A healthy spine cannot be absolutely straight. It has natural curves that help distribute pressure evenly when walking and exercising and help maintain balance. Such bends act as a shock absorber for the spinal column.
A healthy spine has 4 curves:
- cervical lordosis;
- thoracic kyphosis;
- lumbar lordosis;
- sacral kyphosis.
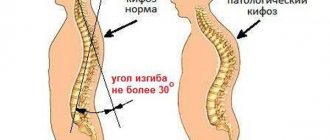
If we consider the spine in profile, then as a result of cervical and lumbar lordosis a convex curve is formed, and thoracic and sacral kyphosis results in a concave curve. But due to the influence of various factors, lordosis may be straightened or smoothed; this is considered a pathological condition and requires correction.
Cervical lordosis is straightened, what does this mean?
Cervical lordosis is an anatomical curvature of the cervical vertebrae with a forward convexity.
The correct angle of cervical lordosis is 20–40 degrees. Deviation from this norm in any direction requires treatment. If the angle of deflection in the cervical spine on the X-ray image is 10–12 degrees, then a straightened cervical lordosis, or hypolordosis, is diagnosed. Develops as a result of dysfunction of the musculoskeletal system. In the early stages, this pathology can be easily corrected with special therapeutic exercises. But if therapy is not started in time, straightened cervical lordosis can lead to general curvature of the spine and poor posture. When the natural deflection in the neck is smoothed out, excessive stress is placed on this part of the spine.
To compensate for this, the deflection of the lumbar lordosis increases, the thoracic vertebrae shift - the chest protrudes forward. As a result, the center of gravity changes, and severe muscle pain occurs, and the blood supply to the entire spinal column is disrupted. Violation of statics in the form of straightening of the cervical lordosis leads to a failure of blood supply and starvation of brain structures.
Diagnostic methods
Based on the results of the examination and medical history, the doctor makes a preliminary diagnosis, noting the location, as well as the presence of other pathological changes in the spine and assessing the degree of lumbar or cervical lordosis. In order to assess the neurological status, as well as to assess reflex activity, range of motion and muscle strength, the doctor prescribes additional consultations and studies:
- X-ray of the spine (frontal and lateral projections) – to assess the degree of deformation and changes present.
- Computer and magnetic resonance imaging - to clarify the degree of damage to the nerve roots, recognize the cause of pathology and identify pathology in soft tissues, to diagnose intervertebral hernias.
- ENMG - (electroneuromyography) - to determine the functional state of peripheral nerves and muscles, recording their electrical activity.
- Laboratory tests - in order to obtain information and determine the type of infection;
- Scintigraphy is the introduction of radioactive isotopes into the body to detect changes in the tissues of the spine and differentiate them from tumors, inflammations and infections.
Lumbar lordosis is straightened, what does this mean?
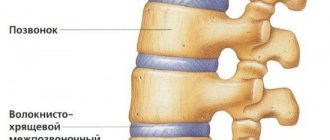
Straightening lumbar lordosis is an unnatural position of the spine with an absent lumbar curve. Straightened lumbar lordosis will not absorb the vertical load on the spinal column; pressure on the vertebrae and intervertebral discs increases and there is a danger of degenerative changes in the bone and cartilage tissue of the spine. Hypolordosis of the lumbar region leads to poor posture, pain and disruption of the functioning of internal organs. First of all, dysfunction of the pelvic organs occurs, a disruption in the functioning of the digestive system.
Straightened lumbar lordosis is accompanied by constant aching pain in the lumbar region. The abnormal position of the lumbar vertebrae changes the center of gravity and increases the load on the joints of the lower extremities.
It is necessary to periodically conduct self-diagnosis for the condition of lumbar lordosis. To do this, stand with your back straight against the wall, pressing the back of your head and buttocks. In this position, the palm should pass freely between the lower back and back. If it is impossible to stick your palm through, then this is a sign of straightened lordosis.
Prevention
To prevent the development of this disease, you must follow a number of simple rules:
- It is important to constantly monitor your posture.
- Avoid serious back strain.
- Control your body weight and avoid gaining excess kilograms.
- Use vitamin-mineral complexes periodically to prevent deficiency of elements important for the body.
- Practice proper and nutritious nutrition.
- Exercise regularly, practice swimming and other types of physical activity.
- Use special orthopedic devices during pregnancy.
- Treat in a timely manner diseases that provoke the development of lordosis - osteochondrosis , arthritis , disc protrusion , etc., by consulting a doctor if you have complaints of back pain.
Physiological lordosis is straightened, what is it?
Physiological lordosis is a natural, anatomical deflection of the spine in the cervical and lumbar spine. Its task is to evenly distribute the load on the back and prevent spinal injuries.
A person is born with a straight spine. Lordosis develops during the first year of life, when the child begins to hold his head up, crawl on all fours, and sit up. This process is completed by the age of 16–18, with the final formation of the skeleton. The normal angle of curvature of the cervical spine is 20–40 degrees, and that of the lumbar spine is 20–30. When natural curves are smoothed by less than 20 degrees, we can say that physiological lordosis is straightened. That is, we are talking about pathological lordosis. A displacement of the vertebrae and intervertebral discs occurs, as a result of which a certain area of the back becomes straight and the natural curve is straightened.
This condition is considered dangerous and requires immediate treatment.
Consequences of straightened physiological lordosis:
- change in the center of gravity, and as a result, curvature of posture; neurological and pain symptoms;
- the load on neighboring parts of the spine increases and there is a danger of degenerative-dystrophic changes in cartilage tissue;
- if not treated in a timely manner, it leads to disruption of the functioning of internal organs.
Complications
If no measures are taken, a number of serious complications may occur with lordosis:
- Impaired respiratory function due to the fact that the diaphragm is deformed.
- Osteochondrosis.
- Chronic constipation.
- Too much mobility of the vertebrae.
- Deforming arthrosis of the joints between the articular processes of the vertebrae.
- Deterioration of disc stability between vertebrae.
- Intervertebral hernia.
- Discs falling out.
- Problems with kidney function, leading to frequent urination , pyelonephritis , etc.
- Compression of the spinal cord, leading to impaired urination and defecation, immobilization of the legs, and infertility .
Causes of pathology
Today, the most common cause of flattened lordosis is sedentary work, prolonged sitting at a desk. In a sitting position, lumbar lordosis is smoothed and the load on the lumbosacral region increases. When working at a computer, it is below eye level, so a person involuntarily stretches his neck forward and down. Staying in this position for a long time eventually causes a gradual displacement of the vertebrae, and lordosis becomes straight.
All reasons for straightening lordosis can be divided into 3 groups:
Primary – pathology is provoked by various diseases or injuries of the spine:
- intervertebral hernia;
- osteochondrosis;
- injuries of the spine, muscles and ligaments;
- neoplasms in the back area;
- osteoporosis;
- spondylolisthesis.
Secondary – the causes are congenital developmental anomalies, birth injuries:
- abnormalities of vertebral formation;
- cerebral palsy;
- hip dysplasia;
- rickets.
Pathological – the result of weakening of the back muscles:
- incorrect posture in children during growth;
- sitting for many hours in an incorrect position;
- excess weight;
- excessive load on the spine, or vice versa, its absence.
Forecast
The prognosis for this disease in adults may vary, but it is generally favorable. Pathological processes proceed slowly, so it is possible to diagnose the disease and treat it before critical complications appear.
A worsening prognosis is likely under the following circumstances:
- Previous spinal diseases or injuries.
- Spinal pathologies that appear in older people.
- Advanced stage of the disease.
How does hypolordosis manifest?
When the natural curve of the neck straightens, external signs of pathology appear:
- the head is slightly tilted back;
- head posture decreases;
- the head moves forward slightly;
- the neck lengthens;
- change in gait;
- limited mobility of the neck and chest.
At the initial stage of smoothing the cervical spine, only mild discomfort is felt in the neck area. But with further progression of the curvature, serious neurological symptoms occur. After all, important vessels pass through the cervical vertebrae, which provide the brain with oxygen and nutrients.
Symptoms of hypolordosis:
- neck pain that becomes more intense with head movements;
- spasm of the neck muscles;
- increased fatigue;
- memory impairment;
- decreased performance;
- dizziness.
Straightening the lordosis of the lumbosacral spine often occurs with osteochondrosis and intervertebral hernia. Already in the first stages of smoothing, external signs of pathology become noticeable:
- the stomach protrudes forward;
- knees unnaturally spread;
- curvature of posture;
- posterior deviation of the pelvis. At advanced stages, the entire body deviates backwards.
The lumbar spine bears the main load. The lack of natural deflection causes overstrain of the ligamentous apparatus and muscular corset of the spine. In this case, you may feel:
- sharp or nagging pain in the lumbar region;
- disruption of the gastrointestinal tract;
- fatigue when walking and standing;
- numbness of the lower back and lower extremities.
Diet for lordosis
Diet for osteochondrosis
- Efficacy: no data
- Timing: constantly
- Cost of food: 1450-1780 rubles per week
Diet for arthritis
- Efficacy: Therapeutic effect after 2-6 months
- Terms: 2-6 months
- Cost of food: 1780-1880 rubles per week
You don’t have to adhere to a special diet for this disease, but it is important to eat in such a way that food easily passes through the gastrointestinal tract, is absorbed and does not cause constipation .
- It is important to drink a lot of liquid per day - at the rate of 30 ml per 1 kg of weight.
- Every day the menu should include a lot of fiber-rich foods - fresh fruits, vegetables, herbs.
- Reduce the amount of sweet and starchy foods.
- Minimize or completely eliminate fried, spicy, fatty, smoked, and alcoholic drinks.
- You can follow diets that are recommended for arthritis and osteochondrosis.
Therapeutic treatment measures
The goal of drug treatment is to relieve pain and inflammation in tissues. For this purpose, medications of the group non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs are prescribed in the form of tablets and ointments. But medications are not able to normalize the pathological bend, therefore the main therapeutic methods for treating straightened lordosis are physiotherapeutic procedures and therapeutic exercises.
Exercise therapy
In 80% of cases, complete recovery can occur with the help of exercise therapy. The doctor selects a set of physical exercises taking into account the characteristics and causes of hypolordosis. To straighten the physiological lordosis of the cervical spine and lumbar lordosis, various complexes of therapeutic exercises are being developed. This complex includes exercises to restore posture and spinal traction. The first complex is performed only under the supervision of a medical professional, then you can perform the exercises at home on your own.
Therapeutic exercises for hypolordosis are aimed at:
- normalization of blood circulation;
- muscle corset training;
- normalization of spinal mobility;
- reduction of pain.
Physiotherapy
Straightening lordosis can be successfully treated with physiotherapy. The most effective of them:
- massage;
- electrophoresis;
- acupuncture;
- magnetic waves.