Features of pain on the outside of the foot
Typically, patients complain that the foot begins to hurt after or during walking and subsides somewhat with rest. There is increased abrasion of the sole of the shoe along the outer edge and deformation of the heel. It is important to determine the cause of the pain in time and take all measures to prevent it from becoming chronic.
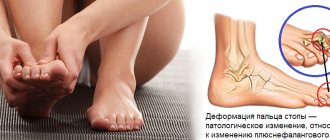
The outer side of the foot is the main “line” of support when walking and running. There are several important anatomical structures in this area, each of which can hurt when overloaded.
Pain in toes: symptoms, causes, associated diseases
Gout
Gout develops due to the deposition of salts in the joints of a substance that is synthesized in the body during the metabolism of purines.
The latter come with meat products. With this pathology, pain occurs in the big toe. Moreover, this symptom often occurs suddenly and becomes intense. A characteristic sign of gout is redness (the skin becomes reddish-brown) and swelling of the affected joint. In the treatment of pathology, specialized drugs are used that restore purine metabolism, and a specialized diet that involves refusing or limiting meat consumption. Most often with gout, the bone on the toe hurts. However, the disease can also affect other joints, including knees, feet, ankles, wrists, and elbows.
The pain of gout can be burning, tearing, throbbing or pressing. The symptom becomes most intense during the night. By morning the patient's condition returned to normal. Pain syndrome can be provoked by the consumption of alcoholic beverages, meat or fatty foods. Also, a person’s condition worsens after visiting a bathhouse.
On average, a patient experiences joint pain in the toes due to gout from two to six times a year. Each attack lasts about 3-4 days. Analgesics, the type and dosage of which are determined by the doctor, help relieve pain in this pathology. To avoid another attack, it is recommended to adhere to a strict diet that includes avoiding or limiting consumption of fatty and meat products, fish, and alcohol. To prevent exacerbation of gout, medications are prescribed that lower uric acid levels.
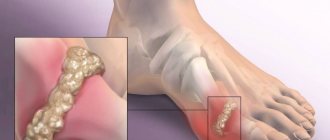
Osteoarthritis of the toe joints
Osteoarthritis affects the joints of the toes, most often localized in the first metatarsophalangeal. This pathology causes a dull pain that intensifies with movement or against the background of increased stress. The intensity of the symptom decreases in the morning.
The presence of osteoarthritis is indicated by the following signs:
- clicks and crunches;
- limited mobility of the affected joint;
- difficulty walking;
- deformation of the affected joint caused by the formation of osteophytes (bone growths).
Due to deformation, the affected finger is more often injured, which contributes to the development of the inflammatory process in the periarticular bursa (bursitis). The duration of relapse of osteoarthritis varies. In some patients, attacks of pain last no more than one day, in others - for several weeks or months.
Physiotherapy methods, massage, and mud therapy help to cope with the relapse of the disease. Swimming demonstrates good results. In case of an acute attack, painkillers are recommended.
Causes of pain on the outside of the foot
Among the most typical causes of pain on the outer side of the sole, we highlight the following:
- Stress fracture of the base of the 5th metatarsal. The so-called march fracture does not occur simultaneously. Traumatic factors accumulate and gradually weaken the bone. The area of the bone begins to hurt when the fracture does not yet appear on the x-ray. Over time, the bone can break completely. It occurs due to an imbalance of the foot and lower leg and significant overload.
- Pain associated with polovarus deformity of the foot. A hollow foot is the exact opposite of a flat foot. In this case, the foot is supinated - “rotates” outward. The outer part is significantly overloaded and hurts.
- Plantar fasciitis. The plantar fascia lata extends from the heel to the base of the toes. The fascia can hurt anywhere: near the heel, in the center, at the toes, on the outer or inner side of the sole.
- Apophysitis of the styloid process of the 5th metatarsal bone. A powerful tendon is attached to the bone on the outside of the foot. If there is excessive tension, it injures the bone and causes inflammation.
Effective means for rehabilitation
The main factors for foot pain are muscle imbalance and mechanical overload. Correcting both factors guarantees the best possible result. The following solutions provide the most tangible results:
- Orthopedic individual insoles. Depending on the reason, you can select the most suitable insole orthoses in terms of density, shape and inclination. They will unload the feet and immediately reduce pain.
- Balancing pads. Exercises on balance machines activate stabilizer muscles. The foot rolls outwards less, the effect is noticeable both in a standing position and when moving.
- Losing body weight and choosing comfortable orthopedic shoes. Every extra kilogram significantly increases the load on your feet. If you also wear bad shoes, the problem will develop even faster.
- If the pain is accompanied by swelling or does not go away after rest, a visit to the doctor is required. If a stress fracture is detected, the leg will have to be fixed in a special orthopedic boot. This type of orthosis makes it possible to walk, but immobilizes the foot.
Phlegmon of the foot
24.09.2019
Cellulitis is a lesion of the subcutaneous tissue and nearby soft tissues. A feature of the disease is the absence of clear boundaries of the inflammatory area. This is due to the fact that phlegmon can spread throughout the soft tissues adjacent to the source of inflammation.
Reasons for the development of phlegmon of the foot
Possible reasons:
- mechanical damage to the foot as a result of wounds of various origins (stab, gunshot);
- diabetes mellitus (suppuration as a result of microtrauma, the occurrence of boils and carbuncles, poor wound healing);
- entry of a foreign body into the tissues of the limb;
- tonsillitis (inflammation of the tonsils );
- caries;
- phlegmon formed in the lower limb (thigh, toes ) ;
- suppuration as a result of callus (subcallosal abscess);
- exposure to chemicals that get under the skin (turpentine, gasoline, kerosene and others);
- cracks in the skin.
The presence of at least one of the above reasons can lead to the formation of pathogenic microorganisms (Staphylococcus aureus, Streptococcus, Haemophilus influenzae, Pasteurella, Proteus vulgaris, Escherichia coli, anaerobes and others) that penetrate the fiber and provoke the onset of phlegmon .
Symptoms of foot phlegmon
- Foot swelling
- Condition of the skin in the affected area: bright red color, shine, elevated temperature
- Bursting pain
- Pain when moving
- Difficulty in determining the source of inflammation
- Increased body temperature
- On palpation, a sensation of fluid moving in the area of inflammation
- The likelihood of enlarged popliteal lymph nodes.
With deep lesions of the tissues of the foot, shortness of breath, weakness, tachycardia (rapid pulse), decreased blood pressure, headache, and thirst are possible.
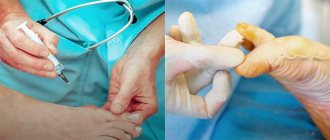
Diagnostics
Correct diagnosis of phlegmon includes a mandatory examination of the affected area, asking the patient about the possible causes of inflammation and the course of the disease. Blood and urine tests will indicate the presence of inflammation in the foot . To accurately determine the causative agent of the disease, the doctor prescribes a bacteriological examination of the purulent fluid, which is taken using a syringe. As a result of the analysis of pus, the type of pathogenic microorganisms involved in the inflammatory process is determined.
Treatment
Phlegmon of the foot is a life-threatening disease and therefore requires immediate hospitalization. In the hospital , the abscess is opened and is removed . Indications for surgical intervention are elevated body temperature and the presence of pus in the area of inflammation. The operation is performed under general anesthesia. As a result of dissection of the abscess and nearby soft tissues, purulent fluid is drained, rinsing is done, and drainage tubes are installed.
A bandage is applied to the wound to prevent recurrence of infection. Additionally, the use of painkillers and antibacterial drugs is expected.
hospital treatment is strict bed rest. During the treatment process, special attention is paid to the normal functioning of the heart muscle, vascular system and blood . In case of deviations from the norm, medications are prescribed to regulate the vital processes of the patient’s body.
Treatment of phlegmon at the initial stage is physiotherapeutic. The doctor's prescription is to use warm compresses and UHF therapy.
Prevention
To prevent foot phlegmon, the following conditions must be observed:
- choose shoes that are comfortable, moderately loose, and appropriate to the size of your feet;
- take care of supporting the immune system , lead a healthy lifestyle, eat more fruits and vegetables;
- pay attention to foot , keep them clean;
- prevent leg .
At the first symptoms of phlegmon, you should immediately consult a doctor to exclude possible complications and get by with light therapy without resorting to surgery .
Published in Surgery Premium Clinic