Pain above the knee may be associated with the localization of pathology in the area of this bone joint or with diseases of the lumbosacral spine and hip joint. It is important at the initial stage to differentiate the correct location of the source of pain. It is not uncommon for such a symptom to cause an inexperienced doctor to begin treating the knee joint, but in fact the patient develops deforming osteoarthritis of the hip joint.
Pain in the leg above the knee is a reason for a comprehensive examination to rule out diseases such as:
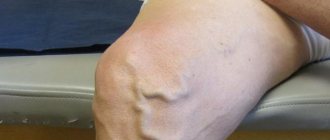
- varicose veins and the onset of thrombophlebitis of the posterior vein of the leg;
- osteochondrosis of the lumbosacral spine with severe protrusion of the intervertebral discs;
- cauda equina syndrome;
- pinching of the sciatic nerve;
- deforming osteoarthritis of the knee and hip joint;
- pathologies associated with the tibial nerve;
- tendovaginitis, bursitis, sprains and ruptures of the lateral and sacral ligaments.
Severe pain in the muscles above the knee may be associated with unusual physical activity. This leads at the initial stage to the accumulation of lactic acid in myocytes (a metabolite released in the mitochondria of cells under severe stress). After an intense workout, discomfort and tension syndrome may occur. To eliminate these signs, we can recommend a professional sports massage and the use of certain warming ointments.
We will consider other reasons for the appearance of similar clinical signs with different localization of pain syndrome later in the article.
Severe pain in the legs above the knee, front and back
Severe pain above the knee can be associated with a number of provocative pathogenetic factors. Most often, pain syndrome is associated with the following types of negative effects:
- trauma (fracture, soft tissue rupture, dislocation, sprain);
- inflammation (arthritis aseptic, infectious, autoimmune, rheumatoid, etc.);
- deformation of bone tissue (osteoarthrosis and destruction of the cartilaginous synovial membranes of the articular surfaces);
- compression (the nerves passing in this area are damaged);
- vascular pathology (thrombophlebitis, vein blockage, deep thrombosis, trophic insufficiency, etc.).
All these reasons can cause pain above the knee in front or behind; depending on the location of the discomfort, a primary diagnosis can be made. Anterior localization most often indicates a traumatic etiology associated with patellar instability. This may be chondromalacia or a partial rupture of the ligaments that support it. An accurate diagnosis can be made only after a visual examination, palpation and MRI.
But pain in the legs above the knees at the back is often caused by vascular and innervation pathology. Here the sciatic nerve splits into the tibial and peroneal branches. The pathways of these axons are located very close to the surface of the skin. Therefore, the habit of crossing one leg over the other while sitting often leads to infringement of the nervous structure. In the initial stages, this gives the effect of temporary numbness and a crawling sensation after restoration of innervation. If compression is applied regularly, the nerve fiber structures become inflamed and severe pain occurs.
Vascular pain above the knee from behind is associated with impaired patency of the venous bed. External collateral veins with a fairly large volume run along the posterior projection of the leg and thigh. When varicose veins develop, these vessels are the first to suffer. The development of thrombosis leads to the fact that the vein becomes clogged and the outflow of blood through it is disrupted. Against this background, an inflammatory reaction and pronounced swelling of the soft tissues occurs. With thrombophlebitis, diagnosing the condition does not cause any particular difficulties.
In some cases, angiography is required for the differential diagnosis of arterial insufficiency. It differs from venous pathology in the absence of external clinical signs. Atherosclerosis of the vessels of the lower extremities often manifests itself for a long time only in the form of soreness in the muscles behind and above the knee.
Why does it hurt above the knee?
Tightness and pain in the knee are familiar to almost every person, but weakness in this area carries a potential danger even with normal walking, not to mention jumping and intense training. It happens that the pain becomes unbearable, bothers you at night, when the load on the knee is excluded, or the discomfort increases when bending on the back of the knee, on the right, on the left.
Knee pain can be divided into 2 large groups: mechanical damage and inflammatory processes. Particular attention should be paid to discomfort on the side of the kneecap on the inside, when you cannot delay diagnosis, because this is a sign of inflammation and infection.
Orthopedic surgeon Andrey Yurievich Sidenkov comments:
If it occurs against the background of prolonged stress, then ligament tears or rupture can be suspected when difficulties in movement, cyanosis, swelling, swelling above the knee in front and pain appear. The characteristic crackling and crunching noises during movements signal a violation of the articular cartilage and poor blood circulation in the joint.
The meniscus, located in the knee joint between the cartilage, serves as a natural shock absorber and also produces dull pain when damaged. In case of rupture, the pain is unbearable, burning with the formation of swelling and hemorrhage. A characteristic click can be heard above the knee and this is already a reason for a tomographic examination.
Pain above the knee on the outside and inside
Pain above the knee on the inside and outside is associated with damage to the soft tissues of this joint. The main causes include the following diseases:
- sprains of the knee joint (lateral and cruciate ligaments are most often affected);
- bursitis caused by internal and external causes, such as arthrosis, arthritis, trauma, shock, hypothermia, prolonged pressure on the bursae;
- tendovaginitis and myositis.
People who lead an active lifestyle and enjoy sports often complain of pain above the knee on the inside. Athletes who enjoy volleyball, football, basketball and other types of active team games are especially susceptible to knee injuries. In most of them, differential diagnosis reveals numerous colloidal changes in the ligamentous and tendon apparatus of the knee joint. This is a consequence of sports injuries, after which full rehabilitation was not carried out. As a result of repeated sprains, physiological tissue is replaced with scars. This can lead to the development of severe myofascial pain syndrome.
We are ready to provide assistance in such cases. In our practice, there are a huge number of cases where we were able to reverse the degeneration process and restore the normal state of damaged joint ligaments. If you are experiencing pain above the knee, either externally or internally, then schedule a free initial consultation at our manual therapy clinic. Already during the first appointment, the doctor will diagnose you, and you will learn about what options exist today for eliminating pain.
In what cases is tingling in the joints safe?
If tingling attacks are one-time in nature or occur extremely rarely, there are probably no dangerous pathologies hidden behind them. This happens, for example, if:
- carry heavy things in your hands;
- hold your arms in an unnatural position for a long time, for example, above your head;
- when there is a sudden change in weather and jumps in atmospheric pressure;
- you were sleeping or sitting in an uncomfortable position.
Due to poor circulation, the joint becomes slightly numb - the person feels a subjective tingling sensation, which quickly passes as soon as the blood supply returns to normal. Unfortunately, this is not always the case.
If you have tingling sensations in your joints, it would be a good idea to consult a neurologist.
Sharp and sharp, burning and aching, throbbing and shooting pain in the leg above the knee
All of the listed characteristics of the pain syndrome allow us to make a preliminary diagnosis. Therefore, the patient should describe the nature of his subjective sensations as accurately as possible.
Sharp pain above the knee that appears suddenly without any visible traumatic impact makes you think first of all about pinching the sciatic nerve. Most often, this symptom occurs in patients amid apparent well-being. If you sit on a hard chair for a long time, suddenly stand up, you will immediately feel a pain in the lower back, and after a few seconds the area above the knee will begin to hurt unbearably. This is a negative clinical sign indicating severe deformation of the intervertebral disc.
Acute pain above the knee can occur with the following diseases:
- instability of the patella, causing injury to soft tissues, including synovial bursae (bursae);
- deforming osteoarthritis of the knee joint at an early stage (an X-ray is required to clarify the diagnosis);
- coxarthrosis of the hip joint (can be distinguished from pathology of the knee joint using a simple test, during which the patient is asked to sit facing the back of a chair with his knees apart);
- Baker's cyst and aneurysms of large blood vessels passing through here.
Burning pain above the knee is usually associated with impaired innervation or deep vein thrombosis. In both cases, immediate medical attention is required. If the innervation is disrupted, the burning sensations gradually subside and the effect of a lack of skin sensitivity appears. If innervation is not restored in a timely manner, it will be very difficult to do so in the future. Paralysis may develop.
Aching pain above the knee is a sign of a long-term chronic process in the cavity of the knee joint. This may be arthritis, arthrosis, soft tissue deformation, old forms of bursitis and tendovaginitis. But throbbing pain in the leg above the knee, on the contrary, indicates an acute process. This may be aseptic tissue necrosis, associated, for example, with traumatic or deformational tissue ischemia. It is also not uncommon for purulent forms of arthritis to manifest themselves as pulsating pain. Visible changes in the joint include swelling, redness of the skin, and pain on palpation.
Shooting pain in the leg above the knee is always a pinched nerve. May be a consequence of exacerbation of lumbosacral osteochondrosis, piriformis syndrome, coxarthrosis, etc. During the initial diagnosis, it is important to detect the place where compression of the nerve fiber occurs and, if possible, eliminate the negative impact factor. So, with lumbosacral osteochondrosis, in order to relieve pain above the knee, it is enough to conduct one or two sessions of traction traction of the spine. And with deforming arthrosis of the hip joint, osteopathy can be used to restore the normal position of the femoral head in the cavity of the acetabulum. This will restore innervation and pain will go away without the use of ointments and painkillers.
Treatment of pain in the legs above the knees
Before you can begin effective treatment for pain in the legs above the knees, you need to establish an accurate diagnosis. Then the doctor will talk about how to eliminate the causes of this pathology. And only after this will it be possible to carry out successful therapy.
In most cases, pain above the knee when walking is a consequence of improper foot placement. Flat feet or club feet can develop both in early childhood and during adulthood. To do this, it is enough to wear the wrong shoes. As a result of incorrect foot placement, deformation of the ankle, knee and hip joints occurs. The nerve channels are deformed. The heads of the bones are displaced, which injures the surrounding soft tissues. All this ultimately leads to deformation of the articular surfaces and the development of osteoarthritis. And at the initial stage, everything manifests itself as pain in the legs above the knees when walking.
After contacting our manual therapy clinic, each patient learns what was the true cause of the formation of a particular disease of the musculoskeletal system. In the future, doctors begin treatment by eliminating these pathogenic factors.
So, if the patient has an incorrect foot position, then it is useless to treat incipient arthrosis, since the effect of the traumatic factor will continue. Therefore, it is advisable to first correct the position of the foot, and then begin to treat the resulting pathologies.
When diagnosing osteochondrosis of the lumbosacral spine, therapy also begins with the treatment of this disease. Techniques are used to quickly and safely relieve pain. An individual course of treatment is then developed. It may include kinesitherapy, therapeutic exercises, massage, osteopathy.
How to help yourself with tingling joints
If the tingling sensations recur, listen to your body. You may also notice other unpleasant symptoms, such as morning stiffness. If the joints tingle only occasionally, complications can be prevented with the help of a special diet and vitamin therapy. Add these joint-healthy foods to your diet:
- Red fish and flax seeds. They are high in Omega-3, a substance that reduces inflammation and slows down the wear and tear of cartilage.
- Celery salad, juice or infusion. This product is a powerful antioxidant and is also used to remineralize and detoxify the body.
- Ginger. Regardless of the form, be it infusion, powder or spice, the product has a strong analgesic and anti-inflammatory effect.
- Nettle. It has cleansing properties, so nettle leaves can be rubbed on an affected or tingling joint, or you can add them to a salad.
“One nettle replaces seven doctors,” says popular wisdom. What are the benefits of this well-known plant for the body and joints?
None of the above folk remedies is a panacea for joint diseases. Sometimes tingling can develop into discomfort and constant aching pain, and an MRI will show arthrosis of the joints.
As a rule, in case of such complaints, the doctor orders an x-ray to rule out injury or prescribe effective treatment for osteoarthritis based on the results, and also recommends a detailed blood test. It will show the presence of inflammation in the body and help you draw the right conclusion.
Therefore, do not rush to write off this seemingly harmless symptom as an accident and be vigilant! Some diseases are very insidious and make themselves felt only in advanced stages.