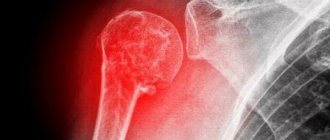
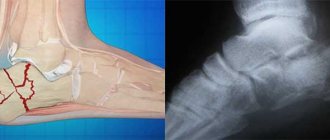
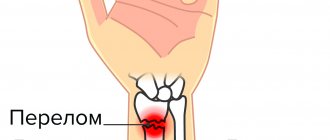
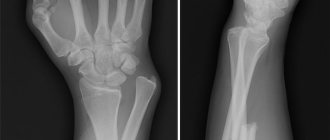
A fracture of the scaphoid bone of the hand is a common injury to the bones of the wrist, which occurs both in everyday life and in the professional environment. Damage occurs most often when falling on an extended palm. In this position, a large load is placed on the scaphoid bone, which leads to its fracture. To ensure high-quality bone fusion, immediately after injury it is necessary to seek help from a traumatologist. Otherwise, complications may arise that will significantly reduce the functional abilities of the hand in the future and can lead to the formation of contractures and the progression of arthrosis.
You can make an appointment with a traumatologist in Yaroslavl at the CONSTANTA Clinic. Patients are treated by qualified specialists with extensive experience. They will conduct a professional examination, prescribe an examination if necessary, and provide effective assistance in case of a fracture of the scaphoid bone of the hand. Self-medication is unacceptable for such injuries, as it leads to improper healing of the fracture and the occurrence of motor restrictions.
Anatomy of the scaphoid bone of the hand
The human wrist is formed by eight small bones, the fracture of which patients often mistake for classic bruises. This explains the late visit to a traumatologist and the delayed start of treatment. Any damage to the wrist joint requires additional examination by a specialist and the appointment of x-ray diagnostics. The scaphoid bone is located in the first row of the wrist. On the dorsal side it connects to the distal epiphysis of the radius.
The scaphoid bone of the hand, due to its anatomical features, is easily damaged. It has an insufficiently branched network of blood vessels, and in the event of a fracture, its proximal system is left without high-quality blood supply and nutrition. Therefore, it is so important to promptly eliminate the consequences of a scaphoid fracture in order to restore the flow of nutrients to the tissues and avoid functional limitations in the future.
Symptoms of a fracture
Fractures of the scaphoid are accompanied by the following symptoms:
- acute pain in the area of the thumb and index finger, which tends to intensify during movement, with palpation and finger movements;
- signs of hemorrhage in the wrist area;
- crepitation (crunching) of bone fragments;
- motor limitations of the hand;
- hyperemia and swelling of soft tissues in the area of injury.
Fractures of the small bones of the wrist often do not have pronounced symptoms and can be confused with ordinary bruises. Therefore, even minor injuries to the hand require examination by a traumatologist and additional diagnostics. You should be alerted by persistent pain in the area of the projection of the scaphoid bone. With a fracture, the pain does not decrease, as with a normal injury, but tends to intensify, and swelling also increases.
Most often, the scaphoid bone breaks into two parts. Both extra-articular and intra-articular injuries may occur. The easiest possible damage is the separation of a bone tubercle. This injury is classified as an external articular fracture. Also, a fracture of the scaphoid bone is often combined - they occur together with a dislocation of the lunate bone.
Diagnostics
A competent orthopedic traumatologist can easily diagnose a pseudarthrosis after a fracture. This requires:
- examination of the patient, palpation of the pathological area;
- radiography in two projections.
In some cases, radiography is also required in oblique projections to create a more clear picture and accurate diagnosis.
False joint can be of three types: atrophic, hypertrophic, true. In the first case, a conical narrowing of bone fragments is observed. The second is their increase. In the third, one part of the bone takes on a convex shape, the other - a concave shape.
The stage of a non-union fracture is also diagnosed: from the initial formation of connective tissue to the formation of the articular capsule and the covering of bone fragments with cartilage tissue. In accordance with this, a decision is made on the treatment method.
Diagnosis of a scaphoid fracture
If fractures of the scaphoid bone of the hand occur, it is very important to promptly seek medical help and conduct an examination, the results of which will allow the doctor to assess the severity of the injury and select effective medical tactics. If the patient does not contact a traumatologist for several days, bone fragments may shift relative to each other, causing swelling and pain to increase. The scaphoid bone has a poor blood supply, which is further deteriorated after a fracture. Therefore, tissues left without quality nutrition begin to die, which in the future can lead to significant motor restrictions in the area of the wrist joint.
The main diagnostic method for fractures of the scaphoid bone of the hand is x-ray examination in three projections. It allows you to assess the nature of the injury, the condition of the surrounding tissues and select an appropriate treatment regimen.
Sometimes, based on the results of an X-ray examination, it is impossible to make an accurate diagnosis and detect a fracture. But the patient complains of persistent pain, which is alarming and suggests serious damage. In this case, the specialist immobilizes the limb with a plaster cast and then repeats the X-ray examination. If there is a fracture, a slit-like space will be visible on the image, which confirms the specialist’s suspicions and requires appropriate treatment.
In case of serious fractures accompanied by crepitation of fragments, specialists prescribe additional studies, in particular, computed tomography of the wrist joint. The study provides a three-dimensional image of the scaphoid bone and allows you to accurately determine further actions, including choosing the correct tactics for surgical treatment of the fracture.
When patients present late with signs of fractures of the scaphoid bone of the hand, their malunion may occur. The risk of this complication is high, since the scaphoid bone has poor blood supply, and the fracture may take longer to heal than with similar injuries to other bones. Due to improper fusion, the nutrition of the joint tissues is further disrupted, the quality of the synovial fluid deteriorates, which leads to destructive changes and progressive arthrosis. This has an extremely negative impact on the patient’s quality of life and the functionality of the hand.
Material and methods
We examined 28 patients (27 men, 1 woman) with a pseudarthrosis of the scaphoid bone of the hand at the level of the middle third, admitted to the 3rd Department of Microsurgery and Hand Trauma of the National Medical Research Center for Traumatology and Trauma named after. N.N. Priorov from 2015 to 2021. The average age of patients was 27 (from 14 to 48) years, the average time from the moment of injury to presentation to the clinic was 19 (from 8 to 34) months. The volume of wrist extension reached 57° (from 65° to 90°), the volume of active wrist flexion was 72° (from 60° to 90°). Pain syndrome on the visual analogue scale (VAS) was equal to 4 (from 1 to points. In 9 patients, pain syndrome occurred only with maximum extension of the hand (in the extreme position). The strength of the fist grip on the affected hand was 28 (from 15 to 56) kg The score on the Disabilities of the Arm, Shoulder and Hand (DASH) questionnaire, which assesses hand function, before surgery was 23.5 (from 10.5 to 36.3) points.
N.N. Priorov from 2015 to 2021. The average age of patients was 27 (from 14 to 48) years, the average time from the moment of injury to presentation to the clinic was 19 (from 8 to 34) months. The volume of wrist extension reached 57° (from 65° to 90°), the volume of active wrist flexion was 72° (from 60° to 90°). Pain syndrome on the visual analogue scale (VAS) was equal to 4 (from 1 to points. In 9 patients, pain syndrome occurred only with maximum extension of the hand (in the extreme position). The strength of the fist grip on the affected hand was 28 (from 15 to 56) kg The score on the Disabilities of the Arm, Shoulder and Hand (DASH) questionnaire, which assesses hand function, before surgery was 23.5 (from 10.5 to 36.3) points.
Before surgery, all patients underwent radiography of the wrist joint in three projections (direct, lateral, semipronation) and computed tomography.
Consolidation was assessed 8 weeks after surgery using radiography and computed tomography. The wires were removed 10 weeks after surgery. Measurements of range of motion (flexion and extension of the wrist) and fist grip strength were assessed 4 and 6 months after surgery.
Surgical technique
All patients underwent arthroscopy of the midcarpal joint, resection of the pseudarthrosis of the scaphoid bone, autologous bone grafting (bone graft was taken from the iliac wing), and fixation with three wires.
With the patient in the supine position, after processing the surgical field three times, the limb was fixed on a distractor. A tourniquet was applied to the shoulder with a pressure of up to 350 mm Hg. The traction force was 5–6 kg. The midcarpal joint was accessed through the ulnar midcarpal port (UMP) with a 2.9 mm arthroscope, angle 30° (Fig. 1).
Rice. 1. Arthroscopic approaches to the pseudarthrosis of the scaphoid. Radial midcarpal port (RuSP) and LoSP.
The area of the pseudarthrosis was visualized (Fig. 2).
Rice. 2. Arthroscopic anatomy of the midcarpal joint. The asterisk indicates the scaphoid bone; triangle - lunate bone; one circle is the proximal fragment of the scaphoid (the proximal pole of the scaphoid); two circles - the distal pole of the scaphoid; arrow—false joint of the scaphoid (scaphoid pseudarthrosis).
Through the radial midcarpal port (MCP) using pliers, scar tissue was removed and the pseudarthrosis of the scaphoid was resected (Fig. 3a ,
Rice. 3. Debridement of the pseudarthrosis area (a); appearance of the scaphoid after resection of the pseudarthrosis (b). b
).
Then, under arthroscopic and X-ray control, 3 wires were inserted: one was axial, passing immediately through the distal and proximal fragments of the scaphoid bone. The other two wires passed only through the distal fragment. Then, a cancellous bone graft was taken from the wing of the ilium using the “chips” type; the average size of one bone graft was 0.2×0.2 cm (Fig. 4, a
).
Rice. 4. Processing of cancellous bone autograft (a); filling the shaft with bone “shavings” (b), introducing bone grafts into the area of the pseudarthrosis (c). The shaft was filled with bone grafts (see Fig. 4, b
) and inserted into the area of the pseudarthrosis (see Fig. 4,
c
) through the LuSP.
On average, 3–5 portions of bone graft were injected into the pseudarthrosis area. Then the two remaining wires were brought into the proximal fragment of the scaphoid bone. The needles were bitten subcutaneously. Next, sutures were placed on the skin, and the hand was fixed in a plaster splint.
Complications from delayed or improper treatment of a scaphoid fracture
Due to deterioration in nutrition of the scaphoid bone, the damaged area may die with the development of aseptic necrosis. As a result of this complication, the patient notes sharp limitations in hand movements and increased pain. Detecting avascular necrosis can be difficult, especially when symptoms are hidden. Signs of this disorder appear on x-rays several months after the injury. But with a highly qualified traumatologist, it is possible to avoid the occurrence of aseptic necrosis. A competent specialist will notice the first signs of a violation in time and will do everything possible to eliminate it and maintain the maximum range of hand movements.
Causes of the problem
The reason for the formation of an acquired false joint lies in the failure of bone fusion.
Problems usually arise in the presence of an infectious disease, endocrine system disorders, metabolic or circulatory disorders. Often, a false joint is a consequence of numerous injuries and destruction of the nerve fibers of the affected area. Pathology develops if:
- soft tissue has embedded itself between the fragments;
- the bones are too far apart;
- fixation turned out to be weak;
- the fixing bandage was removed ahead of schedule;
- loaded the damaged area prematurely;
- blood circulation in the area of damage is impaired;
- suppuration began.
The reasons for the formation of congenital pseudarthrosis lie in malnutrition of the fetus, and this also happens when the nerve fibers in a certain area of the arms or legs are destroyed during intrauterine development.
Treatment of scaphoid fractures
Medical tactics for a fracture of the scaphoid bone of the hand should be individual. It is selected taking into account the severity of the injury, the location of the injury and the general health of the patient. Specialists at the CONSTANTA Clinic in Yaroslavl use all the technical capabilities of modern traumatology and surgery to eliminate fractures and their consequences, as well as to restore impaired functions and range of motion. Innovative diagnostic equipment allows you to conduct examinations of any complexity and obtain reliable research results. The Clinic’s specialists have been diagnosing and treating injuries of varying complexity for many years, providing patients with qualified medical services of high quality.
We will do everything in our power to prevent the development of complications and return you to good health. Treatment of a scaphoid fracture can be conservative or surgical. Conservative therapy includes first aid and maximum immobilization of the damaged bone. Non-displaced fractures are treated conservatively. The patient is placed in a plaster cast in the area of the wrist joint, grasping the first finger and slightly moving it to the side. The hand remains in plaster for 2 months, until the fracture heals completely.
For fractures of the lower third of the scaphoid, healing time may be minimal. These injuries are considered relatively minor and can be treated quickly with proper immobilization. The lower part of the scaphoid is well supplied with blood, which creates favorable conditions for proper fusion.
Fractures of the upper third of the radius, located closer to the forearm, are more difficult due to the obstructed blood supply. In case of such injuries, it is necessary to regularly carry out professional examinations and additional radiographic studies, and in some cases, computed tomography.
The time for fracture healing depends on many factors:
- severity of injury;
- patient's age;
- quality of blood supply to tissues at the site of injury;
- location of injury;
- time of seeking medical help.
Conservative therapy also includes the use of anti-inflammatory and painkillers, which not only improve the patient’s condition, but also prevent the spread of the inflammatory process to neighboring tissues. Specialists apply a circular plaster cast to the forearm area, including the elbow to the metacarpophalangeal region. Immobilization must necessarily involve the proximal phalanges of the thumb. When the proximal and middle parts are fractured, the bone should have a radial deviation. When the fracture area covers the distal part of the scaphoid, it is slightly retracted towards the elbow.
When fragments are displaced and there is a high risk of developing aseptic necrosis, surgical treatment tactics are used. Fractures with severe soft tissue damage deserve special attention. In this case, the risk of developing secondary wound infection increases sharply if aseptic treatment is not carried out in a timely manner and you do not seek help from a traumatologist.
Methods of surgical treatment of scaphoid fractures
If conservative therapy is ineffective, specialists use surgical treatment tactics. Their main goal is high-quality fusion of fragments and restoration of the functional abilities of the hand. The operation is performed under anesthesia, the patient does not feel pain or discomfort.
During surgery, the surgeon restores the anatomical position of the displaced bone fragments and fixes them with a special screw. The results of radiographic examination confirm the correctness of surgical actions. On an x-ray, a specialist can observe the quality of restoration of the anatomical position of the bone and fixation of its fragments.
For old fractures of the scaphoid bone of the hand, surgical treatment is much more difficult, and the recovery period lasts several months. Specialists have to perform an artificial fracture of an incorrectly fused bone in order to restore its anatomical position, fixing the bone fragments with a screw.
Cases when a false joint is formed deserve special attention. End plates appear between the fragments, painless mobility occurs at the site of the scaphoid fracture, and a characteristic gap appears on the x-ray. Treatment of pseudarthrosis is predominantly surgical.