- What is the difference between protrusion and hernia?
- What causes intervertebral disc damage?
- Two myths about hernias and protrusions
Doctors in the capital’s clinics say: the most common reason to do an MRI of the spine in Moscow is pain in the lower back. Back pain is a typical syndrome for residents of large cities. This is a consequence of a sedentary lifestyle, chronic stress, and lack of fresh air. Based on the results of an MRI of the spine, a diagnosis is made. Only in 1% of cases are Muscovites diagnosed with serious pathologies - a vertebral fracture, a neoplasm. About 10% are discogenic diseases - hernias, protrusions. We'll talk about them today.
What is protrusion
The question of protrusion and hernia, what is the difference, is asked by every person who finds himself in the hospital with suspected such conditions. It is worth understanding that protrusion is a displacement of the disc and the appearance of one or more protrusions, the size of which can be quite large.
Causes
The following can cause protrusion:
- curvature of the spine;
- improper organization of work and rest schedules;
- chronic diseases – osteochondrosis, etc.;
- inflammation and infections;
- age-related changes.
If you are at risk, you will have to find out what the difference is between protrusion and hernia, as well as what the symptoms of the conditions are.
Symptoms of the disease
In the question of how disc protrusion differs from a hernia, it is worth considering the symptoms. The disease manifests itself only at a later stage - at first there are no symptoms. So, the manifestations may be as follows:
- Head pain, dizziness.
- Numbness of the arms and legs, areas of the skin of the back.
- Back pain.
- Problems with blood pressure instability.
When wondering how protrusion differs from a hernia, it is worth knowing that protrusion can manifest itself as problems with urination, but this happens in the later stages.
The reasons for disk integrity violation can be summarized under three headings:
Accumulation of microtraumas
- Repeated microtrauma over a long period can lead to disc injury. The best example of accumulated microtrauma is poor body position (posture).
- Poor posture, whether sitting, standing or while working, strains the spine. Slouching or bending the body forward leads to overstrain and weakness of the posterior part of the annulus fibrosus disc. Over time, this leads to disruption of the integrity of the disc and displacement of the disc core fluid backwards. Violation of the integrity of the disc creates excessive stress on the joints of the spine and compression of the nerves.
- To reduce the effect of poor posture on the spine, it is important to continually try to maintain good posture, or even better, change your body position regularly.
- Any stable posture must be changed regularly to allow the spine to move and remain healthy.
Sudden unexpected load
- Sudden unexpected stress on the intervertebral discs can also occur in traumatic situations, such as a car accident. This can happen due to sudden force vectors affecting the human body, and the body tries to compensate for these forces.
- Unexpected stress or twisting of the disc can cause the fibers of the ring to break and therefore damage the disc. It is necessary to use the correct principles of postural lifting when lifting any weight. Using improper lifting techniques, such as bending and extension, can put sudden and unexpected stress on the disc.
Genetic factors
- As in many cases, it is believed that the formation of intervertebral disc protrusion has a genetic predisposition.
Those who have a genetic predisposition have a higher content of elastin fibers in the annulus fibrosus and this reduces the resistance of the disc to stress.
- Other factors that may play a role may be environmental—for example, excess abdominal fat, poor spinal stability, weak lower extremity muscles, and the type of activity the person does (such as heavy, bending exercise or lack of exercise).
- Overall, genetic factors are a minor factor in the development of disc protrusion. However, one must understand that it is impossible to influence this factor and the main thing is to prevent damage to the intervertebral discs.
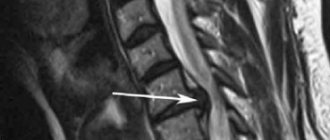
What is a hernia
The difference between the identified protrusion and a spinal hernia is that the hernia is the final stage in the development of protrusion and it appears when the fibrous ring ruptures and its contents extend beyond its limits. In such a situation, many areas of nervous tissue are pinched, and the hernia manifests itself with very unpleasant symptoms.
Causes
A hernia, which is the final stage of protrusion, appears for similar reasons. May occur in patients:
- overweight;
- staying in a sitting position for a long time and neglecting physical activity;
- with excessive stress;
- with a curved spine and incorrect posture.
Also, in order to understand exactly how a protrusion differs from a hernia, you need to know the manifestations of a hernial protrusion.
Symptoms
A hernia is a protrusion of more than 5 mm, which is detected against the background of a rupture of the fibrous ring. The symptoms in both cases are almost the same, but the hernia manifests itself much more clearly than the protrusion. It also causes headaches, dizziness, back pain, disturbances in sensitivity and performance of the limbs.
Causes of spinal hernia
A herniated disc occurs due to a weak musculo-ligamentous system, excessive stress, excess weight, or congenital weakness of the fibrous ring.
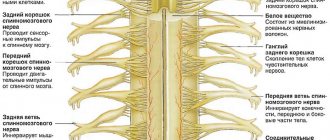
Now let's figure out what a herniated disc is. This, in layman's terms, is the protrusion of cartilage tissue (disc) beyond the fibrous ring. What is the annulus fibrosus?
The fibrous ring is the same disc (cartilage tissue) , but denser and located closer to the edge of the disc. The fibrous ring is a case in which the nucleus pulposus, which is softer in density, is located. The function of the nucleus pulposus is to balance the spinal column around various axes and uniformly distribute the axial load between the vertebrae. In other words, you can imagine a certain oval filled with a viscous liquid, inside of which there is a ball (nucleus pulposus). When you press on this oval, the ball will move in different directions, distributing the pressure.
The spinal motion segment (MSS) is the adjacent 2 vertebrae with the intervertebral disc, nerve structures and musculo-ligamentous apparatus.
The SDS is the structural and functional unit of the spinal column. Simply put, the element of the spine that performs the functions of movement and shock absorption, support for lifting weights, etc.
Why did we talk about the PDS? PDS has many connectives. Let's look at the anatomy of the PDS. So, in front of the PDS there is an anterior longitudinal ligament. It starts from the sacrum and ends with the cervical spine. It is located in front, that is, on the side of the abdomen. It covers the anterior surface of the vertebral bodies and intervertebral discs.
At the back is the posterior longitudinal ligament, which also starts from the posterior surface of the sacral bodies and continues to the cervical vertebrae. For us, the posterior longitudinal ligament is of no small importance.
The function of this ligament is to hold the intervertebral discs. When a hernia forms, the posterior longitudinal ligament tries to prevent this - it stretches, reducing the herniated disc, and prevents their formation for a long time. When it becomes thinner and cannot withstand pressure from the hernia, it ruptures and cartilage tissue falls into the lumen of the spinal canal (sequestration). It is important to prevent osteochondrosis and strengthen the ligamentous apparatus. For example, exercise “Boat”:
Starting position: lying on your stomach on a hard, stable surface. Straight arms are extended along the body, straight legs are slightly apart to the sides.
If your level of physical fitness is weak, place your hands behind your buttocks and perform the exercise with emphasis on them. During normal preparation, raise your arms up, continuing the line of your body.
At the same time, we tear off our legs and arms and raise them to the same distance from the ground. Usually it is 20-30 cm from the floor. You can bend your legs slightly at the knees, and your arms at the elbows and spread them apart. What is more important here is that you feel the tension in the back muscles that hold you in this position.
Time and number of repetitions: hold in this position for 10-12 counts, slowly lower to the floor, repeat 2 more times.
The benefits of the “boat” exercise for the back: the muscular-ligamentous apparatus of the back is strengthened (including the same posterior longitudinal ligament that keeps the discs from forming a hernia).
When prolapsed, the hernia can move both upward (ascending) and downward (descending).
Also in the SDS there is a ligamentum flavum, interspinous and supraspinous ligament, which perform a fixing function. The muscles that run along the spinal column perform various functions (with the elasticity of these muscles, a muscle corset is formed that holds the SMS, preventing it from shifting and forming hernias).
It is very important to engage in the prevention of osteochondrosis, that is, physical exercise. With various exercises, not only muscles, but also ligaments are strengthened. As a result, a muscular-ligamentous corset is formed.
Diagnosis of diseases
If we are talking about how a spinal hernia differs from a protrusion, you need to know that the difference does not lie in diagnosing both types of pathologies. In both the first and second cases, the most informative method will be magnetic resonance imaging, with which you can obtain layer-by-layer images of each vertebra, as well as the cartilage located between them. It will also be possible to assess how damaged the neighboring tissues and nerves are, and how severely the spinal cord is damaged. Based on the results of the research, the doctor will tell you how a herniated intervertebral disc differs from a protrusion, as well as what ailment was diagnosed in you and what treatment is needed.
How to treat protrusions and hernias in honey?
To find out what reasons lead you to the pain that characterizes the diseases “Protrusion” or “Hernia” and make the correct diagnosis today, the doctor at the medical center must carefully examine you and study your MRI results. If necessary, carry out additional types of diagnostics using specialized equipment at our medical center.
After a complete study of the diagnostic results, the doctor will be able to prescribe the patient a comprehensive medical treatment based on the “ Biomechanotherapy ” technique, involving, if necessary, other additional procedures.
You can learn more about the medical staff of the medical center in the “Team” section.
Read more about Karipazim and Karipain
Video about the treatment of disc herniation with Karipazim
Karipazim (Karipain), administered by electrophoresis, affects the hernia itself. It begins to gradually decrease and releases the nerve ending that it pinches, and the pain in the spine gradually disappears. To a lesser extent, the medicine affects the entire intervertebral disc. The drug enhances the regeneration of disc tissue, which restores its normal shape and its function as a shock absorber, while “rejuvenating” as it were. Karipazim also affects several neighboring intervertebral discs, restoring the entire spine. Read more about Karipazim and Karipain here
Treatment of intervertebral disc herniation. How can we help you
| How to relieve pain from a vertebral hernia yourself - video tutorial from the Echinacea clinic. | Video about the treatment of spinal hernia with Karipazim - Echinacea clinic. |
Treatment of intervertebral hernia in our clinic will be structured as follows:
- Quickly relieve pain and stop the pressure of the hernia on the nerve root. If the root is compressed for a long time, there is a risk of its atrophy, and this is fraught with a long and even incomplete restoration of the functions of the muscles of the affected limb. The volume of the disc herniation and pain can be reduced within 1-2 days by reducing its edema and swelling . The method of treating intervertebral hernia in the acute stage is medications, pain blockades, IVs, treatment with position and rest.
- Unload the affected disk. This will allow you to move more freely and without risk, and the damaged disc will be able to gradually heal. Here, it is possible to fix the lower back with a belt/bandage, soft osteopathy or manual therapy on stiff areas of the spine (manipulation is not performed on the affected disc - this is dangerous), and gymnastics for unloading.
- Restoration of the nerve root after compression. The sooner we begin treatment, the faster the transmission of nerve signals along the spine will be restored. This results in a gradual reduction in pain, restoration of strength and sensitivity in the affected limb. For this purpose, we will offer you various nerve regeneration stimulants and B vitamins.
- Disc healing. A disc with a herniated spine heals in a unique way: the affected area grows with calcium compounds and becomes stronger. In this case, calcification of the herniated vertebral disc is the norm. Calcium deposition can be accelerated with the help of medications containing calcium, vitamin D and healing stimulants, chondroprotectors. To reduce the size of the hernia, if necessary, we will offer you Karipazim (Karipain) electrophoresis.
- Spinal mobility and cartilage nutrition. At the end of the acute period, we will offer you to take chondroprotectors on your own for several months. This will improve the general condition of the spine and joints.
- Return to active life and sports is usually possible after 4-12 months.
We will also teach you how to independently maintain your health and select an individual program for preventing the formation of intervertebral hernias, including a personal set of exercises that you can safely perform at home.
In what cases is surgical treatment required - removal of a herniated disc?
If your back hurts
If you experience attacks of acute pain in the spine before visiting a doctor, you can relieve it in the following ways:
- take a non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug or analgesic;
- take a natural sedative (infusion of valerian or motherwort);
- take a horizontal position on a flat, hard surface;
- apply a tight bandage to the source of pain or wear a special corset;
- use for external use an ointment or gel containing a non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug;
- Avoid sharp turns and climbs to avoid new attacks of pain.
Under no circumstances should you take any other medications without a doctor’s prescription.
In most cases, timely diagnosis of the pathology and conservative treatment allow you to completely get rid of it. The spine determines the health of many organs and systems of our body. In addition, the blood vessels passing through it nourish the brain. Therefore, you need to treat his condition very carefully and if you experience any pain, consult a doctor. Only a specialist will be able to select adequate treatment and relieve annoying pain.