Treatment of residual organic pathology of the central nervous system of the perinatal period is an urgent task for neurologists, child psychiatrists, psychologists and teachers, requiring an integrated approach to treatment and rehabilitation [1].
Pathology of the cervical spine (CS), manifested by a high degree of mobility of the vertebrae, deformation of the osteoarticular structures of the skull and the atlanto-axial joint in combination with a rotational component (of varying severity), is a predisposing factor in the development of compression of the vertebral artery (VA) and, as a consequence, the occurrence of various pathological processes, including extravasal compression, which in turn leads to a decrease in cognitive function in school-age children [2-7].
In complex treatment technologies and at the stages of rehabilitation of diseases of the musculoskeletal system, the method of manual therapy has found its rightful place [8]. Nevertheless, manual therapy methods in the treatment and rehabilitation of children are used with great caution. In this regard, there is extremely insufficient reliable data in the literature on the issue of the use of manual therapy in children with SOP pathology.
The purpose of our study is to study the dynamics of cognitive function in school-age children with natal cervical spine injury against the background of complex rehabilitation including manual therapy, for which we studied changes in short-term memory, attention, and well-being.
Vertebral instability
It is not uncommon for your back to hurt after working at a computer for a long time or standing for a long time. There can be quite a few reasons. And one of them (by the way, common) is vertebral instability.
Vertebral instability is excessive movement of the vertebrae relative to each other. Often instability entails many unpleasant symptoms similar to other diseases.
Causes of instability
Instability most often develops in the cervical and lumbar spine, as these sections have significant mobility. When moving, the vertebrae move along a certain trajectory, held by muscles and ligaments. If the muscles and ligaments do not hold the vertebrae tightly enough, pathological slipping of the vertebrae occurs. Most often, the causes of weakness of muscles and ligaments are the anatomical characteristics of a particular person (congenital weakness of the ligamentous apparatus). There are also external signs - usually these are people with a long neck and smoothed curves of the spine, often with a thin build.
Often the cause of instability is a back injury. For example, with a sharp hyperextension, unsuccessful landing after a jump, etc. Another reason is degenerative-dystrophic processes, in other words, osteochondrosis.
Instability that developed after surgery is also distinguished. When removing herniated intervertebral discs, it is often necessary to remove parts of the vertebrae. Changes in the shape of the vertebra, as well as the relative position of the vertebrae after surgery, can lead to excessive mobility.
Constant work at the computer in an uncomfortable position, or if the workplace is not arranged correctly, can provoke an exacerbation of symptoms.
Symptoms of instability
A typical patient with excessive mobility in the cervical spine complains of headaches, neck pain, dizziness, swelling of the face after waking up, a feeling of confusion in the head, and poor sleep. Very often, these complaints appear or intensify after being in a stationary position for a long time. For example, when propping your head with one hand while sitting or lying on your side or stomach, when falling asleep on an uncomfortable pillow or in an uncomfortable position.
Read also: Treatment of disc herniation: is surgery necessary?
Instability in the lumbar region is manifested by back pain during prolonged walking or when lifting heavy objects. The pain may radiate to the legs and intensify when bending over. Quite often, such patients say that after sessions of “preventive massage” their back pain sharply increased and dizziness appeared.
Why instability is dangerous
Excessive mobility of the vertebrae may be an additional factor in the formation of osteophytes - bone growths on the vertebrae. This is due to the fact that with vertebral instability, normal anatomical interactions between bone structures, ligaments, and muscles are disrupted. Conditions are created when the body weight begins to be incorrectly distributed along the axis of the spine. Subsequently, osteophytes can cause restriction of spinal movements and compression of nerve roots.
In the cervical spine, instability can lead to irritation of the nerve plexuses of the vertebral arteries, which in turn leads to the development of dizziness and other reflex vascular manifestations.
How to make a diagnosis
The diagnosis is usually made by a neurologist. The presence of instability can be assumed based on the patient’s complaints. Experienced doctors can, by palpation, determine at what level there is pathological mobility. Very often, excessive mobility is accompanied by local muscle tension, which sometimes leads to reflex muscle spasm and limitation of spinal movements.
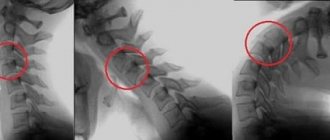
To confirm the diagnosis, an X-ray of the spine of interest is performed with functional tests (additional images - flexion and extension). The photographs may show not a smooth, as normal, but a step-like displacement of the vertebrae. The radiologist describes the amount of this displacement in millimeters. If the displacement is more than 3 mm, instability is indicated.
Additional information about excessive mobility in the cervical spine is provided by ultrasound examination of the neck vessels with functional tests (tests with head rotation - possible compression of the vessel is examined when the head is turned).
How to treat
Treatment of excessive mobility is carried out depending on the cause of instability and the severity of complaints. They use medication, physiotherapy, acupuncture, and manual therapy. In most cases, the exacerbation of instability can be relieved within a few days. Massage during an exacerbation is prescribed with caution. If sessions are still carried out, they try to avoid exposure to areas with instability.
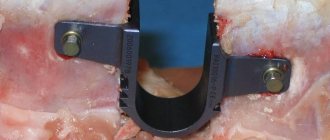
Sometimes the help of a neurosurgeon is necessary. Most often, surgery is performed if instability develops as a result of a vertebral fracture (for example, after an injury, as a result of an infectious, oncological process) or in case of combination with a disc herniation. Instability is eliminated by installing metal structures that fix the vertebrae above and below.
Cervical and lumbar corsets are widely used, which provide stabilization of moving areas, especially during exacerbations. Wearing a corset can reduce muscle tension and, accordingly, reduce pain and reflex vascular reactions (for example, dizziness). Often, wearing a corset very quickly relieves the main complaints.
Physical therapy (especially post-isometric relaxation methods) and proper organization of the workplace are important. Postisometric relaxation is aimed at strengthening muscles and ligaments, normalizing muscle tone. The exercises are simple and quite effective when performed regularly.
Be healthy!
Maria Meshcherina
Photo istockphoto.com
Therapeutic massage of the cervical-collar area for children:
Doctors usually prescribe massage to the cervical-collar area for children for medicinal purposes. Even for prevention, this area is massaged very rarely, everyone expects problems)). Frequently encountered diagnoses in which the collar area is massaged. SRD—speech development delay. Massage for children with mental retardation is prescribed to stimulate speech development. In children of speech development age, massage of the collar area and upper extremities, especially the hands and fingers, can have a reflex effect on the muscles of the speech apparatus and areas of the brain associated with speech.
VSD - vegetative-vascular dystonia. Collar massage for children with vegetative-vascular dystonia helps regulate vascular tone. In general, with such a problem, a general massage is done, but special attention is paid to the cervical-collar area because there are a lot of arteries and veins involved in the blood supply to the head. Instability of the cervical spine. Another disease that occurs in children. With this problem, movements with a large amplitude in the cervical spine are contraindicated, so only static gymnastics can be added to the massage. Otherwise, rubbing and kneading are carried out in the classic version. If the cervical spine is unstable, the child is given a massage to warm up the muscles and ligaments of the neck, improve blood circulation and innervation. Then the statics are done. Cerebrovascular accident. Poor blood circulation in the brain can occur for various reasons and in different parts. The inflow or outflow can be disrupted in the neck area, accordingly, everything above the neck experiences a lack of functioning of the vascular system. The doctor’s task is to find the source, and the massage therapist is to help normalize blood flow. It happens that you can do without a doctor.
Motor disorders of the upper limbs. Whenever it comes to hand treatment, massage of the child’s cervical-collar area is done first. This is because the innervation of the arms originates from the cervical segments of the spinal cord. Large blood vessels also come to the upper extremities from the chest and shoulder girdles. Regardless of the problems, reflex action must be carried out from the sources of innervation. Impaired vision, hearing, facial expressions, etc. In addition to the diagnoses described above, in which the neck-neck area is massaged for children, there are many not very common diagnoses and symptoms that require massage of the neck area. Author of the article: massage therapist Alexey Vladimirovich Matrosov. Dear parents, if you need an experienced children's massage therapist for cervical-collar massage for children, then you can call him by phone 84993941711 or 89266057470. Children's massage center Happy Baby.
Causes and classification of the disease
The classification of spinal instability is based on the causes that cause it. Depending on them, experts distinguish the following types of pathology:
- Degenerative instability is the result of negative processes leading to destruction/change of vertebral bodies due to both internal causes (hereditary predisposition, osteochondrosis of the cervical vertebrae, osteoporosis) and external ones (excessive physical activity or, on the contrary, physical inactivity, an unbalanced diet that promotes leaching of calcium from organism);
- Dysplastic instability - develops as a result of factors that negatively affect the condition of the connective tissues of the joints of the spinal column, intervertebral ligaments, discs, etc. This type of pathology can be caused by systemic inflammatory diseases, as well as infections that destroy the vertebrae, joints and ligaments;
- Post-traumatic instability is a consequence of spinal column injuries - bruises, dislocations, fractures;
- Postoperative instability that develops as a result of surgery on a given segment of the spine.
In addition, experts also distinguish between open and latent (hidden) instability of the cervical vertebrae, in which the symptoms can be quite blurred, which makes timely diagnosis of the disease difficult.
Nerve root entrapment due to vertebral instability
It should be noted that this pathology is dangerous, first of all, because it can lead to pinching of the spinal cord in the spinal canal, not to mention the fact that it can significantly complicate the patient’s life.
What is cervical spine instability?
The cervical region, like the lumbar region, is one of the most mobile segments of the spine. Thanks to the unique design of the neck, a person has the ability to perform various tilts and rotations of the head.
Moreover, in addition to ensuring mobility, the cervical spine is also tasked with maintaining a certain stability, which prevents various injuries and deformations due to various types of physical impact on the spinal column.
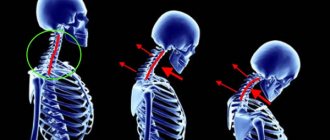
As a result of a number of reasons, which will be discussed below, hypermobility of the vertebrae of the neck occurs. In this case, there is reason to talk about its instability, which is also called functional or segmental. Most often, the pathology is registered in adolescents and the elderly. This is explained by the presence of processes that depend on age-related changes.
Schematic representation of the cervical spine with vertebral instability
This problem can manifest itself as an increase in amplitude when performing traditional movements of the neck and head, accompanied by a shift of the vertebrae and, accordingly, pain.