Cervicobrachial syndrome is pain in combination with neurological clinical symptoms that occurs against the background of cervical and cervicothoracic osteochondrosis. The muscles of the shoulders, shoulder girdles and free upper limbs are captured. The pain spreads to the fingers.
When symptoms of cervicobrachial syndrome appear, treatment should begin with the elimination of pathological degenerations in the area of intervertebral discs. The brachial plexus is responsible for the innervation of the muscles in this area. It is formed from branches of the radicular nerves extending from the 4th, 5th, 6th, 7th cervical and 1st thoracic vertebrae. The nerves responsible for the innervation of the shoulders, shoulder girdles and upper extremities depart from the plexus. The area of their innervation includes ensuring contractile activity of muscles and sensitivity of the skin.
The brachial plexus is divided into subclavian and supraclavicular branches. The first one goes to the armpit area, and the second one goes to the triangle in the neck area. As they move away from the plexus, the branches break up into trunks and branches.
As it develops, cervicobrachial osteochondrosis provokes compression of the radicular nerves, which form a plexus or pinching of branches extending from it due to statistical compensatory muscle tension in the neck and collar area.
Cervicobrachialgia can occur spontaneously or against the background of exacerbation of cervicothoracic osteochondrosis of the spine. This condition is characterized by:
- static muscle strain in the neck, collar area, shoulder girdle;
- compensatory tension of the tendon and ligamentous tissue, resulting in secondary compression of the radicular nerves;
- inflammatory swelling of soft tissues with increased blood supply to the area of the affected paravertebral tissue;
- pinching of the ulnar, radial, or median nerve leads to numbness of the fingers and weakening of muscle strength.
The appearance of a complex of inflammatory and neurological syndromes during the development of degenerative dystrophic disease of the intervertebral discs is due to a sharp decrease in their height and subsequent destructive processes. Nerve fibers can be affected in different areas, from the foramen in the vertebral bodies to tunnels deep in the muscle fibers.
At the initial stage, patients note discomfort in the shoulders and forearms after a day of work. Then persistent pain develops in the muscles of the collar area and shoulder girdle. The muscles are overstrained, spasmed and do not relax without outside intervention. This may be a consequence of compensatory tension in order to remove pressure from the nerve fiber or the result of inflammatory infiltrative edema against the background of increased blood microcirculation along the capillary bed. As pathological changes develop, pain spreads throughout the upper free limb.
In most cases, the syndrome is diagnosed in young active people aged 30 to 45 years. In later life, cervical-brachial syndrome rarely develops fully. More often, degenerative processes occur in the area of the glenohumeral joint of the bones.
If the symptoms described in the article appear, you should immediately consult a neurologist or vertebrologist. In Moscow, you can make an appointment at our manual therapy clinic. The initial consultation for each patient is completely free. During the appointment, the doctor conducts an examination and manual examination, as well as functional diagnostic tests. This allows him to make a preliminary diagnosis and recommend a plan for further examination. Individual recommendations for complex treatment are also provided.
Causes of back and shoulder pain
More often, pain in the neck and shoulders is a sign of diseases of the musculoskeletal system, which are accompanied by damage to tendons, cartilage and joints, as well as inflammation and pinched nerve roots.
Mechanical damage to musculoskeletal, ligamentous, and nerve structures is the main cause of pain.
The neck-shoulder region is the most mobile. It bears significant loads, even when left in a static position for a long time. This part of the spine is susceptible to the following diseases:
- arthritis or arthrosis of the shoulder joint, glenohumeral periarthritis or periarthrosis, tendinitis;
- cervical osteochondrosis, spondylosis;
- osteoporosis;
- scoliosis;
- intervertebral hernia;
- myositis;
- plexitis;
- tumor neoplasms in the cervical-brachial region.
The shoulder often hurts due to damage to the rotator cuff muscles. The pain in this case is localized directly in the shoulder joint. It becomes aching or dull in nature, radiating to the arm above the elbow.
Predisposing factors for the occurrence of diseases of the musculoskeletal system, and, accordingly, back pain in the shoulder area include:
- Injuries to joints, bones, ligaments, muscles. “Fresh” injuries are accompanied by severe pain, but those suffered in the past, especially if they were not treated, make themselves felt as chronic pain. Athletes often experience back shoulder pain after a tendon sprain or rupture.
- Sedentary lifestyle. Physical inactivity leads to weakening of the muscle corset and problems with the spine, shoulders and neck.
- Excessive physical activity. Excessive loads, like physical inactivity, are harmful to the spine and muscles. They carry a high risk of injury. Swimmers, bodybuilders, and athletes involved in contact combat and weightlifting are at risk.
- Excess weight. The more extra pounds you carry, the greater the strain on your neck and shoulders. Fat does not hold the spine in the correct position, but rather acts as additional ballast. You need to build muscle mass.
- Incorrect posture or prolonged heavy load on one side. An uneven load on the spine is fraught not only with scoliosis, but also with deformation of the vertebrae and inflammation of the nerve fibers.
Back pain that radiates to the shoulder can occur not only in an athlete, but also in an ordinary person, since the glenohumeral region is vulnerable to damage to the ligamentous-muscular system. The pain syndrome can be one- or two-sided, sometimes radiating to the arm and chest.
Let's look at the main causes of pain in the neck and shoulder joint, which a doctor most often encounters.
Osteochondrosis or spondylosis
These diseases are accompanied by pathological changes in the spine, which disrupts the functioning of the nerves. The intensity of pain depends on the severity of degenerative processes. At first it is aching and moderate. Without treatment, it becomes acute, can spread to the hand, and cause numbness in the fingers.
Osteochondrosis and spondylosis have a similar cervical pain syndrome and may be accompanied by headache, dizziness, increased blood and intracranial pressure
Periarthritis
Humeral periarthritis is also called “frozen shoulder” syndrome, since the disease has severe symptoms:
- severe pain in the right or left shoulder, which radiates to the neck, intensifies when moving the head;
- increase in pain at night;
- stiffness and limited mobility in the cervical region and upper back.
Unlike arthritis, periarthritis causes inflammation of the soft tissues that surround the joint: the joint capsule, ligaments, tendons and muscles. As a result of the inflammatory process, pain occurs and shoulder mobility is impaired.
Subacute periarthritis is not always accompanied by pronounced symptoms. Sometimes its existence may be indicated by an occasional aching pain between the neck and shoulder.
Note! Humeral periarthritis occupies a leading place among the causes of pain in the neck and shoulder joint.
Neuroma (schwannoma) of the spine
This neoplasm is benign. It is located in the trunk of the brachial plexus, and as it increases in size, it causes pain between the neck and shoulder. Most often, the pain is acute and occurs when the tumor comes into contact with the vertebral body.
Neuroma develops from Schwann cells of nervous tissue
Plexit
It is a neurological disease of an inflammatory nature. With plexitis, various large nerve plexuses can be affected, but the shoulder girdle and cervical region are most often affected. The disease can be recognized by acute pain and muscle weakness.
With cervical plexitis, the phrenic nerve may become inflamed. As a result, accompanying symptoms appear in the form of breathing problems and hiccups. Brachial plexitis may be accompanied by a decrease in the sensitivity of the extremities; the hands often become numb and cold to the touch.
Myalgia (myositis)
Muscle pain in the shoulder and upper back area is often due to muscle spasm or inflammation. Hypothermia, infections, excessive physical exertion, sudden movements, osteochondrosis, intervertebral hernia and other diseases can contribute to the appearance of myositis.
Myositis of the neck or shoulder must be treated promptly, since other muscle groups may be involved in the inflammatory process
With myositis, the pain is acute and severe and does not go away even at rest. The affected area turns red and the local temperature rises. Headache, dizziness, and general deterioration of health are not uncommon.
OSTEOCHONDROSIS OF THE THORACIC SPINE
It is characterized by a varied clinical picture, which is associated with the anatomical and physiological characteristics of this part of the spine. Despite the fact that the number of discs in the thoracic region is twice as large as in the cervical or lumbar region, clinical manifestations of osteochondrosis are observed much less frequently.
This phenomenon can be explained by the lower mobility of the thoracic spine, the small size of the nucleus pulposus and the small thickness of the intervertebral disc, which less often leads to the formation of hernias, however, thoracic physiological kyphosis (bend) contributes to the formation of anterior and lateral osteophytes.
Osteophytes in the area of the spinal-costal and transverse-costal joints come into contact with the spinal nerves, causing intercostal neuralgia or leading to irritation of the sympathetic trunk and the occurrence of autonomic syndromes. The lower cervical and upper thoracic sympathetic nodes connect at the level of C7 - Th1 (Th1 - 1st thoracic vertebra), then the sympathetic branches extend to the heart, esophagus, bronchi, spine, carotid arteries and recurrent nerve.
From the sympathetic nodes Th5 - Th10, the abdominal nerve is formed, passing through the diaphragm and woven into the solar plexus. Clinical symptoms depend on the compression lesion of a particular nerve trunk.
Before using laser therapy for osteochondrosis, consult our specialists. They will tell you the most appropriate treatment option, the type of device and tell you about its use.
Diagnosis of back and shoulder pain
To find the cause of the pain, a computer examination will be required. A doctor from the SmartMed clinic individually selects a set of diagnostic procedures, which may include:
- radiography;
- CT scan;
- Magnetic resonance imaging.
The most accurate and informative method for diagnosing pain in the back and shoulder is MRI. The SmartMed clinic has installed a new Siemens Symphony 1.5 Tesla tomograph, with which you can detect initial pathological changes in the joint and soft tissues, see neoplasms, disorders of innervation or blood circulation. The cost of tomography includes not only the examination itself, but also a consultation with a diagnostician.
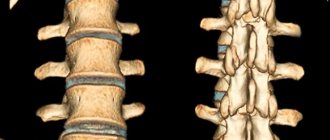
OSTEOCHONDROSIS OF THE LUMBAR-SACRAL SPINE
Damage to this part of the spine (Fig. 1) occurs most often, which is due to both the anatomical features of the structure of the spine and the characteristics of human life, because The lumbar region bears the greatest load. The most common pathologies found in this part of the spine are osteochondrosis and complicated forms of osteochondrosis, compression-radicular syndromes, and dysfunction of the nerve root in the form of neuropathies.
The most common syndromes of the lumbar spine are sciatica, lumbago, lumbar radiculitis (lumbar osteochondrosis) and intercostal neuralgia. Each of these syndromes consists not only of pain in the spine, but also secondary inflammatory changes in the muscles near the affected part of the spinal column, as well as symptoms of poor circulation and swelling of internal organs.
Clinic. Manifestations of the disease can be very diverse, depending on the stage of the process. Long-term pain syndrome, foot paresis (“slap foot”), compensatory scoliosis in the lumbar region, tension of the rectus muscles of the back, pain on superficial palpation, hyporeflexia of tendon reflexes, hypotonia of the lower leg muscles with impaired walking function, etc.
The results of clinical observations indicate a pronounced therapeutic effect of laser therapy in patients with osteochondrosis. After the first RT session, the absence of pain was observed in 60-65% of patients, improvement in motor activity was noted in 20-25%, and normalization of sleep in 50% of patients. After the first course of treatment, a positive effect was observed in almost 100% of patients with an early stage of the disease. When the process is started, it is achieved after 2-3 courses of treatment.
Treatment of back pain radiating to the shoulder
Based on the examination results, the doctor prescribes treatment. What it will be like depends on the cause of the pain. Therapy is aimed at both eliminating pain and treating the underlying disease. If the cause is not removed, the pain will return again, so a specialized specialist should be involved in drawing up a treatment protocol.
Therapy is predominantly conservative - a combination of medications and physiotherapeutic procedures. To treat shoulder pain, the following groups of drugs are prescribed:
- non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs;
- corticosteroids;
- analgesics.
Additionally, mineral-vitamin complexes and chondroprotectors can be used.
Important! For severe pain, a therapeutic blockade is indicated.
The effect of taking medications is enhanced by physiotherapeutic procedures: magnetotherapy, electrophoresis, ultrasound therapy. For diseases of the musculoskeletal system, massage and physical therapy are additionally prescribed.
The duration of therapy depends on the severity of the patient's condition. For example, with chronic osteochondrosis of the cervical spine, several courses are required.
Mild stage of forearm osteochondrosis: symptoms and treatment
The first signs of the disease may appear at the age of 30-35 years. I am worried about pain in the joint; discomfort appears for no reason when moving the joint. The pain causes a reflex contraction of the muscles of the shoulder girdle and leads to stiffness of the joint. The initial stage of the disease is well treated with medication, massages, and physical therapy. There may also be congenital causes of the development of shoulder osteochondrosis - this is an additional cervical rib, fibrous degeneration of the rib with a displacement from the place of muscle attachment.
First aid for back and shoulder pain
It doesn’t matter whether the pain in your shoulders and upper back is severe or tolerable, you need to seek qualified help. Since the nature of pain is often neurological, it is worth making an appointment with a neurologist. Doctors working in the medical field have extensive work experience and high ratings on the ProDoctors review site. They specialize in treating all neurological conditions that lead to shoulder and back pain.
In addition to a neurologist, you may need the help of an orthopedist-traumatologist
Before going to the clinic, in order to reduce the intensity of the pain syndrome, you should follow the recommendations:
- do not put stress on the sore shoulder: do not carry bags, refuse physical work, do not perform exercises, do not make sudden movements or turns;
- refrain from thermal procedures;
- minimize any movements, up to complete immobilization by fixing the shoulder to the body.
If the pain is severe and cannot be tolerated, you can take a painkiller. But it is better to apply ice to the sore spot through a cloth for 10-15 minutes. It will reduce swelling and pain caused by pinched nerve endings.
If the pain syndrome is moderate, before seeing a doctor you should refrain from using medications that can blur the clinical picture.
DYSTROPHIC CHANGES IN THE THORACIC SPINE
Apart from osteochondrosis, these are the most common lesions of the spine.
Clinic. Manifestations of the disease in the form of thoracalgia (chest pain) are associated with reflex syndromes and are often accompanied by cardiovisceral, hyperventilation and other syndromes. Clinically, this usually manifests itself as long-term non-healing gastric ulcers, erosive gastritis, cardialgia of unknown origin with ECG changes in the form of ischemia of various parts of the left ventricle, prolonged bronchitis, and disturbances in emotional stability.
HEEL SPUR"
It is a bone outgrowth at the site of tendon attachment, which is characterized by painful sensations in the area of the sole.
Clinic. At the beginning of the disease, pain occurs when walking. It is especially difficult to start walking when acute pain occurs during exercise. Then, during the day, the pain when walking subsides somewhat, and by the end of the day it intensifies again. Over time, the pain becomes persistent.
People with excess weight, diseases of the spine and large joints of the lower extremities, flat feet, as well as athletes with prolonged local overload in this area are predisposed to the development of heel spurs. Currently, the treatment of heel “spurs” consists of providing relief with the use of various types of insoles and heels, complex physiotherapeutic treatment, and if there is no effect, surgical treatment - surgical removal of the bone outgrowth and excision of the altered tissue.
Laser therapy. Highly effective for this pathology. As a rule, the full effect is achieved after 2-3 courses.
The high efficiency and safety of modern laser therapy allows the population to use it as a home doctor. The manual included with the device allows you to correctly carry out the appropriate treatment of various diseases of the joints and spine. A prerequisite for purchasing a device for treatment at home is to carefully study the attached manual.
Recommendations
A consultation with a neurologist and x-ray of the cervical spine with functional tests are recommended.
| • | Leading specialists and institutions for the treatment of this disease in Russia: |
| Doctor of Medical Sciences, Head of the Department of Russian State Medical University, Professor, Academician of the Russian Academy of Medical Sciences Gusev E.I. | |
| • | Leading specialists and institutions for the treatment of this disease in the world: |
| G. AVANZINI, Italy. |
Conditions of accommodation at the Gelenk Clinic
Orthopedic medical center Gelenk-Klinik in Germany, private ward.
During your inpatient stay at the clinic, you are in a separate room with a shower and toilet. In addition, we provide you with towels, a robe and slippers. There is a TV in the room. You only need to bring your own medications, comfortable clothes and nightwear. After surgery, we guarantee 24-hour care from qualified nursing staff and experienced physiotherapists. Generally, the length of hospital stay is 4 days. Your family members can stay in a hotel, which is located a few steps from the clinic. We will be happy to take care of your hotel room reservation.
RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS
Rheumatoid arthritis.
Belongs to the group of systemic autoimmune diseases. Its characteristic feature is the formation of autoantibodies to various types of collagen. One of the components in the mechanism of development of autoimmune diseases is inflammation. With the development of inflammation under the influence of infectious factors (streptococcus-A - in rheumatism, intestinal microbes - in reactive arthritis), its main signs are revealed in tissues and organs - pain, swelling, dysfunction. Impaired microcirculation is one of the early mechanisms of rheumatic inflammation. It is caused by an increase in the permeability of the capillary wall due to cross-hemocirculatory disorders, leading to the development of edema and hyperemia. The role of hypercoagulation factors especially increases (chronic DIC syndrome in chronic rheumatoid inflammation).
It is necessary to note the systemic, progressive, self-sustaining nature of chronic inflammation in autoimmune diseases. Pathological metabolic disorders are diverse. Often, a complex metabolic disorder leads to inhibition of osteogenesis processes. Disruption of metabolic processes in articular cartilage leads to depletion of its main substance in proteoglycans, which causes the destruction of cartilage and the development of deforming osteoarthritis.
Arthrosis and metabolic arthropathy, as a rule, are generalized in relation to damage not only to many joints, but sometimes to internal organs. The central and peripheral nervous systems, especially the autonomic part, are involved in the pathogenesis of functional changes. Patients with rheumatoid arthritis experience symmetrical joint damage, muscle atrophy, osteoporosis, and various trophic disorders.
Treatment. It should be carried out taking into account all links of its pathogenesis. For this purpose, anti-inflammatory, immunomodulating, and painkillers are used. Modern complex therapy also includes physical factors. The use of physical factors has the following goal: to reduce or eliminate pain, reduce signs of general and local inflammatory activity. Due to the effect on the neuroendocrine and vascular components of trophism, it normalizes metabolism in the affected tissues. Influence the violation of immunoregulatory processes. Considering the fact that laser therapy has all of the above properties, it must certainly be part of the complex treatment being carried out. RT is prescribed both as a local effect on the joints and as laser hemotherapy.