Osteotomy is a surgical operation aimed at eliminating deformity or eliminating anatomical and functional disorders by artificially breaking the bone and correct fusion. This operation is performed to treat both congenital and acquired pathologies, for example, in case of improperly healed fractures.
Indications for osteotomy:
- improperly healed bone fractures;
- ankylosed joints;
- change, shortening of the limb;
- rachitic curvatures;
- formation of a false joint;
- osteomyelitis;
- osteoarthritis, spondioarthrosis;
Depending on the surgeon’s goal and the patient’s clinical picture, the following types of osteotomy can be performed:
- wedge-shaped;
- linear (oblique and transverse);
- hinged (can be arc-shaped, that is, made in one plane, or angular, spherical - in several planes);
- staircase;
- Z-shaped;
- derotational.
By purpose they are distinguished:
- Corrective osteotomy - to correct deformity after complications that led to malunion.
- Hinge osteotomy is an operation to lengthen the limbs.
Osteoplasty techniques are also divided into closed and open. The first is performed with minimal access, through a 2-3 cm incision. The open method involves wide access - an 8-12 cm incision is made exposing the bone. In some cases, when there is a risk of damage to nerves and large vessels, preference is given to open osteotomy, despite its low invasiveness, over closed one.
The choice of method depends on the type of pathology, volume and area for surgical intervention - pelvis, jaw, hip, etc. Most often, the operation is aimed at restoring the function of the musculoskeletal system and removing bone deformations.
To equalize the lengths of the lower extremities, osteotomy is performed according to the principle of oblique cutting of the bone in mandatory combination with extrafocal compression-distraction osteosynthesis. The design for osteosynthesis is selected individually for each patient.
Osteotomy: a scientific view
How does it work and why trim the bones? The entire human musculoskeletal system is penetrated by thin axes. They can only be seen in an anatomical atlas, but it is by them that the correct formation of the skeleton is determined. With pathologies, bones deviate from the anatomical axis. This is expressed by crooked legs, protruding joints, and other symptoms. In addition to aesthetic aspects, deviation from natural axes leads to diseases of the musculoskeletal system and disability. Bone tissue has an amazing ability: it is renewed throughout life. This happens quickly in childhood, but the ability decreases with age. However, bones can repair themselves by growing new tissue. This happens after injuries, fractures, operations with the help of nature. But sometimes the bones need help. Bone tissue is a material. It is the task of an orthopedic surgeon to mold it into beautiful shapes, adjust it and set the direction of correct growth. This is what corrective osteotomy does. An incision is made through the skin into the bone at the site where bone tissue needs to be built up. This position is fixed with a special device. There are many varieties of such devices. The only task is to hold the limb in this position long enough for new bone tissue to form. This usually takes 1-3 months. During this period, the patient can move independently with the device. Then it is removed. In leg surgeries, osteotomies of the femur and tibia are most often performed.
Treatment of hallux valgus
The goal of surgical treatment of hallux valgus is to restore a mobile, weight-bearing foot with a cosmetically beautiful shape.
In this article we will tell you what are realistic goals for hallux valgus surgery.
Please note that more severe hallux valgus deformity requires more complex treatment. Therefore, if you suffer from an unpleasant disease, we recommend that you contact a specialist in advance, who will tell you about gentle methods of correcting the disease.
Contraindications for osteotomy
Osteotomy is an operation. Like any intervention, it has contraindications. According to ISAKOS (International Society of Arthroscopy, Knee Surgery and Orthopedic Sports Medicine), bone correction cannot be performed with the following diagnoses:
- Rheumatoid arthritis;
- Osteoporosis;
- BMI more than 40;
- Impaired blood flow in the lower extremities;
- Extra-articular deformities;
- Previous infection;
- Reduced bone regeneration ability;
- Operations on the meniscus;
- Limitation of flexion more than 25 degrees;
- Some types of arthrosis.
In other situations, surgery can be performed, because for many, corrective osteotomy remains the last chance to return to motor activity, beautiful legs and a full life.
What does hallux valgus mean?
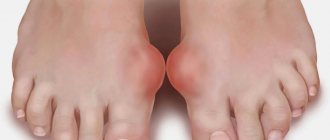
Hallux valgus (crooked toe) is one of the most common diseases of the 1st toe. With this pathology, damage occurs to the transverse arch of the foot at the base of the 1st toe. The first toe noticeably deviates towards the outer edge of the foot and displaces the smaller toes. With this disease, the 1st metatarsophalangeal joint is subject to excessive load, which can cause long-term and painful arthrosis (Hallux rigidus).
As the disease develops, the skin over the bony protrusion on the 1st metatarsophalangeal joint becomes inflamed and painful, and a “bump” or “bone” begins to interfere with walking. Treatment of hallux valgus, as well as pain relief, can be carried out using various conservative methods. By clicking on this link, you will receive the necessary information on the topic “Diagnostic and conservative treatment of hallux valgus.”
Corrective osteotomy at the Ladisten clinic
The clinic specializes in minimally invasive orthopedic surgeries. More than 6,000 patients from all over the world have already undergone osteotomy and are satisfied. Each patient is offered a tour of the facility, a separate room during rehabilitation, and 24-hour medical supervision in the first days after the procedure. The operation itself is bloodless: a small puncture is made in the leg, through which doctors correct the bone. For fixation, a unique device from Dr. Veklich is used. This is an improved design of the Ilizarov apparatus. It is less bulky, weighs little and does not involve dangerous knitting needles. Doctors at the Ladisten Clinic have been performing corrective osteotomy procedures for more than 30 years; the price varies depending on the pathology and severity of the case. To find out the exact diagnosis, consult about contraindications and discuss the cost of osteotomy, just make an appointment by calling us at: +38 +38 or Write to WHATSAPP Write to VIBER We will choose a convenient time for you to visit the clinic or online consultation.
Indications for surgery: In what situations is surgical treatment of hallux valgus deformity performed?
Bursitis of the 1st toe - inflammation of the mucous membrane of the joints
- Due to the constant pressure of improper shoes, the bony prominence (“bump”) becomes inflamed.
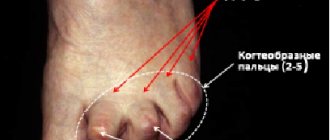
- Curvature of the toes (hammer toes and hook toes) is the cause of additional deformities of the metatarsus of the foot.
- Arthrosis pain in the 1st metatarsophalangeal joint appears due to wear and tear of the joint.
- Arthritic pain in the metatarsophalangeal joint occurs due to wear of the joint.
For many patients who prefer open shoes, the problem of hallux valgus is primarily a cosmetic problem. As a rule, treatment for hallux valgus is not carried out just because the foot is unaesthetic. Despite this, when planning and performing foot surgery, our specialists who offer treatment for hallux valgus deformity also attach considerable importance to the cosmetic result. Thus, doctors at the Gelenk-Klinik in Freiburg provide the patient with professional treatment of the disease and help improve his quality of life.
In order to carry out surgical treatment of hallux valgus, the disease must proceed without pain. Also, we would like to draw people’s attention to the fact that complete treatment of hallux valgus is impossible by replacing shoes, using special orthopedic devices, and even targeted gymnastics for the feet. Orthotics, of course, help relieve pain, but they cannot correct the deformity itself.
Surgical treatment of hallux valgus deformity of the 1st toe: Cosmetic result
- Straightening the 1st finger.
- Normalization of hammertoes and hooktoes.
- Removal of the inflamed “bump” (removal of osteochondral exostoses).
- Minimal scarring.
For medical reasons, surgical treatment of hallux valgus is offered when the patient feels pain in the foot and is unable to move as before.
If conservative treatment of hallux valgus is unsuccessful, specialists begin to plan surgery. Surgery is performed approximately 6 months after conservative therapy.
Conservative treatment of hallux valgus is aimed at eliminating pain and preventing the progression of the disease. Definitive treatment of hallux valgus deformity using conservative methods is only possible on a growing skeleton, that is, if the patient is still young and his body is growing and developing.
Rehabilitation treatment after correction of Hallux valgus
Rice.
10: After surgery, patients need to wear a special forefoot boot with a rigid sole, with which they can immediately step on their foot and become mobile. These shoes transfer body weight to the heel. Sometimes swelling that occurs is easily eliminated by elevating the leg. Typically, the recovery process lasts from 3 to 6 weeks. The stronger the deformation, the longer the rehabilitation treatment will take. To obtain accurate information about the condition of the operated joint, necessary for postoperative examination, an x-ray should be taken after approximately 4 weeks.
If you have been treated for hallux valgus in our clinic in Freiburg, our specialists will offer you functional post-operative treatment, which involves full weight bearing with the help of a special forefoot boot, which significantly reduces the risk of thrombosis. Despite this, we recommend that you still undergo thrombosis prophylaxis. Such orthopedic shoes must be worn for 2 to 6 weeks.
Postoperative treatment/rehabilitation
- Special orthopedic shoes.
- Restorative bandages.
- Valgus splint/night bandage.
- Prevention of thrombosis.
- Actions aimed at relieving swelling by elevating the leg.
- Actions aimed at relieving swelling by elevating the leg.
Once again, we draw your attention to the fact that after the operation it is necessary to keep the leg in an elevated position as often as possible: This promotes faster healing of the wound.
If necessary, a special valgus splint can be used at night.
After approximately 5 weeks, the patient is allowed to wear normal shoes again.
Postoperative treatment of hallux valgus, namely gymnastic exercises, is a necessary component in restoring muscle balance and stabilizing the foot.
If you want to speed up the healing process of your foot, we recommend that you massage the arch of your foot with a soft tennis ball. The period of disability depends on how the recovery process will take place, as well as on the patient’s profession.
Make an appointment
What is a knee osteotomy?
Corrective osteotomy of the knee joint is an operation that eliminates congenital and acquired bone deformities. During surgery, the doctor excises a pre-designated area of bone tissue and connects the loose bone fragments with implants. As a result, the axis of mechanical load is transferred to the healthy area of the joint. The operation is performed under complete or spinal anesthesia. After treatment, the orthopedist immobilizes the patient's lower limb with a plaster cast during recovery. Rehabilitation is underway.
Osteotomy with metal structure.
The described correction method is traditionally compared with knee replacement. Osteotomy is a less traumatic treatment method. This medical procedure is perfect for young patients suffering from late stages of gonarthrosis. The choice of osteotomy as a method of restoring mobility of the lower limb makes it possible to delay endoprosthetics for a long time.
Osteotomy has been used for two centuries. After the discovery of replacement arthroplasty methods, this surgical intervention faded into the background, but this method of treatment is still used. At the beginning of the 21st century, modern methods of fixing bone areas were developed, reducing the duration of rehabilitation.
Knee replacement in the Czech Republic: guarantees, prices, rehabilitation, reviews and statistics.
Find out more
How is minimally invasive surgical treatment of hallux valgus performed?
During the operation, the surgeon makes two small incisions on both sides of the thumb. Due to the low-traumatic nature of the operation, soft tissues are almost not affected, as a result of which the healing process of the suture is shortened, and the percentage of complications is significantly reduced. In the case of open surgery for hallux valgus, the situation looks completely different.
Minimally invasive surgical treatment for this condition straightens the misalignment of the foot bones using small surgical instruments similar to dental equipment. In the next stage of the operation, through a small incision, the shortened joint capsule is opened and expanded, which allows creating the necessary space for the normal alignment of the 1st toe.
Compared to other minimally invasive techniques, lateral release (tightening the medial joint capsule) has several advantages: Soft tissue damage is reduced to a minimum. Also, this operation is low-traumatic. helps reduce the recovery process. Thanks to lateral release, older patients become mobile in a short time. In addition, due to the minimal load on the soft tissues, postoperative foot swelling is significantly lower than after other surgical interventions.
Akin osteotomy - wedge-shaped osteotomy of the main phalanx of the first finger for mild valgus deformity
Osteotomy Akin
Mild valgus deformity of the distal interphalangeal joint: Isolated deformity of the 1st toe outside the 1st metatarsophalangeal joint.
In order to correct the valgus deviation of the distal phalanx of the 1st finger (Hallux valgus interphalangeus), our specialists perform surgical treatment using the Akin Osteotomy method.
During this procedure, the position of the 1st toe outside the 1st metatarsophalangeal joint (Metatarsus interphalangeus) is corrected - a change in direction using a displacement osteotomy. Akin osteotomy is not able to completely correct hallux valgus. For this reason, orthopedic surgeons combine this intervention with other surgical techniques aimed at treating hallux valgus.
A change in direction during Akin Osteotomy is achieved by removing a bone wedge from the 1st toe. Thus, the bone grows together in a new, more correct position.
Also, this operation to eliminate angular deformity helps to normalize the tendon cords on the 1st finger.
Contraindications and other problems of surgical treatment of hallux valgus
Rice.
3: Circulatory disorders are one of the main reasons why surgical treatment should not be performed: With occlusion of peripheral arteries or diabetic foot, the wound healing process becomes more complicated and takes much longer. © Viewmedica Surgical treatment of hallux valgus: Contraindications
The main contraindication is obliterating atherosclerosis of peripheral arteries. Poor circulation can lead to a slowdown in the healing process of a postoperative wound.
For a final cure, good blood circulation is very important after forefoot surgery. The foot is the organ of movement furthest from the heart. The soft tissues of the foot that bear the load are very thin, but the mechanical load is very high. Therefore, all circumstances that negatively affect blood circulation slow down the process of foot recovery after surgery. The following diseases prevent the successful outcome of forefoot surgery:
- Obliterating atherosclerosis of peripheral arteries
- Diabetic foot and the initial stage of polyneuropathy
(systemic damage to peripheral nerves due to diabetes) - Polyneuropathy(nerve condition related to diabetes)
In these cases, before prescribing surgical treatment to the patient, our specialists conduct a more serious examination and determine the state of the blood flow.
Polyarthritis, as well as rheumatic diseases, are not contraindications to surgical treatment of hallux valgus. However, for these diseases, it is necessary to pay attention to the choice of surgical method.
Previous surgical treatment of the forefoot complicates the process of displacing surgery and may negatively affect the desired result.
Prognosis and complications after surgical treatment of hallux valgus
Treatment of hallux valgus: Possible postoperative complications
- Chronic pain.
- Painful sensations due to the use of titanium screws or fixing titanium wires.
- Changes in gait due to load redistribution.
- Stress fractures or stress fractures due to changes in load after surgery.
- Stress fractures or stress fractures due to changes in load after surgery.
- Infections
In order for the treatment of hallux valgus to be successful, it is necessary to weigh the pros and cons of the upcoming surgery to correct hallux valgus. According to international studies, treatment of hallux valgus helped more than 80% of patients regain their former lifestyle. Despite postoperative complaints, approximately 10%-15% felt much better than before surgery. Approximately 5% of patients showed no improvement. In any case, it is always necessary to pay attention to the experience and qualifications of the operating surgeon: Only then can you be sure that the treatment of hallux valgus will be successful.
Specialists at our clinic have found that with the help of special exercises for the feet, the result of surgery to correct hallux valgus deformity is significantly improved.
Treatment of hallux valgus: Frequently asked questions
How long does recovery treatment last after hallux valgus surgery?
Rehabilitation treatment after hallux valgus surgery lasts 6 weeks. However, the duration of sick leave depends on your profession: In the case of “standing” work, you will need more time to recover than in “sedentary” work.
Can I walk immediately after surgery?
By wearing a special orthopedic forefoot boot that prevents the foot from rolling over the big toe, you can walk immediately after surgery.
Is an immobilizing bandage used after surgery?
Postoperative treatment of the foot does not require the use of plaster or an immobilizing bandage. The big toe remains in a passively mobile position.
When can I wear normal shoes?
Even after postoperative treatment is completed, it is recommended to wear comfortable and loose shoes for 4-6 weeks.
What happens after Hallux valgus surgery?
- Surgical treatment causes only minor damage to soft tissues: After a short time, the patients' physical endurance is restored.
- The mobility of the operated joint is restored almost immediately.
- With the help of special orthopedic shoes for the correction of the forefoot, the patient can immediately step on the foot and fully load it.
- The fixation material that was used during the osteotomy is usually not removed. In most cases, it does not have a negative effect on the foot. If the patient still feels uncomfortable, the titanium screws are removed on an outpatient basis.
The surgical method is selected depending on the degree of valgus deformity
To correct such deformities, there are many internationally recognized and proven surgical techniques. Since the Gelenk-Klinik orthopedic clinic is one of the most famous orthopedic clinics in Germany, with the most innovative technologies, each patient will be offered treatment for Hallux valgus at the highest level.
The stronger the deformity, the more difficult the operation
In this case, the following rule applies: The stronger the foot deformity, the more difficult it will be to undergo surgical treatment of hallux valgus.
The stronger the damage, the longer the recovery process and postoperative treatment will take. If treatment is carried out at a progressive stage of the disease, which is often accompanied by arthrosis of the big toes, then the long-term result, as well as the restored physical endurance, will be the same as in the treatment of mild forms of the disease. For the first degree of hallux valgus, the most effective intervention is on soft tissues, which is often performed in combination with the technique of excision of the bony protrusion and subcutaneous mucous bursa in the area of the 1st metatarsophalangeal joint. In the second stage of the disease, surgery is performed on the metatarsal bone. In case of severe hallux valgus deformity, specialists carry out surgical treatment, the purpose of which is to displace or immobilize the metatarsophalangeal joint: The connecting link between the metatarsal bone of the radius of the foot and the tarsal bones.
These methods, aimed at restoring the position of the 1st toe and 1st metatarsophalangeal joint, are often carried out in combination with interventions on soft tissues (muscles, capsules and tendons).
What treatment the doctor chooses depends on the anatomical location of the deformities, as well as their stage. In any case, before prescribing any suitable treatment for hallux valgus, the orthopedist discusses all the necessary details with the patient: After conducting proper clinical examinations and x-rays, the doctor will be able to finally determine what kind of hallux valgus treatment you need.
The choice of surgical technique to treat this injury depends on the degree of valgus deformity (intermetatarsal angle = between the 1st and 2nd metatarsal bones).
Surgical treatment of Hallux valgus using these methods applies to the anatomical parts of the foot indicated below.
Treatment of hallux valgus. Video
Surgical methods for treating hallux valgus deformity
Most hallux valgus surgeries consist of several of the following procedures:
- Corrective osteotomy of the proximal metaepiphysis of the 1st metatarsal bone:
Promotes straightening of the 1st toe. - Correction of soft tissues (lateral joint release):
In case of adequate release, the 1st finger was placed in the required position without force. - Tendon correction:
Correction of tendon length is necessary to prevent re-injury of the 1st toe. - Treatment of the 1st metatarsophalangeal joint:
Joint-preserving cheilectomy (extraction of a bone spur), with progressive arthrosis - immobilization (arthrodesis) of the 1st metatarsophalangeal joint.
Only when all possibilities for conservative treatment of the disease have been exhausted, orthopedics in Germany offers operations to correct hallux valgus deformity of the first toe. Among the long-term and painful consequences of hallux valgus, arthrosis of the 1st metatarsophalangeal joint is distinguished.
How can a patient prevent surgical treatment?
Timely replacement of uncomfortable shoes with special ones that create the necessary space for the toes and regular treatment without surgery prevent the development of the disease. Therefore, after a bony protrusion appears on the foot, immediately consult a specialist.
What to do if conservative treatment of hallux valgus does not bring the desired results?
Due to increasing immobility of the 1st metatarsophalangeal joint and damage to adjacent toes, surgical treatment of hallux valgus becomes more difficult.
Long-term subsequent injuries to the foot, such as hallux rigidus (arthrosis of the 1st metatarsophalangeal joint), become more intense and cause severe pain.
After surgical correction of the first metatarsophalangeal joint, every patient is glad that he no longer feels the same pain and can walk normally. Also, patients are very satisfied with the good aesthetic result of the operation.
The surgical plan for hallux valgus deformity is drawn up strictly on an individual basis.
When treating Hallux valgus, concomitant diseases are also taken into account
- Exostosis on a bump
- Arthrosis of the first metatarsophalangeal joint (Hallux rigidus).
- Bursitis is an inflammation of the mucous bursae in the joint area.
- Bursitis of the small fingers.
- Transient metatarsalgia (painful overload of the small fingers)
- Hooked fingers
- Hammer fingers
Hallux valgus always occurs in combination with various painful processes. So, in addition to valgus deformity of the 1st finger, the patient may experience skin changes or inflammation of the mucous bursa (bursitis). The crooked toe displaces the neighboring little toes, as a result of which it is subject to overload. Before drawing up a surgical plan, our clinic’s specialists will conduct an accurate diagnosis and determine the degree of development of the disease. Below, standard operations for hallux valgus deformity will be presented to your attention in detail. In addition, we draw your attention to the fact that with this disease, in order to refer the patient for surgery, we first need to understand his individual situation and assess the degree of hallux valgus.
Surgical treatment of hallux valgus is performed only by highly qualified specialists with many years of experience. The surgeon discusses all the details and features of the upcoming intervention with the patient in advance.
Restoring support function
Surgeries aimed at creating a weight-bearing, painless joint are mainly used for coxa vara/valga, neoarthrosis of the femoral neck, chronic cervical fractures, congenital dislocations, and osteoarthrosis. The problem of restoring a supporting function convenient for walking and standing is often solved by changing the axis of the femoral neck. The altered neck-shaft angle changes the fulcrum of the head, which was initially pathological, by several millimeters (up to 15 mm). This approach favors not only the restoration of weight-bearing ability, but also decompression of the joint and reduction of pain symptoms. The cutting of the femur is carried out in the most appropriate way, which is selected on the basis of individual radiological data.
results
All patients were assessed for treatment results over a period of 6 months to 3 years using the AOFAS scale, according to which excellent treatment results were obtained in 56 patients, good results in 52 patients. Satisfactory results were observed in 7 patients, poor results in 3.
Among the complications that were noted after surgical correction of forefoot deformity, 7 cases were noted.
When fixing the osteotomy area with Kirschner wires, loss of correction was observed (in 3 patients) in cases where plaster immobilization was not performed and Baruk shoes were used in the postoperative period.
Also in 2 cases, inflammation of the soft tissues in the area of the wires was noted, which required removal and re-insertion of the wires.
When 2 cortical screws were used for fixation, 5 unsatisfactory results were observed due to splitting of the distal bone fragment during insertion of the second screw, which led to loss of fixation stability and required additional external immobilization with a plaster cast.
When using the LCP plate as a metal fixative, no negative results were noted.
Materials and methods
During the period from 2008 to 2011, we observed 118 patients (207 feet) with a transverse-spread deformity of the forefoot and valgus deformity of the 1st toe. Of these, 116 are women and 2 are men. The average follow-up period in the postoperative period was 24 months. The average age of patients is 53 years.
All patients were examined clinically and radiologically. The data from clinical and radiological examinations, namely the values of the following angles, were of decisive importance for choosing the type of surgical intervention:
1) M1P1 - the angle between the proximal phalanx of the first toe and the first metatarsal bone;
2) M1M2 - angle between the first and second metatarsal bones;
3) PASA (Proximal Articular Set Angle) - the angle of inclination of the articular surface of the head of the first metatarsal bone relative to its axis;
4) DASA (Distal Articular Set Angle) - the angle of inclination of the proximal articular surface of the main phalanx of the 1st toe in relation to the diaphysis [3, 13].
The M1P1 angle made it possible to determine the degree of valgus deviation of the first toe. The value of the M1M2 angle determined the level of osteotomy (distal or proximal). Thus, with M1M2 equal to 15° or more, a proximal osteotomy was always performed. If the PASA angle deviated from the norm, a double osteotomy of the first metatarsal bone was performed, and if the DASA angle increased, the surgical intervention was supplemented with osteotomy of the main phalanx of the first toe according to AKIN.
All patients underwent resection of osteocartilaginous exostosis of the head of the first metatarsal bone (Schede's operation), release of the lateral part of the capsule of the 1st metatarsophalangeal joint, adductorotenotomy, release of the sesamoid apparatus, proximal corrective osteotomy of the first metatarsal bone with fixation with Kirschner wires or 2 cortical screws, or angular stability plate (LCP plate). Then plastic surgery of the medial part of the capsule of the 1st metatarsophalangeal joint was performed.
Fixation of bone fragments of the first metatarsal bone was performed:
1) Kirschner wires in 32 patients (55 feet);
2) 2 cortical screws in 15 patients (27 feet);
3) LCP plate and screws in 71 patients (125 feet).
In the postoperative period, patients who underwent osteosynthesis with Kirschner wires were given a functional plaster cast “boot” with a heel and stirrup. Walking on crutches with support on the operated limb was allowed, with a total period of immobilization of 4–6 weeks.
After 4–6 weeks, the plaster cast was removed, Ro-control was performed, and development of movements in the ankle joint began. The period of removal of the wires was determined by the X-ray data on the consolidation of bone fragments of the first metatarsal bone (the average period was 5 weeks).
In 3 patients, plaster immobilization was not performed, but Baruk shoes were used.
All patients for whom osteosynthesis was performed with 2 cortical screws and LCP plates used Baruk shoes in the postoperative period, which allow loading the hindfoot and eliminating the load on its forefoot [4].
In order to illustrate various options for fixing bone fragments of the first metatarsal bone during its wedge-shaped corrective proximal osteotomy, we present several clinical examples.
Patient D., 18 years old, medical history No. 71517, was admitted to the institute’s clinic with complaints of valgus deformity of the first toe of both feet, pain in the area of the first metatarsophalangeal joint when walking, difficulty in choosing shoes.
On the radiograph of the forefoot of the left foot, the angle M1P1right is 30°; M1R1left is 28°, and the angle M1M2right is 15°; M1M2lev - 16° (Fig. 1).
Surgical intervention was performed as planned: reconstruction of the forefoot of both feet in the following volume: Shede's operation, lateral capsulotomy, cutting off the tendinous part of the adductor pollicis muscle, corrective proximal wedge-shaped osteotomy of the first metatarsal bone. The bone fragments are fixed with 2 Kirschner wires (Fig. 2).
In the postoperative period, on the 6th day, both lower limbs are fixed with plaster bandages “boot” with a stirrup and heel. After which weight bearing and walking without crutches are allowed. The plaster immobilization was removed 6 weeks after the operation, the wires were removed, and development of movements in the ankle and foot joints was prescribed. 6 months after surgery, a good result was found on the AOFAS scale (77 points).
Patient K., 54 years old, medical history No. 77354, was admitted to the institute’s clinic with complaints of valgus deformity of the first toe of both feet, pain in the area of the first metatarsophalangeal joint at rest and when walking.
On the radiograph of the forefoot of the left foot, the angle M1P1right is 30°; M1R1left - 30°, and the angle M1M2right - 18°; M1M2lev - 18° (Fig. 3).
Surgical intervention was performed as planned: reconstruction of the anterior part of both feet. Bone fragments of the first metatarsal bone are fixed with 2 cortical screws (Fig. 4).
In the postoperative period, on the 3rd day, weight bearing on the operated lower limbs in Baruk shoes with the use of crutches was allowed for 2 weeks. From the 3rd week after the operation, walking in Baruk shoes is allowed without crutches for another 3 weeks. 6 months after the operation, a good result was found on the AOFAS scale (85 points).
Patient M., 46 years old, case history No. 79629, was admitted to the institute’s clinic with complaints of valgus deformity of the first toe of both feet, pain in the area of the first metatarsophalangeal joint, which intensifies after walking. On the radiograph of the forefoot of the left foot, the angle M1P1right is 28°; the angle M1R1left is 28°, and the angle M1M2right is 18°; angle M1M2left - 18° (Fig. 5).
Surgical intervention was performed as planned: reconstruction of the anterior part of both feet. Bone fragments of the first metatarsal bone were synthesized with an LCP plate and screws (Fig. 6).
On the 3rd day after surgery, walking in Baruk shoes is allowed without additional assistance for 4 weeks. 6 months after the operation, an excellent result was noted on the AOFAS scale (96 points).
The goal of surgical treatment of hallux valgus: Beautiful feet without pain
Rice.
2: Foot with hallux valgus: Clear image of the bony protrusion of the 1st toe. The sesamoid bones (small bones located in the thickness of the tendons and, as a rule, lying on the surface of other bones) of the long flexor of the 1st toe are located under the 1st metatarsophalangeal joint in an eccentric position: They surround the bones of the toes asymmetrically and are displaced to the side . © Dr. Thomas Schneider In addition to straightening the first toe, surgical treatment of Hallux Valgus in the early stages also involves preserving the arthrosis-affected first metatarsophalangeal joint. In this way, an effective and long-term correction of the incorrect position of the 1st toe is achieved. Only when the feet acquire their previous shape is it possible to restore a natural gait: With a healthy gait, the step “rolls”, smoothly and slowly from heel to toe; in the case of foot deformities, the biomechanics of the 1st metatarsophalangeal joint is disrupted. The other toes are responsible for the process of rolling the foot, as a result of which excessive stress is placed on them, which over time leads to hallux valgus.
The main task of surgical treatment of this pathology is to excise the apex or edge of the first metatarsophalangeal joint, as well as remove and compare the soft tissues and bones of the foot in order to reduce pain, restore internal rotation (pronation) and the previous configuration of the joint.
medical request
The main task of surgical treatment of this pathology is to excise the apex or edge of the first metatarsophalangeal joint, as well as remove and compare the soft tissues and bones of the foot in order to reduce pain, restore internal rotation (pronation) and the previous configuration of the joint.