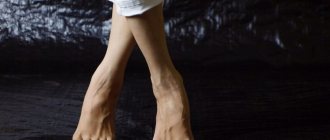
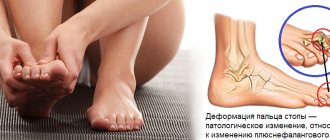
If you experience constant difficulties in choosing shoes, you suffer from pain in the forefoot, and the appearance of your feet is not aesthetic, contact the ORTOWEB foot and ankle surgery center for a consultation. The specialists of our center have extensive experience in surgical interventions for this disease and are proficient in both classical and minimally invasive treatment methods. To make an appointment for a consultation, you can leave a request on the website, write by email, write on Whatsup +7-926-961-71-96, or sign up for a face-to-face consultation with Nikiforov D.A. by phone +7-495-725-31-43
Specialists in foot and ankle surgery will help you permanently get rid of such problems as bunions, as well as other associated diseases, such as: arthrosis of the first metatarsophalangeal joint, bunion on the 5th toe, hammertoe deformity, planovalgus deformity of the foot.
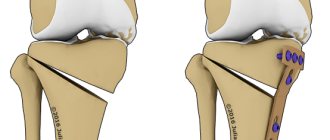
Surgical intervention on the bone consists of removing it in the early stages or correcting the angle between the metatarsal bones in more advanced stages. This allows you to return the toe to its normal position, correct transverse flatfoot and return the foot to its full function.
In each specific case, the surgical plan may vary depending on the degree of deformity and accompanying changes in other toes.
First of all, you need to choose a clinic and a doctor with whom you plan to have surgery. At the initial consultation, the doctor will explain the surgical plan to you and tell you how to prepare for the operation.
If the bunion is not too large and there are no changes in other toes that require intervention, the entire hospitalization will take only one day.
It is a good idea to prepare your home for the recovery period following surgery. You may want to rearrange your furniture to make it easier to walk around. It is also advisable to stock up on food so you don't have to go shopping.
The operation to remove the bone can be performed under either local or general anesthesia. When performing the operation under local anesthesia, after several injections at the level of the ankle joint, you will no longer feel your feet and may not sleep during the operation. It is also possible to perform the operation under spinal anesthesia, in which sensitivity will be completely absent in both lower extremities.
Before any of the listed types of anesthesia, it is recommended not to eat for 6 hours before the planned operation.
Your surgeon will tell you what will happen before, during and after surgery. If you don't understand something, don't hesitate to ask. After you ask all the questions you are interested in, you will be given the opportunity to sign a consent for surgery.
In addition to surgical treatment, there are several other options that can help alleviate your condition. These include painkillers, silicone inserts, individual orthopedic insoles, night orthoses for fixing 1 toe in the correct position, selection of comfortable orthopedic shoes. These measures will help control the pain, but they will not completely stop the progression of the deformity over time.
The operation to remove a bunion most often lasts no more than 1 hour if we are talking about only 1 toe, but the duration of the operation will depend on the degree of deformity. There are many options for surgical treatment of the bunion, both using open and percutaneous techniques. When performing a closed operation, it is most often necessary to create an artificial “fracture,” which surgeons call an “osteotomy,” in order to restore the normal position of the bones of the foot. When performing an open operation, a 5-7 cm long incision is made on the inner surface of the foot, which provides excellent visualization, allowing you to accurately determine the required saw angle and the degree of displacement of bone fragments. If the surgeon has sufficient experience, it is possible to perform an osteotomy in a closed manner using a drill from a 5 mm incision; the sawdust is controlled using X-rays, but the surgeon’s tactile sensations are decisive.
With minimally invasive interventions, large postoperative scars do not remain, and the level of pain after surgery is usually lower, but problems such as incomplete correction of deformity and delayed consolidation of osteotomies are more common.
A combination of closed and open methods is also possible, when the intervention on the 1st metatarsal bone is performed openly, and on the small rays and phalanges closed, using a drill.
You will need to remain in the room until the anesthesia is completely resolved. After the operation, dressings will be required for 2 weeks. If an osteotomy has been performed, you will need to wear shoes with forefoot weight bearing for 6 weeks until the bone fragments have completely healed. We recommend staying in the hospital for at least a day for adequate pain control and performing the first postoperative dressing.
| Our differences: |
| — European quality without flights and overpayments. |
| – Experienced and professional surgeons specializing in foot and ankle surgery |
| — Use of the most modern technologies and techniques, implants and instruments from leading Western manufacturers (Synthes, Arthrex, Smith&Nephew) |
| — Extremely positive patient reviews |
| — Comfort when preparing for surgery, while in the hospital and during rehabilitation |
| — Possibility of performing a full preoperative examination on the day of treatment |
In their work, our specialists use only the most modern and high-tech tools from foreign manufacturers such as: DePuy , Synthes , Arthrex , Integra .
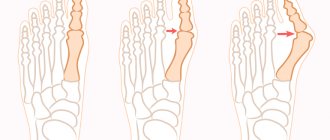
Depending on the degree of deformation, it is possible to perform various types of operations, both minimally invasive and already classical methods. Based on the volume, operations can be divided into 3 groups according to the degree of complexity.
For example, with a slight deformation, it is possible to perform surgical intervention using a drill through a small puncture of the skin (about 5 mm).
For more severe deformities, osteotomy of the first metatarsal bone and the main phalanx of the first toe is used. Below is a clinical example of a Z-shaped or Scarf osteotomy of the 1st metatarsal bone and a wedge-shaped varus or Akin osteotomy of the main phalanx of the 1st finger.
If the deformity affects 2 or more fingers, then a more complex operation is required, affecting several metatarsal bones and phalanges at once and also including intervention on soft tissues. Below is an example of reconstruction of the forefoot with advanced deformity, including a Z-shaped osteotomy of the 1st metatarsal bone and a wedge-shaped varus osteotomy of the main phalanx of the 1st toe, arthroplastic resection of the 2-3-4 proximal interphalangeal joints, and a chevron osteotomy of the 5th metatarsal bone.
The rehabilitation period varies depending on the operation performed; the larger the volume of intervention, the more time it will take to recover.
In order to come to us for surgery you will need:
- Go through an initial consultation, for this you can make an appointment, or send your pictures and photographs of your feet by mail to the following address:
- When deciding to undergo an operation, you can immediately schedule a date, ask all the necessary questions, and you can also sign up for the operation by calling +7-926-961-71-96
- The next step is to undergo a complete preoperative examination. You can take all the necessary tests and undergo examinations in our clinic within a few hours, or you can independently collect everything you need at your place of residence and bring it with you directly to the operation.
- On the appointed day, you arrive at the clinic for surgery, the administrator meets you, draws up all the necessary documents, introduces you to the clinic, after which you go to the ward. Then the operating doctor and anesthesiologist talk with you. On the day of surgery, refrain from eating; you can only drink water in small quantities. It is advisable to remove any possible decorative coatings from the nails, such as varnish, rhinestones, etc., and perform a thorough hygienic treatment of the skin of the feet.
- After the operation, you will be under the supervision of an anesthesiologist for a short time, then you will return to the ward.
- Depending on the extent of the surgical intervention, you will need from 1 to 4 days in the hospital for dressings and adequate pain relief. Walking in special shoes is allowed on the first day after surgery.
Further observation and treatment can be carried out either in our clinic or in any other clinic that may be more conveniently located. The next important points are: removal of sutures 14 days after the operation and taking x-rays 6 weeks after the intervention. Starting from week 3, physical therapy is carried out aimed at developing the range of motion of the toes of the operated foot, as well as physical therapy to reduce pain and swelling.
You can ask any questions you are interested in and receive more detailed information by phone or email
Great news:
Now in our clinic it is possible to perform an operation with financing from the compulsory medical insurance fund, that is, the operation will be free for you! Hurry up, the number of quotas is limited!
Types and rules of operations
Depending on the degree of deformation, the cosmetic defect can be corrected using open or minimally invasive surgery. The chosen intervention method determines the duration of the rehabilitation period, the duration of wearing the cast and the surgical risks.
Resection of exostosis
Resection of exostosis allows you to remove the protrusion of the metatarsus and phalanges. To perform the operation, the surgeon makes an incision several centimeters long and separates the soft tissue from the bones. The pathological protrusion of the bone is knocked down using a surgical chisel, and the remaining rough surface of the affected bone is polished.
After the resection is completed, the soft tissues are sequentially laid over the bones and sutured. A thick cotton wool pad is fixed between the first and second fingers, which protects the injured area from shifting. An immobilizing splint is applied to the entire foot.
The operation is performed under local anesthesia.
Operation according to Hochman
The Hochman method involves removing a section of bone. After applying local anesthesia, the doctor cuts the tissue along the affected bones of the first finger and excises the mucous bursa, which is located at the point of contact of the exostosis with the soft tissues.
After excision of the bursa, the muscle tendon, which is attached to the phalanx, is cut off. A wedge-shaped fragment is knocked out of the bone using a surgical chisel. Removing this fragment allows you to quickly align the articular axis.
The parts of the bone around the pothole are stabilized using additional fasteners (wires, plates, etc.). After restoring the joint axis, the remaining pathological protrusion is cut down.
The previously cut off abductor muscle is shortened and attached to the desired location. This promotes alignment of the metatarsophalangeal joint and fixation of bone fragments.
Once the correction is complete, the tissues are stitched together and a cast is applied to the foot. The Hochman procedure requires a longer recovery period than exostosis resection, but reduces the risk of recurrence.
According to McBride
Correction using the McBride method involves truncation of the abductor muscle. This method is used only when the lump is small and there is no bone degeneration.
To perform the operation, the surgeon cuts the foot from the sole of the foot and separates the muscle tendon from the first phalanx of the toe. After cutting, the muscle is slightly shortened and attached to the metatarsal bone. The tension created helps straighten and stabilize the position of the joint. If other types of deformity are present, other muscles are also subject to surgery.
After truncation of the muscles, the tissues are sewn together and a cast is applied to the foot.
McBride correction is used mainly in young patients with grade 1-2 deformity.
According to Wreden-Mayo
Wreden-Mayo correction involves excision of part of the phalanx, metatarsus, or both bones. It is prescribed mainly to elderly patients with grade 4 finger deformity.
In China, they don’t know what back or joint pain is, and they don’t see a doctor until they’re 80 years old!
Konstantin Kovalev
Read more…
Good afternoon My name is Konstantin Kovalev, I have been treating diseases of the musculoskeletal system in Russia for more than 30 years. Imagine my surprise when I learned about the unique development of our scientists... at a conference in Shanghai!
The surgeon makes an incision and separates the soft tissue. After this, he dislocates the phalanx or metatarsal bone and cuts off the unnecessary part of the bone with a surgical saw. Before joining the joint, the doctor polishes the edges of the cut bone. At the end of the operation, the soft tissues are sutured with silk thread, and an immobilizing splint is applied over the foot.
Osteotomy is performed under local anesthesia.
Attention! The disadvantage of correcting the defect using this technique is the high risk of impaired support function of the leg due to the large volume of excised bone.
According to the CITO method
Correction using the CITO method is carried out using an autograft (a strengthening prosthesis obtained from the patient’s tendons).
Joint strengthening is performed simultaneously with osteotomy. After excision of the wedge-shaped fragment, a graft from the patient's tissue is placed into the resulting cavity. To further strengthen the joint axis, pins are inserted into the bone, and the abductor tendon is shortened.
After this, the soft tissues are sutured and the foot is immobilized using plaster.
Percutaneous minimally invasive osteotomy
Percutaneous minimally invasive bone correction is performed through small holes, which reduces the rehabilitation period and reduces the risk of surgical complications.
The surgeon cuts through the soft tissue and then drills a 2mm hole in the first metatarsal bone. On one side, a knitting needle is placed in the created hole, and on the other, a knitting needle with a screw. 2 knitting needles influence the position of the bones and fix the axis of the joint. Subsequently, both wires are removed under X-ray control, and the inserted screw remains.
With a large degree of deformation, the phalanx and metatarsus are further shortened.
When using a standard hole, an aseptic dressing is applied instead of sutures.
With laser
Correction of a finger bone defect can be carried out using both standard surgical instruments (crowbar, saw, chisel, drill, etc.) and a laser beam. The laser removes exostosis using the burning method, which reduces the trauma of resection, shortens the rehabilitation period and eliminates the risk of infection.
A splint or cast is not required after laser resection.
May be interesting: Pain in the elbow joint - causes, diagnosis and treatment
Will I be able to wear high heels after bunion surgery?
After the rehabilitation period is over, you will be able to occasionally wear high-heeled shoes. It is not recommended to do this on an ongoing basis due to excessive load on the forefoot, which can lead to relapse of the deformity and progression of arthrosis of the 1st metatarsophalangeal joint. It is a bad idea to perform surgery on a bunion for cosmetic reasons, since if there was no pain before the operation, then it may appear as a result of scarring in the intervention area after the operation. Wearing high-heeled shoes and shoes with a narrow toe increases the risk of recurrence of the deformity in the future.
Rehabilitation
The duration of the recovery period depends on many factors: the nature of the operation, age, and general condition of the patient. A working patient is on sick leave after surgery for at least 1 month.
For a speedy recovery and return to normal life, all those operated on for a bunion must adhere to the recommendations of the attending orthopedic doctor, including compliance with several general rules:
- The operated leg should be placed on an elevation (place a pillow or cushion under it) to prevent stagnation of venous blood and lymph in the tissues and the development of edema. Cold compresses also help relieve swelling, reduce inflammation and pain.
- You should regularly come to see a surgeon or orthopedist at the clinic. From a specialist, the patient will learn what care the foot needs, when sutures can be removed, how long the foot needs to be bandaged, what medications (local or systemic) to use, and will receive prescriptions for medications.
- Elimination of intense and prolonged loads on the foot. After major operations, long-term immobilization of the lower limb is required, which is achieved by plaster bandaging the foot, using a fixator (orthosis), as well as bed rest with complete exclusion of movements in the foot for a day or longer. In the future, a careful expansion of motor activity, development of the foot and a gradual return to normal loads under the supervision of a rehabilitation physician are indicated. Walking should be started gradually and crutches may be required at first to avoid putting stress on the operated foot. You cannot play sports after surgery for approximately 6 months. It is best to undergo a rehabilitation course at a specialized center, in a sanatorium-resort setting.
- Wearing orthopedic, individually selected shoes after surgery, as well as using a variety of orthopedic foot correctors (Baruk shoe, which is worn directly over the bandage, insoles, socks, intertoe inserts). Their design is designed taking into account the need to unload the forefoot and evenly distribute body weight over the entire sole. In addition, if you regularly wear similar products (fabric, silicone, plastic), shoes, then blood circulation in the tissues of the foot improves, and they heal faster after surgery.
- If it is impossible to buy orthopedic boots, you should choose comfortable, ordinary, non-tight shoes made from natural soft materials with thick arch support, without high heels, and with a comfortable, non-narrowed toe.
- To exclude postoperative infectious and inflammatory complications, some patients are advised to take a course of antibiotics and anti-inflammatory drugs. In addition, many are prescribed painkillers, since immediately after surgery the leg hurts in almost all patients, as well as diuretics and vascular drugs if the leg is very swollen and physical methods do not work.
- A prerequisite for rapid recovery is special exercises during the rehabilitation period (after removal of sutures and in the absence of signs of edema, manifested by a tumor, or acute inflammation in the tissues of the feet). The doctor selects and then adjusts a therapeutic set of exercises for the feet, which the patient must do 1-3 times a day to develop the leg, and introduces the patient to the technique of performing exercise therapy.
- To relieve swelling, inflammation, improve microcirculation in the tissues of the foot and their regeneration after surgery, it is recommended to undergo a course of physical treatment (shock wave therapy, magnetic therapy and others). For the same purpose, therapeutic massage is prescribed.
- Complete proper nutrition (the patient should eat natural, healthy foods containing sufficient quantities of all necessary nutrients, vitamins, minerals), treatment of chronic diseases.
There are many folk remedies that can be treated at home with the permission of a doctor (baths, compresses with infusions, decoctions based on medicinal herbs, which you can prepare yourself or buy at the pharmacy).
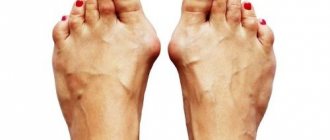
Why is it necessary to remove the lump?
The need for surgery is due to the fact that if the problem is ignored, severe consequences of hallux valgus may develop, which significantly worsen the patient’s well-being and quality of life:
- constant debilitating pain syndrome (leg aches, pulls, pain intensifies when moving the foot);
- depressive states due to disfigurement of the feet and the inability to wear beautiful, familiar shoes;
- changes in the joint of an inflammatory (arthritis) or degenerative (arthrosis) nature, leading to disability;
- purulent-inflammatory complications (bursitis, abscesses);
- secondary deformation of the spine, which manifests itself as pain in the lower back, sacral region, and pathologies of internal organs.
How long will I be on sick leave?
It all depends on the nature of your work and how much time you need to be on your feet. If you can work from a laptop while lying in bed, then you will not have much need for a sick leave. With a predominantly intellectual nature of work, the minimum recommended period of incapacity for work is 2 weeks - until postoperative wounds heal and swelling begins to subside. On average, the time spent on sick leave is 8 weeks, 6 weeks in special shoes and another 2 to adapt to regular shoes. In some cases, with a large volume of surgery, the time on the certificate of incapacity for work can be extended to 12 weeks.
You can see examples of operations to remove a bunion on the big toe in this section.
If you suffer from bunions and want to undergo treatment at the foot surgery center, come for a consultation, or get an online consultation by writing an email
Contraindications
There are also a number of contraindications to surgical treatment, usually associated with hereditary or severe acquired diseases:
- presence of diabetes mellitus;
- disorders of fat metabolism 3 degrees;
- coagulopathy, thrombophilia (hereditary and acquired);
- severe somatic pathology;
- thrombophlebitis;
- trophic changes in the area of the projection of the joint, disruption of the innervation and blood supply of the foot.
Average cost of surgery in Moscow and Russian regions
The average cost of surgical intervention to correct Hallus valgus ranges from 10 to 25 thousand rubles in the region and 45 thousand rubles in the city of Moscow. If minimally invasive techniques are used, the cost of the operation increases by another 6-10 thousand rubles.
The cost of treatment includes pain relief, dressings, consultations with doctors and the intervention itself.
| Type of surgical correction of the foot | Average cost in Moscow (RUB) | Average cost in Russian regions (RUB) |
| Valgus deformity of 1 toe , 1st degree of complexity | 28 000 | 20 000 |
| Valgus deformity of 1 toe , 2nd degree of difficulty | 48 000 | 25 000 |
| Valgus deformity of 1 toe , 3rd degree of difficulty | 56 000 | 30 000 |
| Elimination of hammertoe deformity of the 2nd toe | 25 000 | 20 000 |
Indications and contraindications for surgery
Surgery to correct hallux valgus is prescribed for the following symptoms:
- severe pain syndrome;
- damage to the bone tissue of the foot;
- inflammation of the synovial bursa.
Surgical operations are not performed for rheumatoid arthritis, diabetic foot, obliterating atherosclerosis, purulent infections, and pathologies of the hematopoietic system.
How to get surgery for free?
Surgical treatment according to indications is provided free of charge according to a quota. A referral to a medical institution licensed for this type of activity is given by a traumatologist at the clinic at the patient’s place of residence.
To undergo an operation, the patient will need to undergo a series of medical tests, based on the results of which the doctor decides to send the patient’s documents for consideration by a commission of the health care authority of the constituent entity of the Russian Federation.
The operation can be done according to quota
The list of documents to the hospital should include:
- the results of the treatment;
- patient consent;
- copy of passport data;
- SNILS;
- a copy of the compulsory medical insurance policy and TIN.
After making a decision in favor of the patient, the commission will send all the necessary documentation to the specialized medical institution and the relevant specialists in this profile will already set the final date for the operation.
If the patient is denied free medical care, then an alternative option is paid services. When receiving paid medical services, a working citizen of the Russian Federation can claim a refund of 13% of the payment as a tax deduction.
Where are laser bone correction operations performed in Moscow and St. Petersburg?
Paid medical care is offered by the following clinics:
- “Ortomed” - correction of Hallus valgus from 28 to 56 thousand rubles using mini-invasive techniques (laser), Moscow.
- “Clinic of the Century” - average cost from 55 to 75 thousand rubles depending on the degree of complexity (1 leg) - the price includes anesthesia, 3 bed days, radiography of the feet, Moscow.
- "MedicaMente" - 42 thousand rubles (the price includes inpatient placement, doctor's consultation, anesthesia, suture material), Moscow. "Proportion" - from 15 to 22 thousand rubles , depending on the degree of complexity, Moscow.
- Clinics "Abia" - 28,750 rubles , St. Petersburg.
- “Longevity” - 17,800 rubles , St. Petersburg.
- Russian Research Institute of Traumatology and Orthopedics named after. R.R. Vredena – 20,900 rubles , St. Petersburg.
How to prepare for surgery?
Before surgery, the patient will undergo the following range of examinations:
- general clinical minimum (presence of a general blood test, urine test, blood biochemistry, blood for RW, HIV, viral hepatitis, determination of blood group and Rh factor);
- fluorography;
- ECG;
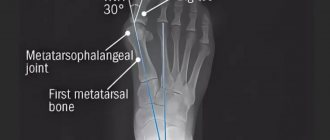
- radiography of the feet in two projections (to clarify the severity of the disease and determine additional deformities);
- MRI, CT (as additional examination methods if the ones described above are not informative).
X-ray in two projections to clarify the severity of the disease
Methods and types of surgical interventions for Hallus valgus
Surgical interventions for this pathology are divided into minimally invasive (not requiring excision of a large volume of tissue) and reconstructive (sufficient in volume and more traumatic techniques).
Minimally invasive techniques
These methods have a number of advantages compared to traditional ones. The healing period is shortened, and the risk of complications after surgery is also reduced.
Correction of joint deformity with laser (“resurfacing”)
A special laser allows you to remove exostosis in thin layers, maintaining joint mobility without first cutting the skin and soft tissues. Unlike traditional methods, the laser method of removal is much less traumatic and does not require long-term rehabilitation.
This technique is used for minor deformities of the first toe and the absence of other complications.
Percutaneous minimally invasive osteotomy
Percutaneous osteotomy is one of the new techniques recently used in foot surgery (about the last 10 years).
The advantages of this method include low trauma, excellent cosmetic effect (postoperative scars are less pronounced), virtually no pain and a much shorter recovery period.
The method of pain relief is epidural anesthesia, which is less often performed with lidocaine solution.
The operation is carried out as follows:
- The skin is first punctured and soft tissue is excised layer by layer.
- Using a special drill, the surgeon creates a hole in the metatarsal bone with a diameter of 3 mm, then a pin is inserted into the hole.
- A knitting needle with a 2 mm screw is installed on the opposite side.
- As a result of their combined effect, the position of the bone along the axis changes.
During the recovery period, it is recommended to wear the bandage for two days. X-ray control is necessary after removal of the wires.
Reconstructive techniques
These techniques are also used in cases where there are indications for their use.
Resection of exostosis
Resection of ecostosis is performed as follows:
- The operation is performed under infiltration anesthesia with a solution of novocaine after pre-treatment of the skin at the injection site with iodopirone.
- A size of 4-5 cm is made with dissection of the skin and soft tissues to the bone.
- The bone deformation is broken up with a special tool - a chisel, and the surfaces are polished.
- The tissues are then restored layer by layer.
- A rigid roller is fixed at the end between the first and second toes.
- The foot is fixed with a splint in a certain position.
Osteotomy of the first metatarsal bone (according to Hochman)
The Hochman operation goes like this:
- Under infiltration anesthesia with novocaine, the surgeon makes an incision in the area of the projection of the joint, then removes the joint capsule in the area of the bone outgrowth.
- Next, the tendon is cut, which is attached to the first phalanx.
- A wedge-shaped section is resected in the metatarsal bone using a chisel, which allows the axis of the joint to be aligned.
- After this, the bone sections are tightly secured to each other with a plate for better fixation of the bone along the axis.
- The tissues are restored layer by layer, the foot is fixed in a plaster cast (for approximately 3 weeks).
IMPORTANT! This technique has the most favorable prognosis, since the percentage of relapses is extremely small.
Muscle truncation (McBride operation)
- Under anesthesia with a lidocaine solution, a skin incision is made on the plantar side of the foot.
- Then the adductor muscle of the first finger is separated, which is attached by its tendon to the phalanx of the first finger.
- It is incised, shortened and sutured to the first bone of the metatarsus (under the influence of tension, the deformed joint is subsequently straightened).
- The tissues are restored layer by layer, the foot is fixed with a plaster splint for 3 weeks.
Scheme of the McBride operation with muscle excision
Osteotomy of the first metatarsal bone (according to Wreden-Mayo)
- Under anesthesia with lidocaine solution, an arcuate incision is made and soft tissue is excised.
- Using a special bone spoon, the surgeon “dislocates” the bone that needs to be shortened into the wound.
- Bone resection is performed using a saw, and the bone is polished.
- The integrity of the tissue is restored and a splint is applied.
This intervention is most effective due to the resection of a larger area of bone than with the Hochman operation (fewer relapses), but it is also the most traumatic (possible future dysfunction of the foot).
Reconstructive surgery using the CITO method
This technique is a modification of osteotomy. The wedge-shaped section of the first metatarsal bone is also excised, then the cavity is replaced with an autograft (the tendon serves as the substrate).
The bone is fixed with two knitting needles, which are subsequently removed, and one of the tendons is shortened, which fixes the bone along its axis. The foot remains in this position for a month.
Result of leg surgery
Endoprosthetics
The point of the technique is to replace the affected joint with an implant, which further facilitates the complete restoration of joint function and the elimination of pain.
The disadvantages are the possibility of repeat arthroplasty (repeated joint replacement after 10-15 years), limitation of motor activity, the possibility of secondary infection, and displacement of the prosthesis.
Surgery on the second toe for hammertoe deformity
With symptomatic correction, the surgeon removes part of the bony protrusion, returning the finger to its physiological position. After this operation, the person is quickly rehabilitated, but relapses are possible.
In radical surgeries, the entire problem area of the foot is corrected, and not specifically the bone or joint. During the operation, the tendon of the adductor pollicis muscle is sutured to the first metatarsal bone. Thus, the muscle does not hold the finger in a deflected position, the angle between the bones changes downward, and the arch gradually takes on its previous shape.
Hammertoe deformity of the foot joints
Relapses with this intervention are minimized, but the rehabilitation period is long and painful.