Description of the disease
Doctors use this term to describe a disease that leads to the destruction of bones and cartilage in the cervical spine. Because of it, the nerve endings suffer, the lumen of the spinal canal narrows - this phenomenon causes pinching of the spinal cord, and the vertebrae themselves are not able to function normally.
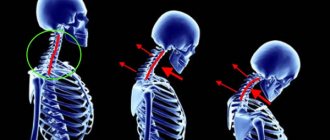
Over time, a person begins to experience pain and discomfort, and growing osteophytes injure adjacent tissues. At risk are people who are forced to spend the entire day in front of a monitor. Few people monitor and maintain their posture - the back, as a rule, is rounded, and the head “goes” forward as the person peers at the image on the screen. As a result, the disease has become significantly “younger” compared to the previous generation.
Consequences
If left untreated, spondylosis can lead to the following problems::
- formation of intervertebral hernias;
- neurological disorders (pain in various areas, numbness of the limbs, malfunction of internal organs);
- vascular problems;
- pinching of nerves and blood vessels.
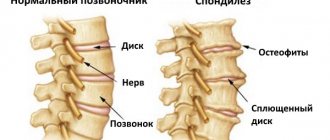
Osteophytes can put pressure on the roots of nerve endings or compress blood vessels. The patient experiences severe pain, dizziness, blurred vision, and pressure surges. Patients often complain of noise and ringing in the ears. Some even lose control of their limbs.
In the third stage, patients may experience pinching of the spinal column . This leads to spasms in the limbs and difficulty walking. Some complain of urinary problems. Bladder control becomes more difficult.
Causes
The progression of cervical spondylosis is usually a long process. Therefore, it is important to understand what leads to such an illness and how to eliminate provoking factors from your life.
Provoking factors are:
- problems with posture;
- age-related changes - cartilage, muscles and bones tend to lose elasticity;
- exposure to cold - drafts, colds, etc.;
- too high loads on the spine;
- the absence of loads as such leads to stagnant processes;
- osteochondrosis, osteoarthritis and other diseases of the musculoskeletal system;
- flat feet, club feet and other disorders of foot placement while walking;
- inflammations and infections that were not treated correctly.
Before looking at the symptoms and treatment of cervical spondylosis, it is important to take a closer look at each of the causes.
Poor posture
Leads to curvature of the spine, pinched nerves, the development of inflammation and other ailments. Their consequence may well be spondylosis.
Natural aging processes of muscles, bones, joints, cartilage
The main function of the neck is to support the head, which means significant loads on it, since this part of the body weighs up to 4.5 kg. With age, the neck cannot cope with such loads, the cartilage wears out, the bone tissue becomes less dense, and the muscles become flabby. Without proper support for the body, the risks of experiencing symptoms and treatment of cervical spondylosis increase significantly.
Hypothermia, exposure to drafts
Any inflammation caused by hypothermia can provoke future degradation of bone tissue and cartilage. Therefore, it is important to protect yourself from the cold, and also consult a doctor at the first signs of hypothermia, without self-medicating.
Injuries of various kinds
Improperly fused and restored bone tissue can lead to the formation of osteophytes. Even a single such growth can significantly worsen the quality of life, and osteophytes in the plural lead to severe pain and impaired mobility of the spine.
Risk factors
The biggest risk factor for developing cervical spondylosis is aging. Cervical spondylosis is usually associated with involutional changes in the joints of the neck. Disc herniation, degeneration and bone growths (osteophytes) are all associated with involutional changes in the body.
Other risk factors:
- neck injuries
- heavy lifting work that places additional strain on the neck
- holding the neck in an awkward position for a long time or repeating the same neck movements throughout the day
- genetic determination
- smoking
- overweight and inactivity
First signs and symptoms
Cervical spondylosis (symptoms and treatment are described on this site) does not manifest itself in any way at first. Doctors may discover it by chance if they are looking for the causes of other problems in the human body. However, as the pathology progresses, it will begin to make itself felt.
Crunching and numbness in the neck
The crunching is due to the fact that the functioning of the joints of the spine is disrupted due to the resulting bone growths. Numbness may be associated with disruption of the nervous tissue, which is responsible for the conduction of impulses from the affected area to the brain.
Limited mobility, neck stiffness
These are the most common symptoms of cervical spondylosis. They arise due to the fact that the processes interfere with the full movement of the head. In this case, the person may not even experience pain, but simply note that he cannot turn his head as usual.
Dizziness often occurs
This is due to the fact that compression of large blood vessels occurs due to bone tumors. All this can even lead to problems with blood pressure, or rather to its sharp jumps. In extreme situations, a person may even lose consciousness.
Feeling weak in the neck muscles
Treatment for cervical spondylosis is often necessary because a person comes to the clinic complaining that it has become more difficult to support his head than usual. This is also associated with pinched nerve tissue. Usually this phenomenon is accompanied by noticeable pain.
Symptoms of cervical spondylosis
Clinical manifestations may be absent for a long time.
Neck pain may indicate direct compression of a nerve, degeneration of the vertebral disc, joint, ligaments, or segmental instability of the spinal motion segment. Discomfortable sensations are local in nature and radiate to the back of the head, shoulder, shoulder blade, and upper limb. The pain may intensify in certain positions and interfere with sleep.
Spondylosis of the cervical vertebrae less often leads to glove-like loss of sensitivity in the hands. If the osteophytic spurs are large, the patient complains of dysphagia - a violation of the act of swallowing. Some people suffer from manifestations of vertebrobasilar insufficiency - dizziness, headaches, unstable blood pressure. Cervical radiculopathy, manifested by lumbago, hyperesthesia, and weakness of the adjacent muscles, is a suspicion of an acute herniated intervertebral disc.
Types and stages of the disease
There are many varieties of this disease. According to the presence of complications, spondylosis is distinguished:
- Uncomplicated – the disease does not progress quickly and has mild symptoms.
- Complicated - osteophytes grow rapidly, the vertebrae are destroyed at a high rate.
Treatment and prevention of cervical spondylosis are necessary in any situation, but the uncomplicated form will be easier to respond to therapeutic interventions. According to the nature of the pathology, spondylosis can be distinguished:
- slow;
- moderate;
- fast;
- fulminant.
The last type is the rarest, but it is also the most dangerous. It is the most difficult to treat because it is the least responsive to medical treatment. There are also two stages of the disease:
- X-ray – here you can identify violations of the structure of the vertebrae and discs, the occurrence of osteophytes.
- Functional deficiency - here everything is assessed as a whole, all internal consequences. A commission often meets to determine a person’s level of ability to work.
If the condition is advanced, then conservative treatment will most likely not produce results and you will have to resort to radical measures.
Spondylosis and surgery
In the vast majority of cases, this condition does not require surgical treatment. This disease is an indication for surgery only in exceptional cases, when there is a threat of compression of the spinal cord and paralysis.
Author: Shogenov Ramish Kurbanovich
Neurologist with 10 years of experience
| Service | Price | Price | Promotion Price |
| Appointment with a therapist | primary 1800 rub. | repeat 1500 rub. | |
| Neurologist appointment | primary 1800 rub. | repeat 1500 rub. | free after MRI of the spine |
| Orthopedist appointment | primary 1800 rub. | repeat 1500 rub. | free after MRI of the joint |
| Consultation with an acupuncturist | primary 1800 rub. | repeat 1500 rub. | free after MRI of the spine |
| Vertebrologist consultation | primary 2000 rub. | repeat 1800 rub. | |
| Consultation with a chiropractor/osteopath | primary 2500 rub. |
| Service | Price according to Price | Discount | Discount |
| Plasma therapy of the spine or joint | 1 session 4000 rub. free doctor's appointment | 3 sessions 10,500 rub. free doctor's appointment | 5 sessions 17,500 rub. free doctor's appointment |
| Classic acupuncture session | 1500 rub. | ||
| Complex acupuncture session | 2000 rub. | ||
| Manual osteopathy session | 2500 rub. | ||
| Manual therapy session | 2500 rub. | ||
| Autohemotherapy | 550 rub. | 5 sessions 2500 rub. | 10 sessions 5000 rub. |
| Novocaine therapeutic blockade | 1500 rub. | ||
| Therapeutic paravertebral blockade | 1500 rub. | ||
| The blockade is therapeutic and medicinal, complex (use of several drugs) | 2000 rub. | ||
| Therapeutic intra-articular blockade with diprospan | 2500 rub. | ||
| Joint puncture with removal of synovial fluid | 2500 rub. | ||
| Intra-articular injection of hyaluronic acid (without the cost of the drug) | 2000 rub. | ||
| Novocaine therapeutic blockade | 1500 rub. | ||
| Therapeutic paravertebral blockade | 1500 rub. | ||
| Therapeutic intra-articular blockade with diprospan | 2500 rub. | ||
| Joint puncture with removal of synovial fluid | 2500 rub. | ||
| Pharmacocupuncture session (drug at the discretion of the doctor) | 2500 rub. | ||
| Pharmacocupuncture session (without the cost of the drug) | 2100 rub. | ||
| Electrophoresis session (without the cost of the drug) | 400 rub. | ||
| Phonophoresis session / Ultrasound therapy procedure (UT) (without the cost of the drug) | 450 rub. | ||
| Magnetic therapy session | 350 rub. | ||
| SMT therapy session (Sinusoidal modulated currents) | 450 rub. | ||
| Vitamin therapy (10 injections) | 4000 rub. free doctor's appointment | 3000 rub. free doctor's appointment | 3000 rub. free doctor's appointment |
| Injections (Vitamins B12) | 800 rub. | 800 rub. | 800 rub. |
| Intravenous administration of drugs | 450 rub. | 5 sessions 2140 rub. | 10 sessions 4050 rub. |
| Intravenous drip administration of drugs (without drugs, 1 bottle) | 800 rub. | 5 sessions 3375 rub. | 10 sessions 6750 rub. |
| Intravenous drip administration of medications (with existing clinic medications, 1 bottle) | 950 rub. | 5 sessions 4050 rub. | 10 sessions 8100 rub. |
| Intravenous drip administration of drugs (without drugs, 2 bottles) | 950 rub. | 5 sessions 4050 rub. | 10 sessions 8100 rub. |
| Intravenous drip administration of medications (with existing clinic medications, 2 bottles) | 1100 rub. | 5 sessions 4700 rub. | 10 sessions 9400 rub. |
| Subcutaneous/intradermal administration of drugs | 250 rub. | 5 sessions 1180 rub. | 10 sessions 2250 rub. |
| Intramuscular administration of drugs | 300 rub. | 5 sessions 1430 rub. | 10 sessions 2700 rub. |
Features of treatment
Regardless of the causes of cervical spondylosis, the treatment regimen for the disease will be approximately the same, with the exception of complex cases requiring surgery. So, the doctor will do the following:
- It will prevent complications of the disease and stop the process.
- Prescribe analgesics and muscle relaxants, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, B vitamins.
- Prescribe physical therapy.
- Select a complex of therapeutic exercises.
- Refer the patient to a chiropractor.
You should notify your attending neurologist
.
How is spondylosis treated with osteopathy?
Osteopathy methods allow achieving effective and maximum results in the treatment of degenerative changes in the cervical vertebra. Using gentle manual techniques and techniques, the osteopath acts directly on the area of the pathological process, which allows eliminating the cause of the disease and improving the patient’s quality of life.
Treatment of deforming spondylosis using osteopathic techniques is carried out in several areas:
- Improving metabolic processes;
- Stimulation of restoration processes (regeneration) of intervertebral discs;
- Activation of nutrition and blood supply in vertebral tissues;
- Neutralization of pain by releasing nerve endings;
- Restoring mobility of the back joints;
- Elimination of muscle spasms of vertebral structures.
Exercise therapy will help consolidate the results of osteopathy treatment. They activate muscle activity and improve blood circulation.
The use of osteopathic techniques in the treatment of spondylosis makes it possible to slow down dystrophic-degenerative changes in the vertebral regions and stop the development of the pathological process. Osteopathy techniques are absolutely safe and do not cause side effects. The number of manual therapy sessions is determined by the doctor individually. The combination of osteopathic techniques and techniques with other therapeutic methods allows you to achieve long-term and lasting results, which significantly reduces the likelihood of developing adverse complications.
Other methods of combating the disease
Other treatment methods include lifestyle modification. This includes training in muscle relaxation techniques and control over changes in body position during work. Such correction will reduce the severity of clinical manifestations and prevent relapses of diseases in the future.
Physiotherapeutic procedures are very effective methods of therapy:
- The traction method is a mechanical stretching of the cervical vertebrae using certain devices. Due to this, the distance between the vertebrae increases, compression decreases, and microcirculation of fluid inside the vertebrae improves;
- acupuncture;
- massage;
- ultrasound therapy;
- electrotherapy;
- electroplating;
- ozokerite baths;
- electrophoresis;
- magnetotherapy.
Therapeutic exercise is designed to get rid of pain. Also, using this method, you can strengthen the muscular system of the cervical spine, improve stretching, mobility and flexibility of the joints of the cervical spine and shoulder girdle, and relieve stress from these sections.
In each specific case, a set of gymnastic exercises is selected. They can be easily done at home. After such treatment, significant improvements occur within three weeks. But this is subject to systematic and regular training.
Therapeutic measures are prescribed by neurologists, orthopedists, and vertebrologists. After the inflammatory process has been stopped, doctors prescribe chondroprotectors that prevent the intervertebral fluid from drying out. Such replacement therapy can last from several months to several years.
In what cases should you visit a specialist?
If shoulder numbness or tingling suddenly appears, paresthesia in the upper or lower extremities, or loss of bowel control, it is important to visit a doctor as soon as possible for diagnosis and appropriate treatment.
If pain and discomfort are so severe that they interfere with a person’s ability to live fully, an early consultation with a neurologist is needed. Even despite the age-related changes, there are currently medications and other measures that can make a person’s life easier and restore his ability to work.
Diagnosis of thoracic spondylosis
You need to contact a neurologist, neurosurgeon or orthopedist. You can start by visiting a therapist, who will write a referral to the right specialist.
Diagnostics is divided into two stages: collecting anamnesis and information about the patient and conducting a hardware examination. The first part is carried out immediately at the reception. The doctor interviews the patient, takes notes, and performs a visual examination to determine what type of disease he is dealing with. If there is not enough data, a hardware examination is performed.
To confirm the diagnosis, you need a method that allows you to visually examine the affected area. For these purposes, fluoroscopy, MRI or computed tomography are used. If there is deformation, it will be displayed on the device screen.
As soon as the data collection is completed, the doctor will draw up a clinical picture and begin treatment of spondylosis of the thoracic spine.
Reasons for the development of spondylosis in osteochondrosis
Spondylosis can be an independent disease, or it can develop as a secondary form of pathology against the background of a long-term degenerative dystrophic process in the cartilaginous tissues of the intervertebral disc. To understand the reasons for the development of pathology, I propose to take a short excursion into anatomy. This knowledge about the structure of the spine will make it possible to imagine the action of destructive pathogenic factors.
The spinal column is the main supporting mechanism of the human body. It consists of several sections (cervical, thoracic, lumbar, sacral and coccyx). Each department has its own characteristics. But practical ones consist of vertebral bodies separated by intervertebral discs. The vertebral bodies are hollow and have processes. The oval openings inside the vertebral bodies form the spinal canal. It houses the spinal cord.
Each vertebra has foraminal openings on its sides. The roots of the spinal cord exit through them. By branching, they provide innervation to the entire human body. Intervertebral discs ensure uniform distribution of shock-absorbing load throughout the spinal column. They also protect the radicular nerves from compression by adjacent vertebral bodies.
All vertebral bodies are connected to each other by joints. These joints provide mobility of the spinal column and a certain flexibility. There are uncovertebral, facet and facet joints of the spine. The thoracic region also contains costovertebral joints.
In the normal state of the intervertebral discs, the joints are in a certain position, which ensures their optimal level of performance. Osteochondrosis is a degenerative dystrophic process that leads to dehydration of cartilage tissue and a decrease in the height of the intervertebral disc. As a result, the anatomy of the intervertebral joint is disrupted, and it is subjected to increased physical and shock-absorbing load. Inside it, the synovial protective tissue begins to break down. The heads of the bones are exposed, and they begin to collapse and deform under the influence of friction.
The main causes of the development of osteochondrosis and spondylosis of the spinal column are:
- heavy physical labor and prolonged static tension of the body in a forced position;
- excess body weight, which increases shock-absorbing pressure on the spinal column and large joints of the lower extremities;
- infectious processes in the body, leading to an increase in the level of sensitization and autoimmune alertness (prerequisites for the development of ankylosing spondylitis and other rheumatoid processes);
- back, neck and lower back injuries, including sprains, bruises, compression fractures and cracks;
- poor posture and curvature of the spinal column;
- incorrect placement of the foot in the form of clubfoot and flat feet;
- deformity of the knee, ankle or hip joint;
- maintaining a sedentary lifestyle with predominantly sedentary work (for example, programmer, cutter, seamstress, etc.).
The doctor must rule out all possible causes. Often, the destruction of the spinal column in people is caused by improper organization of their working and sleeping space. These are the reasons that are excluded first. And only after the patients follow all the recommendations of the vertebrologist, the active phase of treatment of the pathology begins.
Benefits of MBST Therapy
Among the methods that can be considered revolutionary, MBST therapy (nuclear magnetic resonance therapy) stands out. Its peculiarity and at the same time its advantages lie in its effect on the patient’s cells, which begin to regenerate and renew themselves.
The technique has been refined and is used for the treatment of spondylosis of the thoracic spine, even in chronic degenerative diseases of the joints or intervertebral discs. Today, nuclear magnetic resonance therapy is the only way to influence the patient’s cells.
The result of the procedure is the easing of pain, a decrease in symptomatic manifestations, and the healing of crushed or deformed bones. Meniscal rupture, injuries received as a result of vigorous physical or sports activity, intervertebral disc protrusion - all this can be cured using MBST therapy.
Why is MBST therapy so popular and in demand among patients? The methodology involves treating the spine without the intervention of surgeons. There is no risk for the patient, and the therapy has no side effects or complications.