A herniated disc in the spine can be treated in any case. Our goal is to quickly relieve pain and save you from surgical treatment. We use everything that can help you: this is Karipazim, manual therapy and osteopathy, blockades, medications, gymnastics.
TREATMENT RESULTS – REDUCTION IN THE SIZE OF HERNIA
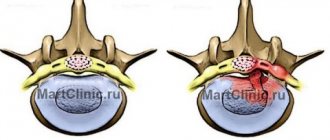
MRI of the lumbar spine, intervertebral disc herniation 1 – normal spinal discs 2 – L5-S1 disc herniation before treatment 3 – disc herniation, treatment (reduction of spinal disc herniation during treatment)
- Treatment of intervertebral disc herniation. How can we help you
- Why intervertebral disc damage occurs and pain occurs
- What is Spinal Protrusion and Intervertebral Disc Herniation
- What is Schmorl's hernia
- Read more about Karipazim and Karipain
- Surgical treatment, removal of disc herniation. When and how?
- Is it possible not to treat a herniated disc?
- Can a herniated disc be repaired?
Treatment of intervertebral disc herniation. How can we help you
| How to relieve pain from a vertebral hernia yourself - video tutorial from the Echinacea clinic. | Video about the treatment of spinal hernia with Karipazim - Echinacea clinic. |
Treatment of intervertebral hernia in our clinic will be structured as follows:
- Quickly relieve pain and stop the pressure of the hernia on the nerve root. If the root is compressed for a long time, there is a risk of its atrophy, and this is fraught with a long and even incomplete restoration of the functions of the muscles of the affected limb. The volume of the disc herniation and pain can be reduced within 1-2 days by reducing its edema and swelling . The method of treating intervertebral hernia in the acute stage is medications, pain blockades, IVs, treatment with position and rest.
- Unload the affected disk. This will allow you to move more freely and without risk, and the damaged disc will be able to gradually heal. Here, it is possible to fix the lower back with a belt/bandage, soft osteopathy or manual therapy on stiff areas of the spine (manipulation is not performed on the affected disc - this is dangerous), and gymnastics for unloading.
- Restoration of the nerve root after compression. The sooner we begin treatment, the faster the transmission of nerve signals along the spine will be restored. This results in a gradual reduction in pain, restoration of strength and sensitivity in the affected limb. For this purpose, we will offer you various nerve regeneration stimulants and B vitamins.
- Disc healing. A disc with a herniated spine heals in a unique way: the affected area grows with calcium compounds and becomes stronger. In this case, calcification of the herniated vertebral disc is the norm. Calcium deposition can be accelerated with the help of medications containing calcium, vitamin D and healing stimulants, chondroprotectors. To reduce the size of the hernia, if necessary, we will offer you Karipazim (Karipain) electrophoresis.
- Spinal mobility and cartilage nutrition. At the end of the acute period, we will offer you to take chondroprotectors on your own for several months. This will improve the general condition of the spine and joints.
- Return to active life and sports is usually possible after 4-12 months.
We will also teach you how to independently maintain your health and select an individual program for preventing the formation of intervertebral hernias, including a personal set of exercises that you can safely perform at home.
In what cases is surgical treatment required - removal of a herniated disc?
Medicines for the relief of acute back pain
These are medications such as nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), used intramuscularly for acute pain, centrally acting muscle relaxants, also used by injection, and local medications: gels, creams and ointments.
Narcotic analgesics are not used in our country for osteochondrosis. Such drugs are prescribed for oncological pathology, for example, with the development of metastases in the vertebrae. Even then, sometimes the patient cannot receive state-guaranteed care. If a doctor, seeing very severe pain, tries to help a patient in Russia by prescribing, for example, Durogesic in the form of a patch, then, unlike a doctor in the USA or Israel, what awaits him is not gratitude, but prison.
As a last resort, when the diagnosis is clear, confirmed by MRI, and the patient really has pain associated with a protrusion or hernia, a therapeutic blockade can be performed. But this manipulation is not performed at home, but in a hospital or treatment room. Let's look at the main groups of medications that help relieve pain in the first days of the onset or exacerbation of a protrusion or hernia.
NSAIDs: relieve pain and inflammation
Drugs from the group of NSAIDs, or nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, represent the “three pillars of the treatment of inflammation.” This is a decrease in body temperature, or an antipyretic effect, an analgesic effect, as well as an anti-inflammatory effect. We are not interested in the antipyretic effect, because with protrusions and hernias the body temperature does not rise, and paracetamol (Panadol) and other medications like ibuprofen (Nurofen) are not needed.
But the fight against pain and inflammation is what you need. The strongest analgesic effect of NSAIDs is the drug ketorolac (Ketanov), and in its strength it approaches the effect of narcotic analgesics. The anti-inflammatory effect, which consists in reducing edema, is expressed in drugs such as ketoprofen (Ketonal) and meloxicam (Oalis). The old drug diclofenac (Voltaren, Ortofen) has a very good anti-inflammatory effect. It can be used as a one-time injection, or in a very short course, no longer than 3 days.
We will not dwell in detail on dosages and administration regimens, since this is a matter for the attending physician. However, if the patient has a gastric ulcer or erosive gastritis, then drugs from the NSAID group are contraindicated for him. As a last resort, in the presence of gastritis and ulcers, you can simultaneously take these drugs along with proton pump blockers, such as Nolpaza, Omeprazole, Pariet. They protect the gastric mucosa from the destructive effects of NSAIDs.
After two to three days of intramuscular injections, they usually switch to tablet forms, which are also taken for several days. At the same time, from the very first day they begin rubbing ointments, creams and gels containing NSAIDs into the lumbar area. These are Fastum gel, Nurofen-gel, Dolgit-cream.
Attention! Warming ointments with capsaicin, for example, Capsicam, or Finalgon, can be used on the second or third day, when the pain has already begun to subside and the inflammatory edema has begun to resolve. On the first day, it is recommended to use ointments and gels with cooling, Deep Relief (ibuprofen + menthol), Ben-gay (methyl salicylate + menthol), or apply cooling and distracting essential oils to the lumbar area, for example, peppermint oil in a ratio of 1/10 s base oil.
Muscle relaxants: muscle relaxation
Unlike the relief of sharp and shooting pain, these medications are designed to relieve the persistent and aching pain component caused by excess muscle spasm. They cannot numb the very first, shooting pain. They were called centrally acting muscle relaxants because they regulate the functioning of spinal cord neurons and do not directly affect the muscle. They deceive her and allow her to relax. And this improves blood flow and allows you to eliminate the products of muscle metabolism. The most popular medications are Mydocalm, or tolperisone, and Sirdalud, or tizanidine. The first of them does not cause drowsiness, but the second is better taken at night or in the evening.
While taking muscle relaxants, it is better not to drive a car or work with moving machinery, since these drugs slightly increase the muscle reaction time. Muscle relaxants are also given intramuscularly during the first days of the disease, but they do not affect the gastric mucosa and can be prescribed as a course of therapy. As a result, chronic muscle spasm caused by protrusion and hernia is resolved, and persistent back pain also decreases or disappears.
Vitamins
The administration of B vitamins, or neurotropic vitamins, from the point of view of evidence-based medicine, does not affect the length of days of disability or the relief of pain. However, in the Russian Federation, doctors often use them for prophylactic purposes. Neurotropic vitamins are vitamins B1, B12 and B6, which take part in the functioning of the central and peripheral nervous system. Therefore, when there is swelling of the nerve roots, they are prescribed to create an excess depot, so to speak, just in case.
The most popular drug prescribed intramuscularly is Milgamma, which contains all these vitamin concentrates along with the local anesthetic lidocaine. He makes the injection painless. After a course of intramuscular injections, you can move on to the drug Milgamma compositum, this is a tablet drug.
Physiotherapy, exercise therapy and massage
All physiotherapeutic procedures associated with heat, mud therapy, balneological effects must be used outside the acute phase. Only then will physiotherapy, physical therapy and massage sessions have a beneficial effect. If you try to carry out a massage on the first or second day of acute back pain, it will only cause worsening, since the muscle is in a state of persistent spasm, and any shaking of the back will cause severe attacks of radicular pain. And standard massage techniques are not only relaxing, but also tonic. It is simply not appropriate to carry out one relaxing massage against the background of acute pain. Acute pain is a contraindication to any type of physiotherapy.
Why intervertebral disc damage occurs and pain occurs
Our spine is structured like a multi-storey building: from strong floors of the same type - vertebrae, connected to each other by elastic intervertebral discs. The intervertebral disc is a closed chamber consisting of an outer part - a very strong fibrous (fibrous) ring and a semi-liquid inner part - the pulpous nucleus. Each spinal disc is designed for a strictly defined volume and direction of movement.
If the volume or direction of the load on the disc is not adequate, overload and gradual destruction of the discs occurs - spinal osteochondrosis with protrusions and herniations of intervertebral discs. If a spinal hernia puts pressure on a nerve root, pain in the radicular syndrome develops. Overload of the intervertebral disc can last for years, and the “last straw” can be physical activity, awkward movement or even sneezing.
Common causes of disc overload and herniation:
1. Idle muscles and deviation of the center of gravity above or below the affected disc , curvature of the spine - scoliosis;
On the left – one of the muscles cannot maintain the correct position of the vertebrae. The load on the discs of the lumbar spine is distributed with a deviation from the normal axis and this over time can lead to a herniated disc in the lumbosacral region. On the right is the normal load distribution.
2. Stiffness of the vertebrae above and below transfers the load to a healthy area of the spine, where a hernia can form due to overload.
Left. The window cleaner is healthy. On right. The washer has poor movement of his right shoulder and thoracic vertebrae. Therefore, he is forced to make movements with his lower back. Overload in the lumbar spine results in a herniated disc causing damage to the sciatic nerve.
First aid for pain syndrome without drugs
Let's consider the principles of first aid, which can be carried out without taking medications and try to get rid of pain, and then - medications used in the first days, and even in the first hours after the onset of such acute pain.
Attention! You should be careful about one very common mistake. On the first day, and especially in the first hours, any warming up is strictly prohibited, and especially with the use of heating pads and physiotherapeutic devices that create excess heat. In the first day, swelling of the nerve roots and muscle tissue only increases, and an attempt to relieve pain by adding heat, according to the laws of physiology, only increases the blood flow to the area of inflammation, complementing and increasing the volume of hyperemia. Treatment of acute lower back pain in the first day with heat will only lead to increased pain.
Therefore, instead of intensive heating, you can, on the contrary, use cooling. If the patient does not have chronic inflammatory diseases of the kidneys or female genital organs, then an ice pack or some cold object can be applied to the lower back for a short time (5-10 minutes) several times a day through dense tissue. This will reduce swelling and relieve pain.
The second thing to do is to try to immobilize the patient by putting a semi-rigid corset on him. It will maintain the necessary distance between the lumbar vertebrae and reduce the risk of acute pain.
The third non-medicinal first aid method is the use of home physiotherapeutic devices, which do not heat, but distract and irritate. These are Lyapko and Kuznetsov applicators. The needles and thorns on which the patient lies, on the contrary, allow the volume of blood to flow from the area of inflammation into the subcutaneous tissue and deep layers of the skin. Thus, the pain syndrome is reduced, and the patient, at least while he lies still, experiences less discomfort. These simple remedies make it possible to alleviate the patient’s condition before using medications.
All other methods of treating acute lower back pain when protrusion and hernia occur or worsen are associated with the use of appropriate medications. Let's take a closer look at them.
What is Spinal Protrusion and Intervertebral Disc Herniation?
The discs, spinal cord and nerve roots are best seen on MRI scans . The condition of the disc and spinal cord can be judged only very roughly from ordinary x-rays.
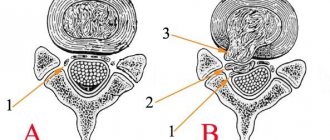
Intervertebral disc protrusion is a protrusion of the disc into the spinal canal of the spine without rupture of the fibrous ring. Typically, protrusions do not cause pinched nerves, but pain occurs in the intervertebral joints or back muscles. If left untreated, spinal protrusion can develop into a disc herniation.
1 – normal discs 2 – spinal cord from which the nerves exit 3 – disc herniation has compressed the spinal cord and the exit site of the nerve
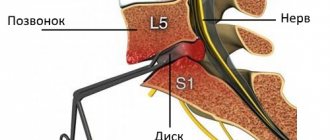
A herniated disc is accompanied by a rupture of the fibrous ring of the intervertebral disc, through which a fragment of the nucleus pulposus protrudes. A prolapsed disc fragment compresses the nerves (compression radicular syndrome), most often the sciatic nerve is affected, causing inflammation and swelling of the surrounding tissues, hence the pain and forced posture. Large herniated discs can compress the vessels or contents of the spinal canal and lead to paralysis of the lower half of the body, bladder and intestines.
The sciatic nerve is damaged more often than others because it begins in the lumbar spine, which is most susceptible to the formation of hernias. Inflammation of the sciatic nerve (sciatica) is manifested by pain from the buttock to the lower leg or foot, and a feeling of tension in the popliteal region. Severe lesions of the sciatic nerve are manifested by weakness (paresis) of the foot and loss of sensation in the leg. Read more about the sciatic nerve
How the disease develops
A herniated disc forms in four stages:
- Prolapse. A small fragment of the nucleus pulposus comes out of the disc, but the shell of the latter is not broken. This occurs due to impaired blood supply, dehydration and cracking of the shell. The patient feels pain after physical activity and gets tired quickly.
- Protrusion. Up to 16 mm of the nucleus pulposus extends beyond the annulus fibrosus. The blood supply to the disc is disrupted. The patient feels pain due to the fact that the core presses on the fibrous membrane. If it compresses the nerve, the patient feels numbness and coldness in the fingers, and their sensitivity decreases. Dizziness may also begin and the functioning of the pelvic organs may be disrupted.
- Extrusion. The nucleus pulposus came out of its place almost completely. The patient feels a sharp pain, his muscles turn to stone. Shooting sensations appear during physical overexertion, sudden movement, colds, stress or injury.
- Sequestration. The core fell out completely. The intervertebral disc pinches the nerve endings, and the patient feels pain constantly. The dropped nucleus dies and becomes inflamed. At this stage, a hernia can lead to failure of internal organs and deprive the patient of the ability to move independently. The consequences of delay may be irreversible.
What is Schmorl's hernia
When the nucleus pulposus of the vertebral disc moves up or down, penetrating the vertebral body, a Schmorl hernia occurs. Read more about Schmorl's hernias here
1 – Normal discs 2 – Schmorl’s hernia 3 – Schmorl’s hernia and wedge-shaped deformity of the vertebra.
The formation of a Schmorl's hernia is accompanied by inflammation , which leads to increased blood flow. The blood washes away calcium, the vertebra becomes softer and, under the influence of body weight, becomes deformed, forming a wedge-shaped deformity of the vertebra.
Most often, Schmorl's hernia occurs in the thoracic spine, less often in the lumbar spine. Then a kind of “chain reaction” of the degenerative-dystrophic process occurs: the part of the spine affected by Schmorl’s hernias becomes inactive and when moving, the vertebrae above and below work for it; due to this double load, after a few years, new hernias may appear in them disks. Damage to the intervertebral discs is caused by increased mechanical stress on the vertebrae. It is usually possible to stop this process with the help of exercises, osteopathic treatment and medications .
Prevention
To reduce the chances of a hernia, you need to monitor your lifestyle.
What to do first:
- stop smoking;
- reduce the amount of alcohol to a minimum;
- do stretching exercises every day;
- undergo a course of massage or manual therapy once every six months;
- avoid stress;
- sleep at least 7-8 hours;
- balance your diet.
A herniated disc is one of the most serious back diseases. You should not start it even if there are no unpleasant sensations - in the most severe cases, the disease can lead to disability.
Read more about Karipazim and Karipain
Video about the treatment of disc herniation with Karipazim
Karipazim (Karipain), administered by electrophoresis, affects the hernia itself. It begins to gradually decrease and releases the nerve ending that it pinches, and the pain in the spine gradually disappears. To a lesser extent, the medicine affects the entire intervertebral disc. The drug enhances the regeneration of disc tissue, which restores its normal shape and its function as a shock absorber, while “rejuvenating” as it were. Karipazim also affects several neighboring intervertebral discs, restoring the entire spine. Read more about Karipazim and Karipain here
Surgical treatment, removal of disc herniation. When and how?
In most cases, a herniated disc can be treated without surgery. Conservative treatment helps most of our patients. The indication for surgery is the presence of severe neurological disorders (paresis of the limbs, bladder, intestines) and there is a risk of developing irreversible changes in the spinal cord and its roots. In these cases, we will not take risks.
How surgical treatment and removal of a herniated disc are performed. There are several methods of surgical treatment of disc herniation. We recommend operations using endoscopic technology, which preserves all the bone structures of the spine. After such an operation, independent walking is allowed within 3-4 days, and further recovery is much faster.
If necessary, we will refer you to highly qualified neurosurgeons with whom we have been successfully cooperating for many years. In the future, we will provide you with postoperative rehabilitation and prevention of hernia recurrence. Recurrence of a disc herniation may be associated with its ongoing overload , so sessions of manual therapy and therapeutic exercises are necessary.
Treatment with drugs
After diagnosis, the patient is recommended to diet and maintain a healthy lifestyle, exercise therapy in combination with taking medications. Massage, manual therapy, and acupuncture are also recommended. Only the attending physician can prescribe medications after examination and a complete examination. Types of drug therapy:
- etiotropic;
- symptomatic;
- pathogenetic.
The patient is prescribed medications:
- to relieve inflammatory processes in the form of injections;
- to relax muscles to tone them;
- chondroprotectors in the form of intramuscular injections to restore the fibrous ring;
- vitamin complexes to improve metabolism in the body.
A correctly drawn up conservative treatment plan and strict compliance by the patient with the doctor’s instructions, as a rule, gives a positive result without the need for surgical intervention.