For today’s conversation, I chose the problem that we, neurologists, most often encounter in everyday practice. The relevance of back pain is high - it is registered annually in 15-25% of the country's adult population. Between the ages of 30 and 45, back pain is one of the most common causes of disability. However, only 40% of patients seek medical help. It is also known that in a third of patients, acute pain subsequently becomes chronic, which persists for more than 12 weeks.
What is cervical spine dorsopathy?
Pain with dorsopathy of the cervical spine is not associated with any internal organs. And this is a big problem in diagnosis. The source of pain always remains the spine itself. According to the causes of origin and consequences for the body, dorsopathy of the cervical spine is divided into several types:
- deforming;
- spondylopathy;
- muscular;
- discogenic.
The diagnosis of dorsopathy of the cervical spine is made to both old and young, and even children. This group of diseases is not caused by age-related changes in bone or cartilage tissue, but has reasons related to the spirit of the times. Dorsopathy of the cervical spine is associated with a sedentary lifestyle, and symptoms of the disease are increasingly being identified in schoolchildren and students.
Why does my back hurt?
As soon as the first man got up from all fours and raised his head proudly, he doomed all his descendants to suffering associated with the spine. The spine in four-legged animals is located horizontally and serves to balance all parts of the body. Such a spine remains in ideal condition for a long time and can withstand any stress, tension and exposure to adverse factors. In humans, the spine began to play the role of a rod, or column, and turned into that part of the body that is very easy to disable. Numerous modern studies have shown that pathological changes in the spine are not inherent to individual people or groups of people, but to all of humanity as a biological species. These changes lead to the fact that by the age of fifty, approximately 80% of men and 60% of women suffer from spinal diseases, and the onset of clinical manifestations of the disease falls on the most working period of life, on average 35 years. The most common cause of back pain is dorsopathies.
Causes
Most of the diseases that are included in the group of dorsopathy of the cervical spine and require similar treatment are mainly caused by degenerative processes in the vertebral discs. There are a number of factors that accelerate the onset of the disease:
- poor (unbalanced) nutrition;
- heredity;
- unfavorable conditions (constant humidity, drafts);
- anomalies of the cervical vertebrae.
However, the causes of dorsopathy of the cervical spine can be a number of pathologies.
Low immunity
Often, the disease dorsopathy of the cervical spine occurs against the background of inflammatory processes caused by various infections. The cause of inflammation can be the most harmless bacteria or viruses. However, low immunity and general weakness of the body can make inflammatory processes long-lasting and permanent. Ultimately, this can lead to the development of cervical dorsopathy and the need for urgent medical or even surgical treatment.
Inactivity
Another scourge of the modern world is a sedentary lifestyle. The human musculoskeletal system is designed for movement. However, we spend more and more time sitting at desks or computers. We study, work and relax in a sitting position. And this is one of the reasons why cervical spine dorsopathy is so widespread.
Lifting excessive weights
Excessive loads can lead to spinal injuries, which lead to traumatic changes leading to dorsopathy of the cervical spine.
Abnormality in posture, incorrect positioning of the back
Poor posture, constantly being in a tense position, and even sleeping on an uncomfortable pillow can lead to painful tension in the muscles. It is this tension that in most cases causes dorsopathy of the cervical spine. Hypothermia and excessive strain on the neck can also lead to similar consequences.
Causes of deforming dorsopathies
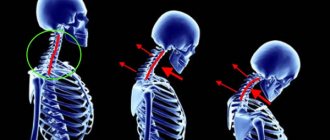
Kyphosis (except congenital) is a curvature of the spine in the form of an arch, the apex of which is directed backward. Acquired kyphosis can be a consequence of rickets, tuberculosis, spinal injuries, and poor posture.
Lordosis (except congenital) is a curvature of the spine in the form of an arch, the apex of which is directed forward. The main causes: poor posture, pathological hip dislocation, inflammation, spinal tumors.
Scoliosis is a lateral curvature of the spine, in which twisting and deformation of the vertebrae occurs. In 80% of cases, the exact cause of the disease is unknown - this is the so-called idiopathic scoliosis.
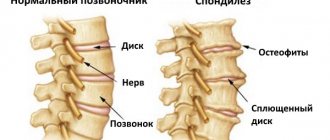
Osteochondrosis is a degenerative-dystrophic disease in which the spine prematurely “wears out” and “ages.” The pathological process begins in the intervertebral disc, then spreads to the vertebrae, intervertebral joints, and ligaments. Mostly older people are affected, but now dorsopathy caused by osteochondrosis has begun to occur at the age of 20–30 years.
Symptoms
Dorsopathy of the cervical spine is accompanied by pain and dizziness, sleep disturbances, pressure changes and difficulty moving in the cervical spine. However, most of these symptoms can indicate many other diseases. To reliably diagnose dorsopathy of the cervical spine, X-ray examination is used. However, there are symptoms that are most likely to occur with dorsopathy.
Increased pain with sudden movements
With dorsopathy of the cervical spine, pain is felt in the area of the shoulder blades. Pain in the head area is also possible. At the same time, an important difference between dorsopathy and other diseases is that pain intensifies with sudden movements.
Extreme fatigue
Severe fatigue is observed with chronic muscle pain (fibromyalgia) caused by dorsopathy of the cervical spine.
Headaches and dizziness
Dizziness can be caused by a complication of dorsopathy of the cervical spine - spasm of the cervical artery. This manifestation of dorsopathy poses a danger to the patient’s life, since spasm of the cervical artery leads to ischemia (decreased blood supply) to the brain and even stroke
. With this complication of cervical spine dorsopathy, the patient experiences visual and auditory disturbances, shooting pains, dizziness and short-term loss of consciousness.
Treatment of dorsopathy symptoms
The main symptom of all types of dorsopathies is pain. It is relieved with the help of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, novocaine blockades (procedures during which an anesthetic solution is injected into the area of damaged nerve roots), and physiotherapy.
They try to restore movement and sensitivity during rehabilitation treatment. It includes massage, physical therapy, mechanotherapy, and physiotherapy.
The above is only an indicative list of general areas of treatment. Of course, dorsopathy can be effectively treated only after its cause has been clarified and a diagnosis has been established. Therapy should be aimed not only at the symptoms, but also at the cause of the disease.
Correspondence consultation with a neurologist
Message sent!
expect a call, we will contact you shortly
Dorsopathies are a fairly large group of diseases. They are united by two common symptoms: they are all associated with lesions of the spinal column and are accompanied by pain in the neck, back, and lower back. All these pathologies are divided into three groups:
- Deforming dorsopathies.
- Spondylopathies.
- Other dorsopathies.
Diagnosis of the disease
Diagnosis of cervical dorsopathy begins with a traditional examination by a neurologist
, habitual questioning and palpation of muscles.
If muscle thickening is detected or there is a suspicion of dorsopathy of the cervical spine, the specialist will refer the patient for an X-ray examination. This is the most accessible and common method for diagnosing such diseases. In some cases, more informative examination methods are required. Then the patient is sent for magnetic resonance imaging
. MRI allows you to diagnose dorsopathy of the cervical spine and identify the most serious complications.
Diagnosis for dorsopathy
Diagnosis of dorsopathy is not particularly difficult. The disease is determined by a neurologist based on the patient’s complaints and neurological tests. To clarify the diagnosis, an X-ray examination of the spine is prescribed. More detailed information is provided by ultrasound (US), computer (CT) and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). Doctors of other specialties often encounter this problem. In this situation, the doctor will definitely refer the patient for consultation or treatment to a neurologist.
Cervical spine treatment
Treatment methods for cervical dorsopathy depend on the cause of the disease. Both the source of the disease and the most dangerous and painful symptoms are treated:
- muscle tension;
- acute pain;
- ischemia
.
Methods may also vary depending on the tactics and purpose of treatment.
Physiotherapy
Physical therapy (physical therapy) is prescribed for the treatment of cervical dorsopathy, when it is necessary to strengthen the patient’s ligaments and muscles. Also, regular performance of a well-thought-out set of exercises increases tone and improves metabolic processes, which is vital for dorsopathy.
Manual therapy
Manual therapy can be used in cases where the doctor knows exactly how to treat cervical dorsopathy in a particular case. The method helps eliminate simple subluxations of the cervical vertebrae and alleviate the patient's suffering from pain.
Massage
A massage course is included in the complex treatment of dorsopathy of the cervical spine along with physiotherapy, laser therapy and exercise therapy. When the disease is at a serious stage, medical or surgical treatments may be required.
Treatment
Therapy, as a rule, is complex and includes medication and physiotherapeutic measures, and gymnastics. Sometimes surgery is indicated.
The following groups of medications may be indicated::
- To combat pain such as Analgin, Ketorolac, Baralgin and others are used For severe pain, a novocaine blockade may be needed - an injection of drugs for local anesthesia.
- In order to reduce inflammatory processes, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs : Naproxen, Diclofenac sodium, Meloxicam and others.
- In certain cases, hormonal anti-inflammatory drugs : Prednisolone, Hydrocortisone and others. They are used only in extreme cases, as they have a large number of side effects.
- To eliminate muscle spasms, muscle relaxants - drugs that reduce muscle tone. The most effective are Mydocalm, Baclofen and Sirdalud.
- Warming ointments with a local irritant effect help improve blood flow at the site of exposure, which reduces swelling, improves nutrition and accelerates regeneration in nearby tissues. Their choice is quite wide, such as Capsicam, Finalgon, etc. are often used.
- drugs may be indicated : B vitamins, Proserin, Nucleo CMF Forte.
- A separate group of medications are proteolytic plant enzymes, such as caripazin, based on dried papaya milky juice. They promote softening and resorption of disc hernias, help improve collagen secretion, and moderately restore disc membranes.
Some medications are very strong and can cause a number of side effects. That is why you can take any of them only with a doctor’s prescription.
Surgical intervention may be indicated in the presence of hernias or in the absence of results of conservative therapy.
Also an important component of therapy is physical therapy . If the technique is followed correctly, it helps to significantly improve the patient’s condition.
The complex is selected by the doctor individually. It may include the following exercises :
- You need to press your palm to your forehead and tilt your head forward, exerting resistance with the inside of your hand.
- Place your palm on the temple area and tilt your head towards your hand, also offering resistance.
- Smoothly lower your head to your chest, press your chin to it and hold for 2-3 seconds, then smoothly return to the starting position.
- Slowly turn your head to the extreme left position, then, also smoothly, return to the starting position. Repeat to the right side.
- Lower your arms straight down, raise your shoulders as high as possible, hold in this position for 10-15 seconds, then lower smoothly.
Exercises are repeated 10-15 times several times a day.
A professional massage aimed at relieving tension may be indicated. You can also learn self-massage, which will help improve your condition at the right time.
At home, you need to adhere to all measures prescribed by your doctor : take prescribed medications, perform massage and exercise therapy if necessary. Various folk remedies can also help, such as garlic compress, coltsfoot, intoxicating infusion, homemade mustard ointment, etc. Despite the safety of traditional methods, you still need to consult a doctor first.
To prevent and reduce risk factors for dorsopathy, it is recommended to adhere to the following recommendations:
- Eat healthy and balanced;
- Stop smoking;
Familiarize yourself with the rules for preventing dorsopathy in the cervical region. Try to do at least a short warm-up every day;- Do a short warm-up a couple of times a day during the day if you work in a sedentary job;
- Swimming and water aerobics are useful;
- Be careful with extreme types of activity, extreme driving style;
- Follow the training regimen and technique.
- Strengthen your muscle corset through special exercises.
- During the cold season, be sure to protect your neck from the cold.
- Excellent prevention - regular relaxing massage of the neck and back;
- Try to avoid sudden head movements.
- It is useful to sometimes undergo sanatorium-resort treatment.
- Avoid sudden head movements.
Video: “Exercises for the neck”
Ways and methods of disease prevention
Preventive measures will allow you to stop the development of the disease before you have to treat cervical dorsopathy. A simple set of measures will help you avoid pain, expensive treatment and dangerous complications in the future. Therefore, the prevention of dorsopathy of the cervical spine should be taken with all possible seriousness. The rules of prevention are simple. Need to:
- Healthy food;
- control body weight;
- move more;
- avoid hypothermia.
Causes of spondylopathies
Ankylosing spondylitis (Bechterew's disease) is a chronic disease in which inflammation develops in the joints of the spine and mobility in the intervertebral joints is impaired. Not only the spinal column, but also other joints and internal organs can suffer. Young men are most often affected.
Inflammatory processes in the spine. They can be caused by various infections, vertebral osteomyelitis, purulent inflammation of the intervertebral discs. Sometimes the cause of the inflammatory process cannot be detected.
Spondylosis is “premature aging” of the spine. Pathological changes in the spinal column can lead to compression of the nerve roots, resulting in pain, movement disorders, and sensitivity.
Forestier's ankylosing hyperostosis is a rare disease in which bone tissue grows in the ligaments and tendons of the spinal column. His mobility is impaired.
Spondylopathies are also caused by vertebral tuberculosis, brucellosis, enterobacterial spondylitis, syringomyelia and other diseases.
How does a neurologist diagnose dorsopathy? What happens in the doctor's office?
First of all, it is important for your doctor to understand the symptoms that are bothering you. Therefore, your appointment at the neurologist’s office will begin with you being asked some questions:
- How long have you had back pain? How often do they occur? After what do they usually intensify? After what do they subside?
- Have you noticed that your neck and lower back have become less flexible?
- Are you bothered by pain in your arms and legs? Have your legs and arms become weaker or moved worse? Do you experience a feeling of numbness or unpleasant tingling?
- Where and who do you work for? Do you often have to lift heavy loads? Sitting at an office desk for a long time?
- Have you recently had a back injury? Have you had any illnesses?
This will be followed by a neurological examination. The doctor will check the strength and tone of the muscles of your arms and legs, skin sensitivity, feel the back muscles to detect their tension, and press on certain points in the spine to identify soreness. After this, you will be given an examination.
What is dorsopathy and how to treat it?
Recently, we have published a number of articles devoted to the pathology of the spinal column and methods of its treatment. Have you heard about the disease, which translated means “back pain”?
Dorsopathy. We talk about what is hidden behind this term with Natalya Vladimirovna Umerenkova, a leading specialist in the neurology department of Clinic Expert Kursk LLC.
- Natalya Vladimirovna, what is dorsopathy and how often in your practice do you meet patients with this diagnosis?
This is not just one disease, but a collective concept that includes various pathologies of the spine and paravertebral structures (ligaments, muscles). They themselves can be specific diseases (for example, osteochondrosis, ankylosing spondylitis and others), but the general name for them is “dorsopathy”. In addition, the appearance of such definitions in domestic medicine is apparently associated with the desire to eliminate or reduce terminological discrepancies with foreign classifications (in particular, with the International Classification of Diseases).
We encounter dorsopathies almost every day: we can say that this is one of the common reasons for turning to neurologists and specialists in related specialties - neurosurgeons and orthopedists.
- What types and forms of dorsopathies are there? How is a disease coded in the International Classification of Diseases?
There are various classifications of them. If you adhere to ICD-10, then these are entire blocks of diseases. These include deforming dorsopathies, which include, for example, various spinal deformities, osteochondrosis, displacement of the vertebrae relative to each other, and others.
Another group is spondylopathies: ankylosing spondylitis, Forestier disease, disc damage in spinal tuberculosis, and brucellosis. The third is other dorsopathies: this includes, for example, pathology of intervertebral discs and dorsalgia.
According to another classification, diseases are divided into vertebrogenic (spondylogenic, associated with the spine itself) and non-vertebrogenic (muscles or ligaments suffer).
There is dorsopathy of the cervical, thoracic, and lumbosacral spine. There is a variety of it with radicular syndrome.
The code for dorsopathies according to ICD-10 is M40-M54.
- What symptoms are characteristic of dorsopathy?
Its signs are very diverse, so I will name the main ones.
This is a pain syndrome in any part of the spine, in the area of the shoulder girdle and shoulder, buttocks, legs; weakness or excess tension in muscles, limbs, decrease in their volume; sensory disturbance; limitation of movements, daily activity, vertebral artery syndrome.
- What is the triggering factor for the development of dorsopathy?
There are also many of them. This is a hereditary factor, poor nutrition, metabolic disorders and excess weight. Also, the causes of dorsopathy can be infectious processes, age-related changes, spinal injuries, poor posture, flat feet, a sedentary lifestyle, or excessive physical and static stress, suboptimal lifting of weights (for example, by jerking or from an incorrect position), vibration, pregnancy and even smoking.
- How is this disease diagnosed?
It depends on the symptoms the patient has and his complaints. Diagnostic examination is, first of all, the task of the doctor. Only he, during the patient’s appointment, will be able to reliably and competently determine the volume of diagnostic studies that is advisable to carry out in each specific case.
To confirm the diagnosis of dorsopathy, a neurological examination is certainly performed. Additional methods include radiography, including functional tests, magnetic resonance and computed tomography, myelography, electroneuromyography, and laboratory tests. If necessary, consultations with related specialists are carried out - for example, a neurosurgeon, orthopedist, rheumatologist, phthisiatrician.
- Dorsopathy is a diagnosis for adults? Or can it occur in children?
This pathology is typical for almost all age groups. Of course, in the structure of dorsopathy, other diseases will be more common in children than in adults and the elderly.
- What is included in treatment measures for dorsopathy?
Here it is probably appropriate to talk about the standards of treatment for individual diseases included in the group of dorsopathies.
If we, for example, take one of the most common syndromes in the structure of dorsopathies - pain syndrome - then the principles of treatment include the correct motor regimen (currently, according to modern ideas, early activation of the patient is used (feasible loads are selected, bed rest is not recommended), prescribing analgesics, anti-inflammatory drugs, medications to relax muscles (the so-called muscle relaxants). Also, for dorsopathy, physiotherapy (including massage), manual therapy, acupuncture, physical therapy are used. Of course, the use of any treatment methods must be clearly justified, must there are no contraindications.
- How effective is the use of manual therapy in patients with dorsopathy?
It all depends, in particular, on the specific diagnosis (for some dorsopathies it may be contraindicated), the severity of the disease, and the qualifications of specialists. For the most part, even when indicated, manual therapy is not used in isolation, i.e. it is combined with various other treatment methods, including medications.
- If dorsopathy is not treated, is it fraught with complications?
Depends on the specific disease, its severity and the treatment provided (or lack thereof). Some dorsopathies can regress on their own. In other cases, for example, with pain syndromes, chronization of manifestations and progression of pathological structural and functional changes are possible.
- What specialty does the doctor treat dorsopathy? And does dorsopathy require dynamic monitoring?
Most often, patients have an initial appointment with a therapist, general practitioner or neurologist. Depending on the established diagnosis, the patient will be treated by a specialist of the appropriate profile: neurologist, neurosurgeon, orthopedist, rheumatologist, infectious disease specialist, phthisiatrician.
Dorsopathy certainly requires dynamic monitoring. This is required both during treatment and after it, to assess its effectiveness. In addition, in many cases, the formed structural changes do not regress, i.e. they tend to persist and, if risk factors are not eliminated, lead to progression of the underlying disease.
- Is rehabilitation carried out for dorsopathy and if so, what does it include?
Undoubtedly. Depending on the type of disease, manual therapy, physiotherapy (including massage), kinesitherapy, and swimming can be used. Preventive measures aimed at eliminating risk factors for the development of dorsopathies are of great importance.
For reference:
Umerenkova Natalya Vladimirovna
In 2004 she graduated from Kursk State Medical University.
In 2004-2005, she completed an internship in neurology at the above-mentioned university.
Since 2015, he has been working at Clinic Expert Kursk LLC, and is a leading specialist in the neurology department.
Other interviews with N.V. Umerenkova:
How to relieve tension headaches?
How to get rid of stuttering in adults?
Spinning until you drop!
Radiation diagnostics of dorsopathy
For dorsopathy, the following radiation diagnostic methods are used:
- Radiography. Typically, photographs are taken in two positions - full face and profile; if necessary, they can be taken in other positions. X-rays help assess the condition of the vertebrae, the presence of bone growths on them - osteophytes, and the height of the intervertebral discs.
- CT scan. A more accurate diagnostic method that helps to study this or that part of the spinal column in more detail and take pictures in which layer-by-layer sections will be visible. CT scans, like radiography, use x-rays.
- Magnetic resonance imaging. This method helps to assess the condition of the intervertebral discs, spinal ligaments, and surrounding soft tissues. During the study, a strong magnetic field is used.
Types of dorsopathy
Based on the nature of the damage to the spine, diseases are divided into deforming diseases, spondylopathies and others.
Deforming pathologies lead to degradation of intervertebral discs - up to their complete destruction, displacement of the vertebrae. This group includes scoliosis, kyphosis, lordosis. Spondylopathies include inflammatory and infectious lesions of the spine, arthritis, osteochondrosis, and spondylosis. The remaining diseases, including vertebrogenic dorsopathy (pathological changes in the disc with subsequent entrapment of the spinal cord) and back pain caused by other causes, are combined into a separate group. Spinal diseases are localized in different parts - cervical, thoracic or sacrolumbar. Dorsopathy of the cerebral palsy is accompanied by muscle spasms and sometimes cerebral circulatory disorders. The patient may experience dizziness and weakness in the arms. The pain may spread to the forearms and shoulders. The thoracic region suffers much less frequently than others due to its lack of mobility. This is the longest section of the spinal column, and diseases here manifest themselves in the most unexpected ways: in the form of heart pain, chest pain, coughing, weakness in the upper limbs.
The most common case of dorsopathy is damage to the sacrolumbar region. This pathology can be found in any adult. It is asymptomatic, or its signs are so weak that the patient does not pay attention to them. During exacerbations, the patient experiences pain in the lower back (lumbodynia) and lower extremities, and a malfunction of the pelvic organs occurs.
There are cases when the pathology is limited to damage to one vertebra, but polysegmental and widespread dorsopathy are more common. In the first case, the disease affects the entire spine, in the second - several vertebrae in different areas.