The wrist joint plays an important role, since fine motor skills of a person depend on its functions. Several types of pathologies in this area have been described, among which synovitis is often found. This is an inflammation of the synovial membrane, which is responsible for nourishing and protecting the joint. As synovitis develops, pain, swelling appears and performance is significantly reduced. Lack of treatment leads to complex complications, among which the most dangerous is sepsis. To combat this insidious disease, both medical and surgical methods are used. This will be discussed in the article.
Description of the disease
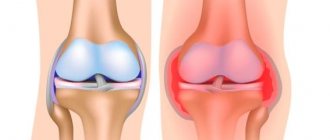
Synovitis of the wrist is an inflammation of the inner lining of the joint. The disease brings discomfort to a person, making it difficult to perform usual activities. A swelling forms in the affected area, which is associated with the appearance of effusion. Swelling is one of the hallmark symptoms of this disease. Synovitis can be acute or chronic. With a long, sluggish course, fibrous changes in the synovial membrane occur, and in the acute form, the inner membrane does not change . Symptoms of the disease do not always appear immediately, which is extremely dangerous, because the disease gradually progresses and leads to serious complications.
Anatomical structure of the wrist joint.
Diagnosis of synovitis
Synovitis, the symptoms of which serve as the basis for diagnosis, requires additional research methods.
Diagnostic puncture to determine the presence of effusion, its quantity and nature (transudate is not inflammatory, but exudate is inflammatory). Hip synovitis is the basis for the X-ray diagnostic method. Its main goal is to determine the extent of the process and the involvement of bone structures in the inflammatory focus. Arthroscopy, arthropneumography and biopsy of the synovial membrane are prescribed for chronic aseptic course of the inflammatory process.
Synovitis of the joint requires a cytological examination of the effusion in order to determine the morphological integrity of the tissues of the articular cavity. Laboratory research methods include general and special indicators of the inflammatory process in the body.
Reasons for development
Several main causes of synovitis of the wrist joint have been studied, among which are:
- wrist injuries;
- endocrine disruptions;
- allergies;
- infections introduced into the synovial membrane;
- stress;
- daily heavy repetitive movements.
Synovitis occurs more often in professional athletes and people who are exposed to stress on a daily basis . In addition, there are diseases that can contribute to the appearance of inflammation of the synovial membrane. Among them are:
- hemophilia;
- acute rheumatism;
- infectious diseases.
Staphylococcal and streptococcal infections most often cause bacterial synovitis. It is necessary to get rid of all infectious diseases in the body to reduce the chance of inflammation of the synovial membrane.
People who are at risk should take regular preventive actions. If you first become ill, you should consult a doctor.
You can learn about minimal synovitis of the elbow joint in this material.
Kinds
Depending on the root cause and distinctive characteristics of the disease, its type is determined. An in-depth diagnosis is required to identify the type of synovitis, namely:
- external examination, palpation;
- X-ray or MRI;
- blood and synovial fluid analysis.
In some cases, the diagnosis can only be made on the basis of an in-person examination. Determining the type of inflammation allows you to choose the right treatment regimen . Once remission is achieved, restorative procedures will need to be used to completely cure the joint damage. If results cannot be achieved, you will need to re-examine and select a new treatment regimen. As a last resort, surgery is used.
Acute and chronic
The disease can occur in acute or chronic form. Sluggish inflammation is much less common. Acute synovitis can develop in a matter of hours. Its distinctive feature is strong and sharp, even flashes of pain. Immediate medical attention is required.
The chronic form of the disease can develop from several weeks to years. All symptoms are less pronounced, while the person experiences slight discomfort constantly. In the absence of proper treatment, both types of disease become more complicated. The doctor must correctly determine the cause and type of inflammation in order to get rid of it and prevent relapses in the future.
The most dangerous is infectious synovitis, which has become chronic. In this case, there is a high risk of complications and infection of internal organs.
Allergic
The allergic form of the disease is rare. As a rule, simply exposure to an allergen on the human body is not enough to trigger the process of inflammation in the synovium. Therefore, the allergic form of synovitis occurs either after previous inflammation, or when the inner lining of the joint is injured. Any irritant can act as an allergen. An allergic type of inflammation requires a competent approach to treatment and the correct choice of antihistamines. In addition, medications are always required that will relieve pain and inflammation in the first hours after symptoms are identified. It is also important to identify the allergen and eliminate interaction with it . Thus, it will be possible to completely get rid of this pathology. In this case, it is recommended to take an allergy test, thanks to which you can accurately identify the substance that triggered the pathological reaction.
Infectious
The most dangerous type of synovitis is infectious. Various pathogenic organisms penetrate the inner lining of the wrist joint due to injury or systemic infection of the body. In most cases, the cause of the inflammatory reaction is microbes, namely streptococci and gonococci. Antibiotics are used to treat them. It is important to choose the right medicine so that it demonstrates high effectiveness against the bacterium that led to the onset of the disease. The infectious type of synovitis almost always occurs acutely, accompanied by high fever and general malaise.
The most rare is synovitis, formed as a result of a prolonged course of syphilis and tuberculosis.
Symptoms of synovitis
Synovitis, the symptoms of which include signs of inflammation, may have a characteristic picture depending on the anatomical location of the process.
The main signs of the disease are an increase in the volume of the joint, a feeling of fullness in the articular cavity, limitation of active movements, a positive symptom of patellar balloting, as well as an increase in local and general body temperature.
Synovitis of small joints, such as synovitis of the wrist joint, leads to limited hand mobility and disruption of the patient's daily life.
It is a mistake to think that synovitis of the meniscus can form, but a meniscus tear can lead to traumatic synovitis.
The most common inflammatory process in older people is knee synovitis, since with age there is a decrease in the tolerance of the articular surfaces to stress. The main mistake is treating this disease with home or folk remedies.
Treatment of synovitis with folk remedies can lead to the development of major complications of this disease.
Symptoms
Synovitis is characterized by the following symptoms:
- pain in the affected area;
- swelling;
- redness;
- increase in body temperature;
- general malaise.
A person is faced with the fact that the wrist swells and ceases to function normally; most often this disease is confused with bursitis of the wrist. If several joints are affected at the same time, then it becomes almost impossible to move the hand. Severe pain occurs, the hand is fixed in one position. At the first signs of acute synovitis, it is advisable to apply a fixing bandage and protect the joint from stress until you consult a doctor and prescribe treatment.
Diagnostics
In order for the doctor to finally be convinced of the correctness of his proposed diagnosis, the patient must undergo examination in the clinic. The doctor will conduct an examination and refer the patient to take a puncture from the inflamed joint. The effusion that fills the synovial cavity is taken for analysis.
If a person has previously been injured, he will definitely be referred for the following instrumental studies:
- Ultrasound;
- CT;
- MRI;
- radiography.
Arthroscopy and blood tests may also be ordered.
Treatment
Treatment of inflammation of the synovial membrane consists of eliminating the root cause of the disease and relieving symptoms. If it is impossible to use conservative therapy, surgical treatment is used. Synovitis can be treated by different doctors. Depending on the type of disease, the treatment regimen can be selected and adjusted:
- traumatologist;
- surgeon;
- therapist;
- endocrinologist
First of all, you need to see a therapist . He, in turn, will decide whether a person needs to contact a specialized specialist.
Conservative
Conservative treatment consists of the use of medications and physiological procedures. The following types of means can be used:
- antibiotics;
- non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs;
- corticosteroids;
- immunomodulatory;
- analgesics.
A conservative treatment regimen necessarily includes physiotherapy. The most effective of them:
- electrophoresis;
- magnetic therapy;
- UHF;
- ozokerite.
Medicines are used both locally and internally. In some cases, drugs are administered during electrophoresis. Thus, it is possible to achieve greater effect.
Operational
Surgical treatment is used when conservative treatment does not bring results or when there is a large amount of pus. In case of infectious synovitis, a puncture is required to pump out purulent contents. A full-fledged surgical intervention is performed if irreversible changes in the membrane occur or if drainage is required . As a last resort, an operation is performed to completely excise the synovial bursa. After surgical treatment, proper rehabilitation is required. A person stays in hospital for a certain period, and then an individual scheme is developed.
Traditional methods
Traditional methods can also help in the treatment of synovitis. Many products can be used on an ongoing basis as a preventive measure. Compresses, dressings and infusions are used internally:
- Comfrey ointment - 4 tablespoons of the herb are mixed with 200 g of lard, which has previously been minced through a meat grinder. After this, the ointment is infused for a week. You need to use it 2 times a day, lubricating the inflamed area. The ointment has regenerating properties.
- Bay leaf infusion - put 10 g of leaves in 300 ml of water and boil for 5 minutes. After this, let the liquid sit for 3 hours. Strain the infusion and drink. Every day you need to prepare 1 serving. The course of treatment is 3 days. Bay leaf has antimicrobial and anti-inflammatory effects.
- Honey compress - a clean cloth should be smeared with fresh honey and a bandage applied to the inflamed area. Honey will help slightly relieve inflammation and pain. The compress can be used every day.
Folk remedies must be properly combined with the main therapy. Before applying medications, it is necessary that the area of inflammation is as clean as possible.
Traditional methods will not replace drug therapy. However, they will be able to supplement it, especially during the period of remission.
How to relieve inflammation of synovitis of the wrist joint can be found in this article.
Therapeutic measures
An integrated approach is used in the treatment of acute synovitis of the wrist. Treatment methods will again vary depending on the cause of the disease.
They all have several goals:
- elimination of the inflammatory process;
- removal of effusion from the joint cavity;
- restoration of range of motion.
First of all, the limbs need to be ensured complete rest. To do this, the doctor places a plaster splint, orthosis or tight elastic bandage on the arm. If the effusion was small, against the background of immobilization of the arm, excess fluid is completely absorbed into the synovium.
To ensure rest of the wrist, an elastic brace is placed on it.
If a large amount of fluid has accumulated or there is a suspicion of purulent effusion, a therapeutic puncture should be performed (see Joint puncture - what is this procedure and how is it performed?). The fluid is removed and sent for testing. The joint cavity is washed with solutions of antiseptics or antibiotics.
Drug treatment
The main group of drugs for the treatment of aseptic synovitis is NSAIDs. They have the ability to eliminate inflammation and swelling and relieve pain.
They use drugs such as:
- Ibuprofen;
- Movalis;
- Aertal.
The instructions suggest their use internally in the form of tablets or externally (creams and ointments).
Hormonal drugs are used for severe synovitis and the absence of effect from non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. Hormones are especially indicated for allergic diseases. They are prescribed for oral administration or injected directly into the joint. Only a doctor can prescribe and discontinue hormonal medications.
Antibacterial drugs are prescribed for joint infections. First, a broad-spectrum drug is used. After inoculating the pathogen from the synovial fluid, the antibiotic is changed if necessary.
Joint puncture is used to remove accumulated fluid.
Surgery
Prescribed when conservative therapy is ineffective, severe joint swelling, purulent effusion. The joint cavity is opened, pus and necrotic areas of the synovial membrane are removed. Then drainage is installed and the cavity is washed with antiseptic solutions.
After surgery, you will need to wear a fixation orthosis for 2 weeks. You can buy it in an orthopedic salon, the price is optimal.
Additional Methods
To increase the effectiveness of therapy and restore limb function, physiotherapy, therapeutic exercises, and massage are prescribed. Additional treatment is prescribed after the acute inflammatory process has subsided. It is necessary to develop the arm to prevent the formation of adhesions in the joint cavity.
Physiotherapy procedures include:
- electrophoresis of drugs;
- magnetic therapy;
- pulse currents.
The procedures improve microcirculation in the area of inflammation, help reduce swelling and resolve the pathological process.
The prognosis for synovitis of the wrist joint in most cases is favorable, hand function is completely restored. Complications develop when you do not seek medical help in a timely manner.
Prognosis for full recovery
In most cases, the prognosis is favorable. After curing the acute form of the disease, it is possible to achieve complete restoration of the wrist joint. Problems arise if irreversible changes occur in the synovial bursa. Severe purulent synovitis leads to the appearance of scars and increases the chances of developing sepsis when the capsule ruptures in the tissue. Slow inflammation causes circulatory disorders and fibrous tissue changes. After surgery, relapses of the disease are possible. If you ignore the symptoms of synovitis of the wrist, there is a possibility of complete loss of functionality of this part of the body.
Hygroma and fibroma are the most common complications of synovitis.
Prevention
To prevent synovitis of the wrist joint, you need to follow simple rules:
- get rid of infectious diseases in a timely manner ;
- avoid injury;
- when playing sports, protect your wrist ;
- observe the work and rest schedule;
- adjust nutrition.
Athletes and people whose activities involve active work of the hands must necessarily protect this part of the body using wristbands and bandages. By avoiding injury and subsequent bacterial infections, it is possible to significantly reduce the risk of inflammation of the synovial membrane.
After suffering from synovitis, it is necessary to adhere to preventive measures on an ongoing basis , since there is a risk of relapse.
conclusions
- Synovitis is a serious disease caused by inflammation of the synovium inside the joint.
- Long-term lack of treatment leads to fibrotic changes in the tissues of the synovial membrane, as a result there is a risk of complete loss of motor functions of the joint.
- Treatment of synovitis should be aimed at eliminating the root cause of synovitis, and only then at combating the symptoms.
- Drug treatment can be enhanced with the help of physiotherapy and traditional methods.
- Simple preventive measures can reduce the risk of synovitis to a minimum.