Osteochondroma
Osteochondroma
- a benign formation over the bone in the form of a smooth protrusion of cartilage tissue up to 12 cm in size with bone marrow contents. Osteochondromas can be multiple or single.
The reasons for the appearance of such formations are not fully understood. The risk of developing osteochondromas is believed to increase:
- Intrauterine anomalies of skeletal formation;
- Hereditary factors;
- Irradiation.
Osteochondroma of the bone occurs:
- In the area of the joints, eventually spreading to the middle of the bone;
- Localization occurs on the ribs, femur, vertebrae, tibia, foot and scapula;
- Less commonly, the hands, heel bone and humerus are affected.
The bones of the skull are not affected. There is no pain or mobility. The tumor has clear boundaries. If the tumor is small, it does not bother you; pain may occur when the blood vessels are compressed.
How is the diagnosis done?
- After an external examination, the patient is sent for an x-ray, which will show the formation and its connection to the bone.
- MRI or CT is used if the situation is unclear.
- Morphological analysis may be performed.
Treatment
The only method used is surgery - removal of the formation with its base and stem. The removal process is necessary if:
- Education is increasing;
- Has large sizes;
- Accompanied by pain;
- Causes skeletal deformation.
In other cases, the patient is observed and monitored using x-rays.
Forecast
The disease has a favorable prognosis - its growth stops with the end of the formation of the skeleton. Degeneration into a malignant state ranges from 1 to 10% (more often with multiple formations).
Recovery after surgery is quick. Patients are prescribed physical therapy and physiotherapeutic procedures.
Treatment around the world with Booking Health
Accurate diagnosis of osteochondroma and selection of the optimal treatment regimen can be quite complex and require the collaboration of experienced orthopedists and surgeons. Choosing a specialized medical institution and a doctor is the first step to a successful result. As an experienced international medical tourism operator, ]Booking Health[/anchor] offers information support, as well as assistance on medical and non-medical issues:
- Choosing the right clinic in Germany or another country, based on specialization and annual qualification profile
- Communication with the treating orthopedist
- Preliminary preparation of a diagnostic or treatment program, preliminary discussion of all procedures
- Providing favorable cost of treatment, without surcharges and additional commissions (savings up to 50%)
- Making an appointment at the clinic or for surgery
- Control of the medical program at all stages
- Insurance against increased cost of treatment in case of complications (coverage 200,000 euros, validity period – 4 years)
- Assistance in purchasing and shipping medications
- Communication with the clinic after completion of treatment
- Organization of control examinations, rehabilitation, remote consultations
- Control of invoices and return of unspent funds
- Booking hotels and air tickets, organizing transfers
- Services of a personal medical coordinator and translator during your stay abroad
Fill out the “Send a request” form on the Booking Health website, and on the same day a patient manager or medical consultant will contact you to discuss all the details with you.
Lipoma
Lipoma
– a benign mobile formation of adipose tissue (wen). It is easy to palpate. Pain usually does not occur unless there are multiple lesions affecting the nerves.
It is most often localized under the skin, but can occur where there is adipose tissue:
- In the liver and lungs;
- In the heart and in the brain.
- On the back;
- On the hand;
- On the arm under the skin;
- On the foot.
- On the mammary gland.
Education can degenerate into malignant.
Types of lipomas
- Fibrolipoma is hard to the touch, as it consists of fibrous fibers.
- Lipofibroma - consists of soft tissue, does not cause pain, grows slowly.
- Myolipoma – includes fat and muscle cells.
- Angiolipoma - consists of adipose tissue and blood vessels.
Reasons for education
- Disorders of metabolic processes and thyroid function.
- Destruction of fatty tissue.
- Diseases of the liver and pancreas.
- Diabetes.
- Heredity.
Diagnostics
- For any localization, an x-ray is prescribed.
- Ultrasound allows you to determine the formation in soft tissues, determine the contours and size.
- CT differentiates wen and other tumors.
- MRI allows you to detail the condition of tissues in the area of pathology.
- A biopsy is performed if it is necessary to clarify the nature of the tumor.
Treatment
With such education you need to contact a surgeon. Since the formations grow quickly and can degenerate into liposarcoma, immediate removal of the lipoma is required. For this we use:
- Operative surgery;
- Ultrasonic removal methods, laser;
- Radio wave and cryogenic effects.
Surgery is resorted to when internal organs, the skull and eyes are affected. When many fatty tumors are diagnosed, only large ones are removed. To draw up a treatment program, you must contact an immunologist and endocrinologist.
Diagnosis of the disease
The diagnosis is made based on a combination of clinical and radiological signs. In this case, radiography usually plays a decisive role in making the final diagnosis. Sometimes magnetic resonance imaging and computed tomography are also used as additional research methods.
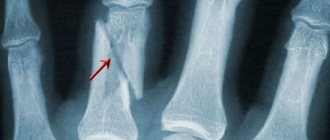
Radiographs reveal changes in bone contours due to the presence of a tumor-like formation associated with the main bone with a wide and thick stalk. The superficial sections of the formation have uneven contours and can resemble cauliflower in shape. In some cases, the pedicle is absent, and the osteochondroma is adjacent to the “mother” bone. The contours of osteochondroma are clear, continuous, directly transforming into the contours of the main bone.
The cartilaginous cap is usually not visible on x-rays unless it contains areas of calcification. Therefore, we should not forget that the actual diameter of osteochondroma may be 1-2 cm greater than the diameter determined by radiography. If an increase in the size of the cartilaginous cap is suspected, magnetic resonance therapy is necessary.
Making a diagnosis usually does not cause difficulties, but in some cases the disease may need to be differentiated from osteoma, paraosteal osteosarcoma, parosteal osteochondral proliferation and chondrosarcoma resulting from malignancy of osteochondroma.
Hemangioma
Hemangioma
- a benign tumor that most often appears on the head and neck in girls. As a rule, vascular formation is detected in newborns.
The reasons for the formation are not clear. Presumably, this is a viral infection carried by a pregnant woman.
Symptoms of pathology
- Superficial formations are red or purple in color and have clear edges. When pressed, the formation turns pale.
- Cavernous hemangiomas are located under the skin in the form of blood-filled nodules.
- Combined hemangiomas are a combination of superficial and subcutaneous.
- Mixed formations consist of different tissues.
- Hemangiomas of the perineum and genital organs are prone to ulceration.
How is the diagnosis done?
- The problem is diagnosed by a surgeon using an external examination and laboratory data.
- Using ultrasound, the depth and location are determined, the speed of blood flow and the volume of the tumor are measured.
- For large tumors, angiography is used.
Hemangioma in adults is a rare phenomenon. Most often, localization occurs on the neck and face, less often - on the arm, on the finger, on the hand, in the anus, on the external genitalia. It does not degenerate into a malignant tumor.
Treatment
The disease is often treated by surgeons. Hemangioma should be treated immediately after detection:
- For deep-lying formations, surgical excision is used;
- For large areas, radiation therapy is used, acting in small fractions;
- Cauterization (diathermoelectrocoagulation) is used for point formations.
- For small complex formations, sclerosing treatment is used - alcohol injections.
- Treatment of combined hemangiomas requires the sequential use of cryogenic and injection therapy.
- Hormonal treatment is indicated for children.
- All simple small hemangiomas must be cauterized with liquid nitrogen.
- Over a large area, the use of hormonal and radiation exposure is indicated.
- For cavernous and combined lesions, surgical, cryogenic and sclerosing methods are effective.
- For formations in the parotid region, complex treatment using angiography and embolization is used.
The disease is often treated by surgeons.
If left untreated in young children, the formation may resolve over time. If the formation increases or complications arise, then it is not recommended to delay. Vascular tumors on the face should be removed early, as the risk of complications is too great.
Advantages of treatment in Israel
- Qualified doctors, many of whom are world famous.
- Equipping clinics with high-tech diagnostic and treatment equipment.
- Professional performance of surgical removal of tumors.
- Comfortable conditions.
- Reasonable prices.
By contacting an Israeli clinic, you will undergo comprehensive treatment under the guidance of leading experts in the field, a full course of rehabilitation, and you will be able to forget about the disease forever and return to your normal life.
- 5
- 4
- 3
- 2
- 1
(1 vote, average: 5 out of 5)
Mesenchymoma
Mesenchymoma
– a malignant formation related to sarcoma. Angiosarcoma and liposarcoma can be found in its composition.
The exact causes of the occurrence have not been clarified. Perhaps this is the effect of carcinogens on the fetus. Risk factors are:
- Vibration, hypothermia and ionizing radiation;
- Chemical exposure – toxic substances, drugs;
- Bacterial and viral infections.
The location is predominantly the chest and abdominal cavity, mediastinum and retroperitoneal space. The formation is manifested by pain, cough, heartburn, shortness of breath and a feeling of fullness.
Diagnosis is carried out using radiography, ultrasound, MRI, biopsy and endoscopic examination. Treatment is carried out surgically. Auxiliary methods are radiation therapy and chemotherapy.
Prices
| Disease | Approximate price, $ |
| Prices for hip replacement | 23 100 |
| Prices for clubfoot treatment | 25 300 |
| Prices for Hallux Valgus treatment | 7 980 |
| Prices for knee joint restoration | 13 580 — 27 710 |
| Prices for scoliosis treatment | 9 190 — 66 910 |
| Prices for knee replacement | 28 200 |
| Prices for treatment of intervertebral hernia | 35 320 — 47 370 |
| Disease | Approximate price, $ |
| Prices for thyroid cancer screening | 3 850 — 5 740 |
| Prices for examination and treatment for testicular cancer | 3 730 — 39 940 |
| Prices for examinations for stomach cancer | 5 730 |
| Prices for diagnosing esophageal cancer | 14 380 — 18 120 |
| Prices for diagnosis and treatment of ovarian cancer | 5 270 — 5 570 |
| Prices for diagnosing gastrointestinal cancer | 4 700 — 6 200 |
| Prices for breast cancer diagnostics | 650 — 5 820 |
| Prices for diagnosis and treatment of myeloblastic leukemia | 9 600 — 173 000 |
| Prices for treatment of Vater's nipple cancer | 81 600 — 84 620 |
| Prices for treatment of colorectal cancer | 66 990 — 75 790 |
| Prices for treatment of pancreatic cancer | 53 890 — 72 590 |
| Prices for treatment of esophageal cancer | 61 010 — 81 010 |
| Prices for liver cancer treatment | 55 960 — 114 060 |
| Prices for treatment of gallbladder cancer | 7 920 — 26 820 |
| Prices for treatment of stomach cancer | 58 820 |
| Prices for diagnosis and treatment of myelodysplastic syndrome | 9 250 — 29 450 |
| Prices for leukemia treatment | 271 400 — 324 000 |
| Prices for thymoma treatment | 34 530 |
| Prices for lung cancer treatment | 35 600 — 39 700 |
| Prices for melanoma treatment | 32 620 — 57 620 |
| Prices for treatment of basal cell carcinoma | 7 700 — 8 800 |
| Prices for the treatment of malignant skin tumors | 4 420 — 5 420 |
| Prices for treatment of eye melanoma | 8 000 |
| Prices for craniotomy | 43 490 — 44 090 |
| Prices for thyroid cancer treatment | 64 020 — 72 770 |
| Prices for treatment of bone and soft tissue cancer | 61 340 — 72 590 |
| Prices for treatment of laryngeal cancer | 6 170 — 77 000 |
| Testicular cancer treatment prices | 15 410 |
| Bladder cancer treatment prices | 21 280 — 59 930 |
| Prices for cervical cancer treatment | 12 650 — 26 610 |
| Prices for treatment of uterine cancer | 27 550 — 29 110 |
| Prices for treatment of ovarian cancer | 32 140 — 34 340 |
| Prices for treatment of colon cancer | 45 330 |
| Prices for lymphoma treatment | 11 650 — 135 860 |
| Prices for kidney cancer treatment | 28 720 — 32 720 |
| Prices for breast reconstruction after cancer treatment | 41 130 — 59 740 |
| Prices for breast cancer treatment | 26 860 — 28 900 |
| Prices for prostate cancer treatment | 23 490 — 66 010 |
Rehabilitation period
After the operation, a plaster splint is applied to the leg. The limb is immobilized for 2 months, during which a gentle regime should be observed and any stress should be avoided. Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs are used, if necessary, to relieve pain.
During the rehabilitation period, the patient may be prescribed physiotherapeutic procedures, classical massage, daily exercise therapy and gymnastics.
Causes
The etiology of the development of solitary osteochondromas has not been definitively established. Many orthopedists and traumatologists adhere to the version that a benign neoplasm is a developmental defect that progresses with growth and the formation of the skeleton. Another reason for the development of osteochondroma can be radiation therapy, which was carried out in childhood. Post-radiation tumors are most often multiple, affecting not only long tubular bones, but also vertebral bone structures. To form osteochondroma, irradiation at doses above 1000 rad is sufficient.
Osteochondromatosis, or the formation of multiple benign tumors, develops due to a genetic predisposition. Hereditary pathology is usually diagnosed in patients under 20 years of age. Transmission of osteochondromatosis occurs in an autosomal dominant manner. One mutant allele, which is localized in the autosome, is enough for the disease to manifest itself.
Osteochondroma in the picture and the tumor removed during surgery.
Classification
Osteochondromas of the femur are sessile, that is, they tightly adhere to the bone structures. And some benign tumors are equipped with a small, strong stalk, so they rise slightly above the bone surface. Neoplasms are also classified depending on their number:
- solitary, resembling a stem or trunk of a plant, formed at various stages of tubular bone growth and representing osteochondral formations. Such tumors are characterized by rather painful symptoms due to constant microtrauma of the tendon. Single neoplasms also provoke poor circulation due to compression of nearby blood vessels;
- multiple (osteochondromatosis). This multicentric form of pathology is usually due to a genetic predisposition. Multiple compactions look like tubercles covered with a shiny fibrin sheath and vary significantly in shape and location.
Osteochondromas of any type can provoke destructive and degenerative changes in bone tissue. This leads to lower limb deformation and stiffness.