Leg pain is the third most common complaint among our patients. The reason for this is the high prevalence of varicose veins, arthritis and the seeming insignificance of such a problem as pain in the legs. At the same time, if your legs hurt from the knee to the foot, you cannot ignore this symptom as unimportant, since it may be the beginning of a more serious disease.
Pain below the knee in the front tends to occur in a few common situations. These include varicose veins, chronic venous insufficiency, myofascial pain syndrome (in which the pain is accompanied by cramps) and, less commonly, deep vein thrombosis, which is essentially an emergency condition.
At the appointment, we explain to our patients that pain in the legs must be treated and all necessary measures must be taken to eliminate it, since it deprives a person of the main factor of health - his mobility.
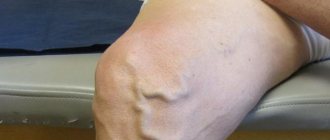
Pain below the knee with varicose veins
A typical situation in which a person is bothered by heaviness in the calves, swelling, “roaring in the legs,” and sometimes cramps. This picture is due to poor outflow of venous blood from the calf muscles, resulting in swelling, fluid accumulation, heaviness and pain. Superficial veins swell, blue venous nodes appear, and the skin of the lower leg takes on a brownish tint (pigmentation). The causes and treatment of varicose veins are described in detail in our article Varicose veins: causes, treatment, symptoms. Osteopathy helps not only to get rid of the symptoms of this disease, but also to prevent its further development, and often, the need for surgery.
Pain of pain - discord! Probable diagnoses
If the bone behind the knee in front hurts, the doctor can try to find out the cause by the nature of the pain.
Aching, nagging pain is most often a symptom of a developing inflammatory process in the joint and erosive-destructive lesions of a rheumatoid nature.
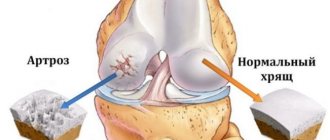
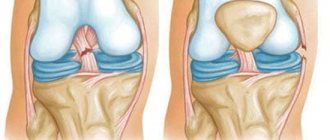
Severe, sharp pain occurs when ligaments, tendons are torn, bruised or fractured elements of the knee, acute inflammation of the synovial bursa, exacerbation of degenerative damage to the cartilage lining (meniscus), which acts as a shock absorber in the joint and stabilizes the knee joint, as well as deforming osteoarthritis.
Acute pain in the leg bone below the knee at the front may indicate meniscal damage.
Aches in the lower leg often indicate the development of osteoporosis, a chronic progressive bone disease characterized by increased fragility.
The boring nature of pain in bones and muscles is observed with osteomyelitis, an infectious and inflammatory disease that affects the structural elements of bones. The pain is often accompanied by symptoms such as redness of the skin, swelling, and an increase in body temperature to 38–39 degrees.
Throbbing pain indicates advanced deforming arthrosis or meniscus injury.
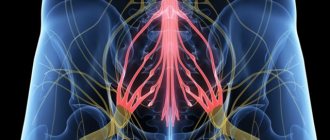
Burning pain is characteristic of pinched sciatic nerve (they can reach the toes), as well as bone tuberculosis.
Shooting pain usually occurs when a nerve trunk is pinched.
Dull pain can accompany inflammation of the bursa of the joint, as well as chronic osteochondritis, a disease in which a small section of cartilage is separated from the adjacent bone and is displaced into the cavity of the knee joint.
Myofascial pain syndrome
Overexertion of the lower leg muscles is the main cause of myofascial pain in the legs. Even in a healthy person, the deep muscles of the lower leg, as a rule, are in spasm, and if you run your hand over them, an acute characteristic pain appears. It is distinguished from venous pain by its greater severity, localization in one or several points, and irradiation into the foot or deep into the lower leg. Often muscle overstrain turns into spasms and cramps. In this case, neither taking calcium tablets nor increasing the dose of vitamins and microelements helps.
Myofascial pain is eliminated using osteopathic methods in 2–3 sessions, and from the first appointment the patient already feels significantly better. But you will have to be patient a little: trigger points on the legs are quite painful when touched, and their relaxation is associated with pressing on the spasmed area of the muscle. However, the positive effect quickly and completely covers the unpleasant sensations from the manipulations.
What examinations should you undergo if you have pain in the leg bones below the knee in front?
Pain in the leg bone below the knee in front should be a reason to contact an orthopedic traumatologist. If necessary, he can refer the patient for consultation to a surgeon, neurologist or other specialist. The examination plan may include:
- a survey to find out under what circumstances pain first appeared, how they are related to external factors, as well as to study the patient’s complaints, information about him and the development of the disease;
- physical diagnostic methods : examination, feeling the diseased limb (palpation), tapping it and analyzing the sounds that arise during this (percussion) - using these methods, the doctor assesses the condition of the area under the knee, finds out whether there is swelling, redness and other deviations from the norm;
- X-ray examination of the lower leg - this method allows you to detect pathologies of the skeletal system: fractures, changes in bone structure, the formation of growths or calcified areas on the surface of the bone and other changes;
- computed and magnetic resonance imaging – highly informative methods of layer-by-layer tissue scanning help to accurately determine the location of the pathological focus, its size and structure, and are used to assess the condition of bone tissue, blood vessels, nerves, and soft tissues;
- ultrasound, Dopplerography, duplex scanning - allow you to study the condition of blood vessels, their blockage or expansion, as well as the speed of blood flow;
- electrophysiological studies : electromyography, electroneurography, electroneuromyography - allow you to assess the degree of damage to the nerve trunk and muscle fibers;
- laboratory diagnostics : analysis of tissues and biological fluids using specialized equipment allows you to assess the severity of inflammatory processes and study the state of the body in autoimmune diseases.
Which specific studies will be prescribed to the patient depends on the results of the doctor’s preliminary conversation with him and the clarity of the clinical picture.
Acute thrombosis of the veins of the leg
An emergency condition that requires immediate hospital treatment. Hospitalization cannot be delayed; a blood clot can completely block the outflow of venous blood and lead to gangrene of the limb. In addition, a detached blood clot can clog the blood vessels of the lungs and cause thromboembolism. If a patient comes to us with symptoms of acute thrombosis, we immediately send him to the hospital. It will be possible to continue osteopathic treatment after discharge - eliminate the causes that led to the development of thrombosis, improve venous outflow from the lower extremities, eliminate blood stagnation at the pelvic level, etc.
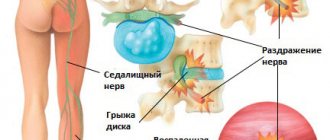
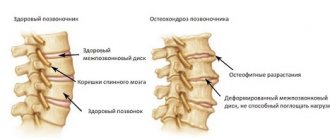
LUMBOSACROSIS OSTEOCHONDROSIS
Shooting pain spreading along the back of the leg from the buttocks to the heels is characteristic of lumbosacral osteochondrosis. Many diseases come from a problematic back - tension, poor lifestyle, and little physical activity aggravate the poor condition of the spine and lead to pain in different parts of the body, including the legs from the lower leg to the foot.
Neurologists, vertebrologists and osteopaths deal with osteochondrosis: you can always contact our doctors for advice and help, which will not only relieve pain, but also eliminate the original cause of its occurrence.
Osteopathy is one of the most effective methods of treating osteochondrosis, relieving pain literally after the first appointment and helping, in addition, to eliminate the original cause of the painful condition.
The leg hurts below the knee, the bone in front: causes
When figuring out why the leg bones below the knee in front hurt, the doctor may suspect the following reasons:
- strong physical stress on the muscles of the lower extremities, which can provoke the appearance of painful convulsive spasms;
- sprains or ruptures of ligaments that occur when performing movements exceeding the amplitude characteristic of the joint;
- any disease of the joint (or part thereof) of an inflammatory or degenerative nature;
- varicose veins, thrombosis;
- injury or bruise received during sports or a fall;
- inflammation of subcutaneous fat;
- violation of water-salt balance;
- radiculitis;
- pregnancy or excess body weight, causing joint damage;
- fracture of the tibia or fibula.
When the leg bone hurts below the knee in front, additional research may be needed to make an accurate diagnosis.
An innovative domestic drug for normalizing metabolic processes in bone tissue and eliminating pain can be purchased in the Parapharm-Shop online store.
FLAT FOOT
The cause of the painful condition of the legs from the feet to the legs can be “normal” flat feet. This pain is characterized by an increase in the evening and aggravation during long walking and other physical activities; it is aching, tiring, and spreads throughout the lower part of the limbs. The feet may become visually larger, and the bone often begins to protrude.
Flat feet are “treated” by choosing shoes after consultation with a doctor, physical therapy complexes, and osteopathy also helps to cope with it. Osteopaths work on the foot, improving blood circulation, eliminating congestion, and stimulating the production of synovial fluid, which works as a lubricant for the joints. After just a few techniques, even an adult who has suffered from flat feet all his life becomes easier and more comfortable to shift.
Pain in the leg muscle below the knee
Pain in the muscles below the knee is a sign of many diseases:
- mechanical damage to muscle fibers and tendons;
- varicose veins of the lower extremities;
- obliterating atherosclerosis and endarteritis;
- inflammation of muscles and nerves.
Most often, the leg muscles hurt below the knee due to high physical activity. Minor tendon injuries do not cause severe clinical symptoms, with the exception of periodic paroxysmal pain when walking. Mechanical damage to muscles over time with constant physical activity is complicated by inflammation, so swelling appears below the knee.
The second most common cause of pain in the knee muscles is diseases of the spine, in which the nerve endings are compressed:
- intervertebral hernia;
- severe osteochondrosis;
- spondylosis.
It intensifies when palpating the back of the lower leg and sharp turns of the body. The reason why the leg muscles below the knee hurt is bursitis (inflammation of the popliteal muscle sheaths). It occurs due to arthrosis of the knee joint or damage to the meniscus. With a pronounced narrowing of the joint space of the knee joint, the cartilaginous structures are damaged with the formation of inflammatory fluid. It accumulates in the tendon sheaths, which is why swelling of the popliteal fossa is observed.
Pain in the muscles below the knee can occur for the following reasons:
- nerve damage (polyneuropathy),
- inflammation of the bones (osteomyelitis);
- taking pharmaceuticals (statins);
- decreased levels of calcium, potassium, magnesium in the blood;
- impaired bone formation in children and adolescents (Osgood-Schlatter disease).
Muscle pain below the knee is not localized. It extends 10-15 cm, which indicates extensive damage to the anatomical structures of the lower limb. The pain syndrome intensifies with physical activity and weakens when it stops. Pain in the muscles below the knee bothers smokers. Severe pain occurs with thrombosis of the deep veins of the leg. It is localized below the knee and intensifies with dorsiflexion of the foot and compression of the lower leg in the anteroposterior direction.
With osteomyelitis of the tibia or fibula, pain below the knee is combined with purulent discharge on the surface of the skin through an open fistula. Its intensity depends on the state of the person’s immune system. When the meniscus is damaged, the pain is combined with limited mobility in the knee joint.
In case of inflammatory changes, doctors prescribe non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs to reduce the severity of pain. Drugs in this group are used in the form of tablets, creams or ointments. For varicose veins, venotonics and wearing compression stockings are prescribed. Treatment of spinal diseases that cause pain below the knee is carried out by doctors at the Neurology Clinic. Vertebrologists prescribe chondroprotectors (Teraflex, Alflutop), muscle relaxants (Mydocalm), non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs to patients and perform blockades with local anesthetics. Rehabilitation specialists provide complex therapy using innovative methods of physical therapy, various types of massage, physiotherapeutic procedures, and reflexology.
LEGS HURT RIGHT NOW! WHAT TO DO?
1. Relax. Lie down with your ankles on a bolster to elevate your legs above heart level. The blood will drain, the swelling will decrease, and the muscles will relax.
2. Apply a cold compress. For example, a thin towel with ice or some package of semi-finished products taken out of the freezer. Keep the compress for up to 20 minutes, repeat several times a day.
3. Take an over-the-counter pain reliever such as ibuprofen. But take only those medications that you are sure of, and if the pain does not go away, be sure to visit a doctor.
4. Get a massage. This is true if your legs have cramps, or if they “hum” after a long period of exercise. You can stretch the muscles yourself, or you can consult a specialist, including an osteopath.
The benefits of osteopathy in the treatment of foot diseases
- Osteopathy restores not only the function of the damaged area, but also the biomechanics of your entire body.
- We find the reason that led to your dysfunction and eliminate it.
- We do not give you injections into the joint cavity, we do not use hormonal drugs, which means you have no risk of infection or other complications.
- We provide all patients with a full osteopathic examination and examination, regardless of complaints. This allows for correction at a higher level, including the body’s reserves and directing them towards self-healing.