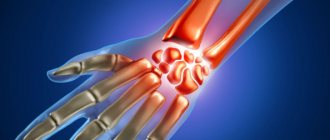
Tunnel syndromes (tunnel neuropathies) are a group of lesions of peripheral nerves due to prolonged compression and trauma in the musculoskeletal canals by chronically inflamed surrounding tissues.
The most common and well-known tunnel syndrome is carpal tunnel syndrome, i.e. compression of the median nerve (lat. nervus medianus) under the transverse carpal ligament. Nerve compression occurs between three bony walls and a tight ligament that hold the tendons of the muscles that flex the fingers and hand.
Carpal tunnel syndrome is more common in women than in men (3-10 times according to various sources). Peak incidence occurs between the ages of 40 and 60 (although the disease can occur at any age, only 10% of sufferers are under 31 years of age). The risk of developing carpal tunnel syndrome is about 10% over a lifetime, 0.1-0.3% per year in adults. The overall prevalence of the syndrome is up to 1.5-3%, and the prevalence among certain risk groups is up to 5%. The syndrome is more common among Caucasians, but in some African countries it practically does not occur.
Chronic Repetitive Strain Injury
Diseases of this group are found in many professions, including such industries as construction, mining, engineering, and agriculture. They are caused by chronic functional overstrain, microtraumatization, and the performance of fast, similar movements.
In particular, such occupational diseases, in addition to the “high-profile” carpal tunnel syndrome, include:
- myositis (inflammation of the muscles) and crepitant tendovaginitis (inflammation of the tendon sheaths with a characteristic crunch),
- stenosing tenosynovitis (de Quervain's disease),
- stenosing ligamentitis,
- snap finger,
- styloiditis (inflammation of the styloid process of the radius),
- bursitis (inflammation of the joint capsules),
- epicondylitis of the shoulder (inflammation in the area of the condyle of the humerus, usually the outer one, the so-called “tennis elbow”),
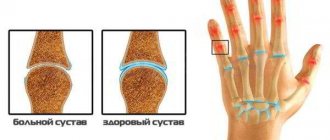
- deforming osteoarthritis of the joints of the hand (gradually increasing deformation of bones and joints),
- periarthrosis of the shoulder joint (dystrophic changes in the soft tissues of the shoulder near the joint),
- osteochondrosis of the spine (damage to the intervertebral discs and other tissues of the spine),
- diseases of the nervous system from overexertion.
Occupations that involve chronic repetitive movements of the hand are characterized by de Quervain's disease and stenosing ligamentitis.
Stenosing tenosynovitis
Chronic stenosing tenosynovitis (synonym: de Quervain's disease, French de Quervain, named after the Swiss surgeon) is a peculiar form of chronic inflammation of the tendon sheaths, which is characterized by damage to the tendons of the muscles of the thumb. In this case, the tendon sheath thickens, and the space between the sheath and the tendon, filled with fluid to reduce friction (synovial cavity), narrows. This disease is characterized by pain when abducting and extending the thumb, which can radiate to the forearm and shoulder, and swelling along the affected tendons.
Stenosing ligamentitis
Close to de Quervain's disease in clinical manifestations is stenosing ligamentitis of the fingers - reactive inflammation of the ligamentous apparatus of the hand. It can occur both with repeated trauma and with certain infectious diseases (for example, influenza). Usually the ligaments between the phalanges of the fingers and near the joints connecting the fingers to the metacarpus are affected. This disease is characterized by inflammatory changes in the area of the affected ligaments (pain during movement, swelling, edema, redness and local increase in skin temperature). There may even be necrosis of the ligaments with impaired tendon gliding and difficulty in bending and straightening the finger with a characteristic clicking sound (the so-called “snapping finger”). Carpal tunnel syndrome in a large number of cases is also actually ligamentitis, but in the wrist area, and with a characteristic neurological picture.
Causes of hand tendonitis
Wrist tendinitis (styloiditis) occurs against the background of other serious pathologies or develops as an independent disease.
The key factors that provoke the onset of the disease include excessive stress on the tendons.
For wrist tendinitis, as an independent pathological process, the following processes are characteristic:
- The appearance of mechanical damage that occurs against the background of prolonged physical activity;
- The occurrence of microtraumas, which is a consequence of tendon tension during physical exercise;
- Pathological processes that manifest themselves as a result of pathogenic bacteria entering damaged tissue.
Patients who have hand tendinitis due to other reasons often turn to medical care, including:
- Deterioration of metabolism;
- Incorrect posture;
- Degenerative processes in the joint area, which can be triggered by hormonal imbalances, metabolic failures, and increased stress;
- A number of diseases characterized by damage to periarticular tissues and joints;
- Infectious diseases caused by the penetration of pathogens;
- Malfunctions of the immune system associated with prolonged exposure to medications or colds.
Tendinitis of the hand is most common in males.
When drawing up a treatment plan, our specialists take into account not only the nuances of the development of the disease itself, but also the age characteristics of the patient, his lifestyle and gender. In case of diagnosing related processes, we are ready to apply an integrated approach based on the latest highly effective techniques.
Thanks to the constant improvement of professional skills, continuous scientific activity and interaction with large research laboratories, the staff of our medical center are able to put innovative therapeutic methods into practice.
Etiology and pathogenesis
Possible causes of carpal tunnel syndrome are:
- Activities that require repeated flexion/extension of the wrist or are accompanied by exposure to vibration (for example, assembling equipment).
- Swelling or injury of any kind (such as fractures) that compresses the median nerve.
- Compression of the median nerve due to edema in pregnant women or women taking contraceptives.
- There is a consistent relationship between excess body weight and the presence of carpal tunnel syndrome. In addition, short people are more prone to the disease.
- Acromegaly, rheumatoid arthritis, gout, tuberculosis, renal failure, decreased thyroid function, early postmenopausal period (and also after removal of the ovaries), amyloidosis, possible connection with diabetes mellitus.
- The syndrome is characterized by a genetic predisposition, particularly due to multiple heritable characteristics (eg, square carpus, transverse ligament thickness, build).
Carpal tunnel syndrome is caused primarily by compression of the median nerve at the wrist due to thickening or swelling of the flexor muscle synovium. As a result of chronic inflammation of the connective tissue due to constant repetitive stress, it becomes rougher, thicker, and swollen, which increases the pressure inside the carpal tunnel. Increased pressure causes venous congestion and edema, which leads to ischemia (impaired blood supply) to the nerve.
First, the sensory fibers are damaged, and only then the motor fibers of the nerve. Damage to the fibers of the autonomic nervous system (responsible for sweating, dilation/constriction of blood vessels, etc.) is also possible.
Symptoms of hand tendonitis
The key nuances of wrist joint tendinitis include the localization of its symptoms in the area of inflammation. The primary stage of the disease is characterized by the following manifestations:
- Pain syndrome that increases during physical activity. Irradiation of pain can be observed in nearby areas;
- Crunching when making motor movements of a limb;
- Swelling in the joint area;
- Feeling of stiffness;
- In the area of inflammation, the temperature often rises;
- The appearance of dense formations under the skin.
If you have wrist tendonitis but other symptoms are present, the symptoms and treatment will also be specific.
The presence of hand tendonitis can be judged from the results of studies carried out using instrumental methods and in laboratory conditions. For this purpose the following are appointed:
- X-ray of the joint;
- General blood analysis;
- Study of the synovial fluid filling the joint cavity;
- Ultrasound, which allows us to exclude the presence of pathological processes in the joint area;
- MRI.
Medical specialists conduct a thorough study of the existing symptoms and determine the degree of joint mobility.
The key objective of our activity is to provide highly qualified services with a guarantee of long-term results. At the same time, you can always clarify information about the cost of future treatment and ask other questions that interest you.
Prolonged use of a computer keyboard and carpal tunnel syndrome
Carpal tunnel syndrome is traditionally considered an occupational disease for activities that require repetitive flexion/extension or twisting of the hands, or involve exposure to vibration. It is widely believed that prolonged daily computer work that requires constant use of a keyboard is a risk factor for developing carpal tunnel syndrome.
A number of scientific studies indicate that there are no significant differences in the incidence of this syndrome in the group of constantly working with a keyboard when compared with the general population. Simply put, carpal tunnel syndrome is not usually caused by prolonged use of a keyboard.
At the same time, carpal tunnel syndrome occurs in every sixth computer worker they examined. According to their data, those users whose hand is extended by 20° or more relative to the forearm when working with the keyboard are at greater risk.
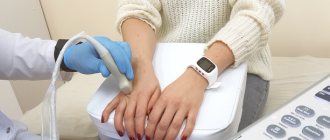
Methods for diagnosing hand tendonitis
Determine the presence of tendinitis of the wrist joint after a thorough examination and palpation of the limb by a doctor. This makes it possible to identify the area of spread of the pathological process.
In addition, to differentiate the disease, the specialist asks the patient leading questions. Sometimes doubts arise regarding the specification of the affected area.
In order to determine infectious pathologies, studies are performed in laboratory conditions. In turn, X-ray examination allows identifying the presence of calcium accumulations. Ultrasound and MRI are indicated if the specialist suspects the presence of tears in the wrist area.
Make an appointment Online booking
- Clinic on Krasnopresnenskaya +7 (499) 252-41-35 Volkov lane, 21
- Clinic on Varshavskaya +7 (499) 610-02-09 Varshavskoe highway, 75, building 1
- Clinic in Annino +7 (495) 388-08-08 Varshavskoe highway, 154, building 1
ORION PLUS
- Retail price:
45,300 rub.
Warranty from 1 year More about the terms of the guarantee
There are currently 13 people viewing this product
Compare devices Quick order Add to cart
Main characteristics
| Emitter type: | Semiconductor Injection AsGa |
| Laser mode: | pulse |
| Emitter type: | 880 - 910 nm |
| Laser pulse power variable: | 5 W; 10 W |
| Pulse modulation frequency variable: | 5Hz, 80Hz, 1500Hz and Bio mode |
| MTBF: | 2,000 hours |
| Exposure time: | from 1 to 5 min (electronic timer with countdown) |
| Built-in photodiode: | for visualization and radiation control |
ALL CHARACTERISTICS
Characteristics
| Emitter type: | Semiconductor Injection AsGa |
| Laser mode: | pulse |
| Emitter type: | 880 - 910 nm |
| Laser pulse power variable: | 5 W; 10 W |
| Pulse modulation frequency variable: | 5Hz, 80Hz, 1500Hz and Bio mode |
| MTBF: | 2,000 hours |
| Exposure time: | from 1 to 5 min (electronic timer with countdown) |
| Built-in photodiode: | for visualization and radiation control |
| Color Effect: | Infrared light: 850 - 980 nm, power 15 mW; 30 mW |
| Color Effect: | Red spectrum: 600 - 680 nm, power 10 mW; 20 mW |
| Color Effect: | Blue light: 350 – 490 nm, power 7 mW; 15 mW |
| Laser safety according to GOST R. 50723-94: | class 1 (highest) |
| Laser safety according to SANiPIN 5804-91 (radiation is safe for the eyes): | class 1 (highest) |
| Electrical safety: | class II protection BF (safety class for household appliances) |
| Device power: | from mains 220V, 50Hz |
| Power consumption: | no more than 15 W |
| Device weight: | 1,200 grams complete with emitters |
| Overall dimensions of the device: | 245x160x70 mm |
| Package size: | 390x280x125 mm. |
ORION STEP
Treatment of wrist tendonitis at various stages
When diagnosing the pathology of wrist tendonitis, treatment should be prescribed by an experienced specialist, taking into account the existing symptoms. As a rule, all doctor’s recommendations can be followed at home. Hospitalization is carried out only in advanced cases.
In addition to medications, hand tendinitis can be treated through massage and physiotherapeutic methods.
In case of acute manifestations of the disease, the patient is recommended to:
- Use cold compresses to relieve pain;
- Secure the joint with a special bandage;
- Use medications;
- Carry out physiotherapeutic procedures.
UVT for hand tendinitis
If you have been diagnosed with hand tendinitis, treatment can be performed using the latest technique - shock wave therapy. This is a modern, highly effective way to eliminate pathological processes in the area of tendon tissue, thanks to which you can easily deal with calcium deposits and avoid surgical intervention.
By using this method in the treatment of tendinitis of the hand, the following positive effects can be achieved:
- Break up calcium deposits;
- Normalize blood flow in the area of localization of pathology;
- Completely eliminate pain;
- Restore metabolism;
- Stop the pathological process;
- Restore motor activity and healthy tissue.
You can get the desired healing effect from the first sessions. Their frequency and intensity should be selected individually. However, in order to obtain a lasting therapeutic result in the process of shock wave therapy for tendinitis of the right or right hand, it is necessary to consult a specialist in a timely manner.
In our clinic, shock wave treatment is carried out using innovative Swiss equipment, which guarantees reliable and prolonged results, as well as an easy rehabilitation period.
How to treat hand tendonitis with medications?
If tendonitis of the wrist joint occurs, it is not possible to carry out effective treatment without the use of medications.
First of all, the patient is recommended to take medications that eliminate pain and reduce swelling. In this case, the best results are obtained by taking anti-inflammatory drugs.
The above medications are taken for at least two weeks. As a rule, after a course of treatment, all unpleasant manifestations disappear and the functionality of the hand is restored.
The necessary therapeutic effect can be obtained by taking the following medications:
- Ibuprofen;
- Ketoprofen;
- Piroxicam;
- Motrin;
- Indomethacin.
For the purpose of local anesthesia, Viprosal, Voltaren, Dolobene gels are applied to the affected area. The method of use is indicated in the instructions.
In case of infectious processes, antibacterial agents are used. If the immune system malfunctions, the specialist will prescribe steroid hormonal drugs.
Therapeutic exercises and massage for hand tendonitis
In order to prevent the development of the disease and quickly restore the functionality of the hand, special exercises are used. However, they can only be performed after pain has disappeared. Moreover, special emphasis is placed on the complex, which allows you to strengthen the muscles of the hand.
Daily exercise helps normalize blood circulation and restore metabolic processes. In this case, rotational movements, bending and stretching are performed. They have a powerful healing effect and help maintain muscle tone.
In addition, those diagnosed with wrist extensor tendinitis need to swim regularly.
If the pathology is chronic, resort to therapeutic massage. You can perform a special complex at home. For those who are interested in how to treat wrist tendinitis through massage, below we will give some recommendations:
- If you have tendinitis, you need to rub the sore spot with your thumb;
- Light stroking and patting movements are carried out in the affected area, as well as along the tendons.
Physiotherapy for wrist tendinitis
You can quickly restore the affected area through physiotherapeutic methods. They can be performed independently or as part of complex therapy - in addition to taking medications.
Thanks to physiotherapy, it is possible to improve metabolic processes and also ensure a rapid process of fusion of tendon fibers and resorption of dense formations.
Some of the most effective physical procedures include:
- Electrophoresis with lidase;
- Use of ultraviolet exposure;
- Magnetotherapy;
- Laser radiation;
- Ultrasound.
Traditional methods
For mild manifestations of the disease, you can use folk methods that can eliminate pathological processes in the affected area and relieve pain. Next you will get acquainted with several effective recipes:
- Consumption of curcumin. Allows you to eliminate pain and minimize inflammation. To achieve the desired effect, it is recommended to use seasoning - about 0.5 grams per day;
- A mixture of sarsaparilla and ginger. The raw materials are crushed, after which an infusion is made - 1 teaspoon of the contents is poured into 1 glass of boiling water. Take 2 times a day instead of tea. The action of the above mixture is aimed at relieving inflammatory manifestations;
- Bird cherry berries. Make a decoction: the raw material (3 tablespoons) is poured with 1 glass of boiling water. Take 2-3 times a day. Due to the presence of tannins in bird cherry, the necessary anti-inflammatory effect is achieved;
- Walnut. Add 500 ml of vodka to 1 glass of partitions. The contents are infused for about 20 days. The course of treatment reaches 1 month;
- Salty water. To prepare the product, take 1 tablespoon of salt and add water. Soak a cotton sponge in the resulting solution, wring it out lightly and place it in a bag, and then put it in the freezer for a few minutes. After removing the sponge from the bag, bandage it to the sore spot and keep it there until it dries completely.
Make an appointment Online booking
- Clinic on Krasnopresnenskaya +7 (499) 252-41-35 Volkov lane, 21
- Clinic on Varshavskaya +7 (499) 610-02-09 Varshavskoe highway, 75, building 1
- Clinic in Annino +7 (495) 388-08-08 Varshavskoe highway, 154, building 1
Surgery
If a patient has advanced tendinitis of the hand, which cannot be treated with ointments, anti-inflammatory drugs and physiotherapeutic methods, the only way out of the situation is surgery. Thanks to it, it is possible to remove adhesions and scars that usually accompany tendonitis of the extensor tendon of the hand.
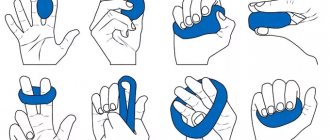
Complex of therapeutic exercises for tendovaginitis of the wrist joint
After acute inflammation has been relieved, you can speed up recovery by performing a simple set of exercises.
They will also be useful to those people who have had a history of an episode of tendovaginitis:
- Place your hand on a flat surface, raise your palm and try to touch the tip of your thumb to the tip of your little finger. Then the palm is lowered. Repeat the exercise 6-10 times.
- The sore hand lies on a flat surface. The palm is raised and, with the help of the healthy hand, pulled back, pressing on the fingers. This tension should be maintained for 10 seconds, then the hand is lowered. Repeat the exercise 3 times.
- Take a small object in your hand, lift it above your head and rotate your wrist 3 times clockwise and three times counterclockwise. Then the hand is lowered. The exercise is repeated 3 times. As you train, the weight of the object can be increased.
- Squeeze the expander in your hand for 5 seconds with a break of 2 seconds. Repeat the exercise at least 5 times.
- Pull the elastic band over the thumb of the affected hand and onto the thumb of the healthy hand. Then you need to stretch the elastic with springy movements, overcoming its resistance. The exercise is performed at least 15 times.
Rehabilitation after treatment of hand tendinitis
An important part of therapy aimed at eliminating the consequences of tendinitis is the rehabilitation period. It includes therapeutic massage and special exercises. However, rehabilitation measures should be started only after pain has been eliminated and inflammation has been relieved.
The main goal of such exercises is to restore the elasticity of the tendons and strengthen the muscle tissue. At the initial stage, the use of special devices is not provided. Over time, they resort to using an expander.
As for massage procedures, they are carried out with the aim of improving regenerative processes in tissues, normalizing blood flow and improving the elasticity of tendons.
Is it possible to return to sports activities after tendinitis?
In case of relapses after wrist flexor tendonitis or other varieties of this disease, the doctor may advise you to avoid sports that involve excessive stress on the hand. But with positive dynamics after treatment, there are no restrictions for resuming sports activities.
For preventive purposes, when performing sports exercises, it is advisable to use a bandage, which will minimize the load. It is also mandatory to stretch the muscles of the hand before and during sports. After training, you need to take a salt bath.