Our specialists
Tarasova Svetlana Vitalievna
Expert No. 1 in the treatment of headaches and migraines. Head of the Center for the Treatment of Pain and Multiple Sclerosis.
Somnologist.
Epileptologist. Botulinum therapist. The doctor is a neurologist of the highest category. Physiotherapist. Doctor of Medical Sciences.
Experience: 23 years.Derevianko Leonid Sergeevich
Head of the Center for Diagnostics and Treatment of Sleep Disorders.
The doctor is a neurologist of the highest category. Vertebrologist. Somnologist. Epileptologist. Botulinum therapist. Physiotherapist. Experience: 23 years.
Bezgina Elena Vladimirovna
The doctor is a neurologist of the highest category. Botulinum therapist. Physiotherapist. Experience: 24 years.
Palagin Maxim Anatolievich
The doctor is a neurologist. Somnologist. Epileptologist. Botulinum therapist. Physiotherapist. Experience: 6 years.
Mizonov Sergey Vladimirovich
The doctor is a neurologist. Chiropractor. Osteopath. Physiotherapist. Experience: 8 years.
Drozdova Lyubov Vladimirovna
The doctor is a neurologist. Vertebroneurologist. Ozone therapist. Physiotherapist. Experience: 17 years.
Zhuravleva Nadezhda Vladimirovna
Head of the center for diagnosis and treatment of myasthenia gravis.
The doctor is a neurologist of the highest category. Physiotherapist. Experience: 16 years.
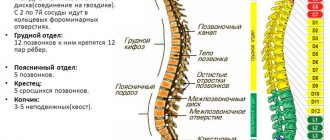
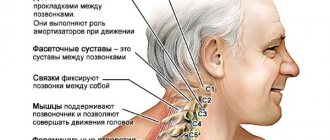
Subluxation of the cervical vertebra
In case of a neck injury, it is necessary to completely immobilize the victim’s head and neck. If the victim is in a car, you should first securely secure the neck, and only then remove him from the vehicle. Special splints are used for fixation. If there are no splints, you can use a homemade collar made from several layers of cotton wool wrapped in gauze, the main thing is that it securely fixes the damaged area and does not interfere with breathing. Self-reduction of a subluxation is strictly prohibited; manipulation can only be performed by a qualified specialist in a hospital setting.
It is advisable to carry out the procedure in the early stages, since over time swelling of the soft tissues increases, and reduction of the subluxation becomes difficult. Typically a Gleason loop is used. The patient is placed on his back with a small flat pillow under his shoulders. It is possible to have both a gradual reduction using a small load and a one-stage manipulation, during which the traumatologist uses a loop to apply traction and then rotate the head.
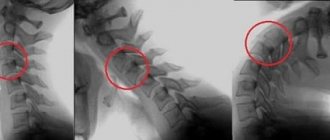
At the moment of reduction, a characteristic soft click is heard, the patient notes a decrease in pain and the disappearance of obstacles to movement. Due to damage to the ligamentous apparatus after reduction, repeated subluxation can easily occur, so the patient is prohibited from moving his head and a Shants collar or craniothoracic bandage is applied for a period of 2 weeks to 3 months (depending on the level and nature of the subluxation). After reduction, a control x-ray must be performed.
Subsequently, drug therapy, physiotherapy, massage and exercise therapy are used. According to indications, tolperisone is prescribed to relax the neck muscles, B vitamins are prescribed to normalize the activity of the nervous system and improve blood circulation, and pentoxifylline is prescribed to improve microcirculation. Massage can be used from the first days after injury; its goal is to relax muscles, improve nutrition and blood supply to tissues. Mostly gentle techniques are used - stroking and rubbing.
Exercise therapy classes begin immediately after reduction and continue until recovery. At the initial stage, only exercises for the shoulders and shoulder girdle are performed. After removing the Shants collar, neck movements are added to the complex. All exercises must be done carefully and carefully, gradually increasing the load. Simultaneously with exercise therapy, physiotherapeutic restorative techniques are used: electrophoresis with novocaine, ultrasound and thermal procedures.
Read also
Osteoporosis
Systemic bone disease associated with metabolic disorders.
With osteoporosis, a decrease in bone mass occurs, a violation of the internal structure of the bone, its frame, as a result of which the bone becomes... Read more
Cervical spondyloarthrosis
The cervical spine includes 7 vertebrae, which, when connected to each other, form movable articular joints (“facets”). Thanks to the presence of facet joints, between the vertebrae there are...
More details
Pain in the neck
Pain in the cervical spine is somewhat less common than pain in the lower back. According to statistics, every fifth person suffers from such pain, and this problem occurs more often among ladies than among gentlemen. In patients with pathology...
More details
Piriformis syndrome
If a person experiences pain in the hips, buttocks, hamstring area, or ischial area, piriformis syndrome should be considered. This syndrome is a disorder...
More details
Sacralgia/pain in the sacrum
Sacralgia is pain in the sacrum, which is localized in the lower back. Causes of sacralgia/pain in the sacrum The causes can be varied, to such an extent that the doctor must...
More details
Causes of atlantoaxial subluxation
A common cause is birth trauma. Vertebral subluxations in children often occur as a result of cesarean section or malpositioning of the baby.
Other reasons include:
- Careless handling of the baby; the head was held incorrectly until the child was able to hold it himself.
- Mechanical injury due to a car accident, fall, somersault over the head.
- A sharp turn of the head to a sudden sound or call.
- Sleeping on a pillow that is too high.
- Muscle hypertonicity, cerebral palsy.
Subluxation of a cervical vertebra in a child affects future lifestyle and well-being. If atlantoaxial subluxation is suspected, the baby should be scheduled for examination.
Degree of injury
There are several degrees of damage to the cervical vertebra:
- I – displacement of the vertebrae occurs by ¼ and is not accompanied by severe symptoms other than minor pain at the site of injury;
- II – the vertebrae are displaced by half, causing aching pain and contributing to weakening of the muscles;
- III – characterized by severe pain spreading from the neck to the back, as well as impaired blood supply and muscle spasm;
- IV – complete displacement of the vertebra, causing severe pain and dysfunction of other organs;
- V - displacement of the vertebra with subsequent sagging, in this condition significant damage to the spinal cord occurs, increasing the likelihood of paralysis.
Note!
In order to prevent serious complications, treatment of dislocation should begin at degrees I and II of complexity.
ICD-10 code
In the international classification of diseases, dislocation of the cervical vertebra is listed under code S13.1.
How should the problem be solved?
To really get rid of symptoms such as headaches, back pain, etc., resulting from a displaced atlas, you need to work with the bones of the skull, says the osteopath. Only a specialist familiar with the nuances of the work of the ligaments of the vertebrae and skull can align their position and restore the mobility of the sutures between them.
“Isolated work with the atlas can crumble the structure carefully built by the body. The body has been adjusting to the crooked skull for years. The displacement of the first vertebra is a compensatory mechanism of the body, striving to preserve its functionality as much as possible and minimize energy consumption. Naturally, if we realign the atlas, the body begins to experience additional tension, and pain in the back, lower back, legs, and feet may appear or intensify. The muscles are forced to strain harder to keep the body upright. What happens if you interfere with the adaptive changes that the body has been building for a long time in order to optimize performance under conditions of damage? Everything is collapsing,” the specialist emphasizes.
Keep it up! Why you need to be wary of vertebral displacement Read more
And another important point: in attempts to return the atlas to its place and improve your condition, you should carefully consider the choice of a doctor. This must be a specialist familiar with basic knowledge of anatomy and physiology. Only a competent specialist, working with the bones of the base of the skull, will restore their correct position, and all the vertebrae, including the first cervical one, will gradually realign and also take a more correct position. And do not forget that such manipulations are not always required. You cannot treat your body as a field for experimentation. Moreover, the price to pay for this can be expensive.
Preventing injury in children
To reduce the risk of injury to the baby’s cervical spine, following a number of rules will help:
- planning conception long before its immediate moment;
- treatment of underlying diseases in parents when planning pregnancy;
- regular visits to the gynecologist;
- timely receipt of professional help in order to prevent the occurrence of a particular pathology;
- maintaining a healthy lifestyle by the expectant mother, including proper nutrition and giving up bad habits;
- surgical treatment of diseases acquired during pregnancy.
The risk of injury can be reduced to a minimum by identifying all pathological disorders in the baby’s body and optimizing the birth process.
Symptoms and consequences
There are several signs of pathology that are worth paying attention to:
- restless behavior;
- poor sleep;
- constant moodiness, tearfulness;
- poor appetite;
- apathy towards surrounding objects;
- no weight gain;
- tilting the head to one side;
- tension in the neck muscles;
- The skin in the neck area may be hot to the touch.
At a later date, with subluxation of the vertebrae, children develop rhinitis. A runny nose does not go away for a long time and is not infectious. In this case, vasoconstrictor drugs are useless, and the otolaryngologist does not find any pathology.
Consequences that childhood pathology leads to:
- scoliosis;
- osteochondrosis;
- flat feet;
- strabismus;
- mental retardation;
- hyperactivity;
- memory problems;
- fast fatiguability.
Why does dislocation happen?
There can be many reasons for this problem. Sometimes a very sudden movement of the head is enough to dislocate one of the cervical vertebrae. Children especially often face this problem, since excessive physical activity can lead to very unpleasant consequences.
Experts say that a problem such as a dislocated vertebra is most often the result of certain actions. Such situations most often occur in sports, but very young children also suffer: newborns can also be diagnosed with cervical dislocation. This becomes a consequence of problematic childbirth. Accidents, falls from heights and other impacts to the human body can lead to dislocation of the vertebrae.
In each of these situations, it is absolutely necessary to consult a doctor and undergo thorough treatment. Don't try to self-medicate or ignore the problem and think it will go away on its own. This is very dangerous and can lead to serious consequences. If the dislocation is not treated, the patient faces death in a difficult situation.
What is subluxation Atlanta
This disorder is hidden behind the ICD 10 code: S13 - “Dislocation, sprain and overstrain of the capsular-ligamentous apparatus at the neck level.” It is very common due to the large number of ligaments.
The Atlas vertebra is the smallest but most important in the neck. It received its name due to the important function of connecting the skull and spine. This vertebra bears all the main tension from the head, protects the arteries and the spinal cord.
Atlas is responsible for attaching the skull to the spine
There are several types of Atlanta subluxation.
- Rotational subluxation . Occurs due to a sharp and unnatural turn of the head. Typically this injury is caused by turning to the right. Most often it occurs during childbirth, when the doctor pulls the baby too actively. Because of this, so-called torticollis is diagnosed.
- Pseudosubluxation or active . It is provoked by strong tension, which causes a painful spasm. It usually goes away on its own without any unnecessary intervention or complications. Most often occurs in adolescence.
- Kienbeck's subluxation . Affects not only the first Atlas vertebra, but also the second Axis vertebra.
- Subluxation according to Kovacs . Its second name is familiar. The vertebra is unstable when the patient tilts his head. As soon as the patient returns the head to the correct position, Atlanta falls into place.
Features of treatment of dislocation in children
The choice of technology is made taking into account several factors:
- patient's age;
- Current state;
- the presence of concomitant diseases and complications.
After adjustment, the child is prescribed to wear a plaster corset or Chance collar. At the same time, therapy is carried out, including:
- exercise therapy;
- physiotherapy;
- taking painkillers and vitamins;
- massotherapy;
- acupuncture.
During the rehabilitation period, the mobility of the injured area is limited as much as possible in order to prevent relapse and possible complications.