The spine and hip joint in humans are closely connected. The spinal column is the central supporting mechanism through which the torso is formed and a person’s upright posture is ensured. The hip joint is the largest joint in the bones of the lower extremities. It connects the iliac bone of the pelvic ring to the thigh.
It bears the maximum shock-absorbing and physical load when moving. Walking, running, jumping, and even just standing in place all place significant stress on the hip joint.
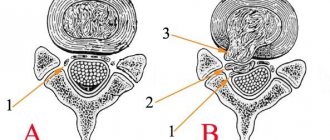
The human spinal column is conventionally divided into five sections. These are the cervical, thoracic, lumbar, sacral and coccyx. Each of them has a certain degree of physiological curvature. These are the so-called shock-absorbing curves of the spinal column. Due to their presence, heavy loads are absorbed and mechanical tension is distributed more evenly. With a properly functioning muscular frame of the spine, a person does not experience any problems with the musculoskeletal system.
But the difficulty lies in the fact that modern people lead a sedentary lifestyle. Their daily routine lacks regular physical activity, thanks to which the muscular frame works and retains its ability to provide complete diffuse nutrition to the cartilaginous tissues of large joints and intervertebral discs.
At first glance, it seems that only the lumbosacral spine can be connected to the hip joints. Indeed, the articular surfaces are located along the lateral projections of the sacrum. They form the sacroiliac joint. It is responsible for the direct attachment of the lower extremities to the spinal column or human body. Mechanical and shock-absorbing loads are transmitted to the iliosacral joints through the hip joints. Therefore, any deviation in the position of the femoral head in the acetabulum can lead to deformation of the iliosacral joint.
In fact, pathologies of the hip joint can provoke the development of degenerative dystrophic changes in the intervertebral cartilaginous discs along the entire length of the spine. Uneven distribution of the shock-absorbing load entails static overstrain of the paravertebral muscles. They block the process of diffuse nutrition of the cartilage tissue of the fibrous ring. This often leads to the appearance of characteristic signs of widespread polysegmental osteochondrosis.
If pain occurs in the trochanteric area of the hip joint or in the spine area, we recommend that you consult an orthopedist or vertebrologist as soon as possible. The causes of pain can be dangerous diseases that require immediate medical attention.
In Moscow, you can sign up for a free consultation with an orthopedist or vertebrologist at our manual therapy clinic. During the initial appointment, the doctor will conduct a full examination, make a preliminary diagnosis and give all the necessary recommendations for additional examination and treatment.
We treat
- Osteoarthritis of the hip joint
For normal joint function, you need to lead an active and healthy lifestyle. The muscles, ligaments of the hip joint and its other components need to be trained. Often you just need to do gymnastics. Take time for yourself. Be healthy!
The hip joint is one of the main elements of the human musculoskeletal system. It performs several functions - it serves as a support for the spine, upper and lower parts of the body, and provides freedom of movement. This connection of bones supports the weight of the entire torso, and when walking or running, the load on it increases to a ton. Degenerative diseases (coxarthrosis, osteoporosis, chondromatosis, synovitis, bursitis), injuries reduce mobility, cause severe pain, worsen the quality of life and can lead to disability. An effective, modern approach to the treatment of such pathologies is hip arthroscopy.
Indications for hip surgery
At the age of 30-40, diseases and injuries of the hip joints are found in 10% of people, by the age of 60 – in 70%. According to the doctor's indications, hip arthroscopy can be performed on patients of any age. The surgical technique has now been developed and today surgical treatment guarantees high efficiency.
Signs that indicate you need to see a doctor:
- pain in the hip joints, in the groin area, aggravated by walking and running;
- change in the shape of the joint, position of the lower limb;
- limited mobility, lameness, change in gait, feeling of stiffness;
- crunching, jamming during movements.
Hip arthroscopy is a surgery on the hip joint in which existing damage is repaired through micro-incisions in the tissue. The operation is performed using high-precision surgical instruments. The advantages of this type of treatment are low invasiveness, shorter rehabilitation period, complete restoration of mobility, low number of complications.
During surgical treatment using an arthroscope, the following procedures are performed on the hip joint:
- removal of osteophytes, bone growths;
- extraction of free bodies;
- elimination of damage to cartilage, synovium, labrum, ligaments;
- correction of the disturbed shape of the joint.
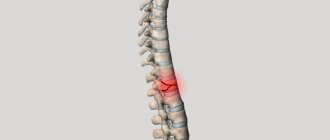
Spinal hernia and hip joint
A lumbar hernia of the spine has a negative effect on the hip joint. It provokes constant inflammation, which increases infiltrative swelling of the soft tissues and complicates the normal innervation of the lower extremities.
But a more serious effect is exerted by compensatory overstrain of muscle fibers in the lumbosacral spine. It causes severe curvature of the spine and disrupts natural posture. A person experiences a sharp change in the physiological curve in the lumbosacral region. As a result, the position of the femoral heads in the articular cavity changes and accelerated degeneration of the protective cartilaginous layer begins.
In patients with a herniated disc L5-S1, deforming osteoarthritis of the hip joint develops over the next 3 to 4 years. This is important to consider when carrying out complex treatment.
But there is also an inverse relationship. In some cases, lumbar intervertebral hernia occurs as a result of dysfunction of the hip joint. If a person has valgus or varus deformity of the lower extremities, or incorrect foot placement (flat feet or clubfoot), then he is highly likely to have abnormalities in the functioning of the hip joint of the bones.
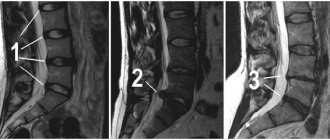
With sudden movements, such people run the risk of rupturing the fibrous ring of the intervertebral disc in the lumbar or lumbosacral spine. If characteristic pain appears, it is necessary to conduct an X-ray examination of the hip joints and an MRI of the lumbosacral spine.
Cost of hip arthroscopy
How much does hip joint treatment cost in Moscow? The costs of surgical treatment and subsequent rehabilitation depend on a number of factors:
- type of disease, its complexity, stage, degree of tissue damage;
- the presence of concomitant diseases;
- used diagnostic and treatment technologies, materials, medications;
- chosen rehabilitation technique;
- type of room, availability of additional services.
The costs of minimally invasive surgical interventions quickly pay for themselves due to the short recovery period and full restoration of mobility, allowing patients to return to normal activities. You can learn more about all the services of our clinic in the section COST OF TREATMENT
Treatment of the hip joint
If you are faced with the question of where to undergo hip joint treatment in Moscow, we offer comprehensive diagnostics and treatment of coxarthrosis, bursitis, dislocations, and fractures in a specialized clinic for sports traumatology and orthopedics. Our medical center implements effective techniques and offers affordable prices for hip arthroscopy.
For patients, the clinic has created:
- modern diagnostic tests;
- innovative treatment protocols;
- comfortable conditions of hospital stay;
- rehabilitation programs.
Patients are presented with two equally effective types of programs – “Premium” and “Economy”, differing in the type of hospital placement and degree of comfort. The key advantage of visiting the clinic is the low cost of hip arthroscopy and the high quality of the treatment provided in Moscow.
How to reduce the cost of fighting the disease?
Timely consultation with a doctor at an early stage of the disease, when the first symptoms appear, speeds up and simplifies treatment and rehabilitation. The sooner the fight against the disease begins, the better the result, the faster the recovery, the lower the costs of medical services. Consultation with a specialist will help you find the answer to all questions about the need and methods of surgical intervention. Our doctors will select an individual diagnostic program and surgical treatment method, taking into account only those procedures that are really necessary for the patient.
By entrusting your health to a specialized clinic for sports traumatology and orthopedics, you receive:
- the work of experienced doctors who have been trained in the methods of performing minimally invasive operations and are constantly improving their skills;
- excellent diagnostic and treatment facilities and modern equipment;
- comfortable conditions and individual approach;
- treatment in a clinic with an impeccable reputation;
- the best ratio of price and quality of services.
Problem markers
Listen to your body. Pain is always a signal of danger. Pay attention to such signals. Then you will have a much better chance of staying healthy and enjoying life!
The hip joint is a supporting joint and bears a significant load when walking, running, or lifting heavy objects. Due to the heavy load, it is quite often subject to various damages throughout a person’s life.
The main factors of pain can be injuries, congenital pathologies and defects, individual characteristics of the joint, and systemic chronic diseases.
Pain may appear due to inflammatory processes on the inner surface of the joint that occur when the joint wears out and the cartilage is depleted. The main problems that arise in the joint are associated with changes in the cartilage surfaces.
The most common diseases we encounter are deforming and post-traumatic arthrosis.
Deforming arthrosis, as a rule, occurs due to excess weight, hereditary factors, and age-related changes.
The impetus for the development of post-traumatic arthrosis is various injuries (most often they occur in road accidents): the occurrence of dislocations and displaced fractures.
The most common fractures are the femoral neck. Such a fracture usually occurs with a strong blow to the pelvis or hip. It is extremely dangerous in old age: as a result, a person’s activity and mobility can significantly decrease. A hip fracture is characterized by: pain in the groin area, which intensifies with movement of the injured leg; pain that occurs during axial load; shortening of the injured leg (within 2–4 cm).
In addition, as we age, our body wears out. And the older we get, the more our joints wear out.
Athletes' joints wear out faster due to excessive loads. Overuse injuries are injuries that develop gradually as a result of repeated overexertion or injury to an organ or area of the body.
Our task is to return the injured athlete back to action as quickly as possible.
Do not waste precious time - if you feel unwell, contact a specialist for help.
Don't waste your precious time
In advanced stages, the chances of a complete cure are significantly reduced. Be attentive to your health. If pain occurs, it is necessary to consult a doctor and, after the diagnosis has been completed, begin timely treatment.
Even when pain occurs, a person is not always in a hurry to see a doctor. He views the problem as a temporary nuisance rather than an actual injury. But if these “temporary troubles” are not cured, then over time the disease progresses and becomes chronic. Impaired gait, severe pain in the hip, pelvis, and sacrum become a constant source of discomfort and a painful ordeal.
Limitation of joint mobility forces you to give up an active lifestyle. In the fight for health, as in any fight, victory comes only to the strong. It is very important to monitor your weight. If you have gained excess weight, you should lose weight immediately. The greater the patient's body weight, the more difficult it is for him to stand on his feet.
Arthroscopy or endoprosthetics?
Each case is individual and requires its own approach. Contact a specialist in a timely manner to get diagnosed. Modern accurate diagnosis at an early stage will help you avoid the development of arthrosis, which subsequently leads to joint destruction and requires joint replacement.
Hip arthroscopy is a technologically more complex operation than, for example, knee arthroscopy. Therefore, not all clinics offer such a solution.
Each case is individual and requires its own approach. We deal with all problems of the hip joint and try to choose the minimum of all possible methods of surgical intervention, which will allow you to recover in a much shorter time.
The accumulated professional experience, special skills, and a high level of high-tech equipment allow us to carry out such operations and put people on their feet.
There are different indications for which we recommend arthroscopy. For example, to stop the development of arthrosis at the initial stage.
We perform such types of arthroscopic operations of the hip joint as suture of the cartilaginous labrum, removal of chondromic bodies; We also perform arthroscopy in case of impingement syndrome, in case of tendon damage, in case of damage to the cartilage of the femoral head and acetabulum.
In cases that are no longer amenable to non-surgical treatment, we offer joint replacement.
Cases from medical practice
People in trouble! Never despair, never give up, and never give up the fight for your health and happiness. Get strong! In the end, the disease will not survive - it will definitely recede.
Olga Petrova, 22 years old, professional athlete (tennis), hip arthroscopy
A young girl came to us with pain in the hip joint. The persistent pain made it impossible not only to continue playing tennis, but also to simply move normally: every step brought agony. Before Olga came to us, several clinics offered her only solution - joint replacement (endoprosthetics).
Who wants to walk with an artificial joint at a young age? Olga did not stop and began to look for another solution that was suitable for herself. Contacted us. We carried out serious diagnostics: MRI, 3D computed tomography, a series of x-rays. During the examination, they discovered the initial stage of arthrosis and came to a common decision - to perform arthroscopy of the hip joint. In our opinion, joint replacement was not required.
All possible materials and instruments that might be needed were prepared for the operation. We were even ready to transplant artificial cartilage onto the damaged part of the head. Fortunately, such a transplant was not required. During the operation, a small defect was discovered on the head of the femur, which we successfully eliminated. Microfracture and cold plasma treatment were performed, that is, we did everything necessary to improve blood circulation in the damaged area.
Immediately after the operation, a lasting positive result was visible - all pain in the hip joint disappeared. Being an athlete, Olga recovered quickly and very soon was able to return to an active life.
Alexey Bogachev, 38 years old, lawyer, arthroscopy of the hip joint
Twenty years ago, during a workout, Alexey felt a sharp pain and a click in the area of his right hip joint while doing stretches and doing the splits. And then the old injury made itself felt all the time - clicks were repeated at maximum flexion. Over time, they were joined by aching pains.
It was decided to perform an arthroscopy operation, during which we identified a defect in the cartilage and subchondral layer of the roof of the acetabulum with cartilage detachment, an osteochondral fragment fixed to the upper edge of the acetabulum. Shaving, cold plasma ablation of the damaged area of cartilage and removal of the osteochondral fragment were performed.
After the operation, Alexey quickly recovered, acting according to the doctors’ recommendations. From the 4th week it was already possible to exercise on an exercise bike and swim in the pool. The pain no longer bothered Alexei, and he was able to return to his previous lifestyle.
Femoral hernia in a child, symptoms, surgery and treatment in children.
Femoral hernia
A femoral hernia is a condition in which the abdominal organs (intestines, greater omentum) extend beyond the anterior abdominal wall through the femoral canal. Under normal conditions, the femoral canal does not exist. It is formed during the formation of a femoral hernia. Between the inguinal ligament (a connective tissue cord between the ilium and the pubis) and the pelvic bones there is a space containing vessels and nerves emerging from the pelvis and serving for blood supply and innervation of the lower limb. Next to the vein there is a gap that is filled with fairly loose connective tissue. This gap is called the femoral ring, through which, under certain conditions, the abdominal organs can emerge, i.e. femoral hernias form. The contents of the hernial sac are usually a loop of the small intestine, the omentum. Less commonly, the large intestine emerges into the hernial sac (on the right - cecum, on the left - sigmoid). Femoral hernias are rarely large and are prone to strangulation.
Femoral hernias are a fairly rare type of hernia that occurs in childhood. Relative to other hernias, femoral hernia accounts for only 5-8%. It is more common in girls due to the anatomical structure of the pelvis. Girls have a wider pelvis than men, which causes larger potential weak spots under the inguinal ligament and less strength of the connective tissue.
The required components of a true hernia are:
- hernial orifice - a natural or pathological opening in the muscular-connective tissue layer of the abdominal wall through which a hernial protrusion emerges.
- hernial sac - is a part of the parietal peritoneum that protrudes through the hernial orifice.
- the hernial contents of the sac are the internal organs located in the cavity of the hernial sac.
Any organ of the abdominal cavity can be in the hernial sac.
Most often it contains well-moving organs: the greater omentum, small intestine, sigmoid colon, appendix. Causes of femoral hernias .
There are predisposing and producing factors, the combined action of which leads to the formation of femoral hernias. Predisposing factors that weaken the abdominal wall include:
- hereditary weakness of the connective tissue of the abdominal wall in children of the first year of life
- degree of fatness (rapid weight loss)
- abdominal wall injury
- postoperative scars
- paralysis of the nerves innervating the abdominal wall
Producing factors are associated with increased intra-abdominal pressure:
- physical overexertion
- difficulty urinating
- constipation, prolonged cough
The effort that contributes to an increase in intra-abdominal pressure may be single and sudden (heavy lifting) or frequently repeated (cough).
Classification of femoral hernias .
There are many classifications of femoral hernias, but the division of hernias according to the possibility of reduction and strangulation is of particular importance for the choice of treatment method. Reducible hernias, in which the hernial contents can be easily reduced into the abdominal cavity. Irreversible hernias, which are only partially reduced or not reduced at all. Strangulated hernias. Strangulation should be understood as sudden compression of the hernial contents in the hernial orifice. It is especially important to distinguish strangulated hernias from irreducible ones, since strangulation threatens the development of acute intestinal obstruction, necrosis and gangrene of the intestine, peritonitis and requires emergency surgery.
Why are femoral hernias dangerous?
The most common and dangerous complication of a hernia is strangulation of its contents. Any organ located in the hernial sac can be subject to compression, but most often this occurs with a loop of the small intestine - with severe straining, coughing, after lifting heavy weights, etc., i.e. with significant tension in the abdominal muscles. Less commonly, compression of the hernial contents occurs in a narrow hernial sac or in the adhesions within it. Pathological changes in the restrained organ depend on the degree of compression and the period that has passed from its onset. The longer an organ remains infringed, the more pronounced the disturbances are. Therefore, after diagnosing a strangulated hernia, the main task is to quickly deliver the patient to a surgical hospital. Acute inflammation of the hernia is less common. It can be serous, purulent and putrefactive. The source of inflammation is most often the hernial contents: the intestine, the appendix, the uterine appendages, etc. Less commonly, the inflammatory process begins with the skin, and then moves to the hernial sac and its contents. Treatment of acute inflammation is only surgical.
Manifestations of a femoral hernia.
During the formation process, a femoral hernia goes through three stages: initial, canal and complete. In the initial stage, the hernial protrusion does not extend beyond the internal femoral ring. In the incomplete (canal) stage, the hernial protrusion is located near the vascular bundle and does not penetrate the subcutaneous tissue of the thigh. Identifying incipient and canal femoral hernias can be difficult. Such hernias can be suspected only on the basis of a child’s complaints of unpleasant sensations in the groin, lower abdomen, upper thigh, which intensifies with walking, physical activity, or changes in weather. But, at the same time, the child may not be bothered by anything, so often the resulting strangulation is the first clinical manifestation of such hernias.
In the full stage, the femoral hernia passes through the entire femoral canal and exits through its external opening under the skin of the thigh.
Characteristic clinical signs of a complete femoral hernia are a hernial protrusion in the area of the border between the groin and thigh in the form of a small hemispherical formation located under the inguinal ligament. A hernial protrusion appears with a vertical position of the body, straining, and disappears when repositioned, sometimes with a rumbling sound. A sign of a hernia is also the symptom of a cough impulse, which can be positive even in the initial form of a hernia.
The clinical picture of a strangulated hernia, both in the inguinal and femoral, is similar and is most often determined by which organ is strangulated. With a reducible hernia, the latter ceases to be reduced, the child is restless and complains of severe pain in the area of the hernial protrusion or in the entire abdomen. The protrusion increases, becomes tense, sharply painful when touched, mainly at the neck. Stool and gases are retained. At first the stomach is soft. Subsequently, as intestinal obstruction develops due to intestinal strangulation, the pain increases, becomes cramping in nature, nausea, hiccups, and repeated vomiting appear. With the development of peritonitis (inflammation of the peritoneum), bloating and muscle tension in the anterior abdominal wall appear. Sometimes the clinic is not so typical and symptoms may not appear for a long time. Therefore, the child’s parents need to be vigilant and, if any protrusion appears in the lower abdomen or upper thigh, immediately consult a doctor.
Diagnostic methods.
Diagnosis in the initial stages, due to the mild manifestations of the disease, presents certain difficulties. The study begins with a thorough interview of the parents, after which the child is examined. If necessary, in order to clarify the composition of the hernial sac, additional examination methods are carried out, such as ultrasound examination of the hernial protrusion, X-ray examination of the digestive tract, bladder, ovaries, to exclude the entry of these organs into the hernial sac.
Diagnosis of a strangulated hernia is usually simple. Difficulties arise with small parietal hernias, especially in obese patients. Careful examination of symptoms of peritoneal irritation in combination with local tenderness in the inguinal or femoral canal helps to make the correct diagnosis. If, upon examination of a child with an irreducible hernia, the slightest suspicion of strangulation arises, he should be immediately taken to a surgical hospital.
Treatment of femoral hernias.
Treatment of femoral hernias, due to their very frequent strangulation and lack of effect from drug therapy, is surgical. The operation is somewhat more difficult than for inguinal hernias. The essence of the operation for femoral hernias also consists in isolating, opening and removing the hernial sac, reducing its contents (most often it is a loop of intestine) and suturing the resulting defect.
There are several methods of surgical treatment of femoral hernias. The choice of one method or another depends on the type of femoral hernia and the choice of the surgeon himself.
The indication for surgery is an established diagnosis of a hernia and the child reaching the age of 1 year. In children under 1 year of age, repeated strangulations are indications for hernia repair.
The main purpose of the operation is the isolation and high excision of the hernial sac. It is most often performed in young children under general anesthesia, and in adults under local anesthesia.
Methods of surgical treatment:
- plastic surgery with local tissues - consists of suturing the defect of the femoral canal with a synthetic non-absorbable thread using the patient’s own tissues
- plastic surgery using synthetic prostheses (mesh) - in this case, the synthetic prosthesis can be placed preperitoneally, and the femoral canal is not sutured
Possible complications.
The fact is that in the inguinal canal in boys there passes the spermatic cord, the elements of which are a vein and an artery that supply the testicle, as well as the vas deferens. Compression of these elements during surgery can lead to the death of the testicle, and insufficient strengthening of the wall of the inguinal canal can lead to recurrence of the hernia. In girls, when isolating the hernial sac, it is imperative to release the round ligament of the uterus, damage to which can cause infertility. In rare cases, bleeding and suppuration of the postoperative wound may develop. The likelihood of these complications is minimized with the correct surgical technique and high skill of the surgeon.
Postoperative period, prognosis and prevention.
Hospitalization lasts on average 1-2 days, depending on the complexity of the situation. .
The prognosis is, in most cases, favorable. The patient returns to a full life.
Prevention of hernias in early childhood consists of preventing any increase in intra-abdominal pressure.
In this regard, tight swaddling, early vertical position, throwing the child up, prolonged coughing, etc. are harmful. In the future, you need to take care of strengthening the muscles of the anterior abdominal wall, which is facilitated by gymnastics, cycling, skating and skiing. Physical education and sports activities must be dosed, since overexertion leads to the opposite effect. author.Androdoctor.ru Go back