Hernias of the back and abdomen are so common that it is quite difficult to find a person who is not familiar with this disease. But Becker's hernia still remains an unknown disease for many. After all, most people, having noticed a swelling on their knee, attribute everything to swelling.
However, in reality, this swelling is often a Becker hernia - an inflammatory process that occurs in the tendon bursa. The reason for its development is the leakage of interarticular fluid between the tendons.
Causes
The disease is often diagnosed in older people. The reason for this is degenerative-destructive processes caused by the aging of the body. However, medicine knows of cases where a hernia appeared in patients under 30 years of age.
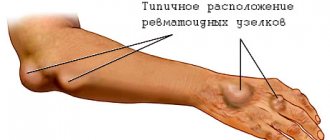
There may be several reasons for this, and all of them are associated with certain diseases (arthrosis, rheumatoid arthritis, psoriasis and osteoporosis). In addition, injuries and bruises of varying severity can also be the cause.
Patients who exercise are at risk. If their sports activities involve stress on the lower extremities, there is a high probability that they will develop this disease over time. Especially if there are excessive loads. They have a negative impact on overall health and can cause a hernia to appear at a young age.
A hernia of the knee joint is a unilateral pathology. However, sometimes it affects both knees. It is worth noting that the disease can manifest itself even at a young age. The reason for this is serious bruises that were not properly treated. But these cases are quite rare, so they are rather an exception to the rule.
Reasons for the development of the disease
The development of a hernia may be a consequence of the aging process of the body, although the disease is often found in young people. The following reasons may cause it to appear:
- systemic lupus, rheumatoid arthritis;
- deforming osteoarthritis;
- psoriasis;
- blood pathologies - hemophilia;
- injury to the joint itself or cartilage tissue;
- inflammatory processes in the knee;
- damage to the cruciate ligaments.
Elderly people and professional athletes involved in active sports can be placed at risk. Over time, the protrusion increases in size, causing a lot of discomfort to the person - he cannot move normally. The reason for this is the pain that appears during bending, and the cyst itself limits mobility.
Symptoms
Diagnosing the disease at an early stage is almost impossible. This is explained by the complete absence of pain and visible changes. The patient does not even realize that he is slowly but surely developing a hernia. Consequently, the person does not go to the hospital.
The first pain sensations appear in the second stage, when the volume of fluid begins to increase, provoking the spread of the inflammatory process. This causes difficulty in straightening and bending the knee.
At this stage, the doctor can detect the disease, since upon palpation it is very easy to feel a small painful lump. However, patients extremely rarely come to the clinic with these symptoms, because they confuse the hernia with ordinary edema, which does not require serious treatment.
Because treatment is not performed properly, Becker's hernia behind the knee increases in size. This leads to the patient feeling discomfort even at rest. In addition to the pain, another unpleasant symptom is added - numbness of the limb, which can manifest itself both in an upright state and in sitting and lying positions.
general information
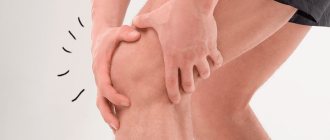
Becker's hernia is a cyst filled with fluid. It is localized in the area of the popliteal fossa, along the back surface of the knee joint. The protrusion appears as a result of the inflammatory process occurring in the knee.
Fluid collecting in the joint compresses blood vessels and nerve endings. This causes pain and also makes it difficult for the patient to move. The size of the formation varies: from a couple of millimeters to three cm. The pathology is diagnosed in children, as well as in people after 35 years.
A characteristic feature of the disease is that Becker's protrusion is considered a unilateral lesion of the knee joint. That is, it appears only on one leg. Bilateral damage is extremely rare.
Diagnostics
As you know, successful treatment of any disease depends entirely on how correctly the diagnosis was carried out. It is with its help that specialists draw conclusions regarding the patient’s condition.
It is customary to begin any diagnostic measures with a routine interview and examination of the patient. These are standard procedures that will be carried out regardless of what specific complaints the patient comes to the clinic with.
Examination of the patient includes not only palpation of the joint. To determine the degree of pain, the amplitude of leg movements is studied. Procedures such as:
- diaphanoscopy;
- MRI;
- artography;
- CT scan.
In most cases, doctors tend to combine two procedures - diaphanoscopy and artography. If the patient complains not only of discomfort when straightening and flexing the knee and pain, but also of elevated temperature, a blood test is additionally prescribed.
Treatment methods
The treatment method is selected based on the size of the tumor, whether there are accompanying diseases (their severity), and also takes into account the presence of certain symptoms. Only by accurately determining the severity of the disease can you choose the right treatment: drug therapy, physiotherapeutic methods, physical therapy.
Drug therapy
Drug therapy involves taking anti-inflammatory drugs (Diclofenac, Ibuprofen). Their mechanism of action is quite simple and is aimed at getting rid of pain and reducing swelling.
There are often cases when the selected remedies do not reduce the manifestations of the disease. Then doctors resort to a more powerful remedy - Prednisolone injections. But the effect does not last long, since the medicine is a painkiller that lasts only a few hours.
Almost always, patients with this diagnosis are prescribed hernia puncture . This is due to the fact that patients often seek medical help when the tumor reaches a significant size and the pain becomes unbearable.
In this case, it is not possible to cure the disease solely with medications.
The procedure is usually divided into several stages:
- at the first stage, the tumor is pierced with a special needle;
- at the second stage, the doctor sucks out the fluid from the joint with a syringe;
- at the final stage, a corticosteroid is injected into the hernia area. This substance helps glue the walls of the joint capsule.
After the procedure, symptomatic relief occurs almost instantly. And this is its main advantage.
Physiotherapeutic procedures
Physiotherapeutic methods are also used in the treatment of Becker's hernia. As part of complex therapy, they can have a positive effect on the course of the disease, significantly alleviating the patient’s condition. Today the following methods are used:
- electromagnetic radiation;
- electrophoresis;
- bioresonance therapy.
Read also: Cyst in the knee joint treatment with folk remedies
It is very difficult to say exactly which of the above procedures is the most effective, because it depends on the individual characteristics of the body and the course of the disease. That is why the choice can only be made by the attending physician who has studied the medical history.
If a patient has been diagnosed with a pathological formation in the knee joint, the doctor prescribes physical therapy. The patient begins to do gymnastics according to a program that is specially designed for him.
All exercises are selected in such a way that joints and muscles are well worked out. Thanks to this, they become stronger. It is worth noting that such physical exercise will be very useful for people whose hernia was caused by another disease - arthritis.
Traditional methods
Treatment of a hernia of the knee joint with folk remedies is very effective, provided that the disease is at an early stage.
Tinctures prepared from herbs such as burdock, celandine, and golden mustache can have a positive effect on the patient’s condition. Their use is due to the fact that they all have an analgesic effect.
It is noted that they are also able to reduce swelling. Therefore, they can be used successfully. However, doctors insist that lotions should be only part of the treatment course, and not a separate method.
- Mix honey and apple cider vinegar in equal proportions, dilute with clean water. Take this medicine three times a day before meals.
- Mix a teaspoon of aloe juice with the same amount of lemon juice . Apply a compress with this mixture to the sore area before going to bed.
- Pour water over dry dandelion and clove leaves . Cook over low heat for 15 minutes. Place the boiled raw material in gauze and apply it to the damaged area twice a day.
Surgical intervention
Surgical intervention is prescribed if the cause of the hernia is any damage. It is simply impossible to get rid of a hernia that appeared after an injury using conservative treatment methods, since it is secondary.
The operation is not classified as complex. It is carried out in several stages:
- a small incision is made directly above the hernia;
- the liquid is sucked out with a special syringe;
- The area where the joint connects to the tendon bursa is sutured and the tumor is cut off.
The arthroscopic method is considered a gentle method for removing a hernia. The main advantage of the technique is the absence of consequences of the operation. It is worth noting that sometimes surgical intervention is necessary not only when diagnosing a secondary hernia.
In cases where drug treatment does not produce results, the patient is required to undergo surgery.
What consequences are possible if Becker's cyst is not treated?
The accumulation of joint fluid causes compression of the surrounding tissues, which is manifested by the formation of a tumor, pain and discomfort in the area under the knee and swelling of its posterior surface, decreased sensitivity of the lower leg and foot, and impaired blood flow in their vessels. As a result of these disorders, the range of motion in the knee is limited, walking becomes difficult, and atrophy of the muscles of the foot and lower leg develops.
If Becker's cyst is not treated , the following serious complications are possible:
- rupture of the cyst: the contents of the cyst flow down the intermuscular spaces and cause non-infectious inflammation. Manifested by swelling, itching and redness of the skin, pain, increased temperature (both local and general);
- deep vein thrombosis of the leg: occurs due to compression of the popliteal vein and causes a feeling of bursting pain in the leg, cyanosis of the skin, swelling of the foot and leg, and increased local temperature. If deep vein thrombosis is not treated adequately, the blood clot may break off, which can lead to pulmonary embolism;
- thrombophlebitis of the deep veins of the leg: develops as a consequence of thrombosis due to inflammation of the vein wall and is manifested by pain, swelling, chills;
- formation of calcifications: the synovial membrane degenerates into cartilaginous tissue, which promotes the formation and local deposition of calcium salts - they cause persistent pain in the knee joint;
- compression of the peroneal, tibial or femoral nerves: the sensitivity of certain parts of the limb is impaired, flexion or extension of the foot and toes of the affected leg is impaired.
Is it possible to cure a Becker's cyst?
Therapeutic methods for treating Baker's cyst
There are two approaches to treating Becker's cyst.
Conservative therapy includes:
- unloading of the knee joint;
- performing a puncture (aspiration): using a thin needle, the doctor punctures the cyst and pumps out its liquid contents;
- drug treatment: intra-articular administration of steroid hormones (hydrocortisone, prednisolone), taking drugs from the NSAID group to relieve inflammation (diclofenac, indomethacin), external use of anti-inflammatory ointments (Fastum-gel, Troxevasin), taking chondroprotectors for the regeneration of cartilage tissue (chondroitin sulfate);
- prescription of physiotherapy: electrophoresis and ultra-high-frequency therapy are the most effective (can be used only after the development of an oncological process has been excluded).
During the period of diagnosis and conservative treatment, the patient is given the following recommendations: refrain from physical activity, avoid occupational stress on the joint, apply cold packs to relieve swelling and pain, fix the knee area with a tight elastic bandage.
Surgical methods for treating Becker cyst
If the treatment is ineffective, complications occur, a significant growth of the hernia or its large size, surgical tactics . It can be implemented in two ways:
- Classic surgery: performed under local anesthesia and involves excision of the cyst, suturing its junction with the articular cavity and suturing the incision. Afterwards a tight bandage is applied to the knee.
- Endoscopic technique: performed using an arthroscope and a special instrument, which is inserted through two incisions in the popliteal cavity. With its help, the fluid is first removed, then the capsular membrane of the cyst.
Rehabilitation rules for the treatment of Becker cyst
Treatment for a Becker cyst is not limited to its removal. An important condition for the effectiveness of surgical therapy is postoperative rehabilitation - it allows you to quickly return to normal everyday life and restore the motor functionality of the operated leg.
The main thing in the initial stage is the safety of exercises that allow you to increase the range of motion of the joint. Since the inflammatory process can persist for up to six months, excessive exercise is contraindicated. It is forbidden to go to the gym, otherwise complications may develop. Acceptable activities include yoga and stretching - they have a beneficial effect on the ligamentous and musculoskeletal system.
The complex should include exercises aimed at relieving muscle tension and relaxing muscles. The following simple exercises help eliminate tension, improve blood circulation and motor activity:
- Straightening your legs, alternately straighten and bend the limb on which the operation was performed.
- Sit on a chair, straighten the operated leg, pull the toe towards you and stay in this position for 30 seconds, lower the leg.
- Sit on the floor, straighten your legs, pull your feet towards you and try, without bending your knees, to reach your toes with your hands.
- Sit on the floor, bend the healthy limb and pull the foot towards the buttock, straighten the operated leg and lift it up, fix it for 5-15 seconds, lower it.
It is recommended to repeat the exercises 10 times daily.
How to get rid of Baker's cyst without surgery?
Treatment of Becker's cyst without surgery using conservative therapy rarely leads to complete elimination of the pathology.
It is also not always possible to cure a Becker cyst with classical intervention - often the formation is detected again after some time. In addition, after surgery, a positive result does not develop immediately, and the rehabilitation period often occurs with complications. Paresthesia, pain of varying intensity, and sensation of a foreign body under the knee are possible. Some patients cannot fully extend the operated leg.
The second method allows you to get rid of a Becker cyst most effectively. If during surgery the doctor performs additional coagulation of the anastomosis between the joint cavity and the hernia, long-term results of therapy improve, and the disease is less likely to recur. Often, even common postoperative complications such as swelling, subcutaneous hematomas, and severe pain are absent. Already in the first 24 hours after the intervention, all patients are able to fully extend their leg.
Is it possible to treat a Becker cyst in another way? Patients who have already tried all available methods should pay attention to one more – innovative, and therefore still little-known.
How it works?
Neurodoctor affects the control centers of the brain.
The brain begins to produce dozens of neurohormones and form “corrective” nerve impulses.
Neurohormones are many times more effective than the most powerful drugs in quickly curing the disease. Nerve impulses eliminate pathological processes at the cellular level and correct the functioning of other organs and systems of the body.
LEARN MORE ABOUT THE METHOD
The use of Neurodoctor in the treatment of Baker's cyst
“Neurodoctor” is a device that works on the principle of pulse therapy. It is based on the law of resonant interaction of shades that coincide with the frequency parameters of human organs. And, as you know, a certain color with vibration frequency corresponds to each organ. The electromagnetic nature determines the effect of color on various structures of the body.
The device consists of special glasses that deliver light impulses directly through the retina to the pineal gland, from where they are transmitted to other structures of the body, including the pineal gland. As a result, the vibrations of organs change, which entails the development of preventive and therapeutic effects.
"Neurodoctor" shows high effectiveness in the treatment of various diseases of the musculoskeletal system, including popliteal cyst. You can use it yourself at home.
At least 60% of patients note a significant improvement in their well-being after just a few sessions. By increasing the synthesis of biologically active substances, pain relief occurs, inflammation and swelling are reduced. Blood circulation is activated, reparative processes are launched. The cyst formation gradually decreases in size. Joint mobility is normalized, range of motion increases.
A full 30-day guarantee for a refund for the device if it is ineffective is a unique opportunity to try Neurodoctor on yourself.
Possible complications
Without proper treatment, Becker's hernia leads to the following complications:
- Leakage of fluid from the cyst cavity into the surrounding tissue.
- The occurrence of blood clots, phlebitis.
- Blood stasis.
- Development of pulmonary embolism.
- Trophic ulcer.
- Osteomyelitis.
Such complications can seriously undermine a person’s health, so at the first unpleasant symptoms, consult a doctor, without waiting for unbearable pain and limited mobility.
Development mechanism
Let us consider the anatomical mechanisms of the occurrence of a popliteal cyst. Some people have an intertendinous bursa on the back of the joint between the muscles, which is normal.
If there is a concomitant disease or injury to the knee, synovial fluid can enter this bursa, gradually stretching the walls. A protrusion (hernia) is formed, which puts pressure on surrounding tissues and blood vessels, causing discomfort, pain and difficulty moving.
The appearance of a hernia of the knee joint is associated with degenerative processes that arise due to the gradual wear and tear of tissues and aging. Therefore, the diagnosis is first made between the ages of 30 and 70 years.
The formation of a Becker cyst is preceded by inflammation of the articular tissue of the knee, or other diseases leading to increased production of synovial fluid and its accumulation.
The following reasons for the appearance of neoplasms in adults are identified:
- Arthritis (rheumatoid or inflammatory origin);
- Arthrosis (degenerative joint damage);
- Synovitis (inflammation of the intertendon bursa with the formation of effusion);
- Bursitis (inflammation of the joint capsule with accumulation of exudate);
- Lupus (damage to connective tissue, including joints);
- Hemophilia (failure of circulation of joint fluid due to bleeding);
- Knee injuries (fractures, dislocations, tendon rupture or cartilage deformation);
- Excessive systematic load on the joint;
At the initial stage, the disease does not manifest itself in any way. Discomfort occurs as the pathological leakage of synovial fluid into the cavity of the intertendon bursa progresses.
Read also: Baker's cyst - what is it?
When the hernia reaches a certain size, pain and discomfort appear in the area of the popliteal fossa, which intensifies when the limb is flexed. Subsequently, swelling and heaviness in the legs are added. In this case, immediate treatment is required.
The size of a Becker cyst may vary depending on the position of the body, in particular the limb itself.
The real size of the hernia can only be assessed with full extension of the knee joint in a standing position.
Visual examination and palpation reveals a neoplasm, often round (also found in the shape of a bunch of grapes, a crescent, a bird's beak or a slit) and painful.
The disease progresses differently in each individual case. Usually the process takes several months or years, but there are also rapidly developing hernias.
The process usually affects one limb; lesions of both legs are extremely rare.
Treatment of Baker's cyst.
Conservative treatment is used if the formation is small. Then, complex therapy treats the underlying disease that causes chronic inflammation, for example, osteoarthritis or injury. With this treatment, excess inflammatory fluid no longer accumulates in the cyst communicating with the joint cavity, since there is no inflammation in the joint itself. Previously, to rid the patient of a cyst, a puncture was used - it was pierced with a syringe, the liquid contents were removed. But with this method of treatment, the relapse rate is high, reaching 50%. Repeated punctures can lead to infectious inflammation of the joint.
A radical way to treat a Baker's cyst is its surgical removal. It is usually prescribed for sizes greater than 5 cm, ineffectiveness of conservative treatment, and repeated punctures more than 3 times. The operation is easily tolerated, recovery after it is quick, and the risk of recurrence is reduced to a minimum. Surgical intervention, depending on the form of pathology, is carried out using the arthroscopic method or extra-articular endoscopic access. Arthroscopically, coagulation of the cyst and synovectomy are performed. Sometimes, when the size is large, an open operation is performed to excise it. The prognosis for the operation is favorable, the relapse rate is reduced to a minimum, and postoperative recovery is quick and easy. The course of rehabilitation measures after arthroscopy includes physiotherapeutic procedures, kinesiotherapy, mechanotherapy, and massages. All procedures must be carried out under the supervision of specialists; only they can correctly assess the patient’s condition over time.
Diagnostics
The study begins with a survey of the patient's complaints and collection of data on the medical history, for example, the presence of previous diagnoses, injuries received and lifestyle (profession, sports).
After this, a visual inspection is carried out. The degree of damage, mobility of the limb in the knee joint and the extent of the spread of edema are checked.
Based on the data obtained, a decision is made to prescribe additional instrumental and laboratory tests.
To carry out differential diagnosis and determine the nature of the neoplasm, it is recommended to perform a puncture followed by bacteriological analysis of the contents.
There are several other methods that allow you to get a complete picture of the disease:
- Ultrasound, CT and MRI (collection of data on the size and contours of the cyst);
- Diaphanoscopy (visualization of a hernia using transmitted light);
- X-ray (checking the condition of bones and joint tissues, identifying concomitant diseases and differential diagnosis);
- Arthroscopy (minimally invasive examination using a probe and camera);
After undergoing a full examination, the doctor prescribes treatment: medication or surgery.
A popliteal hernia can be treated using two methods:
The conservative method (treatment with drugs) is low in effectiveness. It is used as preparation for surgery and for rehabilitation. Analgesics and anti-inflammatory drugs are prescribed, and physiotherapeutic procedures are performed. Even if a therapeutic effect has been achieved, relapse occurs over time.
An intermediate technique is the previously mentioned puncture, but with pumping out the fluid with a needle and administering steroids (Kenalog, hydrocortisone, prednisolone). This is also seen as a temporary measure.
The best option is the surgical method. In addition to recurrence, indications for such treatment include nerve compression, difficulty moving and rapid growth.
Only complete removal of a knee hernia during surgery will get rid of the disease forever.
The surgeon, under local anesthesia, makes an incision in the affected area and removes the hernial sac and closes the canal. The recovery period is rarely more than a week.
Why is a knee hernia dangerous and how to deal with it?
Hernia of the knee joint is equally common among men and women of all ages. Having studied detailed information about this disease, you can quickly cope with it. So what does it take for a successful cure?
The current pace of life means that people are on the move most of the day. The legs are the first to suffer from this. Knee hernia is a common condition that affects athletes and people who have suffered injury. The key to its cure will be timely diagnosis.
What is a knee hernia?
A hernia or cyst is usually called a protruding cavity in the popliteal fossa. It is filled with synovial fluid. It is painful on palpation. Most often it is small in size. The disease affects middle-aged people with an active lifestyle, as well as children under 7 years of age. Associated with increased loads on the knee joint. This leads to the production of synovial fluid and increased pressure in the joint capsule. Excess fluid begins to accumulate and forms a cyst. If treatment is not started in time, the hernia will increase. It can only be removed surgically.
Causes
Hernia is a common disease among athletes. This is due to increased stress on the knee joints. The slightest injury triggers the growth of the cyst. It goes unnoticed, as the pain is mild. A Becker cyst also occurs in people who are not involved in sports. Among the reasons are:
- Rheumatoid arthritis.
- Arthrosis, which leads to a long-term inflammatory process.
- Degenerative changes in cartilage tissue that are congenital in nature.
- Meniscus injury.
- Lupus.
- Hemophilia.
A hernia is diagnosed in 17% of people with joint disease. Only a timely medical examination will help avoid serious health consequences.
Symptoms of Becker's cyst in children and adults
Since the space of the intertendinous bursa is sufficient for some time for the accumulation of fluid, there is no clinical picture as such, or unexpressed unpleasant sensations appear associated with irritation of the bursa, partially filled with fluid.
Symptoms develop mainly when nerve structures are compressed by an enlarged bursa (it can already be identified as a Becker cyst). In this case, the following symptoms of Becker cyst occur in children and adults:
- pain;
- inability to fully flex the knee joint - physical exercises with a Becker cyst are difficult;
- tingling;
- a feeling of numbness in the soft tissues of the sole.
Symptoms of the disease
With small cysts, there are no negative symptoms. The problem can only be identified during a medical examination. Visual signs appear as the hernia grows. In this case, the following signs of the disease are distinguished:
- Acute pain localized in the affected area.
- On palpation, a tubercle is felt on the back of the knee.
- Swelling of the knee joint.
- Increased temperature in the joint area.
- Limitation of limb functionality. It becomes difficult to bend and straighten the joint.
- With large cyst sizes, numbness of the calf muscle is observed.
Read also: Cyst of the popliteal joint
Symptoms and diagnosis of the disease
Treatment of the disease is carried out only after the person has been accurately diagnosed. This does not cause much difficulty if the examination is carried out by a truly experienced doctor. He performs an external examination of the patient and palpates the knee joint. When carrying out manipulations, the doctor notes the following external signs of pathology:
- swelling in the area of the knee joint, more along the back surface;
- pain in the lower leg, radiating to the foot;
- sometimes the cyst is characterized by numbness of the skin due to compression of the nerve endings;
- limited mobility caused by large hernias.
Diagnostic methods
Accurate diagnosis is a guarantee of cure. Medicine offers several simple techniques that will help make a reliable diagnosis:
- Diaphanoscopy. The doctor examines the area of the affected knee under bright lights. During the procedure, it is possible to confirm or refute the accumulation of synovial fluid.
- Artography. The knee is scanned with X-rays. Based on the resulting image, the presence of pathology of the knee joint is judged.
- MRI. Progressive diagnostic method. A strong magnetic field is applied to the affected area. As a result, the doctor sees on the monitor the structure of the joint and the processes occurring in it. This study detects the cyst and also allows us to judge its severity.
- Ultrasound. Exposure using ultrasound. Used to identify the cause of a disease.
The use of such diagnostic methods helps to detect the disease and develop a competent treatment program.
Treatment options
Several methods have been developed for the treatment of knee hernia:
- Medication. It is used exclusively in the early stages of the disease. Involves a course of taking specialized tablets and ointments. Help relieve pain and restore joint mobility. The cause of the disease cannot be eliminated in this way.
- Physiotherapy. Used in conjunction with medications.
- Surgical. It is used in cases where the cyst has reached an impressive size, joint mobility is severely limited, nerve bundles are compressed, or drug treatment does not bring results. The intervention is carried out under local anesthesia. The duration of the procedure is 30 minutes. The surgeon stitches the junction of the joint and the tendon bursa, after which the hernia is cut out. The operation is considered safe. There is no need to stay in the hospital after it. The operated limb must not be stepped on for 5 days. After a week, the doctor will remove the stitches.
Hernias
5245 June 16
IMPORTANT!
The information in this section cannot be used for self-diagnosis and self-treatment.
In case of pain or other exacerbation of the disease, diagnostic tests should be prescribed only by the attending physician. To make a diagnosis and properly prescribe treatment, you should contact your doctor. Hernias: causes, symptoms, diagnosis and treatment methods.
Definition
A hernia is a disease in which internal organs protrude from the cavity they normally occupy through a natural or pathologically formed opening in anatomical structures while maintaining the integrity of the membranes covering them. An organ (or part of an organ) may protrude under the skin, into the intermuscular space, or into internal pockets.
The names of hernias correspond to the anatomical areas where they are formed (inguinal, femoral, umbilical, as well as hernias of the white line of the abdomen, internal hernias, intervertebral hernias).
Causes of a hernia The
cause of an abdominal hernia is the presence of “weak spots” (hernial orifices) in the wall of the abdominal cavity, which are congenital or appear during life. The size of the hernial orifice is very variable - from one or two to ten centimeters. Normally, the abdominal muscles work as a protective corset for the internal organs. When their elasticity decreases, a hernial sac is formed into which the internal organs move.
A hernia can be the result of a hereditary predisposition, age-related changes, sudden weight loss, obesity, pregnancy, an inactive lifestyle or excessive exercise, anatomical features, previous surgery, abdominal trauma or connective tissue weakness. Factors that increase intra-abdominal pressure should also be taken into account: chronic cough due to lung diseases, heavy physical labor, frequent crying in infancy, difficult childbirth, forced vomiting, prolonged constipation, and even playing wind instruments.
Doctors believe that the main reason for the development of intervertebral hernia is acute or chronic overload of the spine, which is facilitated by heavy lifting, prolonged sedentary work, incorrect posture, and constant exposure to vibration.
Inguinal hernia
An inguinal hernia occurs in the groin area above the inguinal ligament. Perhaps this is the most common hernia - up to 75% of the total number of all external abdominal hernias. Occurs predominantly in men. The largest proportion of inguinal hernias are acquired, that is, those that form during life.
Femoral hernia
A femoral hernia is determined in the groin area below the inguinal ligament - more often in women. It is prone to infringement due to the characteristics of the channel through which it exits. There are no congenital femoral hernias.
Umbilical hernia
The prevalence of umbilical hernias is quite high. More often it is a small hole (1-2 cm), and the hernial contents are the fat of the greater omentum. The hernial sac may also contain loops of the small and large intestines, the bladder and other abdominal organs. Umbilical hernias in children are a defect in the development of the anterior abdominal wall. They appear in the first months of life, more often in girls, in most cases they do not require intervention and disappear on their own. Umbilical hernias in adults occur mainly in women over 40 years of age, especially those who have given birth many times and who are obese.
Hernia of the white line of the abdomen
A hernia of the linea alba occurs due to anatomical weakness of the connective tissue and can lead to displacement of the intestine or omentum. Factors that increase the likelihood of a hernia include obesity, pregnancy, difficulty urinating, abdominal injuries, etc. In addition, a hernia may result from a postoperative complication if drains and tampons were used during surgery. The appearance of a hernia can be facilitated by a wound infection or a disruption in the wound healing process - in this case, protrusion of the abdominal organs occurs in the area of the postoperative scar, often accompanied by aching pain. The contents of hernias of the white line are most often the omentum, less often - loops of the small and colonic intestines, and the wall of the stomach.
Rare forms of abdominal hernia
Rare forms of hernias include hernias of the xiphoid process (xyphoidal), Spigelian line, lumbar, obturator, sciatic and perineal. These hernias are usually small, difficult to diagnose and prone to strangulation.
Internal abdominal hernias
Internal abdominal hernias occur when abdominal organs move into pockets, crevices and openings of the peritoneum. The most common internal hernia is a diaphragmatic hernia, in which abdominal organs are displaced through a hole in the diaphragm into the chest.
A hiatal hernia is caused by obesity, pregnancy, wearing very tight, tight clothing, and coughing.
Intervertebral hernia
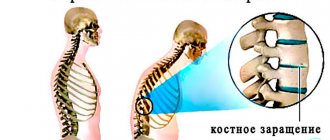
Intervertebral discs play the role of shock absorbers, dampening vibration during walking, running and jumping. They consist of a soft nucleus pulposus and an outer fibrous ring, which provides the necessary stability. If the ring ruptures, part of the intervertebral disc (usually in the lower back) becomes displaced. Increased pressure or its uneven distribution, as well as narrowing of the joint space with osteochondrosis, leads to the formation of first protrusion and then disc herniation.
Classification of the disease
According to the clinical course:
- uncomplicated (reducible);
- complicated:
- disadvantaged,
- irredeemable,
- inflamed (from the skin or from the internal organs),
- coprostasis (chronic constipation), damage and neoplasms of hernias.
Abdominal wall hernias are also classified according to the degree of development :
- initial - they are characterized by the presence of elastic walls of the hernia outlet and a small size of the protrusion, which appears only during excessive loads; such hernias can be self-reduced;
- canal - the hernial opening expands, the internal organs begin to sink into the hernial opening; the hernia is reduced while lying down, but appears again when standing;
- complete - internal organs pass through the hernial orifice and are located under the skin; the hernia cannot be reduced even in a lying position.
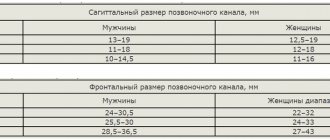
According to localization, intervertebral hernias occur in the cervical, thoracic and lumbar spine.
Hernia symptoms
General symptoms of uncomplicated external abdominal hernias:
- the presence of hernial protrusion, hernial orifice, pain in the hernia area;
- dysfunction of the organs that make up the hernial contents.
The disease is characterized by the following features:
- develops gradually and often begins with discomfort while walking, coughing and during physical activity;
- the hernial protrusion forms later, appearing during exercise and disappearing at rest;
- the ability to reduce a hernia distinguishes it from other space-occupying formations (abscess, lipoma) that are similar in appearance;
- Over time, the visible formation increases and ceases to be reduced or disappears at rest.
The main symptom of the disease is periodic moderate, aching pain.
In a calm state, it may become weaker or disappear altogether. Constant pain in the area of the protrusion indicates the irreducibility of the hernia.
Often the pain is referred, so the patient feels it in the epigastric region, lower back, scrotum, etc. The nature of pain and its intensity are very individual and varied, and the degree of their severity is not proportional to the size of the hernial protrusion.
Development of inguinal hernia
preceded by a painful bulge in the groin area. Pain occurs with physical activity or prolonged sitting. When lying down, the bulge usually disappears. The disease is characterized by frequent urination and enlargement of one side of the scrotum in men.
In the presence of a femoral hernia
the patient experiences sharp, severe pain, more like a spasm, an oval-sized tumor is visible, often complicating movement.
An umbilical hernia
may not cause discomfort at all, or the symptoms are limited to a feeling of heaviness, a sensation of tremors (beating) in the navel area. In rare cases, digestive function is disrupted, problems with urination, frequent constipation, nausea, and bloating appear. Such a hernia is not prone to strangulation.
With hernias
of the white line of the abdomen,
signs of severe pain may be observed, reminiscent of the clinical picture of some diseases of the abdominal organs - peptic ulcer, cholecystitis, pancreatitis, etc.
A distinctive feature of internal hernias
is that outside of strangulation they (with the exception of diaphragmatic hernias) do not have specific clinical symptoms and are not recognized.
A hiatal hernia
is most often manifested by the clinical manifestations of gastroesophageal reflux disease - heartburn, belching, chest pain. A diaphragmatic hernia may be accompanied by painful sensations after eating and in a lying position, because gastric juice enters the esophagus.
To localize a herniated disc
indicates shooting or pulling pain at the site of cartilage destruction. In addition, a number of neurological symptoms indicate a hernia - the pain increases when the nerve roots near the vertebra are pinched, and due to the connection of the nerve fibers with the spinal cord, it is concentrated not only in the damaged area of the back, but can spread to the arm or leg.
Diagnosis of hernias
Mandatory methods of clinical examination of the patient include physical examination, palpation, percussion and auscultation of the hernial protrusion. The examination is carried out with the patient in a vertical and horizontal position, as well as at rest and when straining.
Applied visualization methods:
- .
- Endoscopic studies. These examinations can be performed under general anesthesia.
Traditional treatment methods
Traditional medicine specialists offer their own methods of treating knee hernia. Remember that they can only be used as an addition to conservative treatment and only after consultation with a doctor. Uncontrolled therapy can cause irreparable harm to health.
- Moisten a clean piece of gauze with heated sunflower oil. Apply to the sore knee. Fix and leave overnight.
- Place golden mustache leaves in a glass container and fill with vodka. Leave for 4 weeks. A compress with this remedy is applied to the sore knee. The same tincture can also be taken orally, two tablespoons a couple of times a day.
- Grind three geranium leaves using a meat grinder. Stir in lard. Apply this ointment to the affected joint for three hours every day.
- Prepare a decoction of burdock roots with the addition of celandine. Apply compresses from this decoction to the hernia at night. They will help eliminate inflammation and pain.
- Place the cabbage leaf in boiling water and boil for a couple of minutes. Lubricate the sore knee with a thin layer of honey. Apply a warm cabbage leaf. Secure with a bandage.
- Keep the compress on for as long as possible. Repeat the procedures every day for two weeks.
- Prepare a decoction of raspberry and elderberry leaves. Soak a small piece of cloth in it and apply it to the hernia. Wrap a warm scarf around your knee. Carry out the procedure every day for at least a month.
- Mix one part each of birch buds, dandelion roots, nettle leaves, mint and plantain with two parts St. John's wort. Steam one tablespoon of the prepared mixture with 300 ml of boiling water. Leave for about an hour. Take 100 ml of filtered tincture three times a day. The course of therapy is 3 weeks. If necessary, after a 10-day break it is repeated.
- Grind a couple of aloe leaves and lemon along with the peel. Mix two teaspoons of gruel with 1 gram of streptocide. This composition is used as a compress.
- Chop a tablespoon of cloves and pour in 100 ml of boiling water. Add a spoonful of crushed dandelion roots. Boil on fire for 10 minutes. Add a tablespoon of alcohol to the prepared mixture. Use the liquid as a compress. Apply it every day and leave for at least three hours.
Such simple recipes will help relieve pain and reduce inflammation. If there is no positive dynamics after using them, consult your doctor.