Sacroiliac arthrosis affects women to a greater extent, since the first pathological changes in the joints of the pelvic bones and spinal table begin during pregnancy. Neglecting the doctor’s recommendations about the need to use a prenatal bandage leads to the fact that the pelvic bones begin to diverge. This negatively affects the sacroiliac joint, which normally has minimal mobility.
At the initial stages of its development, arthrosis of the sacroiliac joints gives absolutely no clinical signs. Therefore, in most cases, patients seek medical help already in advanced cases of destruction of cartilage and bone tissue. Conservative treatment at stages 1 and 2 gives a positive result in the form of complete restoration of pathologically altered tissues. With arthrosis of the 3rd degree, when rough bone growths have formed on the articular surfaces, complete recovery can no longer be guaranteed. But with the help of manual therapy methods, the patient’s condition can be significantly alleviated, the destructive degenerative process can be stopped and the quality of life can be improved.
If you have arthrosis of the sacroiliac joints, we recommend that you sign up for a free consultation with a vertebrologist at our manual therapy clinic in Moscow. An experienced doctor will review the medical documentation (medical history, results of examinations) and give individual recommendations for treatment. The doctor will tell you about all the prospects and possibilities of using manual therapy techniques in your individual case.
What is arthrosis of the sacroiliac joints?
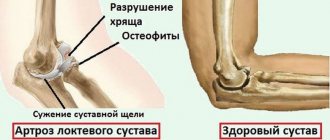
First, let's look at the question of what arthrosis of the sacroiliac joints is and why it develops. So, arthrosis is a degenerative dystrophic form of joint destruction with the formation of pathological tissue. For example, in the joint cavity, cartilaginous synovial tissue disintegrates and its place is taken by osteophytes, bone growths, which significantly complicate mobility and cause severe pain.
The main pathogenic cause is a violation of the anatomical structure, destructive external influences and a deficiency of diffuse nutrition of cartilaginous synovial tissue.
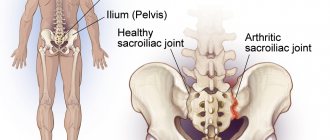
The sacroiliac joint is responsible for the movable connection of the pelvic bones and the spinal column. By the age of 25, each person's five sacral vertebrae transform into a single bone - the sacrum. Until this time, each sacral vertebra is separately attached to the ilium. Therefore, pregnancy and childbirth before the age of 25 do not cause destruction of this joint.
By the age of 25, the sacral vertebrae fuse together. Their lateral surfaces are transformed into a single surface, covered with a dense layer of hyaline cartilage. On the side of the ilium there is also an articular surface covered with synovial cartilage tissue. There are a large number of ligaments and tendons around the joint. Nutrition of cartilage tissue is carried out through diffuse exchange with the pelvic muscles. Therefore, with insufficient physical activity and leading a sedentary lifestyle with predominantly sedentary work, gradual degeneration of cartilage tissue occurs. It disintegrates, dehydrates and exposes areas of bone. When moving, the bone surfaces rub against each other. In places where they touch, chips and cracks form. They begin to fill with calcium salts. This is how rough bone growths are formed.
The main functions of the sacroiliac joint of the bones are as follows:
- shock-absorbing – participate in the uniform distribution of the mechanical load on the bones of the pelvic ring and the lumbosacral spine;
- stabilization – fix a certain position of the body in a sitting, standing and lying state;
- auxiliary - take part in bending the body forward and backward;
- provide vertical stability in a standing position.
The joint has low mobility. It is covered with a dense capsule of connective tissue. Inside there is synovial fluid. With enough of it, arthrosis does not develop. The amount of synovial fluid is replenished through diffuse exchange with muscle tissue located next to the joint. The moment they contract, fluid is released. They are absorbed by cartilage tissue and released into the joint capsule.
Physiotherapy
Daily gymnastics exercises are an excellent preventive measure. Physical therapy includes a variety of movements that involve the muscles of the lower back. This can be turning the torso to the right and left, rotating the torso clockwise and counterclockwise, bending forward, backward and to the sides. All movements should be performed at a slow pace, but with a large number of repetitions, listening to your own sensations.
Causes of arthrosis of the sacral spine
Deforming arthrosis of the sacroiliac joints often develops in fairly young women. In men, arthrosis of the sacral region can form under the influence of heavy physical activity. Often weightlifters and people engaged in physically demanding types of work (loaders, carpenters, builders, installers) suffer from this disease.
The main reasons for the development of arthrosis of the sacral spine are:
- overweight, alimentary type of visceral obesity with impaired pressure difference in the thoracic and abdominal cavities;
- heavy shock-absorbing loads falling on the area of the lumbosacral spine (lifting and carrying heavy objects);
- incorrect posture with flattening of the lumbar lordosis and worsening of the coccygeal kyphosis;
- destruction of the hip and knee joints, as a result of which the entire process of distribution of shock-absorbing load on the pelvic bones and lower part of the spine changes;
- injuries to the back, pelvic bones, hips;
- incorrect placement of the foot (clubfoot and flatfoot) - entails divergence of the pelvic bones under the influence of improper distribution of the shock-absorbing load;
- pregnancy complicated by a large fetus, multiple pregnancy and polyhydramnios, symphysitis, etc.;
- prolonged labor with a physiologically narrow pelvis;
- osteoporosis, osteomalacia against the background of menopause in women;
- leaching of calcium salts from bone tissue in pathologies of the large intestine, vitamin D deficiency in the human body;
- tumors of bone and cartilage tissue in the area of the sacroiliac joints of the bones;
- autoimmune and hormonal pathologies of various origins.
Identifying and eliminating the potential cause of the development of arthrosis of the iliococcygeus joint of the bones is the most important stage of future treatment. If you miss it, then no treatment, even the most effective, will completely get rid of this disease.
Prevention
To prevent this pathology, it is important to lead an active lifestyle. Eat a balanced diet to prevent excess weight gain. It is useful to do gymnastics every day to strengthen the muscles of the musculoskeletal system.
It is necessary to avoid bruises and injuries to the back, hips, and tailbone. Preventive measures include:
- Increasing the body's defenses;
- Timely disposal of infectious diseases;
- Refusal to lift heavy objects;
- If necessary, wearing a support bandage;
- Emotional relaxation;
- Complete cessation of bad habits.
Symptoms and signs of arthrosis of the sacroiliac joint
The first signs of arthrosis of the sacroiliac joints appear only at the second stage of the pathological process. At first the disease does not manifest itself. Gradually developing, it destroys the inner cartilaginous layer, which protects bone tissue from destruction and deformation.
Clinical manifestations may be vague, resembling lumbosacral osteochondrosis. At first, the pain is not acute. Women experience nagging pain in the lower back during menstruation. They can radiate to the groin area or leg. Then, stiffness will gradually develop in the morning. As the disease progresses, stiffness will persist throughout the day.
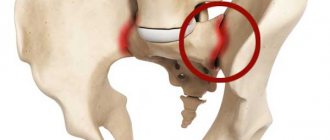
Symptoms of sacroiliac arthrosis, such as crunching and clicking when bending forward, indicate that the patient is already developing the second stage of the pathology. It is necessary to urgently seek medical help. At this stage, successful conservative treatment is still possible.
Clinical symptoms of arthrosis of the sacroiliac joints may include:
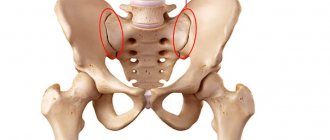
- pain that is localized in the area of the sacrum and coccyx (intensifies when walking and while sitting, decreases when lying on the back);
- with an exacerbation of the inflammatory process in the joint area, swelling and redness of the skin appears;
- spread of pain in the groin area and along the outer surface of the thigh and lower leg;
- morning stiffness that lasts longer and longer as the disease progresses;
- spasm and excessive muscle tension in the pelvic and thigh areas;
- crepitating crunching and clicking sounds when bending and lifting the body;
- gradually increasing lameness that occurs after prolonged sitting on a hard surface.
When carrying out differential diagnosis, first of all, ankylosing spondylitis, lumbosacral osteochondrosis, L5-S1 intervertebral load, disc protrusion and extrusion, spinal canal stenosis, piriformis muscle syndrome, etc. are excluded.
To exclude rheumatic processes (ankylosing spondylitis, systemic lupus erythematosus, scleroderma, rheumatoid polyarthritis), a blood test is performed for rheumatoid tests. In the absence of these diseases, it is negative. To exclude gout, a biochemical blood test is performed to determine the level of uric acid.
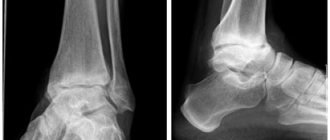
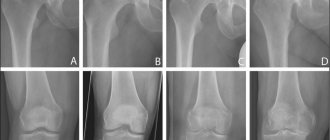
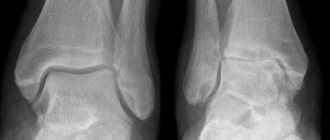
Arthrosis of the sacroiliac joints can be diagnosed using an X-ray, CT or MRI examination. The photographs show a narrowing of the joint space. In the third degree of development of the disease, osteophytes and thinning of the cartilaginous synovial layer are determined.
Professional diagnostics
Arthrosis of the sacrococcygeal joint can be accompanied by different symptoms, therefore, to differentiate this disease from other diseases that have a similar clinical picture, a medical examination is necessary. During the initial examination of the patient, the specialist palpates the inflamed area where discomfort is noted. During the examination, muscle tone is checked and the location of greatest pain is determined.
The patient is also prescribed:
- Radiography;
- MRI;
- CT.
The specialist directs the patient to undergo a biochemical blood test to determine how elevated the ESR level is. Sick women are recommended to be examined by a gynecologist, since pain can be caused by other diseases of the reproductive system. Using radiography, they determine the condition of the bone elements, whether they are deformed, whether there are internal injuries, or changes in the width of the lumen of the cracks. MRI and CT help to identify tumor processes (benign formations and oncology), soft tissue growths, as well as their damage.
Degrees and stages of development of arthrosis of the sacroiliac joint
There are 4 degrees of arthrosis of the sacroiliac joints:
- The first is characterized by a complete absence of clinical manifestations; the X-ray image shows a narrowing of the joint space;
- 2nd – vague pain appears, slight stiffness of movements appears, the X-ray image shows partial contact of the bone articular surfaces;
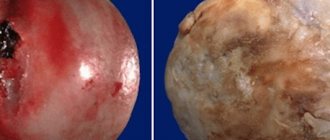
- 3rd – osteophytes are formed, the cartilage tissue is completely deformed, exposing the bone surfaces;
- 4th – complete stiffness, constant pain, strong crunching noise when moving.
Only grade 2 arthrosis of the sacroiliac joints can be successfully treated without surgery; when moving to grade 3, it is impossible to guarantee a positive, sustainable result. Advanced arthrosis of the sacroiliac joint at stage 4 can lead to disability and a complete lack of mobility.
Etiology
It is often difficult to determine what caused the joint damage.
On March 15-20, a seminar by Georgy Temichev “RehabTeam. Block_1 (Lumbar, Thoracic, Pelvis).” Find out more...
- One of the most common causes of problems in the SIJ is injury. The force from this type of injury can damage the ligaments around the joint. A tear in these ligaments is characterized by too much movement in the joint, and over time this can lead to degenerative arthritis.
- Pain may also be caused by an abnormality of the sacrum, which can be seen on x-rays.
- Pregnant women are more likely to develop SIJ syndrome. Female hormones are released during pregnancy, relaxing the sacroiliac ligaments. This stretching causes changes in the SIJ, making it hypermobile. After the fifth decade of life, the SIJ grows together.
Treatment of arthrosis of the sacroiliac joints
Arthrosis of the sacroiliac joints can be treated using conservative and surgical methods. In the early stages, manual therapy methods give positive results. When visiting our clinic with the second stage of pathology, patients fully recover and restore their health. In the third stage, we can help stop the destruction of joints and partially restore mobility and relieve pain. However, it is no longer possible to hope that the damaged cartilaginous synovial tissue will be restored. With stage 4 arthrosis, we will not be able to provide any significant assistance. In such patients, surgical intervention for plastic surgery of the iliosacral joint of the bones is recommended.
We use the following methods to treat arthrosis of the sacral spine:
- laser exposure to start the process of regeneration of damaged cartilage tissue;
- massage and osteopathy - to accelerate the processes of microcirculation of blood and lymphatic fluid, improve the diffuse nutrition of cartilage tissue;
- kinesiotherapy and therapeutic exercises - to increase the tone of muscle tissue;
- reflexology – to influence biologically active points on the human body;
- physiotherapy and much more.
You can make an appointment for a free appointment with a vertebrologist or orthopedist at our manual therapy clinic in Moscow. An experienced doctor, after conducting an examination and reviewing the examination results, will be able to tell you about the possibilities and prospects for using manual therapy techniques in your individual case.
Therapy
Treatment of SIJ arthrosis is carried out in several directions. To achieve the necessary dynamics, the attending physician prescribes all available options for conservative therapy.
To relieve the inflammatory focus and begin the recovery reaction in the diseased joint, the following groups of drugs are used:
- Corticosteroids;
- Analgesics;
- Hormonal agents with anti-inflammatory effects;
- Glucocorticosteroids;
- Chondoprotectors;
- Vitamin complexes;
- Food mineral supplements.
The drugs are used in the following forms:
- Pills;
- Injections;
- Ointments;
- Warming patches.
At the time of severe symptoms of arthrosis of the coccygeal joint, a joint block is performed. To quickly relieve pain, injections of anesthetic medication are used. In case of purulent pathology of adjacent tissues, specialists prescribe antibacterial agents that belong to the penicillin group.
To eliminate inflammation, the patient is recommended to take a course of corticosteroids. They are prescribed in the form of injections or in the form of topical medications. These include Dikloberl and Diclofenac, Ketorolac and Indomethacin. In case of severe pain attacks, drug blockade is carried out using Lidocaine, Kenalog, Hydrocortisone, Diprospan.
The administration of chondroprotectors solves the problem of restoring cartilage in the joint. The preparations contain chondroitin and hyaluronic acid, which trigger the regeneration mechanism of inflamed cartilage tissues, restoring their smoothness, firmness and elasticity.
Gels and ointments are used in the treatment of pathology. They help eliminate pain by significantly warming up the muscles in the joint area. Pharmaceutical drugs are divided into 2 types:
- Warming medicines based on red pepper along with snake or bee venom;
- Anti-inflammatory pain relieving ointments.