Pain in the calves: main causes
Minor pain may occur after a long walk, cycling or sports training due to overwork or microtrauma. In this case, the discomfort will probably go away after resting, taking a bath and light self-massage. You should consult a doctor if pain in your legs appears regularly. It can be associated both with improper load and with the development of serious diseases. Painful sensations can be caused by:
- infections;
- inflammatory processes;
- vascular pathologies;
- injuries;
- lack of microelements;
- dehydration.
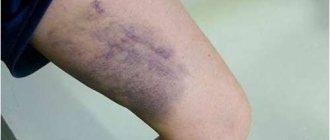
If your legs “hum” and veins clearly appear on them, then the unpleasant sensations are most likely due to vascular diseases. If the leg swells and becomes hot, this may indicate an inflammatory process. If there are bruises and hematomas, you must urgently contact a traumatologist: this could be a fracture, sprain or other injury. Often, when men have pain in their calves, the cause of the discomfort lies in acute or old injuries that were not treated in time. If women's calves hurt, the reasons for this may be related to hormonal fluctuations, pregnancy or menopause, respectively, and treatment should be aimed primarily at normalizing hormonal levels and eliminating other causes of discomfort. Thus, during pregnancy, legs often swell and hurt due to deterioration of kidney function, so you should immediately inform your doctor about the presence of such a symptom. The following factors can lead to soreness in the calf muscles:
- obesity (a combination of metabolic disorders and increased load on the legs);
- hypothermia;
- wearing uncomfortable shoes;
- overwork;
- frequent consumption of salty and smoked foods;
- physical inactivity.
With a lack of physical activity in people of any age, blood circulation is impaired, tissues lack oxygen and nutrients. Deterioration of blood flow leads to the development of stagnant processes, the formation of edema, and muscle atrophy.
What diseases cause severe pain in the calves?
s legs?
- Varicose veins lead to poor circulation, the development of edema and congestion. Due to stagnation of blood, strong pressure occurs on the nerve endings, which causes increasing pain in the legs, which bothers a person both when walking and at rest.
- Another common disease that causes pain in the leg muscles is atherosclerosis. With this pathology, the walls of blood vessels become denser, which causes a narrowing of their lumen and stagnation of blood. Without treatment, the disease can even lead to blockage of veins and death. Characteristic symptoms of atherosclerosis are cold feet and aching muscle pain.
- Unpleasant sensations can also be associated with an inflammatory disease – myositis. It develops due to various infections or the presence of parasites in the body. With this pathology, cramps, intense pain and gradual muscle atrophy are observed.
- Sometimes swelling and pain in the legs are caused by heart or kidney failure. In this case, the patient may feel pain in the abdomen, heart, and lower back. Other signs are difficulty breathing, difficulty urinating, changes in heart rate, pressure surges
- If your leg in the calf area hurts during the period when you are on a diet, the cause of the discomfort may be a lack of microelements - calcium, magnesium, potassium and others. In this case, you must immediately switch to a balanced diet and do therapeutic exercises. You need to understand that a long-term lack of nutrients leads to muscle wasting, including the heart.
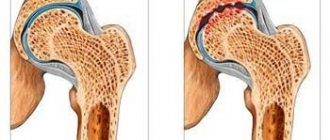
- Another reason why the calves hurt when walking may be diseases of the musculoskeletal system. Arthritis and arthrosis lead to the development of stagnant and inflammatory processes that affect not only cartilage, but also muscle tissue. In addition, with these diseases, the load on the lower extremities is incorrectly distributed, which causes excessive muscle tension, causing cramps and pain in the legs.
Meniscus injuries – rupture, cyst
A meniscus tear usually occurs at the peak of physical activity and is accompanied by acute pain. If the tear occurs in the back of the meniscus, the pain will radiate below the knee and back. Injuries of this kind occur in people who are actively involved in sports, usually at a professional level. A meniscus tear can be diagnosed using MRI; x-rays are useless in this case.
A meniscus cyst can appear with severe arthrosis of the knee joints and is not always associated with injury. Wear and tear of the joints and constant stress on them play a big role. A meniscus cyst can be diagnosed using MRI data.
Treatment in both cases should be carried out by an orthopedic traumatologist. As a rule, this is a surgical operation; for athletes, it can be meniscus replacement. More gentle methods in traumatology include injections of anti-inflammatory drugs into the joint and artificial synovial fluid.
We successfully use osteopathic methods in such patients at the stage of rehabilitation and recovery after injury. Soft fascial techniques allow you to achieve what is impossible to achieve with rough intervention - improve the functional state of the fascia, ligaments and tissues around the joint, and achieve proper distribution of the load on the joint.
Self-help for sore calf muscles
Before deciding what to do if your calves hurt, you need to understand why this happens. Try to determine the cause of the discomfort yourself - to do this, you need to remember whether you have recently had injuries, hypothermia, long walking, lack of fluid in the body, or insomnia. With dehydration, stress and fatigue, leg pain decreases after:
- light massage;
- warm foot bath with mint, chamomile or salt;
- taking enough fluids;
- recreation.
If injury, vascular pathologies or inflammatory processes are suspected, massage and foot baths are contraindicated. If the pain is very severe, you can take a pain reliever. Local agents in the form of gels and ointments help well.
If you experience frequent pain in your legs, you should consult your doctor as soon as possible. Self-medication can lead to the development of thrombosis, sepsis and other dangerous complications.
Baker's cyst
This is an outgrowth of the synovial membrane of the joint, filled with joint fluid. It occurs quite often, usually in women after 40 years of age. A Baker's cyst can cause aching pain under the knee and swelling in the popliteal fossa; with large cysts, the leg does not bend at the knee completely, and a “bump” can be felt behind the knee. To clarify the diagnosis, ultrasound of the knee and MRI are used.
Baker's cysts can be caused by inflammatory diseases, injuries, or arthrosis of the knee. Despite the fact that it is not a tumor, the cyst must be removed or punctured, since it can compress the vessels under the knee and cause complications such as thrombophlebitis and thromboembolism.
Which doctor should you see if your calves hurt?
To receive medical care, you must visit a physician or orthopedist. If the pain is caused by vascular pathologies, then further treatment will be carried out by a phlebologist. In case of pain after injuries, the treatment plan is drawn up by a traumatologist. To determine the cause of pain, various diagnostic procedures are required:
- ECG;
- Vascular ultrasound;
- blood and urine tests;
- in rare cases - joint puncture;
- X-ray;
- MRI;
- CT.
Infections of the popliteal fossa, enlarged lymph nodes
The soft tissues of the popliteal region can become inflamed after undetected injuries, cuts, or punctures of the skin. Severe pain, swelling and temperature are caused by an abscess of the popliteal fossa, in which pus accumulates under the skin. Treatment is only surgical.
Enlarged lymph nodes under the knee can also be accompanied by discomfort and swelling. Since lymph from the lower part of the leg flows into the popliteal lymph nodes, their increase indicates an inflammatory process somewhere below. It is necessary to check the condition of the veins, the presence of ulcers on the lower leg or foot, suppuration, cuts and deep punctures, which can cause infection and suppuration.
Features of treatment
The choice of treatment plan for pain in the calves is determined by the causes of the ailment. In most cases, surgical intervention is not required; conservative methods are sufficient: drug therapy, physiotherapy and exercise therapy. These measures help:
- improve blood circulation;
- suppress inflammatory processes;
- eliminate pain and swelling;
- remove toxins;
- strengthen the ligaments and muscles.
Selecting medications and other treatments on your own is dangerous. For example, if there is a tendency to thrombosis, heparin-based drugs are prescribed, but in case of insufficient blood clotting or weakness of the vascular walls, these drugs can cause bleeding. Excessive physical activity can lead to damage to the musculoskeletal system, and insufficient physical activity will not provide the desired therapeutic effect. Therefore, only a doctor should be involved in developing a treatment plan, including a set of exercise therapy exercises.
In the network of clinics “Hello!” Modern diagnostic equipment is used, which makes it possible to accurately diagnose even in the early stages of diseases. Experienced doctors develop individual treatment and rehabilitation regimens for patients based on classical and latest techniques, which allows them to get rid of pain quickly, without side effects or the risk of relapses.
Diseases of the soft tissues of the joint, tendons
The knee joint has 6 ligaments and up to 10 bursae (depending on individual characteristics), a thin capsule surrounding the joint. In untrained people, even minor long-term exercise can cause tendonitis (inflammation of the tendon) or bursitis (inflammation of the bursa). With awkward movement, the joint capsule can be pinched between the ligaments. All this causes pain, which is often nagging in nature and is often localized in the back of the knee and under it.
Diagnosis of knee ligament diseases necessarily includes MRI. Treatment uses cold, rest and anti-inflammatory drugs. We perform osteopathic manipulations on our patients that allow us to release the pinched joint capsule or relieve tension from the ligaments and fascia of the knee. Pain under the knee goes away several times faster after complex treatment.
Diseases of the nerves and blood vessels of the popliteal fossa
There are three large structures running beneath the knee: the tibial nerve, the popliteal artery, and the popliteal vein. Acute pain radiating to the lower part of the leg accompanies damage to the tibial nerve, for example, due to injury and pinching. A throbbing, aching pain under the knee is characteristic of a popliteal artery aneurysm. Popliteal vein thrombosis is not common and may be a complication of Baker's cyst. The pain is aching, not severe, and often the disease can only be recognized at a late stage. Ultrasound with Doppler is of decisive importance, which allows identifying a blood clot in the popliteal vein.
Prevention
So that problems with your legs do not arise and you never have to experience what it is like when the calf muscle is pulled and cramps occur, you should always take care of them. Measures to prevent problems with calves :
- Comfortable shoes. Both high heels and constant wearing of flat soles are harmful. The optimal heel height is 2-4 centimeters.
- A balanced diet rich in potassium, calcium, magnesium and vitamin D. You should also periodically take complex vitamins for prevention.
- Healthy lifestyle. Bad habits such as smoking, alcohol abuse, as well as sweet and fatty foods harm the veins, so you should give them up.
- Sufficient amount of liquid. Fluid is necessary for normal blood circulation, as well as the functioning of muscles and ligaments. Its volume is 1.5-2 liters per day, but you shouldn’t force yourself to drink “because I don’t want to.”
- Regular gymnastics. Physical activity is necessary for the lower extremities. You should also avoid prolonged immobility.
Paying attention to your health will help you avoid many problems.
What is not recommended to do
Such a symptom of the disease - pain in the calf muscles, can also indicate many serious diseases; without knowing the cause, you should not do the following:
- Warm the affected area - take a hot bath, go to the sauna, apply warming ointments. For many diseases - for example, varicose veins, thrombosis and thrombophlebitis - this can aggravate the situation.
- Do massage. A light massage is indicated only for problems caused by physical activity or, conversely, long-term immobility. For vein diseases, inflammation of muscles and bones, massage will aggravate the situation. The only thing you can do if discomfort occurs is to gently rub your calves.
- Increase the load. If the problem was caused by yesterday's workout, light, moderate exercise today will help you quickly cope with the unpleasant symptom. However, the load should be reduced. If you increase it and work through the pain, it will only get worse. If the causes of the problem are not clear, it is even more necessary to ensure rest for the limbs.
- Do not go to the doctor if your symptoms are severe. If the calf is swollen, red, blue, or changed color, and it is impossible to step on your foot, you must immediately go to the doctor or call him at home. Most likely, the reason is serious, and delay can be life-threatening.
Also, immediately contact a specialist if your overall health has worsened - weakness, dizziness, fever are observed.