First aid for a knee injury
A knee injury can vary in severity, and not all require immediate medical attention. First of all, you need to examine the joint and assess how strong the pain is: carefully stand on your feet, move the damaged joint, and walk slowly.
The damaged joint should be at rest, preferably in an elevated position for better blood flow from the site of the injury. If possible, apply a piece of ice or any cooled object to the injury site (hold for no more than 15 minutes).
If there is a wound at the site of the injury, rinse it with running water, treat it with an antiseptic and apply a clean, dry bandage. Extensive wounds require immediate medical attention for professional treatment.
Causes of knee pain
People with osteoporosis are susceptible to knee problems. Osteoporosis is a decrease in calcium levels in the bones. The disease is common among postmenopausal women and people with metabolic disorders. Osteoporosis causes bones to become brittle. This destroys the knee joint.
The appearance of pain in the knees is facilitated by high physical activity, abnormalities in the structure of the knee joint, flat feet, and different leg lengths. Risk factors include old injuries, untreated chronic joint diseases, and old age.
If you regularly have knee pain, consult a specialist.
When to see a doctor
Within a few days after first aid, the patient’s condition should gradually improve, and pain should subside every day. If the pain has not gotten better a week after the knee injury, you should consult a doctor.
Also, immediate consultation with a specialist is necessary if the following symptoms appear:
- hematoma that has increased in size;
- lump at the site of the injury;
- pain when moving and crunching in the knee;
- swelling, redness;
- numbness of the knee, or, conversely, spontaneous movements;
- joint deformity;
- increased body temperature after injury;
The doctor will examine the site of the injury, order an x-ray or ultrasound if necessary, determine the risk of complications and prescribe treatment.
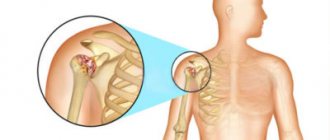
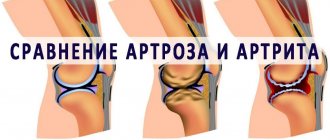
Despite its apparent harmlessness, a knee bruise can be associated with a crack or fracture of the bone, a meniscus tear, tears and inflammation in the tendons, twisted ligaments, internal bleeding, and hematomas.
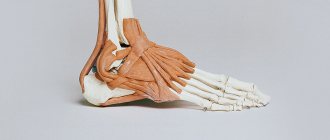
Because there are many nerve endings in the knee joint, even a slight bruise can cause severe pain. Also in the knee joint there are muscle tissues, ligaments, cartilage, and blood vessels, damage to which leads to various disorders. For example, an untreated joint injury can cause arthritis (inflammation of the joints) or even osteoporosis (increased bone fragility).
For children, injuries are especially dangerous. The child’s body has not yet fully formed, and improperly provided care for a bruise can provoke a serious disruption in physical development.
How to recognize and treat swelling of the knee joint?
It is not difficult to detect swelling: soft tissues increase in size and pain occurs. What are the pathological changes associated with? The answer to this question will be given by various studies, for example, radiography and MRI.
Etiology of the disease
joint treatment
begins with searching for the cause of the disease. Swelling in the knee area occurs for a number of reasons, including:
- Infection. A person is injured, the integrity of the joints is damaged, microbes enter the open cavity, and infection occurs.
- Pregnancy. Severe gestosis appears in the second and third trimester.
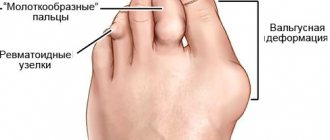
- Psoriasis. It is a systemic skin disease. Swelling occurs when psoriatic arthritis develops.
- Allergy. Soft tissues swell if there is a lot of allergen in the body. It is found in medicines, foods, insect bites and household chemicals.
- Overwork. A person gets tired after a heavy load. The knee joint suffers the most.
- Gout. Soft tissues increase in size because a lot of salts are deposited in them. Uric acid also accumulates in the joint itself. During movements, a person experiences pain.
- Excess fluid in the legs. This is typical for summer time, in the heat.
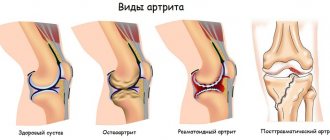
- Arthritis. Cartilage tissue wears out and ossifies. The disease affects older people.
- rheumatoid arthritis. Chronic disease progresses. Autoimmune processes begin in the body. Connective tissue suffers.
- Impaired blood circulation. It leads to peripheral edema.
- Overweight, obesity. The joints experience enormous stress when moving - swelling is inevitable.
- Violation of lymph outflow. Products of cellular metabolism accumulate in the intercellular space, which leads to stagnation.
- Venous stasis. The disease most often affects the lower extremities: blood moves well through the arteries, but poorly through the veins.
- Bursitis, synovitis. Synovial fluid accumulates in the bursae of the joint.
Symptoms of edema
Edema is a manifestation of the underlying disease. Symptoms depend on the causes of pathological changes:
- If the cause lies in arthritis or gout, the knee joint swells and nearby muscles begin to ache.
- If we are talking about psoriatic arthritis, in addition to the appearance of swelling, the skin turns red. Over time, individual spots merge into one whole.
- Another type of arthritis - septic - is accompanied by joint swelling and elevated body temperature.
- When the underlying disease is bursitis, hot skin at the site of inflammation is the main symptom. The patient feels pain. Soft tissues swell.
Medical therapy
If the pathology has just appeared, medications will cope with it. This is a conservative and effective treatment method at this stage. The doctor prescribes medications to:
- Eliminate harmful microbes;
- Stop inflammatory processes;
- Relieve pain syndrome.
If you take a set of medications, you can get rid of swelling, prevent the spread of infection, restore metabolism and normalize blood circulation in the knee area.
In addition to medications, the doctor prescribes physiotherapeutic procedures. This can be therapeutic massage, reflexology, hirudotherapy, shock wave and manual treatment.
Complex treatment (even conservative) will have a positive effect - the swelling will subside.
But this is only a symptom of the underlying disease. Until the root cause is eliminated, the knee joints will continue to swell. If you start the situation, only surgery will help. Surgeons will restore the integrity and functionality of the joint, remove excess fluid and pathological growth. If the treatment plan is drawn up correctly, rehabilitation will go quickly. Its duration is determined by the severity of the disease. The speed of recovery is also influenced by the physiological characteristics of the patient’s body. Author: K.M.N., Academician of the Russian Academy of Medical Sciences M.A. Bobyr
Treatment of the consequences of a knee injury
After diagnosis, the surgeon or traumatologist prescribes treatment depending on the severity of the injury.
For cracks and fractures, a plaster cast is applied. When a meniscus ruptures, measures are taken to restore or remove its broken parts.
In cases of blood accumulation inside the joint, a specialist performs a puncture (medical removal of accumulated fluid). To relieve pain and inflammation, special medications, physiotherapeutic procedures and vitamins are prescribed.
Why is knee pain dangerous?
Without treatment, gonarthrosis destroys cartilage and deforms the knee joint. As a result, a person may experience lameness and bowed legs. In the final stages of the disease, the knee becomes immobile and the joint is completely destroyed.
Damage to the meniscus can lead to stiffness of the knee joint.
Due to Baker's cyst, the patient may develop thrombophlebitis, deep vein thrombosis of the leg, and varicose veins. When a cyst ruptures, sharp pain appears, the temperature rises, and the skin in the area of the cyst swells.
In Hoffa's disease, the fatty tissue around the knee joint no longer serves as a buffer. Without treatment, the disease becomes chronic, increases the risk of developing gonarthrosis, and provokes constant pain in the knee.
Koenig's disease leads to the separation of cartilage from the bone, increased pain in the knee, the development of synovitis, and difficulty bending the leg. In advanced cases, the person begins to limp, the range of motion in the knee decreases, and the quadriceps femoris muscle atrophies.
Diagnostics
Often people spoil the development of the disease with their own interference, causing harm to themselves. It's better to wait to see a doctor. Before visiting the clinic, you should not take drastic measures to eliminate the tumor behind the knee.
At the appointment, the doctor will ask the patient questions regarding lifestyle and heredity. It happens. selected nervous, muscle and bone diseases are transmitted from parents to children. Genetics does not guarantee the inevitable incidence of disease, but the doctor must take into account the hereditary factor during the examination.
The doctor will examine the leg from the front, from the back - at the knee and below. By listing an exhaustive list of symptoms, the diagnosis is made quite quickly, and the clinical picture will emerge clearly and distinctly. In opposite cases, treatment will take on a gentle nature with a preliminary diagnosis, often becoming ineffective.
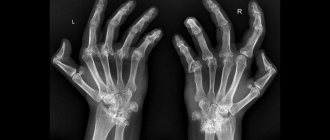
X-ray of the knee
When determining the cause of pain in the knee and swelling in the back, radiation is used as diagnostic measures: a common method is x-rays. In equipped medical clinics there are devices for computer and magnetic resonance imaging. Any radiation has sufficient permeability, demonstrating what is happening under the skin, including processes in the bones.
Remember, the best examination is comprehensive; a lot of procedures and tests mean that doctors are trying to find the optimal treatment for the patient.
Prevention
Swelling behind the knee can be prevented by following these rules:
- Eat the right foods containing essential vitamins and minerals. Consume fresh vegetables, fruits, natural juices, nuts, cereals, lean meat.
- Avoid overloading the limbs.
- Perform daily physical exercises appropriate to your age and health status, and play sports.
- Lead a healthy lifestyle.
- Take vitamin complexes in consultation with your doctor.
It is necessary to take care of your feet and maintain healthy joints. Because movement is life that must be preserved. Swelling under the knee can be managed, but it is better to prevent it from occurring.
I write articles in various areas that, to one degree or another, affect such a disease as edema.
otekoff.ru/avtor
Every person has encountered leg tumors in their life. However, chronic edema is a malaise that is noticeably uncomfortable. Such a nuisance is no longer associated with simply being in the wrong position, causing blockage of blood vessels and a feeling of wobbly legs. If the swelling rises higher - from the toes to the foot, then to the knee, problems with blood circulation are considered serious and can become symptoms of diseases.
Treatment methods
In all cases of pathologies that cause a tumor under the knee, the symptoms, its severity and treatment differ. Conservative and surgical methods are used.
Drug treatment is supplemented with physiotherapy and traditional medicine recipes. To eliminate a tumor under the kneecap in front, caused by Hoffa's disease, exercise therapy is used.
Traditional treatment
In complex conservative treatment, general and local drugs are used:
- non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs with analgesic properties (Ibuprofen, Nimid, Advins, Diclofenac, Naklofen);
- anti-inflammatory ointments and gels for external use (Finalgon, Apizartron, Fastum gel);
- ointments that relieve swelling (Troxevasin, Allantoin, Lyogel, Benitan).
To treat a cyst (tumor behind the knee), corticosteroid hormonal drugs (Hydrocortisone, Diprospan, Methylprednisolone) are prescribed. They are injected into the synovial bursa to suppress inflammation and reduce fluid production.
Helps cope with swelling and inflammation UHF, magnetic therapy, massage. To restore motor function after drug treatment, exercise therapy is prescribed.
Aneurysm and inflammation of the tibial nerve are treated only with surgery. A thrombus from the popliteal vein is removed using a special method of endovascular balloon thromboextraction. Tumors that cannot be treated conservatively are excised surgically.
First aid for injury
After a limb injury, the area behind the knee swells. It is necessary to prevent swelling from increasing. To do this, perform the following steps:
- Create rest conditions for the injured leg.
- Secure the knee with an elastic bandage or improvised means, without tightening the bandage.
- Apply ice or something frozen above the injury for no more than 15 minutes. After 20 minutes, repeat again.
- Severe pain is relieved by taking painkiller tablets.
- Call an ambulance or a doctor. You can deliver the patient to a medical facility yourself, carefully transporting.
Further treatment of the tumor is carried out as prescribed by the doctor. According to his recommendations, it is possible to use traditional recipes.
Folk remedies
Traditional medicine with an anti-inflammatory effect in the form of compresses is successfully used to treat tumors under the knee. Apply crushed potatoes, cut aloe leaf or its juice, a clean leaf of fresh cabbage, burdock, lemon juice, warm sunflower oil, and a decoction of celandine.
For swelling under the knee at the back, take an infusion of golden mustache herb, apple cider vinegar with an equal part of honey, dissolved in warm water.
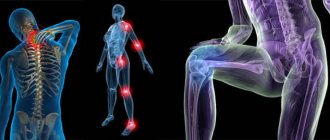
How to prevent arthritis?
It is important to understand: there is not a single guaranteed way to avoid developing arthritis. It is not always possible to accurately determine the cause of the disease, which is why it is difficult to protect against it. You can only try to reduce the risk of arthritis and its complications.
- Follow a daily routine. Sleep at least 8 hours at night, during the day - according to your needs and capabilities. Adequate sleep strengthens the immune system and reduces the risk of developing infectious diseases - one of the causes of arthritis.
- Move more. Swimming, walking, yoga, gentle jogging, fitness - all this will benefit your joints.
Running with a partner is highly motivating
- Eat right. The diet should contain foods rich in polyunsaturated fatty acids (fish, vegetable oil), calcium and phosphorus (milk and dairy products). They strengthen the bone cartilage tissue of the joints. Add sources of vitamins to your daily menu - fresh fruits, vegetables, herbs. Reduce the proportion of fast carbohydrates and animal fats.
- Watch your weight. With obesity, the load on the joints increases, metabolism is disrupted, and the risk of arthritis increases.
- Get rid of bad habits. Quit smoking, limit your alcohol intake.
- Strengthen your immune system. There is no magic pill that can activate the body's defenses. Hardening and sunbathing will be beneficial. Eliminate stressful situations, don’t work too hard, take care of yourself.
- Don't get too cold. Dress for the weather, keep your feet warm, and maintain a comfortable room temperature.
Arthritis is a serious disease that can dramatically change your life for the worse. If you have swollen or reddened joints, pain or stiffness in movement, do not hesitate to visit a doctor. The sooner you start treatment, the easier it will be to slow down the progression of the disease and avoid complications.