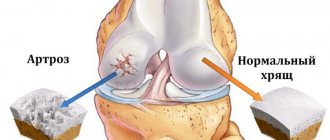
Gouty arthrosis is considered one of the most severe secondary joint lesions. Being a very specific process, it is characterized by a long and severe course. Destructive-dystrophic changes can cause loss of performance and disability. In combination with the deposition of uric acid salts, they cause rapid destruction of bone tissue.
What is gouty arthrosis
Gout is a form of arthritis caused by a disorder of purine metabolism and the accumulation of urate crystals in one or more joints, usually the first toe. The disease can develop independently or in combination with deforming osteoarthritis.
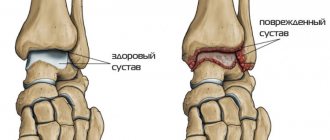
In the gouty course of arthrosis, not only cartilage is involved in the pathological process, but also the subchondral portion of the bone, capsule, ligaments, inner layer of the joint capsule and periarticular tissues. Deposits of monosodium urates in joints and cartilage lead to acute pain and inflammation unusual for osteoarthritis.
The disease most often affects small joints of the hand, first toe, joints of the vertebral and cervical segments of the spine, knees and pelvis.
According to the ICD-10 code, gouty arthrosis is classified as class XIII with the wording: “Diseases of the musculoskeletal system and connective tissue.
How does gouty arthritis occur?
The disease occurs due to increased levels of uric acid in the blood.
This happens in two cases. In the first case, the body produces too much uric acid, and the kidneys do not have time to remove it. In the second case, the amount of uric acid is normal, but the kidneys cannot cope with their function. When the concentration of uric acid in the blood exceeds the permissible level, its salts in the form of crystals are deposited in the joints and organs. This destroys the joint. Gouty arthritis affects the joints of the fingers, hands, elbows, knees, and feet. Most often, the disease affects the toes.
Characteristic symptoms
The development of gouty arthrosis is usually rapid, sudden and acute, with the rapid formation of irreversible destruction in cartilage tissue. This type of osteoarthritis can cause multiple lesions of the joints, which significantly worsens the patient’s condition, leading to loss of mobility and rapid disability.
The gouty form of arthrosis is not a disease of cartilage tissue only. The deposition of monosodium urate crystals in soft structures and organs forms a complete symptom complex of the lesion, which also includes extra-articular manifestations.
The clinical picture of the disease includes the following symptoms:
- severe discomfort when walking and at rest;
- morning stiffness;
- deformation and decreased functionality of the joint;
- growth of tophi;
- swelling, redness and glossiness of the skin over the joint;
- accumulation of urate in the renal tubules with the formation of urolithiasis.
In addition, the gouty course of arthrosis manifests itself in sudden attacks with acute pain and swelling in the area of the first toe or other joint. A gouty attack is accompanied by chills, fever, and local hyperthermia.
Representatives of the fair sex tolerate the disease much easier than men. In women, pain during an acute attack is not as pronounced and tophi appear less frequently.
Osteoporosis
Source of the problem . Osteoporosis is a systemic disease associated with a decrease in bone density, which often leads to fractures (including the femoral neck), disability and even death of the patient. Moreover, arthrosis and osteoporosis are often combined with each other in older people.
Symptoms . For the time being, osteoporosis may not manifest itself in any way. A person can consider himself healthy for decades and not even be aware of the problem. An indirect manifestation of the disease are fractures with a low level of injury (falling from your height, awkward movement) and a decrease in height by more than 2 cm per year or by 4 cm compared to the height you had in your youth, which may indicate compression fracture of the vertebral bodies, which most often goes unnoticed by the patient.
Treatment . With osteoporosis, as a rule, there is a deficiency of calcium and vitamin D, which is necessary for its absorption. This deficiency can be compensated by taking vitamin D, as well as by eating a diet high in dairy products, fish, organ meats, nuts, cabbage, raisins, and prunes.
When osteoporosis is combined with osteoarthritis, you cannot do without taking chondroprotectors.
Question answer
Why is gout a disease of kings?
Causes
The main cause of gouty arthrosis is considered to be deterioration in the nutrition of the joint capsule and cartilage tissue as a result of blockage of blood vessels with urate salts. This provokes a pronounced inflammatory reaction with rapid progression of destructive changes.
Degenerative changes in cartilage tissue are typical for men over 40 years of age and postmenopausal women.
A distinctive feature of the disease is the complete lack of connection between the exacerbation of symptoms and excessive physical activity or injury to the joint. The provoking factor in this case is poor nutrition with a predominance of protein foods and alcohol.
Types of disease
Depending on the clinical symptoms, several options for damage are considered:
- Gonarthrosis.
- Coxarthrosis.
- Intervertebral osteochondrosis.
- Disease of the distal interphalangeal joints.
- Spondylosis.
Gonarthrosis affects the knee joints and occurs equally often in men and women. It manifests itself as painful bending of the legs caused by ulceration of the synovial membrane and its swelling.
Coxarthrosis is more often diagnosed in women. It is characterized by the appearance of a duck's gait, the inability to lie on one's side, pain in the groin, perineum and buttocks. With age, symptoms increase noticeably.
The gouty form of arthrosis of the interphalangeal joints leads to curvature of the fingers, limited mobility, and frequent subluxations, with 1 metatarsophalangeal joint of the foot most often affected.
With spondylosis deformans, deterioration in cartilage nutrition leads to destruction of the vertebrae and the growth of marginal osteophytes. Osteochondrosis is often combined with disc degeneration.
Why is gouty arthritis dangerous?
Without proper treatment, gouty arthritis becomes chronic. Chronic gout disrupts the functioning of the kidneys and bladder, causing kidney stones and gouty nephritis. Attacks of the disease are repeated more and more frequently and involve new joints.
When tophi form, the body perceives them as a foreign body that needs to be fought. As a result, the number of leukocytes in the body increases and inflammation begins.
Gout without treatment leads to urolithiasis. Kidney stones are formed from crystallized uric acid. They can cause kidney failure and death.
Diagnostic procedures
Detecting gouty joint destruction is not difficult. The combination of a high concentration of urates in the blood with the typical symptoms of arthrosis and X-ray data does not allow us to doubt the nature of the disease.
The basis for diagnosing gouty arthrosis is the detection of urate crystals in the synovium. To confirm the diagnosis, additional studies of synovial fluid and the contents of tophi are prescribed.
X-ray examination data allows us to identify joint deformities typical of gout and osteoarthritis, determine the presence of marginal defects and tophi, and atrophy of bone joints.
Classic methods of treatment
Therapy for the gouty form of osteoarthritis can be successful only if the level of uric acid salts in the body is normalized. The leading principles of treatment include the use of basic and symptomatic remedies, physiotherapy, balanced nutrition and orthopedic control.
Drug treatment
The basis of treatment for urate arthrosis is Allopurinol.
The basis of drug therapy for urate arthrosis is anti-gout drugs:
- uricostatics - Allopurinol, Febuxostat;
- uricosuric drugs - Probenecid, Benzbromarone, Sulfinpyrazone.
Complex treatment of gouty arthrosis often includes alkalizing medications and solutions that reduce the risk of developing renal nephropathy. These include Uralit, Blemaren, Magurlit.
Herbal medicines are very effective for this form of the disease: Urolesan, Phytolysin, knotweed herb, Avisan, Lespenefril, Olimethin. They not only have a mild anti-gout effect, but also have a moderate anti-inflammatory and analgesic effect.
For clinical manifestations of gout, NSAIDs (Indomethacin, Diclofenac, Ortofen, Nise) and Colchicine are used. Severe symptoms of arthritis are relieved by external means
- Bishofite-gel;
- Nimulid;
- Dolgit;
- Dicloran plus;
- Finalgon;
- Dolobene.
In the phase of early pain, when arthrosis can be complicated by inflammation of the synovial membrane, intra-articular administration of hormones - Hydrocortisone, Triamcinolone, Diprospan - or solutions of hyaluronic acid is used.
Chondroprotectors (glucosamine and chondroitin sulfate) will help stop the destruction of joints.
Surgery for gouty arthrosis is rarely resorted to, unless significant joint destruction has occurred due to lack of treatment. Sometimes surgery is required to remove overgrown tophi.
Physiotherapy
Physiotherapeutic treatment provides a good analgesic and anti-inflammatory effect for osteoarthritis. Patients suffering from salt deposits and destructive changes in joints are well helped by:
- laser therapy;
- exposure to ultra-high frequencies;
- electrophoresis;
- magnetotherapy.
For quick rehabilitation of patients, sanatorium-resort treatment in the health resorts of Krasnodar, Pyatigorsk, and Belokurikha is ideal. Medical institutions offer complex therapy, including the effects of mineral baths, therapeutic mud, exercise therapy, massage and nutrition.
Diet therapy
The correct diet for gouty arthrosis should be determined by the concomitant illness. Patients should completely avoid offal, lamb, caviar, fatty fish, chocolate and other delicacies, cocoa, alcoholic beverages, black tea and carbonated water.
The diet for joint diseases should be as close to vegetarian as possible.
It is recommended to include more vegetables and fruits, grains, lactic acid products and light soups in your diet. It is necessary to maintain a drinking regime, consuming at least 2–2.3 liters of clean liquid per day. Alkaline mineral water, sugar-free compote, cranberry or lingonberry juice, and oatmeal jelly are perfect.
Treatment with traditional methods
Folk remedies cannot save you from degenerative destruction, but they can improve the breakdown of urate crystals and speed up excretion.
Recipes for infusions and decoctions to eliminate signs of gouty arthrosis
Garlic juice will help get rid of painful symptoms and relieve inflammation. Freshly squeezed concentrate is taken 3-4 times a day, washed down with hot milk and honey.
A tincture of 5 heads of garlic and ½ liter of vodka can help relieve pain. The composition is kept in a dark place for 7 days and consumed 1 tsp. before eating. This treatment is not suitable for people suffering from gastrointestinal diseases.
A decoction of barberry berries is good for removing salts from the body. It is prepared from 20 g of fruit and 250 ml of liquid. Leave it for a day and drink it like tea.
To prepare medicinal infusions, you can use horsetail herb, angelica root, St. John's wort, and string. A spoonful of dry raw materials is poured with 200 ml of boiling water, infused and consumed warm 2-3 times a day.
An old Russian recipe will help you cope with gouty pain: drink a hot potato decoction every morning on an empty stomach. Some herbalists recommend eating a raw vegetable, grated along with the peel, additionally during the day.
Baths, lotions and homemade ointments
For local treatment of diseased joints, all kinds of homemade creams and rubs are used. For example, ointment from fresh poplar or birch buds, ground with unsalted lard, is excellent at drawing out salts.
Pure fir oil, which is rubbed into the affected area after a hot bath with soda or sea salt, effectively relieves inflammation and warms tissues. For the same purpose, a composition of a piece of camphor, turpentine, unrefined oil and alcohol is used. Shake the solution before use. Rub into the inflamed area before bed and wrap well.
To reduce pain and swelling, apply a rub of henbane infused with sunflower oil. Use it during the day and at night.
Arthritis
Source of the problem . Unlike arthrosis, which is a degenerative disease (also called cartilage wear disease), arthritis is an inflammatory disease associated either with a malfunction of the immune system (rheumatoid arthritis) or with a previous infection - genitourinary, intestinal (reactive arthritis) or other reasons. Moreover, if arthrosis most often affects the joints of the legs (hip, knee) and spine, which bear the maximum load, rheumatoid arthritis affects the joints of the hands, feet, wrists, as well as the elbow and knee joints (usually symmetrically). With reactive arthritis, joint inflammation is often asymmetrical.
Article on the topic Rescue for joints.
What diet is indicated for arthritis Symptoms .
With arthrosis, pain in the affected joint is initially periodic, for example, it occurs after loading the joint: when walking, squatting, when going down or up stairs. Moreover, it often has a starting character (occurs at the beginning of walking). As the disease progresses, the pain becomes chronic, occurring not only when moving, but also at night. The joint gradually deforms, its function is impaired, significantly limiting human activity. Arthritis is more characterized by an acute onset of the disease - with sharp pain, swelling, redness of the skin around the affected joint, and increased temperature.
Treatment . The basis of treatment for osteoarthritis is an integrated approach using non-drug and drug treatment methods. As a basic treatment, the use of chondroprotectors (biological drugs that affect the very nature of arthrosis and promote better nutrition of cartilage) is indicated. It has been proven that a course of taking chondroprotectors can reduce pain and improve joint function. Anti-inflammatory and hormonal drugs in the case of arthrosis are used mainly during an exacerbation of the disease.
If you have rheumatoid or other inflammatory arthritis, you cannot do without long-term use of anti-inflammatory drugs.
Article on the topic
A silent epidemic. Who is at risk for osteoporosis?
Gouty arthropathy
Gouty arthropathy as a symptom can occur with joint diseases of various etiologies. The malaise completely depends on the course of the underlying illness and manifests itself as arthralgia - pain in the joints of a volatile nature.
Arthropathy manifests itself as fleeting pain and disappears immediately after the underlying disease is eliminated. The pathological condition can occur in the early stages of gouty arthrosis, even before objective signs of joint destruction.
It is necessary to distinguish gouty arthropathy from ordinary arthritis. A clinical blood test, fluoroscopy and polarization microscopy will help to cope with this difficult task. An appropriate diagnosis is made if articular and extra-articular symptoms do not meet the diagnostic criteria for arthritis.
External manifestations of arthropathy due to gout are the frequency of acute attacks, the presence of tophi, and damage to the big toe. In the area of the diseased joint there is always a disturbance of sensitivity similar to dissociative anesthesia.