in a child in the womb;
- chronic calcium deficiency in the body;
- receiving birth injuries due to medical errors;
- hereditary or congenital predisposition to bone injury;
- consequences of physical impact (impact or fall) to the chest, ribs or shoulder;
- weakness or pathologies of the musculoskeletal system;
- injury to tissues and bones during sports training;
- car crashes;
- greater physical activity on the upper body.
A clavicle fracture in a newborn during childbirth is diagnosed extremely rarely, but such situations exist.
Symptoms of a clavicle fracture
A closed clavicle fracture is accompanied by the following characteristic symptoms:
- intense pain in the bone, while the intensity of pain in the collarbone area does not decrease when taking any position;
- limitation of available movements on the side of the bone injury, severe pain when performing previously habitual actions;
- the occurrence of swelling in the area of the shoulder girdle, its shortening;
- changing the standard shape of the collarbone;
- drooping of the shoulder, its displacement inward and slightly anteriorly.
Often, a doctor may suspect a clavicle fracture based on the patient’s characteristic posture. So, a person often holds a limb that has been injured with his healthy hand. The patient may also press the injured limb against the body, explaining this by reducing pain when using this position.
As a rule, in the first seconds of a collarbone injury, a person feels a sharp and severe pain in the supraclavicular or infraclavicular area. The pain syndrome intensifies when the limb hangs freely, which explains the forced position - pressing the injured limb to the body. The free position of the injured side leads to the fragments of the collarbone shifting in different directions, changing their position in the wound, causing the person additional discomfort. Thus, a person needs to make a minimum number of movements so as not to provoke displacement of bone fragments when the clavicle is fractured.
Over time, the body's physiological response to a clavicle fracture is observed. Edema, hyperemia (redness of the damaged area), hyperthermia (increased temperature in the damaged area) is formed. This is a typical inflammatory reaction of the body to trauma to the bone base and soft tissues. Then the pain syndrome increases and the dysfunction of the hand progresses. Above the area of the broken clavicle, a significant swelling is visually visible, corresponding to the area of displacement of the clavicle under the tension force of the sternocleidomastoid muscle.
During an objective examination, the doctor pays attention to the following symptoms of a clavicle fracture:
- the presence of areas of hemorrhage in the damaged area;
- the formation of pathological mobility in the supraclavicular or subclavian region, with any movement causing pain to the patient;
- crepitation (crunching) of bone fragments.
In addition, open fractures are accompanied by the formation of a wound from which some portion of the clavicle protrudes, depending on the area of the fracture. If a collarbone injury has led to a violation of the anatomical integrity of any neurovascular bundle located in the neck, then the patient complains of severe limb weakness, numbness, and crawling.
Often, dizziness and general weakness are added to the list of symptoms of a clavicle fracture, which can be explained by internal bleeding. In severe situations, shortness of breath and lack of air are added to the typical signs of a collarbone injury, which are caused by damage to the pleura covering the lungs by fragments of the collarbone. This leads to the formation of pneumothorax in a person, and is accompanied by symptoms characteristic of such a complication.
Signs of a clavicle fracture and its treatment
Fortunately, this problem is almost always detected in the maternity hospital, so it is important to immediately pay attention to the baby’s behavior and well-being. The baby, of course, will constantly cry and sleep poorly. Also, a new mother should be alarmed by the fact that her child hardly moves one arm, and there is a significant swelling or hematoma in the area of the collarbone. If you carefully touch this area, the baby will become restless and capricious. Moreover, under such circumstances, he will suck the breast poorly or refuse food altogether. If such symptoms occur, it is necessary to immediately inform the medical staff.
First of all, the injured limb is securely immobilized. This is done using a roller, which is placed under the armpit, a sterile bandage and a special elastic bandage. However, the fabric should not put too much pressure on the baby’s body, as this can seriously impair blood circulation. Therefore, if your fingers turn blue, you should ask your doctor to loosen the bandage. A newborn's bones grow together very quickly. After a week, the fracture heals, but you cannot stop bandaging, since the functionality of the hand must be fully restored.
If there are serious hematomas, a three-day course of Kanavit injections is prescribed, which are administered intravenously. You should also treat your baby’s collarbone with Traumeel C ointment, which consists exclusively of nutritious natural ingredients. This medication will not only stop bleeding, but also relieve swelling, have an analgesic effect and gradually reduce inflammation.
Rehabilitation plays an equally important role. The baby must undergo a course of magnetic therapy, electrophoresis and therapeutic massage. A new mother must learn how to properly place a sick baby to the breast, but under no circumstances stop feeding. The woman herself needs to consume more foods rich in phosphorus, calcium and other micronutrients.
What could be the consequences?
If the medical staff correctly provided care to the newborn, then unwanted complications are completely excluded. But if the baby’s body is too weakened, then an infection can enter the fracture, which provokes a severe inflammatory process. Of course, this rarely happens, but it is very important to carefully monitor the baby’s condition and not let him become hypothermic.
In addition, the formation of a so-called false joint cannot be ruled out if, in addition to the fracture, there was displacement or the bandages were constantly applied incorrectly. Severe pain occurs extremely rarely if the neurovascular bundle has been seriously damaged.
Complications
Like any disease, a bone injury can be complicated by many pathological conditions if treatment for a clavicle fracture is not started in time. Fortunately, complications from injury are quite rare because patients often seek medical attention immediately. However, possible complications due to poor-quality or untimely medical care cannot be excluded:
- Injury to a vascular or nerve formation. A displaced clavicle fracture can cause damage to a large vascular trunk or nerve formation, which leads to the formation of characteristic symptoms. In the case of damage to the nerve fiber, disturbances in the motor or sensory sphere in the injured area are observed as long-term consequences of the damage. The severity of neurological symptoms depends on the nature and extent of nerve damage, however, one should not forget about the likelihood of injury to nerve fibers. Damage to the vessel often leads to serious bleeding, especially if a sharp bone fragment has injured a large major vessel, resulting in serious blood loss.
- Damage to the pleura . A life-threatening condition for a person, pneumothorax, is formed when displacement during a clavicle fracture causes damage to the parietal pleura. Air enters the pleural cavity, which is accompanied by a characteristic clinical picture (shortness of breath, lack of air, lag of one of the halves of the chest when breathing). Pneumothorax requires prompt action by medical professionals and immediate treatment.
In most cases, fracture complications can be prevented thanks to competent and proper care for a clavicle fracture.
Causes of birth injuries to the collarbone in infants
Even after completing all the preparatory measures, unforeseen circumstances cannot be avoided. During childbirth, the body of a woman and baby experiences enormous stress - the nervous, cardiovascular and musculoskeletal systems take the brunt. The baby's bone tissue is not yet fully formed, which is why the child's bones and joints are quite flexible and fragile. There is no need to worry prematurely, since bone damage during childbirth goes away without a trace in the vast majority of cases.
Why does dislocation happen?
The shoulders are the widest part of the baby's body, and, for anatomical reasons, are inactive, which significantly increases the likelihood of displacement or fracture in this area during birth. Clavicle injuries (especially the right one due to fetal position) are the most common injuries.
Dislocation is the release of the head of the bone from the articular cavity under the influence of mechanical factors (pressure, stretching, sudden displacement). When the baby comes out, the obstetrician can help him by pulling his arm. Among the reasons, one can note congenital underdevelopment of the joints, which can also cause the clavicle bone to come out of the joint.
For what reasons is a fracture possible?
A fracture is primarily a mechanical damage to the collarbone that occurs due to a load that is not typical for this part of the body.
The causes and factors that increase the risk of a fracture are in many ways similar to the reasons for joint displacement in an infant:
- the impact of medical personnel on the position of the child (when presentation changes), the use of forceps, vacuum extraction,
- atypical presentation of the fetus (transverse, breech), in such positions children are often born with injuries,
- rapid labor process - the child does not have time to take the correct position, which leads to a fracture or other injuries,
- narrow and unprepared birth canal.
Diagnosis of a clavicle fracture
Diagnosis of a clavicle fracture with or without displacement is carried out by a traumatologist. As a rule, the doctor performs the entire list of diagnostic measures in the emergency department of a hospital or in a trauma center. The main methods that the doctor uses are as follows:
- Objective research data . The traumatologist conducts a thorough examination of the injury site. A clavicle injury is characterized by severe deformation of the area, severe swelling of the damaged area, and in some cases, especially with a displaced fracture of the clavicle, crepitus (crunching) of bone fragments is observed. During an objective examination, the doctor necessarily checks for the presence of neurological damage: determines the sensitivity of the hand on the side of the injury, the presence or absence of active movements. In addition, the doctor needs to evaluate possible complications. Thus, during the examination, the traumatologist determines the presence of symptoms of blood loss due to damage to large vascular bundles or difficulty breathing, shortness of breath as symptoms of the formation of pneumothorax.
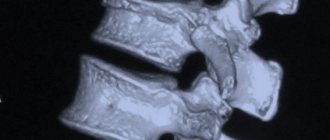
- X-ray diagnostics. X-ray is the standard examination method for suspected clavicle injury. With its help, the doctor determines the site of the fracture and the displacement of the collarbone. A clavicle fracture in a child is often accompanied by an angular injury. In this case, displacement of bone fragments occurs, however, the integrity of the periosteum is preserved. X-rays are traditionally performed in a direct projection, but in difficult cases, if the traumatologist is unable to determine the location of all fragments of the clavicle, the diagnosis is additionally carried out in a lateral projection.
- An additional research method, if X-ray diagnostics is insufficiently informative, is computed tomography . Three-dimensional reconstruction allows you to fully see the picture of the clavicle injury and determine the degree of displacement of bone fragments when the clavicle is fractured.
Finally, if the traumatologist suspects complications in the form of trauma to large neurovascular bundles, he refers the patient for consultation with a neurologist and vascular surgeon.
Typical symptoms of birth trauma
A collarbone injury is diagnosed immediately after childbirth, but sometimes the initial examination reveals nothing. According to some signs, it is determined over the next few hours or days:
- swelling and/or redness, hematoma in the clavicular area (we recommend reading: how is a hematoma on a child’s head that appears during childbirth treated?),
- pain when touching the injured area,
- decreased appetite, anxiety,
- limited limb mobility,
- crunching sound when you move your hand,
- uncharacteristic position of the shoulders relative to each other,
- hand hanging,
- incorrect head position.
To read: The correct regimen and consequences of discontinuing Metipred during pregnancy, indications for stopping use
Treatment
The therapeutic tactics chosen by the doctor depend on many parameters. the degree of clavicle fracture matters , whether the clavicle fracture occurred in a child or an adult, and whether there is displacement of bone fragments. In addition, when deciding on treatment tactics, the doctor also evaluates the presence of developed complications. If there is no threat of damage to large nerve or vascular formations, and a person has a well-reduced clavicle fracture, then the patient does not require long-term hospitalization.
If there is a high risk of complications or exacerbation of the clinical situation, then treatment of the collarbone must be carried out in the trauma department. According to statistics, in a significant number of cases, patients do not require surgical intervention; only ordinary therapeutic treatment is sufficient.
About childbirth and fracture
Often such damage occurs during rapid childbirth, when neither the female nor the child’s body has time to prepare for the process. Many expectant mothers dream of giving birth quickly, rather than suffering for days, but you should know that this can lead to additional complications.
In 90% of cases, a clavicle fracture is a consequence of inept actions of a gynecologist or obstetrician. When the baby's head has already come out, they begin to pull him by the shoulders, helping him to be born faster. Because of this additional physical impact, fractures occur.
Few people know that you can get such an injury during a caesarean section. If the doctor does not grasp the baby correctly when removing him from the uterine cavity, there is a possibility of breaking the integrity of the bone. Another common injury is a dislocated collarbone in an infant.
Regardless of the diagnosis, urgent treatment is required to avoid negative consequences during growing up.
Providing first aid for a fracture
At the first stage, you must definitely call an ambulance . Within a few minutes after a clavicle injury, active swelling begins to form in the damaged area, which subsequently creates difficulties in performing closed reposition of the fragments. The more time passes, the more likely it becomes that the patient will undergo open reduction. Treatment of a broken collarbone by a traumatologist consists of a surgical operation, during which special access to the site of injury is performed, and then comparison of bone fragments. Of course, if closed reduction is not possible, then the open method is used to treat the clavicle. However, when performing an open surgical operation, the risk of infectious agents, pathogenic microorganisms entering the wound, as well as the occurrence of purulent complications (abscess, phlegmon, secondary osteomyelitis) naturally increases. The ambulance transports the victim to the emergency department of the trauma hospital, and during the provision of first aid, medical workers will provide high-quality pain relief, as well as immobilization of the fracture site. Thus, the ambulance carries out primary actions aimed at reducing the likelihood of complications developing in the long term, as well as transporting the patient as carefully as possible. It is important to remember that a certain amount of time will pass before the ambulance arrives, which can be properly used to alleviate the patient’s condition.
The main rule that you need to remember when providing assistance with a fracture of the collarbone is that you cannot independently try to carry out medical procedures to eliminate the displacement of the collarbone by performing sudden movements or jerks. It is imperative to limit the mobility of the injured limb : due to sudden movements, secondary displacement of fragments or complications may occur. Competent first aid consists of immobilizing a limb (reducing its mobility by fixing it to the body) using a scarf. In this case, the arm must be fixed in a special way: press the humerus to the body, and only then bandage it using a scarf. However, there is a rule: if a person reports increased pain during shoulder adduction, then it is necessary to leave the injured limb in a position that provides minimal pain.
Immobilization is considered an important aspect when providing first aid. Primary immobilization before the arrival of the ambulance team will reduce the severity of pain in the patient, because the injured area will be firmly fixed and immobilized with a bandage. Secondly, immobilization will help to avoid the development of complications in the form of traumatization by bone fragments of vascular or nerve formations during transportation of the injured person to the emergency department of a trauma hospital. For immobilization, a scarf bandage is actively used on the arm, during which the limb is bent at the elbow joint and pressed against the body. It should be remembered that during long-term transportation of the patient to the hospital, the supporting function of the bandage weakens over time. Therefore, rewinding of the bandage may be necessary to maintain sufficient fixation force. Often, for immobilization, in addition to the scarf dressing, the following types of dressings are used:
- Velpo;
- Deso;
- 8-shaped bandage;
- Delbe rings.
We must not forget about painkillers . Pain from a broken collarbone is a strong irritant to which a person may have an unexpected reaction. This, in turn, can complicate the provision of first aid to the victim: he may resist and refuse any action. Besides. intense pain during the arrival of an ambulance will complicate the diagnosis of the condition and the collection of anamnesis, because the person will not be able to correctly and clearly answer the doctor’s questions. Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs are actively used as painkillers at home. Ketanov, Ibuprofen, Spazmalgon, Paracetamol are actively used. However, before using these medications, you need to be sure that the person is not allergic to one or more components of the drug. In addition, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs should be used very carefully in patients with gastric or duodenal ulcers. The drug will begin to act within 15-30 minutes when taken orally, 5-10 minutes after intramuscular administration. If the effect of the drug is not observed, you cannot increase the dosage or introduce a new dose of the drug, because there is a possibility of an overdose of the drug, which requires special assistance for intoxication.
If you do not have the opportunity to use painkillers to relieve pain, then you can use a proven and effective method - applying cold to the injured area. Cold has a local effect without affecting other tissues and systems of the human body. Additionally, applying cold is the only option if you don't know if the person has an allergic reaction to the pain medications available to you. The mechanism of action of cold is very simple: in the area of the collarbone fracture, a cold object reduces the temperature of the soft tissues, where many nerve endings are located. When the tissue reaches a temperature of 4-5 degrees, the intensity of the transmission of pain impulses in it decreases, which means that irritation does not enter the brain. Thus, there is a temporary reduction in the severity of pain in a person. However, a broken collarbone requires a special approach in applying cold. You should not apply a whole piece of ice to the damaged area, but crushed ice. The specificity is explained by the anatomical structure of the area: in the clavicle area there is a supraclavicular and subclavian fossa, which forms an uneven relief. Crushed ice will work much better on the damaged area than a single piece of ice. In addition, you need to apply ice exclusively over the fracture site: if you move the ice pack to the neck area, the body may react in the form of a sharp drop in blood pressure and heart rate. The fact is that in the neck area there is a sinocarotid nerve plexus, and careless influence on this formation can lead to serious consequences.
Birth trauma of newborns
Birth injuries of soft tissues
The most common manifestations of birth trauma in newborns are damage to the skin and subcutaneous tissue.
These include scratches, abrasions, petechiae, and ecchymoses on various parts of the body. Such damage is detected during a visual examination of the newborn by a neonatologist; usually they are not dangerous and require only local antiseptic treatment and the application of an aseptic dressing. Minor birth injuries to soft tissues disappear by the end of the first week of the newborn’s life. A type of birth injury in newborns is a birth tumor, which is characterized by local swelling of the soft tissues of the head. The birth tumor has a soft elastic consistency, bluish color with multiple petechiae and ecchymoses. Its occurrence is usually associated with prolonged labor in the cephalic presentation or the application of obstetric forceps. The birth tumor does not require treatment and disappears on its own after 1-3 days.
A more severe type of birth injury in newborns is damage (hemorrhage, rupture) to the sternocleidomastoid muscle, usually its lower third. In this case, a small tumor of moderately dense or doughy consistency is determined at the site of damage. Damage to the sternocleidomastoid muscle may not be detected immediately, but after about a week, when the child develops torticollis. In the treatment of birth injury of the sternocleidomastoid muscle in newborns, corrective position of the head with the help of rollers, dry heat, electrophoresis of potassium iodide, massage are used; if ineffective - surgical correction.
Cephalohematoma, as a type of birth injury in newborns, is characterized by hemorrhage under the periosteum of the parietal or occipital bones of the skull. Typical signs of cephalohematoma are elastic consistency, lack of pulsation, painlessness, fluctuation, and the presence of a ridge along the periphery. In the future, newborns with cephalohematoma may experience jaundice caused by increased extravascular production of bilirubin. The cephalohematoma decreases in size by 2-3 weeks of life, and completely resolves by the end of 6-8 weeks. Complications of subperiosteal birth trauma in newborns include anemia, calcification and suppuration of cephalohematoma. Children with large (more than 6 cm in diameter) cephalohematomas require radiography of the skull to exclude bone cracks. Since cephalohematomas in premature infants are often associated with intrauterine mycoplasmosis, PCR or ELISA diagnostics are required.
In most cases, birth injuries to soft tissues in newborns pass without consequences.
Birth injuries of the skeletal system
Among birth injuries of the musculoskeletal system in newborns, injuries to the collarbone and limb bones are more common. They always refer to purely obstetric types of injuries. Subperiosteal fractures of the clavicle without displacement are usually detected 3-4 days after birth by the presence of a fusiform dense swelling - a forming callus. A displaced fracture of the clavicle is accompanied by the inability to perform active movements, pain, crying with passive movement of the arm, swelling and crepitus over the fracture site.
When the humerus or femur is fractured, there is no active movement in the limbs, a painful reaction to passive movements occurs, there is swelling, deformation and shortening of the damaged limb. For any types of fractures, newborns need consultation with a pediatric traumatologist and X-ray diagnostics (radiography of the clavicle, radiography of the long bones). In case of a clavicle fracture, short-term immobilization of the arm is carried out by applying a Deso bandage or tight swaddling. For fractures of the humerus and femur, the bones of the upper or lower limb are repositioned and a plaster cast is applied (if necessary, traction).
A type of birth injury to the skeletal system of newborns is traumatic epiphysiolysis of the humerus. Its manifestations include pain, swelling and crepitus in the area of the shoulder or elbow joints, and limited range of motion in the affected arm. The outcome of such an injury can be paresis of the radial nerve and the formation of flexion contracture in the joints. Treatment consists of immobilization of the limb, physiotherapeutic procedures, and massage.
Birth injuries of internal organs
Damage to internal organs occurs due to mechanical effects on the fetus during abnormal labor. The most common hemorrhages are in the liver, spleen and adrenal glands. Clinical manifestations of birth trauma of internal organs in newborns develop on days 3-5 due to internal bleeding. When the hematoma ruptures, bloating occurs, intestinal paresis develops, muscle hypotonia (or atony), suppression of physiological reflexes, arterial hypotension, persistent regurgitation and vomiting.
If a birth injury to internal organs is suspected, the newborn undergoes a survey radiography of the abdominal cavity, ultrasound of the abdominal organs and ultrasound of the adrenal glands. Treatment consists of hemostatic and symptomatic therapy; if necessary, laparoscopy or laparotomy with revision of internal organs.
If there is hemorrhage in the adrenal glands, the child may develop acute or chronic adrenal insufficiency. The prognosis for birth trauma of internal organs in newborns is determined by the volume and severity of the lesion, and the timeliness of detection of the damage.
Birth injuries of the central and peripheral nervous system
Damage to the nervous system in newborns constitutes the most extensive group of birth injuries. In this review, we will focus on birth injury of the spinal cord and peripheral nervous system; A detailed description of intracranial birth injuries in newborns will be given in the corresponding article.
Birth injuries to the spinal cord in newborns can include hemorrhage, stretching, compression, or rupture of the spinal cord at various levels, with or without a vertebral fracture. Severe injuries are characterized by the clinical picture of spinal shock: lethargy, muscle hypotonia, areflexia, weak cry, diaphragmatic breathing. The death of children can occur from respiratory failure. In more favorable cases, there is a gradual regression of the phenomena of spinal shock; hypotension is replaced by spasticity; Autonomic disorders develop (vasomotor reactions, sweating), trophic changes in muscle and bone tissue. Mild birth injuries in newborns are accompanied by transient neurological symptoms: changes in muscle tone, reflex and motor reactions.
The diagnosis is facilitated by examination of the child by a pediatric neurologist, X-ray or MRI of the spine, electromyography, lumbar puncture and examination of cerebrospinal fluid. Treatment of birth injury to the spinal cord in newborns includes immobilization of the damaged area, dehydration and antihemorrhagic therapy, and restorative measures (orthopedic massage, exercise therapy, electrical stimulation, physiotherapy).
Birth injuries of the peripheral nervous system in newborns include damage to the roots, plexuses, peripheral and cranial nerves.
Taking into account the localization, brachial plexus paresis (obstetric paresis) can be upper (proximal), lower (distal) or total. Superior Duchenne-Erb paresis is associated with damage to the plexuses and roots originating in the C5-C6 segments, which is accompanied by dysfunction of the proximal upper limb. In this case, the child takes a characteristic position with the arm adducted to the body, extended at the elbow joint, rotated inward at the shoulder and pronated at the forearm; with the hand bent in the palm and the head tilted towards the sore shoulder.
With lower obstetric Dejerine-Klumpke paresis, the plexuses or roots originating from C7-T1 are affected, resulting in dysfunction of the distal arm. Manifestations include muscle hypotonia, hypoesthesia, limitation of movements in the wrist and elbow joints, fingers, and the “clawed paw” symptom. With the total type of obstetric paresis, the arm is completely inactive, muscle hypotonia is pronounced, and muscle atrophy develops early.
The diagnosis and localization of damage is clarified using electromyography. Treatment of birth injury of the brachial plexus in newborns consists of immobilization of the arm using a splint, massage, exercise therapy, physiotherapy (applications of ozokerite, paraffin, electrical stimulation, electrophoresis), and drug therapy.
With paresis of the diaphragm, the newborn develops shortness of breath, paradoxical breathing, cyanosis, and bulging of the chest on the affected side. The detection of paresis is facilitated by fluoroscopy and chest radiography, which determines the high standing and inactivity of the dome of the diaphragm. Against this background, children may develop congestive pneumonia. Treatment of birth injury involves transcutaneous stimulation of the phrenic nerve; if necessary, mechanical ventilation until adequate spontaneous breathing is restored.
Facial nerve paresis is associated with damage to the trunk or branches of the facial nerve. In this case, the child has facial asymmetry, lagophthalmos, upward displacement of the eyeball when crying, mouth asymmetry, and difficulty sucking. Birth trauma in newborns is diagnosed based on clinical signs, electroneurography, and recording of evoked potentials. Often, paresis of the facial nerve goes away without special treatment; in other cases, heat treatment and drug therapy are performed.
More rare types of birth injuries in newborns include injuries to the pharyngeal, median, radial, sciatic, peroneal nerves, and lumbosacral plexus.
Who should I contact?
Letay.org is the best assistant in finding a doctor!
The organization is engaged in providing treatment for complex orthopedic injuries in clinics in Spain, selecting a attending physician for each patient in accordance with the established diagnosis. Letai will organize a preliminary consultation with a doctor for you, find a hotel and arrange a flight. Letai guarantees examination and treatment in the best Spanish clinics!
Why will you definitely choose Letai? Due to the large number of advantages of the organization:
- Modern equipment and use of innovations. Letai uses only the latest techniques for treating and rehabilitating patients. This allows you to shorten the period of hospital stay or treatment. In addition, innovative approaches ensure maximum restoration of the functions of the human body in a fairly quick time.
- Fast reaction. Letai is not affiliated with any one clinic. This is a significant advantage, because mobility allows you to organize an operation for the patient in the shortest possible time!
- Doctors are professionals. Letai provides patients with the opportunity to be treated by the best Spanish doctors who have significant clinical experience. Specialists from the best clinics in Spain, recognized in European countries, and some throughout the world, guarantee patients high-quality treatment and a responsible approach to therapy!
- Price policy. It is worth noting that the cost of all services provided by Letai is within acceptable limits for each person! Thus, anyone in need of quality treatment can take advantage of Letai’s help in the treatment and rehabilitation of injuries.
Letai's activities cover three main areas:
- Joint diseases. An experienced orthopedic doctor will diagnose and treat diseases of the human musculoskeletal system. Why endure discomfort if you can turn to a competent specialist who will ensure timely diagnosis and correct treatment?
- Treatment of injuries. Often, patients come to Letai because of an injury that causes significant pain and significant discomfort. The doctors of our clinics guarantee treatment of any injuries according to the latest protocols used in the world!
- Rehabilitation after injuries. The recovery period after injury is no less significant. Doctors at Spanish clinics will write you an individual rehabilitation program, and then monitor the dynamics and adjust the plan depending on the activity of restoring the functions of the musculoskeletal system.
Letay.org will find the best doctor for your speedy recovery and quick rehabilitation!
Treatment in children
The main method of therapy is strong fixation, that is, immobilization of the limb. In children, the immobilization time is 2-3 weeks. To firmly hold broken bone fragments, special Delbe rings are often used. Pediatric clavicle fractures often occur as a “greenstick” type, that is, with preservation of the integrity of the periosteum. In this case, a fixing bandage on the collarbone is used. A fixing bandage is sufficient even if the clavicle injury is not accompanied by displacement.
In cases where the fracture is characterized by displacement of fragments, reposition is performed.
Why did the child's collarbone break during childbirth?
Of course, all babies are born the same way, but the course of this process directly depends on the course of pregnancy and labor activity of the expectant mother’s body. Sometimes everything happens very quickly and the fetus simply does not have time to occupy the required position, so it cannot leave the womb without any problems. In this situation, a clavicle fracture occurs, but it does not always happen.
Sometimes specialists are forced to turn the baby over themselves in order to simplify the process of his birth into this world. But if the medical staff is careless and in a hurry touches the child’s hand with instruments, a fracture may occur. In this case, responsibility for the health of the baby lies solely with the doctor. But expectant mothers must understand that all manipulations were carried out so that the baby was born alive.
As you know, the fetus can be quite large in size compared to the woman’s pelvis. Under such circumstances, labor is very difficult and painful, since due to its large size the baby cannot move forward unhindered. In most cases, even in the late stages of pregnancy, expectant mothers are informed about the possible risk and are offered a cesarean section, but if the decision was made to give birth on their own, then the problem is extremely difficult to avoid.
If the baby is in the wrong position in the mother’s tummy, and the buttocks are closer to the birth canal, then excessive pressure is exerted on all bone tissues, including the collarbones. Normally, the baby should be positioned head first. Thus, virtually the entire load goes on the skull, and the fetus easily comes out into the light.
Also, the cause of a fracture is often pathologies in which the baby’s bones become too soft and fragile; any impact on them can cause serious injury. This often happens if the expectant mother has not carefully monitored her own diet. Under such conditions, the child’s body receives an insufficient amount of useful microelements responsible for the proper formation of the skeleton and its strength.
Treatment in adults
Immobilization of the limb is carried out for 1 month, using a Chizhin frame or other bandages. If displacement of the fragments occurs, then reposition is required (returning the fragments to their normal physiological position) with local anesthesia. Then fixation occurs with a soft or plaster cast.
The reposition is followed by a recovery period, and after some time a control photograph is taken. It is actively used during the rehabilitation period of UHF; in the presence of severe pain, the doctor prescribes painkillers. As soon as the need for immobilization disappears, the doctor refers the patient to massage and physical therapy.
Conservative treatment consists of using soft or plaster casts, as well as fixing the limb. This type of therapy is used for uncomplicated fractures in both adults and children. Immobilization is carried out by a traumatologist who actively monitors the restoration of the integrity of the patient’s bone.
The main goal of conservative therapy is to ensure the correct position of the bone and rigid fixation of the clavicle in this position for a certain time. If displacement of the fragments has not occurred, then immobilization of the shoulder girdle is sufficient for high-quality healing to occur. In cases where displacement has occurred due to a clavicle fracture, preliminary reposition is required; at the next stage, immobilization occurs. In traumatology, there are two types of reposition - closed and open techniques.
Closed reduction is non-invasive, that is, the doctor does not perform an open surgical approach. Using non-invasive medical techniques, the traumatologist performs temporary immobilization, and then x-rays are taken. If the bone fragments have been juxtaposed correctly, then temporary immobilization is changed to permanent plaster fixation. In the case where the bone fragments could not be compared as accurately as possible, a repeated closed reduction or open reduction is performed according to the decision of the traumatologist.
Open reduction has a number of strict indications, because during its use open surgical access to the fracture area is performed. Then the doctor compares the bone fragments in the wound and fixes them, which is called intraosseous osteosynthesis and refers to the surgical treatment of a clavicle fracture.
Procedures and care for a child during the rehabilitation period
During the recovery period, it is necessary to strictly follow the recommendations of specialists. In the first week after the injury, decongestants may be prescribed for the hematoma (administration of vitamins K), if there is one. The consequences of the bone coming out of the joint pass faster than with a fracture, however, even such an injury in newborns heals within 7-10 days, if there are no complications. The rehabilitation period may take about 30 days.
READ ALSO: natal birth injury of the cervical spine in a newborn
After the bone has healed, procedures may be prescribed to restore mobility, such as massage and exercise therapy. In some cases, electrophoresis or magnetic therapy is used. Sometimes the attending physician may prescribe vitamins (calcium, magnesium, phosphorus) or recommend adding foods rich in these elements to the mother’s diet (for breastfeeding).
To read: Can a nursing mother eat plums: the benefits of fresh fruits and compote while breastfeeding
Surgery
surgical treatment is necessary if the patient has an open fracture of the clavicle or a closed injury, however, complicated by acute conditions. For example, a bone fragment damaged a large nerve trunk, which caused a disruption of the innervation on the side of the injury or a major vessel, which caused bleeding. In some cases, bone fragments damage the parietal layer of the pleura, which threatens the development of an emergency condition - pneumothorax.
Surgical interventions are routinely performed for a clavicle fracture if the patient has a significant displacement of bone fragments or the shoulder girdle area is externally significantly deformed. Surgical treatment consists of performing osteosynthesis of the clavicle using one of the following techniques:
- Intraosseous method. Used for comminuted fractures. During the operation, a special pin or Bogdanov nail is used.
- Bony technique. During the operation, a curved plate is used. This method is used for injuries with many fragments in the wound.
- Spoke method . Rigid fixation is performed using wires that are literally passed through fragments of the bone base. The ends of the knitting needles are fastened, and they are first brought outside the collarbone.
In the postoperative period, antibiotics are used to prevent the development of infectious complications, and painkillers are used to relieve pain. Physiotherapeutic procedures provide faster and more complete restoration of the functions of the injured limb. Discharge from the hospital becomes possible after the stitches are removed, which occurs on the 8-10th day of hospital stay.
We suggest adding your company to a thematic directory of organizations, for example in Sport365days - this is an excellent example of a thematic aggregator tied to topics such as sports, health, sporting goods and beauty. If you are the owner of a business focused specifically on these areas, you can create your own website absolutely free, find business partners with the ability to post information on your page or a partner’s page. (Example: Medart).
Recovery
Physiotherapy is widely used in medicine for more active recovery.
Physiotherapeutic methods of rehabilitation after a clavicle fracture are actively used in medicine to accelerate the healing of the injury, as well as reduce pain and discomfort for the patient. In addition, physiotherapy has an anti-inflammatory, anti-edematous effect, stimulates metabolism in the area of damage and tissue regeneration.
The classification of physiotherapeutic procedures is based on the time of their implementation. Thus, there are methods of physiotherapy that are used only during the period of plaster immobilization, after removal of the plaster, and also regardless of whether the patient has a plaster cast.
During plaster immobilization, SUV irradiation in erythemal doses . At the local level, the procedure provides relaxation of muscle tissue in the damaged area, expansion of the capillary network, which stimulates blood flow in the irradiated tissue. Finally, tissue swelling is reduced, as well as the severity of pain due to a decrease in the sensitivity of pain receptors. The general effect of SUV irradiation in erythemal doses is manifested in stimulating the formation of vitamin D, which accelerates the process of callus formation. The second procedure, electrophoresis of painkillers, ensures the accumulation of painkillers in the subcutaneous fat and muscle tissue, which long-term reduce the intensity of the patient’s pain syndrome.
After the moment when a person's plaster cast is removed, it is possible to use new physiotherapeutic procedures. If the traumatologist has removed the plaster, then the callus has already formed quite well, which means that it is possible to put small loads on the bone to increase its strength. For this purpose, therapeutic massage, high-frequency magnetic therapy, amplipulse therapy, UHF therapy, ultrasound therapy, and remote shock wave therapy are used.
Therapeutic massage provides active and persistent dilation of blood vessels in the injured area. Active blood flow accelerates the transformation of formed callus into healthy functioning bone tissue. Therapeutic massage has a significant overall effect through a reflex effect on the vasomotor center located in the brain. Thanks to therapeutic massage, blood pressure in patients is normalized.
High-frequency magnetic therapy provides an analgesic effect by influencing nerve tissue. In addition, the tension in the patient's skeletal muscles decreases.
Amplipulse therapy creates an analgesic effect and leads to relaxation of muscle fibers. The physiotherapeutic method actively influences blood vessels, dilating them, which enhances tissue trophism. Thus, amplipulse therapy stimulates the reduction of swelling, the resorption of infiltrates, and also activates recovery processes in the injured area.
UHF therapy creates an active warming effect, which directly affects cellular metabolism. Thus, microcirculation processes are activated, the muscle layer of blood vessels relaxes, and the swelling of the damaged area decreases. As a general effect, UHF therapy reduces the tone of the sympathetic nervous system, increasing the tone of its parasympathetic department.
Ultrasound therapy actively stimulates blood circulation processes, as well as lymph circulation. At the local level, capillary permeability increases, which affects the intensity of wound healing.
Remote shock wave therapy activates the synthesis of special biologically active components. They provide vasodilation in the area of injury, which stimulates the processes of proliferation of cells and tissues in the injured area. Cell division ensures the direct process of repair of the bone and cartilage base.
Regardless of immobilization, electrophoresis of vasodilators, low-frequency magnetic therapy and mineral water intake can be performed. Low-frequency magnetic therapy becomes an excellent stimulating factor for reparative processes. In addition, this method has a good anti-inflammatory effect. Mineral waters restore the balance of electrolytes in the human body and provide the necessary minerals for the active healing of damaged bone and cartilage tissue.
Question answer
What is the prognosis for clavicle fractures?
In the majority of cases, if a bone injury occurs without complications from other pathological conditions, doctors note a favorable prognosis for the patient. As a rule, bone fragments heal well, and even if there is some residual displacement, this does not affect the active movements of the arm on the injured side. In the case when a person develops complications (for example, damage to the pleura or a large nerve trunk, a great vessel), the outcome of the disease depends on the quality, time and literacy of first aid provided to the patient.
What is the patient's recovery time after surgery?
Absolute restoration of the structure of the clavicle and the function of the damaged limb occurs within 6 to 8 months. After surgery, removal of auxiliary structures (wires, screws or medical plates) is performed approximately 6-12 months after the intervention, depending on the intensity of the restoration processes in the bone.