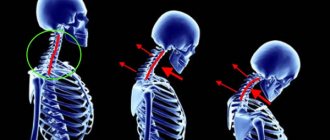
Osteochondrosis of the cervical spine is diagnosed in many patients over 25 years of age. The disease is characterized by deformation of the discs between the vertebrae, which causes pinching of the spinal nerves and blood vessels. Then various complications arise, the list of which includes panic attacks with cervical osteochondrosis. An attack can last from a few minutes to 1 – 3 hours. They are repeated twice a month, but over time the frequency of attacks can increase to 1 - 2 times a week. Then you need to urgently visit a doctor.
Anxiety disorders in neck osteochondrosis occur as a result of cerebral circulation disorders. However, they are observed only in some patients. To understand why this happens, you need to conduct a thorough diagnosis and proper treatment. It will be useful for patients with osteochondrosis in the initial stages to know how to prevent panic attacks.
Causes of panic attacks in cervical osteochondrosis
An unreasonable feeling of fear that arises suddenly should alert a person. During a panic attack, the patient fears for his life, feels self-doubt, and hopelessness.
Anxiety disorders in osteochondrosis of the cervical spine arise due to impaired cerebral circulation. This occurs as a result of damage to the intervertebral discs, which lose moisture, become more fragile, become thinner, and then neighboring vertebrae begin to rub against each other. Panic attacks are observed in many patients with neck osteochondrosis; they are provoked by the following factors:
- Disturbance of calcium metabolism.
- Change in amino acid profile.
- Disturbance of acid balance in the blood.
Reference. According to medical research, osteochondrosis and panic attacks have a direct connection. Anxiety disorders appear when the vertebral artery is compressed by intervertebral hernias, osteophytes or displaced vertebrae.
At the early stage of the disease, discomfort appears, as well as aching pain, which quickly passes. In the second stage, the pain becomes more pronounced. At the next stage, the pain decreases, this indicates complete destruction of the discs between the vertebrae. Then severe headaches appear and the sensitivity of the upper extremities is impaired.
Panic attacks indicate compression of the vertebral arteries. Then the blood supply to the brain is disrupted, this organ suffers from a lack of nutrients and oxygen. This condition provokes anxiety disorders and other unpleasant symptoms.
In the absence of treatment, the pathology continues to develop, and the clinical picture becomes more diverse, and cases of panic attacks become more frequent. Due to constant attacks, the risk of heart disease, dysfunction of the thyroid gland, and metabolic disorders increases.
In addition, doctors identify the following factors that can trigger panic attacks:
Radicular syndrome of the cervical spine
- Genetic predisposition to increased production of adrenaline (adrenal hormone) in the body.
- Poor nutrition, deficiency of magnesium, zinc in food.
- Taking certain medications, for example, oral contraceptives, psychostimulants.
- Excessive mental or physical stress.
- Condition during pregnancy or after childbirth.
- Mental illnesses.
- Hormonal imbalance.
- Prolonged stay in an uncomfortable position (with a bent neck).
- Meteosensitivity.
In addition, the likelihood of panic attacks increases with regular alcohol abuse.
No ads 1
Panic attacks and similar conditions. Definition of concepts
A panic attack is an inexplicable, painful attack for the patient, an attack of severe anxiety, accompanied by fear, combined with various vegetative symptoms.
For many years, patients live with “VVD” (vegetative-vascular dystonia), “NCD” (neurocirculatory dystonia), “sympatho-adrenal paroxysms” and many other bizarre diagnoses. Which “hide” the true cause of such an unpleasant condition – panic disorder. At the same time, attacks become more frequent and anxiety intensifies.
Panic disorder (episodic paroxysmal anxiety) is a disease whose main symptom is repeated attacks of severe anxiety (panic) that are not limited to a specific situation or circumstance and are therefore unpredictable.
In 5% of the population, attacks occur annually, and in 10% this disease has an erased form. And every sick person believes that he alone suffers from this disease. And the list of various studies that he receives when contacting general practitioners confirms for him the complexity of the situation. Often, all these actions prevent both the patient and the doctor from recognizing the main cause of suffering - panic disorder.
Panic disorder is included in the International Classification of Diseases (ICD-10).
Symptoms
A panic attack occurs suddenly and is accompanied by severe symptoms that frighten the patient. Strong fear arises without objective reasons. Then the patient feels strong anxiety or tension, but does not understand why they appeared.
Other symptoms of a panic attack with cervical osteochondrosis:
- Increased heart rate (100 – 120 beats/min.), interruptions in heart contractions.
- Excessive sweating.
- Sleep disorders.
- Breathing disorders.
- Trembling of limbs.
- Chills.
- Nausea, bowel movements (constipation or diarrhea).
- Frequent urge to urinate.
- Painful sensations in the area under the ribs.
- Discomfort or pain in the heart area.
As the condition progresses, the patient ceases to understand who he is and what is happening around him. Thoughts become confused, consciousness is disturbed, the patient becomes dizzy, feels unusually light, his vision becomes dark, and he may lose consciousness. A person is afraid of dying or going crazy.
Osteochondrosis manifests itself as hearing and vision disorders
In the later stages of osteochondrosis, the following symptoms may appear:
- Sensory disturbance: burning, tingling, crawling sensation, numbness of the hands.
- Loss of balance, falling while moving.
- Convulsive seizures.
- Limitation of mobility.
- Vertigo (dizzy).
- Hearing and vision disorders.
The severity of the clinical picture during panic attacks depends on the stage of cervical osteochondrosis. In the early stages of the pathology, degenerative-dystrophic disorders in the cervical segment are minor, so cerebral circulation is practically not impaired. In this case, panic attacks do not appear or occur easily and end quickly.
Starting from the second stage of osteochondrosis, protrusions, hernias, bone growths on the vertebrae compress the vertebral arteries. Then the blood supply to the brain is disrupted, hypoxia (oxygen starvation) occurs. Panic crises are accompanied by severe symptoms (severe anxiety, fear of death) and last longer.
Reference. A panic attack lasts from 2 minutes to 3 hours. In most patients, signs of an attack persist for 25 to 30 minutes and then disappear. At first, fear occurs 1-2 times a month, and then the episodes become more frequent up to several times a week or day. Over time, the patient begins to fear the most panic attacks, which aggravates his condition.
Cervicothoracic syndromes causing panic disorders
Cervical and thoracic osteochondrosis is accompanied by syndromes that manifest themselves with certain symptoms:
- Radicular - pain syndrome from the neck radiates to the shoulder blades, arms and right up to the fingers. In addition, visual acuity decreases, tinnitus appears, and breathing is impaired.
- Cardiac – there is a pressing pain in the left side of the chest, the heart rate increases. The duration of the attack can reach several hours.
- Vertebral artery syndrome: the patient feels sick, hearing and vision are impaired, and an unsteady gait appears.
- Diencephalic - internal trembling appears, heart rate increases, blood pressure rises.
All these symptom complexes with cervicothoracic osteochondrosis can provoke a panic attack.
[node:field_similarlink]
First aid
During the next attack, you should lie down and try to relax as much as possible. The most effective method of controlling your condition and quickly improving it is proper breathing. You need to inhale as deeply as possible, holding your breath for 1-2 minutes, and then exhale slowly, smoothly, closing your eyes and relaxing your muscles.
Breathing exercise helps eliminate panic disorder if repeated 10-15 times. Between approaches, doctors recommend taking a 3-5 minute break, during which you should breathe at your usual rhythm. Slow and calm breathing should be practiced between attacks by patients with severe cervical osteochondrosis. During an attack, it helps to stop hyperventilation and avoid paroxysms.
VSD and cervical osteochondrosis
Degenerative-dystrophic changes in the intervertebral discs of the cervical spine are often accompanied by VSD (vegetative-vascular dystonia), which in turn provokes panic crises. Autonomic dysfunction develops due to compression of the vessels that pass on both sides of the spinal column. Then inflammatory processes occur, swelling occurs, and the canal narrows against the background of degenerative disorders of the vertebrae.
The combination of cervical osteochondrosis and autonomic dysfunction often provokes panic crises. With the further development of these pathologies, the clinical picture becomes more diverse. VSD is caused by a dysfunction of the central nervous system, and in particular the brain. With osteochondrosis of the cervical segment, brain function is also disrupted due to compression of the blood vessels that transport blood to it. That is why the clinical manifestations of both diseases are similar.
Autonomic dysfunction and osteochondrosis are similar in terms of development. Pathologies can be caused by chronic diseases, infections, stress, metabolic disorders, and injuries. These diseases are often combined and treated comprehensively.
Reference. With autonomic dysfunction and cervical osteochondrosis, pressure may increase or decrease. In the first case, pressure surges are caused by a violation of the central regulation of autonomic functions, and in the second - by stenosis of the vessels of the cervical segment of the spine.
With a combination of VSD and cervicothoracic osteochondrosis, the manifestations of a panic crisis become more pronounced. During an attack, acute pain in the chest (intercostal neuralgia) often appears. In addition, the heartbeat, frequency, and depth of breathing are disrupted, and a feeling of lack of air appears. Then the patient has a strong fear that he will die from cardiac arrest.
No ads 2
Symptoms of anxiety
Before an attack, anxiety increases and a person’s psycho-emotional state worsens. Patients at doctor's appointments complained of the feeling of “being in an aquarium.” The sounds became muffled, coming as if from afar, and the surrounding objects seemed unstable, their contours looked fuzzy and blurred.
Panic attacks are accompanied by other characteristic clinical manifestations:
- feeling of lack of air, shortness of breath;
- arrhythmia, rapid heartbeat;
- trembling, chills;
- increased sweating, cold sweat;
- dull or sharp pain in the cardiac region;
- sensation of “crawling goosebumps” in the back of the neck, shoulders, forearms, hands;
- dizziness, impaired coordination of movements.
Often during an attack, the urge to urinate becomes more frequent, nausea and vomiting occur. During the first panic disorder, there is a fear of death, which can reach a state of passion. Subsequent attacks are accompanied by specific phobias, for example, a person is afraid of dying due to lack of air. Instead of fear, the patient may feel internal tension and inexplicable anxiety.
Diagnostics
If you notice symptoms of cervical osteochondrosis and panic crises in yourself or your loved ones, then urgently contact a neurologist. The examination begins with collecting anamnesis and examining the cervical spine. The doctor is interested in information about how symptoms have changed over time.
Diagnosis consists of two stages: first, the specialist confirms cervical osteochondrosis, and then determines its connection with panic attacks.
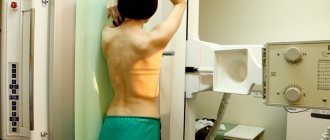
To identify degenerative-dystrophic changes in the cervical spine, the following studies are prescribed:
- Radiography.
- Computer or magnetic resonance imaging.
If a neurologist suspects that osteochondrosis is combined with autonomic dysfunction, then in addition to the diagnostic methods described above, an electrocardiogram, functional tests to assess the state of the autonomic nervous system, and rheoencephalography (a study of the vascular system of the brain) are prescribed.
Reference. It is important to identify the true cause of panic disorders. The doctor must make sure that the attacks are caused by osteochondrosis. To do this, differential diagnosis is carried out with vegetative-vascular dystonia, mental illness, hormonal imbalance, etc.
To identify changes in the amino acid profile and calcium metabolism disorders, laboratory tests are carried out. For this purpose, the patient is prescribed blood tests.
After determining the nature of panic attacks, the doctor draws up a treatment regimen.
Why panic attacks need to be treated
The syndrome may not appear too often: the interval between attacks can be quite significant, but sooner or later, the panic will return anyway, that is, nothing will go away on its own.
The consequences of this are:
- Since a panic attack can take you by surprise at any time, in any place, in public, the person suffering from the disorder begins to avoid loved ones, friends, does not go anywhere, and withdraws into himself.
- Various phobias develop - fear of open space, darkness, phenomena, i.e. anything.
- Psycho-emotional disorder leads to personality disorder.
- Self-doubt develops, which affects personality, appearance, family relationships, and professional activities.
- Sleep is disturbed, appetite is lost, and the body becomes dehydrated. As a result, the body suffers.
- Refusal to share problems causes problems in the nervous system.
It is imperative to get rid of this problem, since, judging by the above, it brings problems in social adaptation, worsens the quality of life, interferes with normal work, and negatively affects the physical and mental state.
Stages and methods of treatment
Treatment of panic attacks is aimed at stabilizing the patient’s mental state. For this purpose, medications, physical therapy, physiotherapy, and manual therapy are used.
Analgesics, NSAIDs, muscle relaxants, antidepressants, chondroprotectors, etc. are used to treat osteochondrosis with panic attacks.
Therapy can be divided into 3 stages:
- Eliminate pain, relax the muscles that compress the nerve roots, as well as blood vessels. For this purpose, the patient is prescribed analgesics and NSAIDs. Drugs from the first group (Ketoral, Baralgin) help relieve pain. And medications from the second group (Ibuprofen, Diclofenac) relieve inflammation, relieve pain, and restore mobility, which was impaired due to compression of the spinal nerves. Muscle relaxants relieve tension in muscle tissue.
- Restoration of metabolic processes. Patients are prescribed Vinpocetine, Vasobral, which activate blood circulation and improve metabolic processes. Drugs from the group of chondroprotectors (Chondroitin, Rumalon) affect the metabolism in intervertebral discs, stimulate their regeneration, and slow down destruction. Vitamin and mineral complexes strengthen the immune system and speed up metabolism. Antidepressants (Afobazol, Bellaspon) help fight depression and relieve anxiety attacks. Neuroprotectors protect nerve cells from pathogenic factors.
- Prevention of relapses and strengthening of tissues. To get rid of the causes that provoke panic crises, you need to undergo treatment with a psychologist. For this purpose, methods such as meditation and auto-training are used. It is recommended to avoid excessive stress on the cervical spine, walk more often, swim, and periodically stand up and stretch the cervical collar area when working at the computer.
No ads 3
Reference. In case of autonomic dysfunction, it is recommended to visit a psychotherapist if the pathology is caused by neurotic disorders.
Complex therapy includes physiotherapy. To do this, the damaged area of the cervical spine is exposed to a magnetic field, ultrasound, laser radiation, and low-frequency currents. To relieve pain, electrophoresis with solutions of magnesia, novocaine, etc. is prescribed. Stone therapy (hot stone massage) and aromatherapy are also indicated. These procedures increase the effectiveness of other therapeutic methods, speed up recovery, and improve overall well-being.
Acupuncture (acupuncture) can help relax tense muscles in the neck. During the procedure, the specialist pierces biologically active points on the damaged area with thin needles.
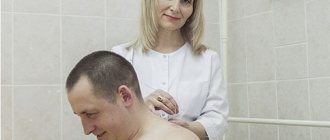
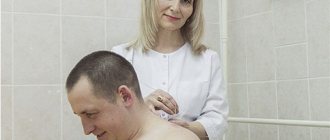
Classic or cupping massage sessions accelerate blood flow, metabolic processes, tissue trophism, as well as their healing. For cervical osteochondrosis with panic attacks, manual therapy is often prescribed, during which a specialist acts on the cervical segment of the spine with his hands.
Important. Massage, as well as manual therapy, should be carried out by an experienced specialist, since inept actions can aggravate the situation and cause complications (damage to nerve roots, blood vessels).
With the help of physical therapy, the patient can strengthen the muscles in the damaged area, speed up metabolism and blood circulation, restore motor activity of the spine, and improve overall physical and psychological condition. But to get lasting positive results, you need to train daily. The complex for each patient is compiled separately by the attending physician.
The patient must change his lifestyle:
- Adequate sleep of 8 hours per day.
- Moderate physical activity.
- Proper nutrition.
- Maintaining a daily routine.
- Rejection of bad habits.
In addition, it is recommended to wear a Shants collar. This orthopedic device relieves stress from the cervical spine, allows it to relax and correct posture. Wearing a collar is indicated for osteochondrosis of the cervicothoracic region. You need to wear it no longer than 2 – 3 hours a day, otherwise the muscles will weaken.
Treatment can be supplemented with herbal medicines that normalize the activity of the nervous system, stabilize the psycho-emotional state, improve the transmission of nerve impulses, restore metabolic processes, and increase the body’s protective properties. Remedies based on herbal components reduce the duration of panic attacks, improve brain functionality, as well as the general condition of the patient.
Treatment
For severe pain during an attack of osteochondrosis, painkillers are used: Amelotex in injections, tablets, gel and suppositories. It is best to use an injectable drug or suppositories only when other forms are not suitable for the patient for some reason. For the same purpose, you can use Ketorol and Baralgin.
Neck muscle tension is relieved with NSAIDs: Ibuprofen, Diclofenac.
Once the effect is achieved, they begin to improve or restore metabolic processes, paying special attention to the normalization and improvement of microcirculation. Among the drugs used, Stugeron stands out favorably, leading to normal blood flow in the brain. Preparations based on Piracetam help improve metabolic processes in the brain.
The most effective remedy for relieving the syndrome, manifested by dizziness and unsteady gait, is Betaserc.
The cessation of destructive changes in the intervertebral discs is achieved by the administration of Chondroitin and its derivatives.
Attention is paid to the patient’s anxious state and the appearance of depressive syndrome. In such situations, the tablet medicine Afobazol will come to the rescue.
Get a consultation on MRI diagnostics. Consultation on the service does not oblige you to anything.
Main conclusions
Panic attacks with cervical osteochondrosis are a serious condition that worsens the mental and physical condition of the patient. It is not so easy to cure the pathology, so you should consult a doctor when the first suspicious symptoms appear. After a thorough diagnosis, the neurologist will determine treatment tactics. Therapy should be comprehensive: medications, physiotherapy, massage, manual manipulation, lifestyle correction. To avoid relapses of the disease, you need to lead a moderately active lifestyle, avoid stress, limit the consumption of coffee and alcohol, take a hot shower every day, sleep on an orthopedic mattress, and eat right.
Who to turn to for help and how to diagnose
Poor awareness among people about panic disorder leads to the fact that some consider it completely frivolous, while others consider it a dangerous incurable mental illness. Therefore, they believe, you should not go to doctors: in the first case there is no need, and in the second the main role is played by the fear of being branded as mentally ill. Both opinions are completely unfair: it is both very serious and completely controllable and treatable. A competent approach will allow you to successfully and fairly quickly get rid of the problem.
First of all, you need to understand that you need to contact only experienced, highly qualified specialists - a psychiatrist, who will develop treatment tactics based on the causes of a panic attack, because they are the ones that need to be eliminated. The doctor will determine why the patient’s nervous system could not withstand the load and malfunctioned in the form of panic manifestations.
The doctor must carefully examine the patient to establish an accurate diagnosis and study the symptoms. The selection of therapy is made based on the characteristics of the patient’s body on an individual basis. The work of a professional consists not only of recommendations and prescribing certain medications, but also of carefully monitoring the progress of treatment and, if necessary, its correction.
As for the psychologist, such a specialist is useless in this case - he is not able to identify the causes of the pathological disorder and prescribe medication and psychotherapeutic treatment, which, in case of getting rid of this problem, are necessary. The picture is the same with sorcerers, psychics and “wise” advisers from the Internet - they will only bring harm to the patient, which is then quite difficult to correct, aggravating his not the best condition.
The psychiatrist, first of all, will seek advice from a cardiologist, therapist, endocrinologist, neurologist, or psychotherapist. This is necessary to exclude the presence of somatic and serious mental illnesses.
It should immediately be noted that a therapist in ordinary clinics does not have the opportunity to carefully and competently examine the patient. In addition, long queues and the nervous atmosphere in them often serve as an impetus for another panic attack, and the person generally loses all desire to be treated.
In specialized paid clinics, such a picture is not observed: any person who comes here receives great attention. In addition, it is usually comfortable; highly qualified doctors work here, “armed” with advanced techniques and equipment for accurate diagnosis and successful treatment. The latter implies the use of pharmacology, psychotherapy, physiotherapy in combination, as well as changing the usual lifestyle.
The attitude of the patient himself to the treatment of panic attacks is also important - he must understand his problem, that this, in essence, is not a disease at all, but a sign of a disorder of higher nervous activity. For a successful result, you need the desire and good will of the patient, compliance with all the doctor’s recommendations.
Methods for diagnosing and treating osteochondrosis of the cervical spine
The diagnosis is made by an orthopedic doctor or neurologist based on examination, X-ray or computed tomography of the spine. If an intervertebral hernia is suspected, an MRI will be required, and to assess functional circulatory disorders, rheoencephalography and fundus examination will be required.
Conservative therapy includes symptomatic measures (pain relief, anti-inflammatory therapy, antispasmodics), as well as restoration of natural cartilage tissue with the help of chondroprotectors. Acupressure massage, physiotherapy, and therapeutic exercises are also effective.