Diathesis in children is not at all “reddened cheeks of a baby,” as many are accustomed to believe. This concept hides a number of pathologies. But the main thing you need to understand is that diathesis is not an independent disease. This term is used by doctors to describe a child’s tendency to certain diseases or reactions to specific stimuli. In fact, this is a hereditary feature of the body, which manifests itself at a very early age and, due to individual reasons, can develop into serious pathologies in the future.
What is neuro-arthritic diathesis?
It is based on a metabolic disorder of certain substances in the body . This condition is characterized by eating disorders, a tendency to ketoacidosis (an increase in ketone bodies in the blood), and increased nervous excitability.
The frequency of neuro-arthritic diathesis is about 5%, that is, it develops much less frequently than all other constitutional anomalies.
It most often occurs in children aged two to ten years, and by adolescence, all its symptoms, as a rule, are leveled out. However, in some cases in adults, its manifestations persist for life and over time can lead to the development of many ailments: diabetes mellitus, arteriosclerosis, gout, urolithiasis and others.
Reducing the manifestations of diathesis in children
To effectively treat diathesis in children of the first year of life, the following types of therapy are used:
- breastfeeding or careful selection of formula milk;
- daily baths with decoctions of medicinal herbs - chamomile, string, oak bark;
- taking antihistamines;
- applying anti-inflammatory ointments to affected areas of the skin;
- in the presence of dysbacteriosis, take probiotic medications;
- ultraviolet baths.
Children over one year old are advised to have an individual diet that excludes the consumption of allergenic foods.
Causes
The basis of diathesis is:
On the one hand, there is a hereditary defect in the metabolism of purine bases (substances found in meat and some other products), as well as increased formation of uric acid in the body.
On the other hand, there is environmental factors overloading the diet of a pregnant woman and young child with foods containing proteins (meat, liver, kidneys).
In such families, neurasthenia, gout, gallstones or urolithiasis, arteriosclerosis, arterial hypertension, and diabetes are more often detected.
Prevention of diathesis
Prevention of the development of constitutional anomalies should begin during pregnancy and continue at least during the first year of life. Main events:
- regular monitoring during pregnancy;
- prevention and treatment of gestosis, other anomalies of pregnancy and childbirth;
- proper diet and emotional peace of the expectant mother;
- early attachment of the newborn to the breast;
- breastfeeding with the correct, gradual introduction of new products;
- hypoallergenic diet of the child and mother feeding breast milk;
- use only cotton linen, wash with baby soap or special powder;
- gymnastics, massage, hardening procedures, starting from a very early age;
- compliance with all vaccination instructions;
- upon admission to kindergarten or school - a course of adaptogenic drugs as prescribed by a doctor.
Development mechanism
Quite complicated. However, discarding most of the complex specific terms and without going deep into the pathophysiology, it boils down to the following:
Against the background of impaired metabolism under the influence of unfavorable factors (stress, errors in diet), and ketone bodies (acetone, acetoacetic and beta-hydroxybutyric acid) increases
All changes that occur in the organs and systems of the baby are caused precisely by the influence of these substances.
Manifestations
They depend on the age of the small patient, as well as the severity of the symptoms of diathesis. There are several syndromes:
*Neurasthenic syndrome . It occurs most often and already observed in infancy: the baby is restless and fearful for no reason, sleeps poorly and little. And as the baby grows up, it becomes even more excitable: it can even scream from a mosquito bite or slight itching of the skin.
Since purine bases stimulate the nervous system, the baby is ahead of its peers in mental and emotional development. The baby is very inquisitive, quickly masters oral and written language, and easily remembers what he read and heard. Such a child is often called a child prodigy.
However, this is just external well-being. In fact, the problem lies much deeper.
Often an older child with neurasthenic syndrome experiences:
- emotional lability: unstable mood, increased irritability and tearfulness
- excessive physical activity
- short and shallow sleep, night terrors
- increased sensitivity to odors
- sometimes habitual vomiting
- obsessive cough, tics
- enuresis (bedwetting)
- persistent anorexia, difficult to treat
- stuttering (logoneurosis)
- headaches, as well as abdominal and muscle pain
- large bowel movements despite poor appetite
- breath smells of acetone (overripe fruit) in the morning
In addition, a child with neuro-arthritic diathesis has a small body weight. However, sometimes he tends to be overweight (especially girls).
* Dysmetabolic syndrome. With this form, due to disruption of metabolic processes, the following changes occur in the child’s body:
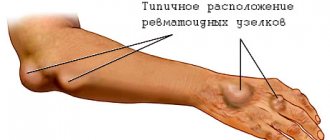
- Urates in the intraarticular fluid may crystallize. Therefore, sometimes the child complains of night-time transient pain in the joints.
- Often, salts (urates, oxalates, phosphates) and red blood cells appear in the baby’s urine (due to damage to the mucous membrane by salt crystals). Therefore, the child may complain of pain and burning during urination, which are not associated with hypothermia or infection.
In addition, with this syndrome, due to a sharp increase in ketone bodies in the blood and tissues, an acetonemic crisis sometimes develops. Its causes can be errors in diet (abuse of meat and fatty foods), any disease or stress, as well as increased physical activity.
Why does the anomaly develop?
Among the causes of diathesis, doctors name a number of hereditary and prenatal factors, environmental features and care for the newborn. Among them:
- complications of pregnancy - toxicosis, infections suffered by the mother during pregnancy, taking certain medications during pregnancy, bad habits and eating disorders, fetal hypoxia;
- unfavorable heredity, the presence of anomalies in close relatives;
- too small or increased body weight of the child at birth;
- perinatal pathologies of the central nervous system;
- artificial feeding;
- dysbacteriosis;
- improper child care, temperature irregularities or poor nutrition;
- vaccination;
- chronic infections;
- emotional distress.
The mechanism of formation of physiological adaptation of a newborn is quite complex and fragile, it is influenced by many factors.
Symptoms of acetone crisis:
* Suddenly or after a short-term malaise (headaches, nausea, constipation, slightly grayish-white color of the stool), repeated indomitable vomiting and a pronounced smell of acetone from the mouth appear.
* The baby complains of abdominal pain, his body temperature rises , and he can quickly lose weight .
* The baby refuses to eat and drink.
* The baby rapidly develops symptoms of dehydration: severe thirst and dry mouth, decreased elasticity of the skin (if it is squeezed too much, it slowly returns to its normal position), lack of tears.
* In severe cases, consciousness is sometimes impaired and convulsions develop.
The attack lasts from several hours to one or two days (sometimes up to five) and in most cases stops as suddenly as it began. Usually after an attack the child recovers quickly.
Changes in tests during an attack
- Ketone bodies, acetone, ammonia and leukocytes increase in the blood
- in the urine .
If a severe acetonemic crisis develops, the child needs urgent medical attention.
Spastic syndrome
It is characterized by the appearance of migraine-like headaches, bronchospasm, pain in the heart, as well as a tendency to increase blood pressure, constipation, renal and intestinal colic.
Possible development of bronchial asthma. As a rule, it is not severe and responds well to treatment.
Skin syndrome
It develops infrequently and mainly in older children. It is characterized by the development of urticaria, Quincke's edema, eczema, and neurodermatitis.
Note! There is not always a clear boundary between these syndromes. Therefore, for example, the same child may exhibit signs of two syndromes, but with a predominance of the symptoms of one of them.
When is treatment needed?
The child needs treatment in severe cases.
To improve general well-being, the following are prescribed:
- Soothing herbs (valerian, mint, horsetail, motherwort) or drugs (phenobarbital and others).
- Medicinal substances that disrupt the synthesis of uric acid (alopurinol) or remove it from the body (ethamide, urodan) prevent the formation of ketone bodies (calcium pantothenate).
However, most often the baby needs treatment for an acetonemic crisis. It is aimed at combating dehydration and acidosis (a condition in which the blood is acidic), accelerating the elimination and destruction of ketone bodies, and stopping vomiting.
For this it is recommended:
- In case of an unexpressed crisis (acetone in the urine is no more than “++”), give the child plenty of water. Sweet tea, alkaline mineral waters, and freshly prepared fruit juices are suitable. It is recommended to drink frequently (every 10-15 minutes) and in small portions so as not to provoke attacks of repeated vomiting.
- If the symptoms of a crisis are severe and the acetone in the urine is more than “++”, the child is hospitalized and treated with medications : glucose, saline, cerucal and others.
However, combating the acetone crisis and prescribing certain medications is not the basis of treatment. Such a child is much more in need of a protective regime and balanced nutrition.
Can you help your baby?
Certainly! Indeed, in this case, much more depends on you than on the doctor. So try to follow some tips:
* Protect your baby from excessive negative emotions and mental overload , since emotional lability makes it difficult for the baby to tolerate them.
* Limit the time your child spends in front of a computer monitor and watching TV shows (especially if he is addicted to “shooting games”).
* Gradually harden your baby: morning exercises, walks in the fresh air, wet rubdowns.
* It is advisable for the child to engage in physical activity (but not intense sports!).
In addition, to prevent excess intake of purines, the formation of uric acid and ketone bodies, it is important to adhere to a certain diet.
Diet
— Try to ensure that diet includes foods in sufficient quantities that prevent the formation of ketone bodies in the body. At the same time, make sure that the content of purine bases and oxalic acid in them is minimal.
These include:
* dairy products (milk, cottage cheese, cheese, sour cream)
* most vegetables and fruits: potatoes, zucchini, eggplant, apples, apricots and others
* “protected” cereals (contain starch): pearl barley, buckwheat, oatmeal
* flour products
* eggs (no more than one per day).
- Try to ensure that your baby receives a sufficient amount of alkaline drinks (especially in the afternoon): mineral water, lemon water, freshly prepared fruit juices.
— Pamper your little one and add some “yummy” things : marmalade, berries, dried fruits (raisins, dried apricots), jelly candies.
- Limit (or in severe cases eliminate) foods that are moderately rich in purine bases:
lean meats (veal, beef, turkey, rabbit, lamb)
sea fish: mackerel, flounder, haddock, salmon, cod
crayfish
river fish: carp, pike perch, pike
hazelnuts, walnuts, almonds
porcini mushroom, chanterelles, champignons.
— It is advisable that you completely exclude from your diet foods that are very rich in purines and oxalic acid, and can also increase acidosis:
strong meat and fish broths
chicken
offal (brains, kidneys, liver, tongue)
industrial canning products (if they are not marked “For baby food”)
carbonated drinks, including any other drinks that have been stored in the refrigerator for a long time
legumes (beans, soybeans)
spinach, sorrel, cauliflower, parsley, green peas, rhubarb
Diet
As a rule, the first signs of an allergy appear in a child 4-6 hours after eating. Therefore, to accurately identify the allergen, do not mix products!
If you are sensitive to any product, it is excluded from the child’s diet for some time. Then you can try again. Scientists have proven that allergies can only be cured with the help of an allergen. After all, even to poison in small doses the body gets used to it.
Important: if a reaction to complementary foods occurs in the form of rashes, it is necessary to prescribe antihistamines and sorbents that help remove the allergen faster.
If a woman is breastfeeding, then she needs to carefully monitor her diet and give up some “tasty” things. Highly allergenic foods such as chocolate, coffee, marinades, and smoked foods should be excluded from the diet.
Children suffering from allergies are especially careful when introducing their first complementary foods. As a rule, it is recommended to start with vegetables (zucchini, cauliflower). Doctors recommend using industrially produced ready-made food, as it is made from proven quality products and contains the required amount of vitamins.
Cow's milk intolerance is one of the causes of diathesis. In infants it usually appears when the child is transferred to artificial feeding. In this case, doctors recommend abandoning formula milk and switching to formulas based on soy protein (also called lactose-free), hypoallergenic, or using goat milk. If a child has been experiencing allergic symptoms for a long time in the form of frequent, loose and foaming stools, it is recommended to introduce fermented milk products containing bifidobacteria into his diet.
In any case, you cannot independently choose baby food for children with diathesis. This should be done by a doctor, based on the child’s characteristics.
The body of a one-year-old child is still very weak and susceptible to influence. Diathesis in such children can also be caused by familiar foods. Even an extra spoonful of your favorite porridge, eaten “for dad,” can cause anxiety. Try not to overfeed your baby. It is advisable to feed him more often, but in small portions.
When a child reaches the age of three, parents often stop paying due attention to his nutrition and seat the child at a common table. This is a huge burden even for a completely healthy baby, not to mention one with allergies. It is necessary to minimize the consumption of salt and sugar, as well as hot seasonings and spices.
Recommendations for regimen and nutrition for various forms of diathesis
| Appointments | Exudative-catarrhal diathesis | Lymphatic-hypoplastic diathesis | Neuro-arthritic diathesis |
| Diet, including for mothers breastfeeding | Hypoallergenic, with the exception of obligate allergens, red and yellow-colored vegetables and fruits. Limiting broths and whole cow's milk. Boiled meat and fish. Fermented milk products, vegetables, fruits. In severe cases - an elimination diet, identification and exclusion of the causative agent | Age table with limitation of flour products and cereals. The predominance of vegetables, fruits, and lactic acid products in the diet. For allergic manifestations - the same as for exudative-catarrhal diathesis. | Age table with the limitation or exclusion of broths, fried, stewed and canned meat, sausages, smoked meats, spicy dishes, coffee, cocoa, citrus fruits and a number of vegetables (sorrel, spinach, radishes, radishes, cauliflower, green peas). Dairy-vegetable table, boiled meat and fish. |
| Observation | Keeping a food diary, individual vaccination schedule. Monitoring the regularity and quality of stool. If necessary, treatment of dysbiosis. | ||
| Careful care | Constantly | Constantly | Constantly |
| Home education | Up to 3 years | Up to 5-6 years | Up to 3 years |
Recommendations for the regimen
Be sure to maintain a hypoallergenic environment in the house - regularly ventilate, carry out wet cleaning at least 2 times a day. It is recommended to remove all carpets and interior items that accumulate dust. Books and toys should be stored in closed cabinets. The presence of animals in the house is undesirable (an allergic reaction is caused not by the fur itself, but by the scales of the animal’s skin). Even harmless fish can cause an exacerbation of diathesis; it is also better to remove indoor flowers.
For children suffering from diathesis, vaccinations are administered after a preliminary course of antihistamines.