HomeClinical MedicineDiseasesDiseases of the musculoskeletal system
Painful sensations in the elbow joints have probably occurred to everyone at least once: an unsuccessful fall, prolonged monotonous loads, and some diseases can cause inflammatory processes in the elbow. Many means are used for treatment; an integrated approach is extremely important, including medication, injections, physiotherapeutic procedures, and various ointments for pain in the elbow joints.
What to put on your elbows when they hurt
If pain occurs, there is swelling, or redness of the skin on the elbow, this most likely indicates inflammatory processes in the joint. Various ointments for pain in the elbow joints are designed to eliminate unpleasant symptoms. Preparations for external use are affordable products, often available without a doctor’s prescription and yet effective. But let’s not forget that they mainly fight only the symptoms, but not the cause of the pain syndrome. The ointment for elbow pain acts quickly, its active ingredients immediately penetrate the damaged tissues, providing long-awaited relief and restoration of motor functions. External preparations have much fewer side effects and contraindications, unlike tablets and injections. The products cannot be used if there are open wounds on the elbow: scratches, sores, etc.
Aertal
A cream for joints based on the drug aceclofenac, relieves pain, inflammation, and swelling well. When the cream is applied to the appropriate places, it treats torticollis, lubago, myositis, tendinitis, and arthritis.
pros
There are no effective analogues of such a cream, which, coupled with its effectiveness, makes it unique. Economical spending, average price up to 350 rubles. Acts locally on the site of the disease. Restores joint tissue.
Minuses
Practically not, unless you are allergic to aceclofenac. However, it is not used in pediatrics. The texture of the cream is greasy, not everyone likes it and is poorly absorbed.
Types of ointments for elbow pain
Ointment for pain in the elbow joint can be of several types: non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, chondroprotectors, local irritants, combination drugs.
What to anoint the elbows and joints with depends on what causes the pain, i.e. from the cause of the symptoms.
Perhaps the most popular drugs are non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs - NSAIDs. They quickly relieve pain, eliminate swelling and are affordable. These are ointments for pain in the elbow joint: Bystrumgel, Emulgel, Diclofenac, Ortofen, Finalgon, Ketoprom and others. These drugs do not treat the disease, but only eliminate the symptoms; they cannot be used for a long time without a doctor’s prescription. For example, if your elbow hurts and your fingers go numb, non-steroidal painkillers alone are definitely not enough.
Ketoprofen
The basis of the cream is the medicine ketoprofen. It has analgesic, antipyretic and anti-inflammatory effects. Additionally, the composition includes ethanol, trolamine, carbomer and lavender oil. The cream quickly relieves not only pain, but also swelling. Widely used for gout, lumbago, bursitis and other inflammations.
pros
Relieves pain well. Wide range of applications for various diseases of the musculoskeletal system. Has no allergic reactions. Inexpensive - up to 200 rubles. Can be used during pregnancy and for children over 6 years of age. Combines with other treatment methods.
Minuses
Do not use for more than 2 weeks in a row. Long treatment period. It is undesirable to use if there is damage to the gastrointestinal tract, liver, kidneys, or heart diseases. Use with caution in elderly patients.
Are there any contraindications?
Despite the fact that external forms of release of drugs are the most “gentle” compared to tablets and injections, they have a number of contraindications and side effects.
Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, ointments and gels, are considered the most dangerous; their long-term use without medical supervision can lead to serious damage to internal organs. These products contain analgesics and other substances that accumulate in our tissues.
External products should be used strictly following the instructions. Some ointments should be applied with a rubbing motion, others should be lightly smeared on the affected elbow, and others should be used for applications. And of course, a qualified doctor should determine what to apply to the elbow for pain after making an accurate diagnosis. It doesn’t matter what to smear the elbow joint with, if the treatment is limited only to the use of external agents, it will only be possible to eliminate the pain. But the joint will continue to deteriorate. Therefore, complex therapy should be present, even if the pain has been eliminated.
October 21, 2021 Contents
The elbow is a complex joint between the three bones of the shoulder and forearm, a fragment of the human arm. Its anatomical structure also provides for the presence of a nerve, which is located as close as possible to the skin. Pain in the elbow of the right or left hand is always unpleasant.
They need to be treated, but first you need to deal with the reasons, the main ones of which are:
- The elbow of the right hand hurts when extending, pressing, or loading. How to treat, relieve pain, folk remedies, ointments
- disorders of bone and joint structure;
- inflammation of muscles and ligaments;
- diseases of the cardiovascular and nervous system.
Survey
Healthy elbow joints in anteroposterior and lateral projections
- Radiography.
- If possible, the history data should correlate with the radiographic results.
Objective examination
Visual examination
- Upper quadrant position: A patient's elbow problems may be related to structures overlying the joint.
- Cervical and thoracic spine (particular attention to cervical lordosis and thoracic kyphosis).
- Scapula position.
- Angle between the shoulder and forearm (bearing angle): this angle averages 10 degrees in men and 13 degrees in women, and the figure can change up to 14-15 years.
- Edema, ecchymosis, deformation, muscle atrophy.
- "Triangular sign".
Functional tests
The point of performing functional tests is to find the so-called. “asterisk sign” (literally – asterisk sign), that is, those positions or movements that intensify symptoms. This is necessary in order to check and double-check the effectiveness of the intervention.
- Identifying the asterisk position (what activities increase symptoms?).
- Pain-Free Grip Strength test.
- Push-off Test: This test is used to evaluate how the upper quadrant handles weight transfer. This helps determine functional/occupational limitations (ICC=0.31-0.97).
- Functional Impairment Test of the Arm, Neck, and Shoulder (FIT-HaNSA): A standard physical therapy test that assesses overall activity of the upper extremity. Testing of its sensitivity and specificity specifically for the elbow joint has not yet been completed.
Palpation
- Medial and lateral epicondyles.
- Olecranon process and olecranon fossa.
- Head of the radius.
- Lateral ligament of the elbow joint.
- Soft tissues of the shoulder and forearm/hand - for provocative tests, detection of edema, local increase in temperature.
Elbow joint in front (the biceps tendon is marked with a marker)
Elbow joint posteriorly (the circle marks the lateral epicondyle)
Medial epicondyle (marked with a dot)
Neurological assessment
- Reflexes: C5-C7.
- Myotomes: C5-Th1.
- Dermatomes: C5-Th1.
Motor Capability Testing
- Range of active movements/range of passive movements with or without additional load. Elbow: - Flexion. - Extension. — A positive elbow extension test may indicate a fracture, in which case the patient should be referred to a physician.
- Pronation/supination of the forearm.
- Brush: Flexion.
- Extension.
- Range of motion in the cervical spine, shoulder and elbow joints with and without additional load.
- Elbow flexion/extension.
- Pronation/supination of the forearm.
- Flexion/extension of the hand.
- Pain-free grip strength test.
- Thumb.
- Fingers of the hand (second to fifth).
- Humeral ulnar traction.
- Brachioradial traction.
- Proximal/distal radioulnar joint, anteroposterior and posteroanterior glides.
- Cubital Tunnel Syndrome: Elbow Extension Test.
- Passive elbow extension, pronation, wrist flexion (Mill's Test).
- Varus stress test.
- Median nerve tension: neurodynamic test for the upper limb 1.
Friends, this and other questions will be discussed in detail at the seminar “Elbow joint: diagnosis and treatment.” Find out more...
Source: Physiopedia - Elbow Examination.
Types of diseases that cause elbow pain
The most common injuries to the bone and joint structure are as follows:
- Bruises are closed injuries without compromising the integrity of the joint. Mild bruises go away within a few hours or days, severe bruises are accompanied by an increase in the volume of the damaged organ and aching pain.
- A tumor is a complication that often occurs with bruises. May be benign or malignant. Often associated with pathologies of bone and joint tissue.
- Arthritis is an inflammation of the joint, which can be a side effect of a number of other ailments. Accompanied by pain during physical activity.
- Arthrosis is a disorder of the structure of cartilage, leading to its thinning. For the elbow joint, this disorder is extremely rare.
- Gout is a type of arthritis that occurs due to the accumulation of uric acid salts in the joints. Occurs in diseases associated with metabolism.
Muscle inflammations include:
- Bursitis is a lesion of the joint capsule. It occurs due to excess accumulation of fluid in it.
- Fasciitis is inflammation of muscle tissue cells. Accompanied by nagging pain.
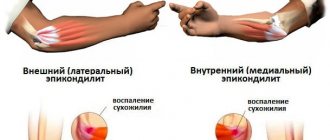
- Epicondylitis is a disease affecting the attachment of muscle fibers. Develops from microtraumas received under excessive loads.
- Tendinitis – Damage to tendons where they attach to joints. The disease is common among athletes due to excessive stress.
- Osteochondrosis is the destruction of ligaments, tendons, cartilage or bone tissue. One of the painful and dangerous diseases. It is difficult to treat.
Cardiovascular and nervous diseases that manifest themselves in the elbow joint:
- Inflammation of the ulnar nerve occurs due to pinching. May cause pain even at rest.
- Cardiac ischemia is an insufficient blood supply, leading to organ necrosis. In this case, the vessels and circulatory system need to be treated.
- Hemophilia is a blood clotting problem. On the elbow joints it is reflected in periodic hemorrhages.
Diagnosis of elbow pain
You can find out the reason why problems arise in the elbow of your right or left hand with your local therapist. Having the patient’s medical record in hand, he can quickly diagnose the problem and prescribe treatment. Sometimes, in more complex cases, a conclusion from a more specialized specialist - a neurologist, cardiologist or surgeon - is necessary.
Again, a local doctor can write a referral to them. But if the problem is not obvious, additional research will be needed. Some of them can be carried out at a local medical facility, while others can only be carried out in hospitals or medical centers for an additional fee.
| Type of study | Where to spend | Approximate cost |
| X-ray of the elbow joint | Hospital, medical center (MC) | 350 – 9100 rub. |
| Blood analysis | Clinic, hospital, MC | 0 – 980 rub. |
| Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) of the elbow joint | Hospital, MC | 2000 – 20300 rub. |
| Arthrography of the elbow joint | Hospital, MC | 1500 – 9100 rub. |
| Puncture (fluid collection) from the elbow | Hospital, MC | 990 – 3000 rub. |
When to see a doctor
The elbow of the right hand hurts (it can be treated without going to the doctor) - with a slight bruise, it is enough to immobilize the hand and apply a cooling compress to the site of injury so that the condition will soon return to normal.
But in some cases, consultation with a specialist is necessary:
- if the pain does not subside despite immobilization and compress;
- if swelling and redness appear on the elbow with any movement;
- if pain in the elbow is accompanied by an increase in general body temperature;
- if the shape of the joint has changed, the bone protrudes;
- if your arm hurts and it is impossible to bend or straighten it.
Preventing Elbow Pain
You can prevent elbow pain by avoiding muscle strain. To do this, it is worth taking breaks from time to time in work where the elbow joint is constantly involved. It is better to choose the right position and use convenient equipment.
When moving your arms monotonously, it is useful to periodically bend and unbend them, as well as do self-massage. When reading books or talking on the phone, you should not constantly lean on your elbows.
- Knee braces
Methods for treating elbow pain
The elbow of the right hand hurts (it must be treated immediately) - in case of a serious injury, the doctor suggests orthopedic devices to immobilize the damaged joint:
- fixing bandage;
- bandage;
- gypsum;
- splint;
- orthosis
The specialist can also recommend medications suitable for each specific case.
Medications
They are the mainstays in treating elbow problems. The most commonly prescribed drugs are non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs). Their action is quite fast, but superficial. Non-steroids fight inflammation and eliminate pain, but not the cause itself. They are designed to eliminate pain in order to alleviate the patient's suffering.
There are currently dozens of NSAIDs available in various forms.
The most common of them:
| Name | Form | Approximate cost |
| Diclofenac | Ointment/Gel, 30 g Solution for injection, 25 mg/ml Tablets, 50 mg | From 16 rub. From 42 rub. (for 5 – 10 ampoules) From 27 rub. (for 20 tablets) |
| Nimesulide | Tablets, 100 mg | From 30 rub. (for 20 tablets) |
| Indomethacin | Ointment 10%, 40 g Tablets, 25 mg Rectal suppositories, 50/100 mg | From 36 rub. From 15 rub. (for 30 tablets) From 52 rub. (for 10 pcs.) |
| Celecoxib | Capsules, 200 mg | From 141 rub. (for 10 capsules) |
| Meloxicam | Solution for injection, 15 mg/ml Tablets 7.5/15 mg | From 291 rub. (for 5 ampoules) From 152 rub. (for 10 tablets) |
| Ketorolac | Solution for injection, 30 mg/ml Tablets 10 mg | From 51 rub. (for 10 ampoules) From 15 rub. (for 10 tablets) |
| Ibuprofen | Ointment 5%, 25 g Tablets, 200 mg | From 28 rub. From 28 rub. (for 50 tablets) |
| Naproxen | Tablets, 250 mg | From 131 rub. (for 10 tablets) |
| Piroxicam | Capsules, 10/20 mg | From 19 rub. (for 20 capsules) |
Ibuprofen will help relieve pain in the elbow of the right hand.
These medications should not be used constantly. They are sold without a prescription, but have many side effects.
Another group of drugs prescribed for elbow pain are chondroprotectors. Their functions are the healing of cartilage tissue, while relieving pain, and leveling the process of dystrophy. The basis of such drugs are 2 components – chondroitin and glucosamine. They are a natural building material of cartilage tissue.
Treatment with these drugs takes a long time - over 3 months. First they are prescribed in injections, and then in tablets. To maintain maximum effect, the course of treatment is repeated annually.
The most popular chondroprotectors:
| Name | Form | Approximate cost |
| Structum | Capsules, 500 mg | From 1200 rub. (for 60 capsules) |
| Alflutop | Solution for injection, 10 mg/ml | From 1453 rub. (for 10 ampoules) |
| Chondroxide | Cream 8%, 50 g Gel 5%, 40 g Tablets, 250 mg | From 499 rub. From 318 rub. From 500 rub. (for 60 tablets) |
| Teraflex | Cream 30/50/100 g Capsules | From 307 rub. From 979 rub. (for 60 capsules) |
| Noltrex | Syringe 2.5 ml | From 2500 rub. |
| Chondrolone | Solution for injection, 0.1% 1 ml | From 778 rub. (for 10 ampoules) |
For severe pain, injections may be prescribed directly into the joint. Such injections provide quick relief. But doctors do not recommend using this treatment constantly - along with the injection, an infection can be introduced into the joint.
For intra-articular injections use:
- chondroprotectors;
- hyaluronic acid;
- corticosteroid hormones
The last group of drugs has an almost immediate effect on the sore joint, effectively copes with inflammation, but has many contraindications. However, they are extremely popular with patients.
Most often used:
| Name | Form | Approximate cost |
| Diprospan | Suspension for injection | From 110 rub. (for 1 piece) |
| Kenalog | Suspension for injection, 40 mg/ml | From 451 rub. (for 5 pcs.) |
| Flosteron | Suspension for injection | From 3950 rub. (for 5 pcs.) |
| Metipred | Powder for injection, 250 mg | From 199 rub. (for 1 piece) |
| Depo-Medrol | Suspension for injection, 40 mg/ml | From 678 rub. (for 1 piece) |
Injections are prescribed 1 every 2 weeks. A full course includes 3-5 injections. Corticosteroids do not affect the disease itself, so they cannot provide complete treatment.
My right elbow hurts (can also be treated with hyaluronic acid) as a result of injuries or joint diseases. The drug is injected into the joint when there is a lack of fluid in it. As a result, nutrition improves and restoration of cartilage tissue accelerates.
Today, the following medications with hyaluronic acid are used:
| Name | Form | Approximate cost |
| Ostenil | Syringe, 20 mg/2 ml | From 2800 rub. |
| Fermatron | Syringe, 1% solution, 2 ml | From 3190 rub. |
| Sinokrom | Syringe, 1% solution, 2 ml | From 2950 rub. |
CAUSES OF PAIN IN THE SHOULDER AND ELBOW JOINTS
Shoulder dislocations: The most common cause is trauma: sports injury, fall, car accident. Like any dislocations, a dislocated shoulder is also very painful, and if a person himself cannot return the shoulder to the anatomically correct position, he needs to seek help from an orthopedic traumatologist. Dislocations resulting from trauma are usually accompanied by more extensive damage - ruptures or fractures. They require separate treatment. In young people under 30 years of age, a shoulder dislocation has an 80% chance of re-dislocation. Therefore, young people are recommended to undergo surgery to restore the anatomical balance in the joint to prevent re-dislocation. In case of repeated dislocations, not only the ligaments of the joint are damaged, but also the bone. As a result, arthrosis may develop.
Lateral epicondylitis, or tennis elbow , is an inflammation of the outer part of the elbow where the muscle tendons attach to the bone growth. These muscles connect the hand to the humerus. The work of the muscles ensures the movement of the hand. Tennis elbow is the most common elbow problem caused by specific strain, overuse, or injury. Tennis elbow causes swelling and pain in the outer edge of the elbow that gets worse when you move your hand, such as shaking your hand. One of the most common causes of epicondylitis is working at a computer. To treat tennis elbow, you need to relieve the elbow joint. It is recommended to take anti-inflammatory drugs, and after consultation with an orthopedic traumatologist, attend physical therapy classes. In some cases, if the problem cannot be resolved in this way, surgery is used to repair or release the affected tendon. During the operation, the inflammation focus is eliminated (by resection), the approximate location of which is determined before the operation using ultrasonography. In the postoperative period for a long time (up to 8 weeks), it is necessary to provide a gentle regime for the elbow. Computer work should also be limited. Lateral epicondylitis, or tennis elbow , is an inflammation of the inside of the elbow where the muscle tendons attach to the bone growth. Golfer's elbow occurs as a result of repeated wrist flexion movements, which results in overexertion of the wrist and finger flexor muscles and excessive stress on the tendon insertions of these muscles, resulting in inflammation, swelling and pain in the elbow joint. To treat golfer's elbow, you need to relieve the elbow joint. It is recommended to take anti-inflammatory drugs, and after consultation with an orthopedic traumatologist, attend physical therapy classes. In some cases, if the problem cannot be eliminated in this way, surgery is used to repair or release the affected tendons. During the operation, the inflammation focus is eliminated (by resection), the approximate location of which is determined before the operation using ultrasonography. In the postoperative period for a long time (up to 8 weeks), it is necessary to provide a gentle regime for the elbow. Computer work should also be limited. Frozen shoulder in medicine is an obscure but fairly common condition affecting the shoulder joint. The disease can begin suddenly, with pain in the shoulder that progresses, causing restrictions in movement. Frozen shoulder causes scar tissue to form in the shoulder joint capsule. The cause of the disease has not yet been discovered in the world, but its course has been studied. The illness can last up to three years. When the pain can be relieved with the help of drug therapy, the patient, after consultation with an orthopedic traumatologist, is recommended to go to physical therapy to restore movement in the joint. In cases where drug and physical therapy treatment does not produce results, surgical treatment is recommended to free the joint from scar tissue, which restores range of motion and eliminates the cause of pain. Rotator cuff tears. The four muscles of the shoulder joint that anchor the humerus in the shoulder joint and allow movement are called the rotator cuff. These four muscles attach to the scapula, and their tendons attach to the greater tubercle of the humerus. Rupture of these tendons can occur as a result of injury, as well as wear and tear due to the aging process. When tendon injuries occur, the pain is usually more severe at night and is felt in a specific location - in the arm above the elbow, where the deltoid muscle attaches to the humerus (upper third of the shoulder). If the ruptures in the tendons are small, the restrictions on movements are not pronounced, and only movements performed with a very large amplitude can be difficult. In cases of rotator cuff inflammation, the problem is treated using anti-inflammatory medications, physical therapy, and hormonal steroid injections. If such treatment does not produce effective results, surgical intervention is used - the damaged areas are sutured, eliminating pain and restoring range of motion. Rotator cuff tears are treated surgically. Anti-inflammatory therapy in case of rupture is used only to eliminate symptoms (pain and inflammation). If rotator cuff injuries are left untreated, there is a good chance that the problem will eventually need to be addressed with shoulder replacement. Shoulder recoil syndrome. Regular overuse of the shoulder joint through the full amplitude of swimming, playing baseball or tennis, microtrauma, or natural wear and tear of the joint as we age are the most common causes of shoulder recoil syndrome. At the initial stage, there is a slight pain in the shoulder, which a person can feel both at rest and during movement, pain radiating from the shoulder down the arm, sudden, sharp pain when lifting or grasping objects. As the syndrome progresses, pain appears at night, weakness and limitations in movement; it is difficult to move your hands behind your back, for example, unzipping a dress. To treat recoil syndrome of the shoulder joint, it is necessary to unload the joint. It is recommended to take anti-inflammatory drugs and, after consultation with an orthopedic traumatologist, study and regularly do a set of physiotherapeutic exercises. In some cases, if the problem cannot be solved in this way, surgical intervention is used. Elbow recoil syndrome often occurs after injury or repeated microtrauma, such as in athletes. The patient experiences restriction of movement in one or more directions (unable to straighten or bend) or in both directions (unable to achieve full range of motion). To treat elbow recoil syndrome, it is necessary to unload the joint. It is recommended to take anti-inflammatory drugs and, after consultation with an orthopedic traumatologist, study and regularly do a set of physiotherapeutic exercises. In some cases, if the problem cannot be solved in this way, surgical intervention is used. In the postoperative period, already on the first day after surgery, a course of physical therapy begins to restore the full range of motion of the joint. "Mouse" of the elbow joint. As a result of injury or disease of the joint, a fragment of cartilage or bone enters the joint capsule. It usually causes a feeling of locking and sharp pain when moving. “Mouse” of the elbow joint is treated surgically. During the operation, a fragment “floating” freely in the joint (articular mouse) is removed. Bursitis of the shoulder joint is an inflammation that occurs in the mucous membrane of the shoulder joint. Signs of inflammation: pain, swelling, limitation of movement and pain when moving. Inflammation is caused by overexertion of the shoulder joint, repeated microtrauma or separate trauma to the shoulder joint, as well as calcific tendonitis, as a result of which lime crystals settle in the rotator cuff tendon, forming a cavity or cavities and causing inflammation of the tissues surrounding the tendon. Bursitis of the elbow joint is an inflammation that occurs in the mucous bursa of the elbow joint. The inflammation usually causes pain, swelling and, in rare cases, limited movement. The cause of bursitis can be injury, infection, arthritis, as well as prolonged pressure on one or both elbows, for example, in representatives of specific professions - tinsmiths or refrigeration / heating installers, who have to do part of the work resting on their elbows. Arthritis of the elbow joint is an inflammatory process in the joint, manifested by pain and limitation of movement. One of the most common types of arthritis affecting the elbow joint is rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis can also be caused by physical activity, which regularly strains the elbow joints and causes injury. Non-surgical treatment for arthritis involves removing stress from the affected joint, taking pain medications, steroid injections, and physical therapy. If this treatment fails to reduce pain, severe limitations of movement in the elbow joint are observed, surgical treatment is required. Emergency surgical treatment is necessary in case of purulent arthritis (arthritis caused by an infection - a microbe). Infectious arthritis can be caused by, for example, diabetes mellitus, as well as regular use of steroids (usually in people with autoimmune diseases). Timely and adequate surgical treatment of the joint increases the likelihood of a positive result. Arthrosis of the shoulder joint. As a result of injuries, diseases, and the natural aging process, a person's shoulder joint is gradually damaged. The cartilage that protects the surfaces of the two bones from direct contact and friction in the joint is damaged. When the cartilage wears out, as a result of direct contact and friction of the bones, inflammation in the joint occurs, pain, and as a result, limited movement. Arthrosis is an irreversible process, but it can be limited or slowed down. To effectively treat arthrosis, anti-inflammatory and painkillers are used, as well as physical therapy - procedures aimed at activating blood circulation around the damaged bone. After consultation with an orthopedic traumatologist, it is recommended to study a set of physiotherapeutic exercises, the regular implementation of which allows you to maintain or even improve the existing range of motion of the diseased joint. If this treatment fails to reduce pain and severe limitations of movement in the shoulder joint are observed, surgical treatment is required.