Causes of pain in the spine in the middle of the back
Most often, pain occurs due to the following phenomena and pathologies:
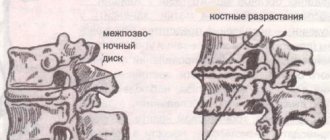
- Osteochondrosis is the most common cause of discomfort. A disease that affects the thoracic and lumbar spine can be caused by hereditary factors, metabolic disorders, and heavy physical exertion.
- Scoliosis and arthritis of the spine, accompanied by degenerative processes, lead to deformation of the vertebrae, damage to ligaments and connective tissues, which causes severe pain between the shoulder blades or in the lower back. As a rule, it intensifies with movement and sharply contracts when the human body is at rest.
- A herniated disc is a very dangerous condition in which the slightest load on the spinal column can lead to rupture of the fibrous ring and protrusion of the nucleus pulposus. This condition is accompanied by acute pain, requiring immediate medical attention.
- Diseases of internal organs. Pain in the spine in the middle of the back is caused by damage to the organs of the abdominal and thoracic cavity. Soreness can act as a signal of a pre-infarction state. Kidney pathologies (inflammatory process) are accompanied not only by discomfort, but also by elevated body temperature and swelling of the extremities. Pain caused by diseases of the gallbladder or stomach intensifies with palpation and may be accompanied by vomiting.
- Excessive physical activity leads to the fact that the spinal ligaments are under tension, which is characterized by severe pain.
- Sudden inept movements and injuries can lead to displacement of the intervertebral joints, which leads to discomfort.
- Congenital pathologies of the development of the spinal column have a characteristic symptom - a constant pressing sensation in the center of the back.
- Pain as a reaction to prolonged overexertion and depression. In a state of psycho-emotional instability, the muscles are in constant tension. By spasming, they make a person involuntarily slouch. This leads to the formation of an angle in the spine, where pain occurs. The joints become dislocated and muscle pressure appears. Doctors call this condition “spinal block.”
- Pregnancy. Increasing body weight and increasing loads often lead to a woman having pain in the spine in the middle of the back.
- An infectious process in the body can also cause discomfort. The thing is that the blood spreads the infection throughout the body, affecting different organs. Soreness in such a situation will be accompanied by high fever.
- Lumbodynia can occur as a response of the body to muscle strain. The main symptom is severe, throbbing pain. X-ray examination will help to more accurately determine the affected area.
The cause of pain that occurs during sleep may be trivial: an uncomfortable pillow or a too soft mattress. Changing bedding will help get rid of unpleasant sensations.
Mid back pain
The thoracic spine consists of 12 thoracic vertebrae, each of which has a pair of ribs attached. Together they provide protection for the chest organs. The size of the thoracic vertebrae gradually increases, starting from the 1st thoracic vertebra and further to the beginning of the lumbar spine - this is explained by a gradual increase in the load placed on them. The mobility of the middle part of the back is much lower than the mobility of the neck, the ribs provide additional protection, which is why traumatic spinal cord injuries in the thoracic spine are less common.
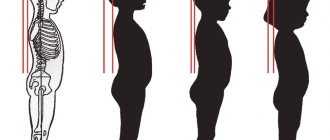
Curvature of the spine or scoliosis
Scoliosis or scoliotic disease is a pathological curvature of the spine in several planes. The exact causes of scoliosis are still unknown; the disease begins in childhood. Predisposing factors are considered to be lack of physical activity, weakness of the back muscles, incorrect posture and organization of the workplace for school-aged children. Due to pronounced curvature, disturbances in the distribution of loads and biomechanics of the spine, overstrain of the muscles that compensate for part of the load ,
chronic
back pain.
Shpidonov Gennady Stanislavovich
Neurologist
Rostov State Medical University (neurology)
10 years of experience
Arthritis (spondyloarthritis)
The intervertebral joints together with the intervertebral discs unite the spine into one whole. Each vertebra has 4 articular surfaces that form articulations with neighboring vertebrae. Like any other joint, intervertebral joints can become inflamed. This pathological condition is called spondyloarthritis. There are two main reasons that cause inflammation of the intervertebral joints. These are systemic rheumatic diseases (such as rheumatoid arthritis or ankylosing spondylitis) or reactive inflammation that occurs in response to increased stress due to osteochondrosis, scoliosis and other pathologies of the spine. Inflamed joints lose their function: stiffness of movement, stiffness of the spine, and prolonged back pain occur.
Gastrointestinal diseases and back pain
Diseases of the abdominal organs often cause referred pain in the back and spine. There is also a direct connection between pathologies of the gastrointestinal tract and diseases of the musculoskeletal system. Diseases such as chronic colitis or gastroenteritis are the background to spondyloarthritis or osteochondrosis of the spine.
Most often, referred pain in the back occurs with peptic ulcers of the stomach and duodenum, with a hiatal hernia, acute or chronic pancreatitis. This phenomenon occurs due to the characteristics of the sympathetic and parasympathetic systems, the nerve fibers of which are present in each organ of the abdominal cavity. Some of the pain impulses perceived by them return to the roots of the spinal cord, simulating pain in the spine and back.
Kidney disease and back pain
The kidneys are a paired organ located in the retroperitoneal space, which, as in the case of the abdominal organs, is intimately connected by nerves to the roots of the spinal cord. In the presence of inflammation, stones or other pathologies of the urinary tract, some of the pain impulses reach the spinal cord, simulating a spinal disease. Back Pain Symptoms
may occur with acute pyelonephritis, renal colic, kidney abscesses. A characteristic symptom is considered to be tension in the back muscles in the projection of the kidneys, which occurs due to inflammation of the kidneys or an abscess of the tissue surrounding them.
Shpidonov Gennady Stanislavovich
Neurologist
Rostov State Medical University (neurology)
10 years of experience
How to find out what is causing pain in the vertebrae?
It is very difficult to independently understand why pressure on the spine causes pain in the vertebrae. Only a doctor can make a correct diagnosis after the patient has undergone a comprehensive examination. The main diagnostic methods that help determine the mechanism of origin of pain in the back:
- X-ray – allows you to see the condition of the vertebrae (the degree of their displacement relative to each other, the presence of bone growths).
- Computed tomography is informative for pathologies of the bone structures of the spine. Used for suspected cases of: scoliosis, vertebral trauma, cervical osteochondrosis, spondyloarthrosis, tumor. CT scans are often used in preparation for surgery.
- Magnetic resonance imaging - provides clear information about the pathology of the soft tissues of the spinal column. Using MRI, the condition of the spinal cord and blood vessels is assessed, the degree of destruction of the intervertebral disc, and the size of the pathological neoplasm in the spine and surrounding tissues are determined.
- Myelography is a study of the spine using a contrast agent. Based on the results of such diagnostics, you can see the place of pinching of the spinal cord and its roots, the localization of an intervertebral hernia or tumor.
- Electrospondylography makes it possible to identify degenerative changes in the spine and the degree of damage to its tissues in the early stages. ESG is often used to monitor the treatment process.
- Contrast discography is necessary to assess the condition of intervertebral discs. Helps determine whether there are cracks on them, whether a protrusion or hernia has formed.
In severe cases, additional examination may be necessary:
- general blood test, urine test;
- blood chemistry;
- biopsy (examination of material to establish the exact etiology of the pathological process).
Regardless of the diagnosis, it is important to begin treatment for the disease in a timely manner. Otherwise, there is a high probability of developing complications: paresis or complete paralysis of the limbs, sepsis, respiratory and cardiovascular failure, cerebral ischemia, stroke.
Diagnostic features
During the initial examination, the doctor will first inquire about your health, symptoms of the disease, and also ask a number of questions about your work and usual level of physical activity and stress. This is followed by a physical examination. If necessary, additional tests may be prescribed, both visual (X-ray or MRI) and laboratory (for example, blood tests). This is done in order to accurately establish the cause of pain and find its source - for example, damage to a vertebra or a herniated disc.
Sharpness of pain
The sensation of pain in the central region of the back is sharp and cutting, hindering the movement of the arms, legs and body. Such pain sensations are provoked by nerve endings. The sudden movement pinched the nerve between the vertebrae, causing sharp pain, but short-lived. It is worth lying quietly on a flat surface for a while; if it does not go away and continues to cause discomfort, you should seek medical help. Sharp and persistent pain in the middle of the spine is a sign of a disease that needs to be investigated at the facility. Firstly, it could be an intervertebral hernia. Secondly, heart disease, for example, a heart attack.
Throbbing pain that lasts a long time is lumbodynia.
Symptoms:
- The disease occurs after lifting weights;
- The back hurts severely when walking;
- Appears after sudden movements;
- A shooting sensation appears in the spine.
Lumbago involves throbbing or dull pain in the middle of the spine between the discs. Prolonged exposure to the street and hypothermia can cause lumbodynia. If treatment is not started in time, the pain will spread throughout the spine. Often after lumbodynia, osteochondrosis occurs during exercise, which is a common cause of back pain.
Bubnovsky: exercises for the spine after sleep and other pain
Bubnovsky and exercises for the spine after sleep and other pain
Doctor Bubnovsky has developed his own technique that helps a person get rid of back pain. Exercises for the spine are very simple and can be performed after sleep or in the evening. They help with various back pain associated with joints, muscles and neuralgia.
Learn the method of Dr. Bubnovsky using a detailed article on our website at this link. You will also find a video that explains in detail how to do the exercises, in what position of the body and for how long.
We advise you to study - What are osteophytes on the spine
If a person has something that hurts, especially the back and after sleep, then this condition spoils the mood for the whole coming day. Therefore, if unpleasant symptoms occur, immediately consult a doctor for help and treatment so that you can suffer and live life to the fullest. Good luck!
Diagnosis of nagging pain in the back above the lower back
If pain occurs, you should visit an orthopedist or neurologist. If necessary, these specialists will refer you for additional consultations with other doctors. To determine why the lumbar region hurts, various diagnostic procedures are required:
- X-ray;
- MRI;
- CT;
- urine and blood tests;
- lumbar puncture;
- Ultrasound of internal organs.
The examination will reveal the cause of the pain and associated disorders: narrowing of the arteries, deformation of the intervertebral discs, and so on.
Prevention
Clinical recommendations for the prevention of intervertebral hernias and osteochondrosis:
- move more, do gymnastics in the morning, do yoga;
- take a contrast shower followed by rubbing with a towel to enhance metabolic processes;
- undergo a massage course every six months (up to 10 sessions);
- maintain liver health, because collagen production depends on it;
- increase immunity;
- avoid stress, establish a smooth psychological background;
- control your weight, because every extra 10 kg is approximately 0.5 kg of additional load on one vertebra, which leads to rapid wear.
In addition, it is important:
- Stand and walk correctly. Correct posture is when you stand against the wall and touch it with the back of your head, shoulder blades, buttocks and heels. When walking and standing, you should try to maintain exactly this position.
- Sit in the correct position: do not lean too far back, do not lean forward. You should press your back tightly against the back of the chair, have support for your lower back and neck. Every 15 minutes – change the position of your legs, stretch.
- Sleep on an anatomically correct or orthopedic mattress.
- After waking up, while still in bed, do simple exercises with your legs and arms, stretch before getting up (this should be done without sudden movements).
- Do not carry heavy bags in one hand. It is better to distribute purchases evenly into two packages.
- Do not carry a bag over your shoulder. Better for your back is a backpack with two straps.
- A small child should be carried with a straight back, without bending backwards. It is best to carry a very small baby on the chest in a special sling, and a slightly older one - on the back.
- When carrying heavy objects, do not bend or turn your body.
- Do not bend over when cleaning - use an extension cord for the vacuum cleaner handle and a mop (do not wash the floors with just a rag while kneeling).
- Eat grapes, apples, strawberries, pears, lentils, hazelnuts, pumpkin, green salad, and raspberries more often.
- Monitor the balance of magnesium and potassium in your diet. Eat nuts, fish, seafood, spinach, cabbage, beans, peas.
- Eliminate bad habits - alcohol and smoking.
- Swimming, running (but only with shock-absorbing insoles and special sports shoes), skiing.
Be sure to visit doctors for preventive examinations to prevent the situation from worsening if you have an illness and to begin treatment on time.
What to do to prevent back pain? Prevention of back pain
In order to reduce the risk of diseases that can cause back pain, Family Doctor doctors recommend:
- sleep on a comfortable bed with an elastic and hard mattress;
- try to maintain correct posture;
- do not stay in one position for a long time. When working at a computer or driving a car, you need to take breaks that give you the opportunity to stretch, warm up, and move around;
- When working while sitting, organize your workplace correctly. The chair should have a back, preferably with armrests and a headrest, so that you can lean back and relax the muscles of your back and neck. The forearms should not be suspended; it is necessary to ensure that they lie completely on the table;
- do not walk in high-heeled shoes for more than two hours at a time;
- Avoid sudden turns and bends of the body. If you need to pick something up from the floor, it is advisable to sit down and not bend over;
- when standing for a long time (when traveling on public transport or waiting in a public place), find a point of support (lean on something with your hand or lean your back);
- do not gain excess weight;
- avoid lifting heavy objects;
- engage in physical therapy, swimming or fitness.
Causes
The causes of pain in the spine in the middle of the back can be very diverse. If a person feels a nagging pain, this indicates physical strain. Often this pain syndrome occurs in people who lift weights and are pregnant.
Moderate aching pain in the middle of the spine can occur due to a sedentary lifestyle or prolonged stay in an uncomfortable position.
But most often, unpleasant sensations between the shoulder blades are a sign of the following pathological conditions:
- Trauma to the thoracic spine. Any damage to the spine can cause vertebral displacement, pinching of a nerve or vessel, which causes severe pain. If a pinched nerve occurs, a sharp short-term pain occurs, which subsides in a supine position. Often when a bruise occurs, one vertebra in the middle of the spine hurts when pressure is applied.
- Scoliosis. If you have a curved spine, you may experience severe back pain during long periods of walking, sitting, or standing.
- Radiculitis. The pathology is infectious in nature and is characterized by inflammation of the nerves of the spinal column. It manifests itself as sharp lumbago in the sternum, intensifying with movement.
- Osteochondrosis. As a result of heavy stress, the thoracic discs are destroyed, cartilage and joints are deformed, and osteophytes form. This condition is accompanied by pain of varying intensity, radiating to the ribs. The pathology is also manifested by sensory disturbances and digestive problems.
- Intervertebral hernia. A hernia in the thoracic spine is rare and is manifested by burning, nagging pain that intensifies during movement and can radiate to the arms, shoulders, and neck. There is a loss of sensitivity in the back, numbness in the arms, weakness, and limited mobility.
- Heart diseases. Pain in the left middle back may be a sign of myocardial infarction or angina. The pain has a sharp, burning character, is observed even at rest and can radiate to the arm and jaw. Sometimes an unpleasant squeezing pain occurs in the collarbone or abdominal area. In addition to painful sensations, arrhythmia, tachycardia, increased sweating, burning in the sternum, and shortness of breath are observed.
- Pneumonia. With infectious pneumonia, sometimes there is an aching pain in the spine in the middle of the back, which occurs when trying to take a deep breath. Signs of pneumonia can also include shortness of breath, cough, difficulty breathing, and hyperthermia.
- Bronchitis. Inflammation of the bronchi causes pressing painful sensations in the middle of the spine, which intensify during sudden movements, coughing and deep breathing. The main sign of the pathology is a painful cough, accompanied by high body temperature, increased sweating and general weakness.
If the spine in the middle of the back hurts when pressed, this may indicate the presence of inflammatory processes. Pain syndrome can also be neurological and psychosomatic in nature. Unpleasant sensations slightly above the lower back can be caused by diseases of the urinary system. Gallbladder, gastrointestinal tract.
Diagnostics
Neurologists are most often involved in clarifying the causes of pain in the spine. Patients with traumatic injuries of the spinal column are referred to traumatologists or neurosurgeons. The following diagnostic procedures can be performed:
- Questioning, general examination
. The doctor finds out when and under what circumstances the pain first appeared, how it changed over time, what factors provoked it, and what symptoms were combined with it. Examines and palpates the affected area, determines the range of movements. - Neurological examination
. The specialist evaluates superficial and deep sensitivity, muscle strength, and coordination of movements. Explores reflexes. - X-ray of the spine.
It is performed in two projections and, according to indications, is supplemented with functional tests. Allows you to identify the main causes of pain: fractures, dislocations, fracture-dislocations, anomalies, degenerative changes, areas of destruction due to infection, aseptic necrosis. Myelography can be performed to study the condition of the spinal canal. - Other imaging techniques
. Appointed to clarify data obtained during radiography. A CT scan of the spine clearly shows changes in hard structures; an MRI of the spinal column provides detailed information about the condition of the ligaments and intervertebral discs. - Functional diagnostics
. Electromyography is prescribed to assess muscle structures. If the development of radicular syndrome is suspected, a study of evoked potentials and electroneurography is performed.
Therapeutic exercises for the spine
Cervical myositis
The influence of internal organs on the spinal column
Our internal organs have a huge impact on the condition of the spinal column. In particular, these are the heart, kidneys, lungs, stomach, gall bladder, etc.
Particular attention should be paid to the fact that increased body temperature is associated with back pain in the middle. This is a signal for you.
It is quite possible that there is a disease of some internal organ. There is no way to ignore such a signal.
What to do if your back hurts in the middle of the spine?
Modern medicine offers many different ways to diagnose and treat diseases of the spine and internal organs, which focus pain in different areas of the back.
There are drug and non-drug treatments.
Acupuncture, extensive manual therapy, massage, exercise therapy, reflexology. For each patient with his disease, his own treatment and recovery program will be selected.
Acupuncture for spinal diseases
This method of treating the spine is currently very controversial. Some experts claim that acupuncture has a positive effect in the complex treatment of the spine, for example, osteochondrosis. Other experts question this method.
We advise you to study: Pain under the right shoulder blade from the backSo, what is acupuncture? It is considered one of the most ancient methods of treatment. Moreover, treatments for various kinds of diseases.
There are points on the human body that, when impacted, improve the flow of vital energy to a specific unhealthy organ. Acupuncture helps to identify and eliminate channels that are clogged in a person, but through which vital energy should move freely. During acupuncture treatment, the movement of vital energy throughout the human body is resumed. And this leads to recovery.
When treating osteochondrosis, supporters of acupuncture recommend this type of treatment to their patients in combination with massage. Why is it recommended? According to their observations, such treatment gives an excellent effect in treating the spine. Because around the spine there are a large number of exactly the same points that were described above.
If you are offered this treatment method as an addition to the main treatment, then this option should still be considered.
Manual therapy
Another very effective treatment method is manual therapy, used in combination with reflexology and physiotherapy.
What is good about manual therapy is that it eliminates not just the symptoms of the disease, but, most importantly, eliminates the causes of the development of spinal diseases, in particular osteochondrosis and hernias. Manual therapy is treatment with the hands.
The doctor works with his own hands on the joints of the spine, limbs, ligaments, and muscles in order to eliminate identified disorders of the human musculoskeletal system.
Manual therapy is treatment with the hands. The doctor works with his own hands on the joints of the spine, limbs, ligaments, and muscles in order to eliminate identified disorders of the human musculoskeletal system.
This therapy was able to combine the best from orthopedics, neurology, and neurophysiology.
Massage
When treating the spine, do not forget about massage. People who lead a sedentary lifestyle and spend a lot of time in a sitting position primarily need a massage.
Massage is also a treatment. With its help, discomfort is relieved, and subsequently such a massage becomes not only useful, but also pleasant.
It is important to remember that massage can be done at home if there are no contraindications or serious illnesses, for example, cancer. In order not to face the problem of back diseases, you should be attentive to your health.
Avoid heavy stress on the spine, do physical exercise regularly, move more, give preference to walking, eat right, avoiding junk food, choose the right position while lying down, sitting, etc.
In order not to face the problem of back diseases, you should be attentive to your health. Avoid heavy stress on the spine, do physical exercise regularly, move more, give preference to walking, eat right, avoiding junk food, choose the right position while lying down, sitting, etc.
By taking all preventive measures, you will be able to maintain your health and live without spinal diseases.
Features and causes of pain syndrome
Doctors distinguish between acute and chronic manifestations of ailments. The pathological condition is considered acute if pain appears for the first time. If a person experiences discomfort constantly, with a periodic increase and decrease in the intensity of unpleasant symptoms, the pain is chronic.
Painful sensations may be:
- pulsating;
- sharp, sharp;
- piercing or cutting;
- pulling.
Sometimes the pain is accompanied by swelling or numbness of the back, arms, legs, and face.
The reasons for back pain in the thoracic spine may be associated with problems in different body systems. Most often they are caused by diseases of the musculoskeletal system. Referred pain is less common in pathologies of internal organs. In some cases, both factors occur: diseases of the spine, which is the “axis” of the entire body, often lead to prolapse, displacement or compression of internal organs.
Pain with increased stress
After intense physical work, a nagging pain often appears. Most often it is caused by muscle tension and fatigue. Such sensations may occur after carrying heavy objects, sitting for long periods of time (static load) or sports training. Women sometimes experience nagging pain during pregnancy.
Spinal diseases
If the soreness is accompanied by tingling, burning or burning sensations in the spine, then it is most likely not due to muscle fatigue. These symptoms usually indicate spinal diseases:
- arthrosis;
- retrolisthesis;
- osteochondrosis;
- deformations;
- protrusion or hernia.
These pathologies are characterized by chronic pain, which sharply intensifies after emotional stress, physical exertion or hypothermia.
The following signs indicate that the spine hurts in the middle of the back:
- crunching or clicking noises when moving;
- increasing stiffness;
- increased pain when changing body position, turning the head and other movements;
- coldness of hands and feet;
- periodic numbness of the hands, face, back, legs, neck;
- feeling of “current” in the body;
- frequent dizziness, migraines.
If the spine in the middle of the back becomes numb, this indicates compression or damage to the nerve roots. Without treatment, this problem can lead to spinal cord damage, sensory loss, and loss of mobility.
If your spine hurts in the middle of your back when pressed, the pain is most likely caused by myositis or another inflammatory disease of the muscle tissue.
Pain due to stress
Diseases of the musculoskeletal system are not always the cause of pain. Often, pain in the collar area, thoracic region and lower back is caused by a stressful condition. Due to strong emotional stress, a person constantly tenses his muscles, slouches, raises his shoulders - all this leads to uncomfortable sensations. To get rid of pain, you must first cope with stress. Sanatorium-resort treatment, manual therapy, massage and physiotherapy, including medicinal baths, are highly effective.
Referred pain
If the malaise is caused by diseases of the internal organs, the pain may be accompanied by the following symptoms:
- cough;
- dyspnea;
- temperature increase;
- heart rhythm disturbances;
- constipation, diarrhea;
- vomit;
- bloating;
- the appearance of a yellowish tint to the eyes and skin;
- coating on the tongue.
With tuberculosis, the back hurts in the area of the lungs at the back. With inflammation of the gallbladder or liver disease, pain occurs in the back and on the right under the ribs, nausea appears, and sometimes the temperature rises. When the kidneys are inflamed, pain is accompanied by difficulty or frequent urination.
Treatment
Help before diagnosis
In case of traumatic injuries, the victim should be placed on a backboard and given an anesthetic. For pain of non-traumatic origin, functional rest is required. Patients need to avoid sudden movements and take regular breaks when working in a static position. In the absence of signs of an acute condition or severe inflammatory phenomena, short-term use of NSAIDs and the use of local agents are acceptable. Sharp, increasing pain, disturbances in general condition, and neurological disorders are reasons to immediately consult a specialist.
Conservative therapy
Therapeutic tactics are determined by the nature and stage of the pathology. In case of injuries, a protective regime is prescribed, and various methods of traction are occasionally used. The basis of treatment for most traumatic and non-traumatic injuries are medications and physiotherapeutic techniques. The following medications are used:
- NSAIDs
. Effective for acute and chronic pain. Eliminate pain, reduce the severity of inflammation. Prescribed in tablets, injections, and local forms. - Local anesthetics
. Local anesthetics alone or in combination with other drugs (usually glucocorticosteroids) are injected into the affected area during a therapeutic blockade. - Antibiotics
. Indicated for infectious processes. As a rule, they are administered by injection. They are selected taking into account the sensitivity of the pathogen. - Neurotropic vitamins
. A good result is provided by B vitamins, which enhance the effect of other medications and increase the amount of endogenous compounds with an analgesic effect.
Physiotherapy is prescribed after acute symptoms have resolved. Ultrasound, magnetic therapy, electrical stimulation, acupuncture, and other methods are used. Patients are recommended massage, exercise therapy, and manual therapy if indicated.
For diseases of internal organs
Arthritis, which affects people of all ages, causes pain in the middle of the back that makes it difficult to straighten your shoulders. The body gradually bends, and this leads to disruption of the functioning of all internal organs. There are both mild and severe forms of arthritis, and all require treatment.
We advise you to study: Setting up DPT and polio vaccination at the same timeOsteochondrosis of the thoracic spine gives impetus to the development of degenerative processes, which causes growths and destruction of the vertebrae. If sudden painful sensations appear, this indicates that a nerve fiber is being pinched.
With kidney disease (inflammatory process), body temperature rises, pain occurs in the back, and parts of the body become swollen. Acute renal dysfunction is accompanied by very high fever.
Pain in the middle of the back also occurs with diseases of the gallbladder or gastrointestinal tract. If your back hurts to the left of the spine, in the middle, this may indicate a stomach ulcer. Pain in the upper abdomen on the right, subsiding and intensifying, accompanied by vomiting, indicates cholelithiasis.
Your back may hurt in the middle even due to an infection in the body. This kind of pain is rare, but still worth mentioning. The blood flow can carry an infection between the shoulder blades, which begins to cause pain of varying degrees. In this case, there will definitely be an elevated temperature.
Lower back pain on the right side can occur due to diseases of the lumbar and sciatic muscles. Often this is a spasm. The cause may be prolonged physical activity improperly distributed on the spine; curvature of posture, due to which the muscles in the curved area are constantly tense; physical inactivity.
Treatments include manual therapy (various types of massage), acupuncture, apitherapy, and physical therapy.
Due to inflammation of internal organs, pain can radiate to the right side and lower back.
Intestines
The inflammatory process in the intestines is accompanied by stabbing or cutting pain in the abdomen, lower back, right side, abnormal bowel movements, and elevated body temperature. A gastroentrologist diagnoses and treats the disease. Diagnosis is carried out through clinical tests.
Right kidney
Lower back pain on the right side may indicate inflammation or prolapse of the right kidney. This process is accompanied by a nagging pain, noticeable in the morning and after physical activity, and pain when urinating. If these symptoms are present, you should contact a urologist. Diagnosis is carried out using clinical tests, palpation, and ultrasound of the kidneys. Treatment is prescribed depending on the test results.
It consists of anti-inflammatory drugs, analgesics, and kidney teas.
Liver
If liver diseases occur, the localization of pain is on the right under the ribs. However, it can radiate to the right side and lower back. This disease is accompanied by yellowing of the skin, heaviness in the liver area, pain, and indigestion. Diagnosis is carried out by a gastroenterologist or hepatologist (specializing only in liver diseases).
A diet is required.
Gallbladder
When the right hypochondrium, as well as the right side and lower back, hurt, this may indicate the presence of gallbladder diseases. They are also accompanied by a feeling of bitterness in the mouth, loss of appetite, weight loss, nausea, and vomiting bile. A gastroenterologist diagnoses and treats gallbladder diseases. Surgeon intervention may be required.
Diet adherence is mandatory.
Right ovary
The characteristic pain in the right side behind the lumbar region can be caused by inflammation of the right ovary. This disease is accompanied by pain on the right lower front, during sexual intercourse and physical activity, and discomfort when urinating. If you have these symptoms, you should immediately contact a gynecologist.
Complications of this disease can lead to infertility and chronic diseases of the genitourinary system.
In what cases should you urgently consult a doctor?
Trying to cope with pain on your own, much less endure severe pain, is unacceptable. However, in some cases, if there is severe pain in the lower back, a visit to the doctor must be arranged immediately. This:
- recent injury to the lumbar region or spine;
- a rise in body temperature in parallel with an increase in pain;
- acute pain that does not go away within several hours (days);
- feeling of numbness in the legs, lower back;
- movement and coordination disorders;
- problems with urination or defecation.