Diagnosis of de Quervain's disease
The leading symptom is pain in the area of the styloid process of the radius (along the lateral surface of the wrist joint on the side of the thumb). The pain is more pronounced with movements of the hand and thumb. In some cases, the pain continues at night and radiates to the hand and forearm. Palpation of the area of the styloid process of the radius is painful. The Finkelstein symptom is important: the patient presses the thumb to the palm, and presses it on top with the other fingers (the hand is clenched into a fist, but the first finger is not above, but below the others). In this position, the patient moves the hand to the elbow side, which, if the symptom is positive, is accompanied by severe pain.
Treatment of de Quervain's disease: non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (Voltaren, Nimesil, etc.) are used orally and locally, physiotherapy, rest. Blockades with diprospan or Kenalog have a good effect.
Treatment
In the first and second stages of the disease, the patient is prescribed anti-inflammatory drugs, physiotherapy, and painkillers. Maximum wrist immobilization is also indicated. If the third degree of arthritis is diagnosed, only surgical treatment will be effective.
The orthopedist prescribes treatment based on the stage and cause of arthritis. So, for example, if the disease is represented by an acute purulent form, arthrotomy may be prescribed. This procedure involves installing a drain to drain pus. Based on bacteriological analysis, the traumatologist identifies the causative agents of the inflammatory process in order to select the most effective antibiotic. If the patient’s chronic arthritis has worsened, in addition to immobilization, rheumatologists use physiotherapeutic techniques. Professional massage helps well, relieves the condition of exercise therapy, ultrasound and other hardware techniques. Also, patients suffering from a chronic form of arthritis of the wrist joint should constantly remember about the reasonableness of the load on the sore hand. It is recommended to adhere to a diet and include special therapeutic exercises in your lifestyle.
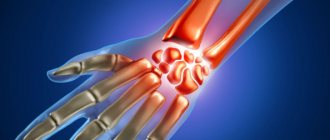
Diagnosis of arthritis of the wrist joint
The main manifestation is joint pain and swelling. There is often slight redness in the joint area, and sometimes morning stiffness. The clinical picture can be quite varied, depending on the cause of the arthritis. X-ray examination may show no changes. The tests showed an increase in ESR and C-reactive protein (this is typical for all arthritis). In arthritis caused by a certain disease, other indicators may change (increased blood uric acid in gout, increased rheumatoid factor in rheumatoid arthritis, etc.).
Diagnostics
To obtain an accurate clinical picture, the following types of diagnostic procedures are prescribed to a patient with suspected arthritis of the wrist joint:
- laboratory complex - urine and blood tests;
- if a purulent process occurs, a sample of synovial fluid can be taken to determine the bacterial strain;
- ultrasound examination of the wrist and hand;
- targeted x-ray of the affected area;
- CT or MRI.
If during the examination there are still doubts about the accuracy of the diagnosis, the patient can be referred for additional consultation to specialized specialists of the Central Clinical Hospital of the Russian Academy of Sciences.
Symptoms of hand arthritis
To understand how to treat arthritis of the hands
, it is necessary to understand
what symptoms the pathology has
.
The symptoms of degenerative-dystrophic processes may vary, depending on the reasons for their occurrence. Common symptoms of hand arthritis include:
- pain experienced when performing various actions with the upper limbs;
- “torsion” of the joints of the hands due to changing weather conditions and changes in atmospheric pressure;
- decreased mobility and stiffness of joints, which manifests itself mainly in the morning;
- the appearance of redness, locally elevated skin temperatures and swelling on the knuckles;
- symmetrical damage to joints by inflammatory processes;
- crunching and squeaking (crepitus) when moving your fingers;
- formation of subcutaneous nodules.
In rare cases, symptoms of arthritis of the hands include weight loss, as well as increased fatigue and general weakness of the body, caused by the presence of inflammatory processes in the body.
Caption: Symptoms of arthritis of the hands affect the course of treatment of the disease
Types of arthritis of the joints of the hand
According to the existing classification, there are several most common types of arthritis of the hands:
- infectious (caused by infections);
- metabolic (caused by the accumulation of uric acid salts);
- rheumatoid (starts mainly in small joints);
- post-traumatic (the result of damage to cartilage tissue);
- proximal, middle or distal;
- rhizarthritis (affects exclusively the thumb);
- secondary arthritis.
Who's at risk
Arthrosis of the hands occurs not only after injury. Often the disease becomes a consequence of professional overload and microtrauma, so the risk group includes:
- athletes;
- construction workers;
- those who deal with a jackhammer and a hammer drill (an additional provoking factor is vibration), etc.
Sometimes the cause of arthrosis of the hand is a congenital or genetic predisposition
Causes of the disease
The etiology of arthritis is different. Prerequisites for its development may be:
- bacterial infection,
- pathologies of metabolic functions, for example gout,
- rheumatic changes in bones,
- autoimmune diseases,
- injuries leading to dysfunction of the joint - sprains, fractures.
The disease negatively affects the entire system of protective functions of the body. On this basis, autoimmune arthritis : the body reacts aggressively to its own organs, perceiving them as foreign.
How it manifests itself
Diseases of the wrist joint are indicated by:
- crunching sound when moving;
- pain in extreme positions of flexion and extension;
- pain at rest - after intense physical activity;
- reduction in joint mobility by 30-50%.
If the cause of the disease is a displaced fracture of the wrist bones, deformations of the wrist joint, visible to the naked eye, are possible. In all other cases, it remains practically unchanged, in contrast to the clinical picture of rheumatoid arthritis with severe edema.
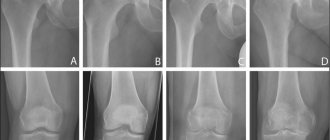
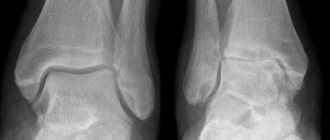
The degree of arthrosis of the joints is diagnosed using x-rays
Arthrosis of the wrist joint. Symptoms of arthrosis of the wrist joint
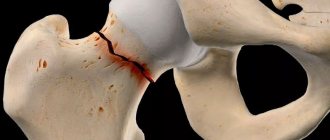
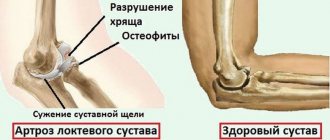
Arthrosis of the wrist joint is not very common. Basically, it is post-traumatic , that is, it develops as a complication after a dislocation or fracture of the wrist bones (it should be clarified that arthrosis usually does not occur immediately, but several weeks or months after the injury).
Arthrosis of the wrist joint is characterized by symptoms such as crunching in the joint during movement and pain that occurs only with certain movements or in extreme positions of flexion-extension of the joint - i.e. when trying to bend and straighten the joint to the maximum, “all the way.” At rest, without movement, pain appears only if a person overloaded the sore joint a few hours earlier.
The mobility of the wrist joint with arthrosis is always reduced by 30-50%. But the appearance of the wrist joint affected by arthrosis remains practically unchanged - from the outside it looks almost healthy, or the joint is deformed quite a bit. Severe deformations of the wrist joint with arthrosis occur only when the disease was caused by a fracture of the wrist bones with their displacement.
Attention! We must remember that the wrist joint is one of the “favorite places” for inflammation in rheumatoid arthritis. And it is important not to confuse arthrosis of the wrist joint with this serious disease. Fortunately, distinguishing arthrosis from arthritis is usually quite simple. With arthritis, unlike arthrosis, pain is most often more severe at rest, late at night or in the morning.
When moving, the pain, on the contrary, often decreases (although extreme attempts to flex-extend the joint with arthritis, as with arthrosis, are also almost always painful). In the afternoon, especially in the evening, arthritic pain almost always subsides completely until late at night.
The appearance of the wrist joints affected by rheumatoid arthritis, as a rule, changes significantly: there is either pronounced swelling and “swelling” of the wrist joint, or a “sinking zone” in the area of this joint due to atrophy of its muscles.
It is also characteristic that with arthritis, damage to the wrist joints alone is extremely rare - any arthritis most often leads to inflammation of several joints at once; on the contrary, arthrosis of the wrist joint is an isolated post-traumatic pathology, usually affecting a single damaged wrist joint. Another distinctive point: the general condition of those suffering from arthrosis of the wrist joint usually does not change, and with arthritis, fever, weakness, chills, body aches, etc. may be observed.
The mechanism of development of arthrosis of the wrist joint
As mentioned above, arthrosis of the wrist joint is most often post-traumatic and usually develops after fractures and dislocations of the wrist bones. But, in addition, “occupational” arthrosis of the wrist joint also occurs, associated with its professional overload or microtrauma. Such overloads and microtraumas often occur in athletes and construction workers who actively load their hands.
Arthrosis of the wrist joint also often develops in people who, due to their profession, are forced to work a lot with a jackhammer, a drill with a perforator, etc. Indeed, in such cases, another damaging factor is added to overloads and microtraumas - vibration.
As a result of the above-mentioned unfavorable effects, the joint begins, as doctors say, to “degrade”: the small bones of the wrist joint are deformed, and the articular cartilage loses some of its moisture, becomes dry and less smooth, rough. In addition, it becomes thinner and loses its ability to absorb the load on the bones of the joint. And to top off the troubles, the amount of healthy joint fluid in the joint, which performs a “lubricating” function during the movement of articular components, may decrease.
All this leads to the appearance of those unpleasant symptoms mentioned above: a decrease in the mobility of the wrist joint, the appearance of a crunch in it and pain when moving.
Diagnosis of arthrosis of the wrist joint
First, it is necessary to conduct an X-ray examination of the wrist to clarify the degree of arthrosis changes in the diseased wrist joint. And also in order not to miss a possible inflammatory process (i.e. arthritis).
And, secondly, again, in order to “not miss” arthritis, it is necessary to conduct blood tests: clinical (from a finger) and an analysis for rheumatic tests (from a vein). It is characteristic that with arthrosis, blood tests from a finger and from a vein remain within normal limits, and with arthritis, some deviations are almost always observed (increased indicators such as ESR, C-reactive protein, seromucoid, uric acid, changes in the level of globulins, etc. ).
Treatment of arthrosis of the wrist joint
Proper treatment of arthrosis of the wrist joint almost always gives a good result. But this only happens if we can eliminate the damaging effect that led to the disease - if we prevent further overload of the joint, eliminate the possibility of repeated microtraumas, immobilize the wrist joint with a fixing bandage or a special orthopedic wristband, etc. In such a situation, treatment of arthrosis of the wrist joint will almost certainly be successful.
If our patient continues to overload his arm or continues to work in traumatic work without taking care to protect the joint with the help of any orthopedic devices (for example, wristbands), the effect of treatment will be reduced to zero or will be minimal and short-lived.
Now let's talk about those treatment procedures that bring maximum benefit for arthrosis of the wrist joint.
Firstly, as with any type of arthrosis, we need to take care of saturating the damaged joint cartilage with special nutrients - chondroprotectors. The course treatment of arthrosis with chondroprotectors is described in detail here >>
Secondly, we must try to restore the “joint game”, i.e. restore the mobility of the bones that articulate in the wrist joint. Manual therapy (mobilization method) is well suited for this. Typically, 3-4 sessions of manual therapy are enough to maximize the mobility of a sore wrist joint.
The third task facing us in the treatment of arthrosis of the wrist joint is to improve blood circulation in it and accelerate metabolism in the joint. To solve this problem, we have a large selection of treatment procedures. So, we can successfully use:
- compresses with bischofite or medical bile;
- healing mud;
- ozokerite;
- paraffin therapy;
- massage or self-massage with ointments based on anti-inflammatory substances (Voltaren gel, Fastum, Dollit cream, etc.);
- laser therapy;
- magnetic therapy;
- electrophoresis.
And finally, when treating the most severe cases of arthrosis, we can use the method of saturating the diseased joint with special “lubricating” substances - derivatives of hyaluronic acid (preparations Ostenil, Fermatron, Go-on, Giastat, etc.). With the help of 3-5 injections of hyaluronic acid into the diseased joint, carried out after manual reposition of the joint (and sometimes without it), it is possible to dramatically improve the condition in 70-80% of patients (hyaluronic acid preparations are described in detail in Chapter 26).
And if the treatment is carried out comprehensively, in all four areas (the use of chondroprotectors, manual therapy, improving blood circulation in the joint and intra-articular injections of hyaluronic acid), the result of therapy will be even higher.
Article by Dr. Evdokimenko© for the book “Pain in the Legs”, published in 2004. Edited in 2012 All rights reserved
Other articles about hand diseases >>
Prerequisites for the development of hand arthritis
The disease is an inflammatory process affecting the small joints of the hands, which is treated by our experienced kinesitherapists. The disease occurs more often in women.
It is important to promptly begin treatment for arthritis of the hand, since in the later stages the lesion leads to deformation of the joints and loss of the ability to self-care.
Among the main causes of inflammation are:
- age;
- injuries;
- professional factor;
- heredity;
- past infectious disease;
- allergies;
- psoriasis;
- rheumatism;
- diabetes;
- gout, etc.
Diagnosis and treatment of hand arthritis
If suspicious symptoms appear, you should see a kinesiotherapist. Today, traditional treatment for arthritis of the hand includes taking medications that dull the pain, temporarily relieve swelling, but, unfortunately, do not restore limb mobility. Patients are also prescribed products for nutrition and improvement of joint trophism, vitamins, but due to chronic inflammation, these substances are simply not absorbed by the joint tissues.
Physiotherapy may provide temporary relief from symptoms. Physical therapy is also prescribed to treat hand arthritis. In advanced stages, medicine can only offer the patient surgery (endoprosthetics).
Kinesitherapy for the treatment of hand arthritis is a fundamentally new approach, which is based not on relieving symptoms, but on eliminating the very cause of the pathology. A set of special exercises provides a natural effect on the joints and surrounding tissues.
During the first consultation at our center, the kinesiotherapist examines and interviews the patient, conducts testing on multifunctional simulators and myofascial topographic diagnostics.
Based on the results of the examination, a treatment program for hand arthritis is drawn up. It is based on strictly dosed effects of loads on certain muscle groups, which are performed with a safe amplitude. Kinesitherapy helps improve blood supply to the joint, normalizes the trophism of its structures, helps relieve swelling, as a result of which pain and stiffness disappear.
The advantages of kinesitherapy are:
- versatility (suitable for patients of any age and size);
- affordability (compared to expensive surgeries and medications);
- soft and natural effect on the articular-ligamentous apparatus.
Modern approach to treatment
Whatever the treatment, it is very important to eliminate the provoking factors at the start - joint overload, repeated microtraumas and injuries. For this purpose, it is recommended to use special fixing bandages or orthopedic wristbands during physical work, and, if necessary, to temporarily abandon potentially dangerous professional activities.
Arthrosis of the hands develops in those who perform monotonous movements
Therapeutic measures for gouty arthritis
Optimal, effective therapy is chosen by experienced specialists after a comprehensive examination of the patient. Doctors at the Arthro-clinic medical institution successfully cure the disease. Innovative equipment and productive techniques make it possible to quickly establish the causes of the disease, determine the degree of pathology and immediately begin to cure the patient.
A necessary condition for successful therapy is adherence to a gentle regimen for the affected joint. The doctor will be able to choose the appropriate means to ensure immobility of the affected organ - an elastic bandage or an orthosis.
Take care of yourself and be healthy!