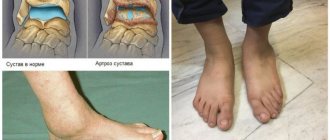
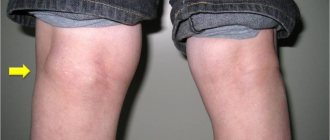
Arthrosis of the jaw (temporomandibular) joint is a degenerative disease characterized by wear and tear of cartilaginous structures: decomposition of articular cartilage, architectural changes in the bone and degeneration of synovial tissue. This hinge joint is located between the temporal bone and the jaw in front of the ear on either side of the face. Its cartilage is not as strong as other joints, so the disease can lead to severe pain.
Such problems often occur in people over 50 years of age (50% of cases) and mainly in women. After overcoming the 70-year mark, the probability of developing arthrosis reaches 90%. People often ignore the disease, afraid of visiting a doctor. Therefore, in order to react in time to the first signs of the disease, you need to know everything about arthrosis of the jaw: symptoms, treatment and causes of its occurrence.
What is arthrosis?
The jaw joint is where the lower jaw bone attaches to the skull. The jaw articulation is one of the most complex, combining multiple muscles and ligaments that allow for different movements. Any problem that interferes with the proper functioning of muscles, ligaments, discs and bones can cause a painful condition called temporomandibular dysfunction, or arthrosis of the jaw joint.
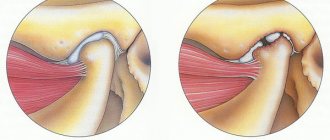
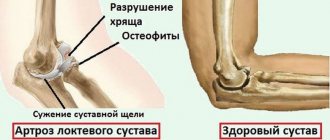
With arthrosis of the TMJ, the macroscopic structure of the cartilage undergoes changes: histologically, there is a loss of proteoglycans, breakdown of the collagen fiber network and fatty degeneration. Microcracks appear in the bone tissue, its density increases, and osteophytes can form. Such violations deprive a person of many things in everyday life: the process of talking, eating becomes more difficult, and hearing is impaired.
Osteoarthritis of the jaw joint develops in four stages:
- the initial stage (I) is characterized by articular instability caused by uneven narrowing of the joint space against the background of degenerative changes in the cartilaginous structures;
- progressive stage (II) is accompanied by a decrease in joint mobility, an increase in pain, and an exacerbation of symptoms of the disease. The worsening of the condition is associated with ossification of the condylar process of the mandible;
- late stage (III) leads to limitation of the functions of the TMJ as a result of complete degeneration of cartilage tissue, the appearance of osteophytes, reduction of the condylar process and other destructive changes;
- advanced stage (IV) with fibrous fusion of joints.
Depending on the identified radiological changes, the type of arthrosis of the TMJ is determined, which can be sclerosing and deforming. In the first case, a narrowing of the joint space and the development of bone sclerosis are noted. The second is characterized by widening of the joint, bone growths in the form of tubercles on the articular surfaces and alignment of the articular fossa, severe deformation of the lower jaw.
Depending on the origin of TMJ arthrosis, it can be primary or secondary. Primary arthrosis occurs without previous joint disease at the age of 40 years and is polyarticular in nature. Secondary develops in a previously changed joint due to an impaired relationship of articular surfaces against the background of concomitant diseases.
Temporomandibular joint dysfunction (TMJ)
Causes of joint dysfunction.
The temporomandibular joint (TMJ) is a complex apparatus
consisting of muscles, ligaments, cartilaginous discs, bones.
This system provides a movable articulation of the temporal bone of the skull with the lower jaw, facilitating its movement in three planes, back and forth, up and down, left and right. At the same time, the temporomandibular joint is considered one of the most active structures of the human body; it is involved in such important processes as chewing food, swallowing, breathing, yawning, and speech. Any problem that results in a disruption in the normal functioning of a joint is called TMJ dysfunction. According to statistics, such violations are by no means rare. According to various sources, they occur in 30-70% of cases of dental diseases. The dysfunction of the TMJ is based on a multifactorial process. It is believed that the development of symptoms is caused by pathology of the joint itself or damage to the masticatory muscles. More specifically, the development of negative signs may be due to:
- Anatomical features, discrepancy between individual elements of the articulation, the articular fossa and the head of the articular bone and others
anomalies of the dental system. - Trauma to the joint, facial bones and jaw, their improper fusion after a fracture.
- Malocclusion due to tooth loss, increased wear
, or other factors. - Bruxism, involuntary jaw clenching and teeth grinding;
- overstrain of the jaw muscles due to their overload (professional activity of lecturers, teachers, habit of biting nails, incorrect position of the telephone, long-term, more than three hours, dentist appointment without rest breaks).
- Stress and mental disorders that also affect joint movements.
- degenerative-dystrophic disorders (arthrosis).
- Inflammatory process in the joint (arthritis).
- Endocrine disorders, infectious diseases.
IMPORTANT:
A fairly common cause of TMJ dysfunction is professional errors by dentists. The violation can be caused by incorrect placement of a filling on a chewing tooth or incorrectly performed prosthetics.
Characteristic symptoms.
Diagnosis and treatment of TMJ dysfunctions is difficult, since this type of disorder is characterized by many different manifestations.
At the same time, TMJ dysfunction must be differentiated from a number of other diseases. It can be difficult for patients to understand that the root of the problem is a malfunction of the joint. Specialists at the Dentist clinic often encounter the fact that before getting an appointment with a gnathologist, people underwent long-term and ineffective treatment from neurologists, therapists, and ENT doctors. The following symptoms are considered typical for temporomandibular joint dysfunction:
- Clicking and noise effects in the joint. Joint clicking and other sounds
occurring when moving a joint, chewing, or yawning are so loud that others can hear them. They may be accompanied by pain that is limited to the joint or radiates to the face and neck. - Headache concentrated in the temples, back of the head, radiating to the forehead, neck, shoulder. Such sensations can be so intense that the patient undergoes examinations to rule out dangerous brain diseases.
- Bite problems, manifested by a violation of jaw closure.
- Facial asymmetry.
- Change in the amplitude of mouth opening.
- Jaw jamming.
- Soreness and tension in the jaw muscles.
- Toothache in the absence of manifestations of caries and other dental damage.
- Signs of damage to the ear area, manifested by pain and ear congestion, hearing loss, ringing and noise in the ears, which is associated with the anatomical proximity of both structures.
Less typical complaints should also be treated with the utmost care:
dry mouth;
burning sensation in the nose, throat, tongue; photophobia; insomnia; snore; apnea (holding your breath during sleep). IMPORTANT:
Because TMJ dysfunction is difficult to diagnose and many dentists are not adequately trained to care for these patients, people may not always be able to get the help they need. To avoid this, if questionable symptoms appear, contact the dentists of the Dentist clinic.
Which doctor treats TMJ dysfunction.
Treatment of TMJ dysfunction is the responsibility of a gnathologist dentist
. Exactly
This specialist, through his actions, helps set the patient’s lower jaw in the correct position, ensuring balanced operation of the entire system.
After conducting a diagnosis, the doctor will determine the causes of failures and suggest the most optimal ways to solve existing problems. Having outlined the correction methods, he will monitor the progress of treatment.
Despite the importance of this dental specialty, not every center is ready to provide a consultation with a gnathologist in Moscow. The issue of conducting diagnostic studies is not always fully resolved. In search of the most suitable center, pay attention to the Dentist clinic. Our center offers a full range of services in this area.
Diagnosis of the disease.
Diagnosis of TMJ dysfunction
is multi-stage and includes a whole
range of procedures
:
- The patient's complaints and anamnesis data are studied;
- The patient's posture, head position, facial symmetry, as well as functions such as breathing, swallowing, and chewing are assessed.
- A study of the closure of teeth in different positions of the lower jaw is carried out; the condition of the masticatory muscles, the tension of the muscles of the head, neck, and back are studied by palpation.
However, purely objective examination and functional tests are not enough. Additional studies are needed
for a complete clinical picture :
- X-ray diagnostics (panoramic image, survey X-ray in different projections, cone-beam and magnetic resonance imaging);
- Functional analysis, which involves taking impressions, making diagnostic models, and analyzing occlusal contacts. Electromyography is prescribed to determine the strength of muscle compression.
All techniques necessary for reliable diagnosis can be fully used by the specialists of the Dentist clinic. In their work, doctors use modern expert-level equipment that provides the most accurate research results. Diagnosis and processing of the results of diagnostic studies takes about a week, after which the dentist-gnathologist prepares a conclusion regarding the nature of the disorders, ways to solve the problem, possible treatment options, and prognosis are discussed.
Treatment methods used.
The goal of treating TMJ dysfunction is to reduce pain, expand the functional activity of the joint, and therefore improve the patient’s quality of life.
and depending on the nature of the detected disorders, conservative, reconstructive and surgical tactics are distinguished. Typically, treating TMJ pain and dysfunction requires a comprehensive approach. It is carried out through the interaction of a number of techniques and the efforts of dentists of different specialties. However, not in all cases, sound phenomena require corrective procedures. Treatment will be required if clicking in the joint is combined with limited mobility and accompanied by pain. Main areas of treatment:
- Elimination of pain, restoration of the normal process of opening the mouth and movements of the lower jaw.
- Bringing the masticatory muscles to normal tone.
- Improvement of the bite, which is ensured by the formation of correct closure of the teeth, restoration of the number of teeth.
Conservative methods include:
- Myogymnastics, when with the help of special exercises it is achieved
improvement of muscle tone; - Psychotherapy, during which a specialist teaches the patient how to properly close the jaws;
- Drug therapy, including non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, muscle relaxants, corticosteroids, botulinum toxin injections;
- Deprogramming of the masticatory muscles.
- Tire installation. This removable device made of polymer material is used to prevent the dentition from closing during sleep, as well as to relax the masticatory muscles and protect against tooth decay during bruxism.
- The use of devices aimed at limiting the mobility of the lower jaw. This is also facilitated by recommendations such as changing the diet in favor of softer foods and reducing speech load.
Reconstructive tactics
in the treatment of these disorders consist of restoring the height of the bite, the number of teeth, and the formation of correct closure of the dentition.
This task is achieved by installing dentures, inlays, using orthodontic techniques, as well as grinding the surface tissues of teeth that prevent the correct closure of the dentition. IMPORTANT:
Treatment for TMJ dysfunction in Moscow can be done at the Dentist clinic. If necessary, some of the activities will be entrusted to dentists of other specialties, orthopedist, orthodontist, periodontist, and surgeon.
Forecast and prevention.
If signs of TMJ dysfunction are detected, it is imperative to
consult a gnathologist and carry out the corrective procedures prescribed by him. If treatment is started in a timely manner, the prognosis is favorable and a lasting improvement in the situation will be achieved.
Ignoring treatment will invariably cause the condition to worsen. Over time, functional disorders will lead to the development of organic degenerative processes, accompanied by immobilization of the joint.
IMPORTANT:
Prevention of damage to the temporomandibular joint consists of taking care of the health of the oral cavity, preserving natural teeth, their timely treatment, and, if necessary, prosthetics.
Advantages of dentistry "Dentist".
In Moscow, a highly qualified consultation with a gnathologist dentist is available
get it at the dental clinic "Dentist". Using the services of our center, each patient can count on high-quality diagnostics using modern techniques, as well as a full range of treatment procedures.
The cost of gnathologist services in Moscow is in a wide price range, but often does not correspond to the professional training of the specialist or the level of diagnosis. If you make an appointment with a gnathologist at the Dentist clinic, then during the free consultation you will be able to verify the professionalism of the doctor and the excellent diagnostic and treatment capabilities of our center. Since doctors use the most advanced technologies in their medical activities, this allows them to achieve success in the most complex cases of pathology.
Reasons for development
Arthrosis occurs as a result of uneven load on joint tissues, which leads to gradual wear and tear of cartilage tissue. Joint overload can occur due to parafunctional habits (bruxism, nail biting), myofascial pain, misalignment and loss of teeth, misalignment of the upper and lower jaws, dental clefts, degenerative and inflammatory changes, also as a result of stress and trauma. Provoking factors:
- sedentary lifestyle;
- bad ecology;
- unbalanced and unhealthy diet;
- untimely visit to the dental office.
Causes of TMJ arthrosis:
- altered bite;
- chronic arthrosis;
- tooth decay;
- abnormalities of the jaw structure;
- excessive load on the joint (sports);
- incorrectly placed filling or prosthesis;
- wear of the disc or joint cartilage;
- macro- and microtrauma of the jaw or TMJ;
- jaw surgery;
- unsuccessful orthodontic treatment;
- genetic predisposition;
- diseases of the vascular system;
- infections;
- rheumatoid arthritis, gout, diseases that cause inflammation of the jaw;
- neuroses and stress;
- pathologies of the endocrine system;
- menopause;
- staying with your mouth open for too long (at the dentist);
- hormonal imbalance;
- The patient's age is over 50 years.
Risk factors also include dental deformation, missing side teeth, or tooth wear as a result of other pathology.
How to help yourself:
Main reasons
The list of factors contributing to TMJ damage includes various causes:
- Mechanical injuries and damage;
- Defects in bite formation;
- Partial or complete edentia;
- Genetic predisposition;
- Infections, including through the ear canals.
In addition, pathology often occurs in adolescent patients, which is caused by intensive development of bone tissue. Experts also note the influence of vitamin deficiency and poor nutrition, leading to demineralization of the structure and deterioration of the condition of cartilage tissue.
Symptoms
At first, the pathology makes itself felt with a slight aching pain in the joint area. Under no circumstances should such spasms be ignored, otherwise you may end up in the hospital. To cure arthrosis of the jaw joint, you need to know the symptoms in person. These include:
- pain when moving the jaw (even slightly) or loading the joint, occurring on one or both sides at once (appears due to depletion of cartilage, bone or connective tissue), which can radiate to the neck, eyes, ears;
- pain in the muscles or joints of the jaw;
- clicking or crunching of the jaw joint during movement;
- distortion of the lower part of the face;
- displacement of the jaw to the side when opening the mouth;
- decreased joint mobility after prolonged inactivity;
- possible hearing loss, migraines;
- limited mobility, inability to fully open the mouth;
- stiffness in the jaw muscles;
- muscle spasms around the jaw.
Chewing or yawning may make symptoms worse. They also become more pronounced under stress.
Arthrosis of the maxillofacial joint may not be accompanied by pain due to diabetes mellitus or diseases associated with metabolism and the thyroid gland.
What symptoms should you see a doctor for?
The earlier the diagnosis is made, the more favorable the prognosis. So seek help if:
- you experience pain in the lower jaw - intense or mild;
- you cannot fully move your jaw, you feel limited;
- hear a painful clicking or crunching sound when opening and closing your mouth;
- pain and noise in the ears appeared (especially if the otolaryngologist did not find any pathologies);
- There was a feeling of incomplete bite.
Arthrosis of the TMJ is not a very common phenomenon, but quite dangerous. Our usual comfort during conversation, eating, and other household activities is at risk. To avoid this, do not attribute alarming symptoms to fatigue and do not rely on “it will go away on its own”: be sure to find time for yourself and your health!
How dangerous is the disease?
Often, arthrosis of the jaw in the first stages is asymptomatic, which leads to prolonged inactivity in the treatment of the pathology. However, ignoring the disease is dangerous. If you notice at least one of the symptoms, you should visit a doctor. In advanced forms of pathology, medications, orthopedics and even surgery are used.
The risk group includes persons:
- over 50 years old;
- females who have reached menopause;
- those who have had injuries and surgeries of the jaw;
- with malocclusion, diseases in the jaw area;
- with damaged or missing teeth;
- with chronic inflammatory diseases;
- with arthrosis of other joints;
- whose family members suffer from jaw joint dysfunction.
Accurate diagnosis
Since the jaw joint has a complex structure, there are many possible causes for the development of arthrosis. This significantly complicates the process of diagnosing and identifying the problem causing it. The dentist questions and examines the patient for facial asymmetry, sunken lips, cracks in their corners, palpates the muscles, determining the stiffness of movements. The doctor will determine arthrosis of the jaw joint immediately after these actions.
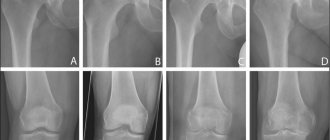
To determine the stage of development of the disease and its localization, radiography is most often used. An x-ray allows you to see the resulting deformations, bone growths, and changes in their shape. Less commonly used are CT scans, electromyography, contrast radiography, or braces (orthodontic brackets).
Treatment options
Treatment of arthrosis of the jaw joint is carried out comprehensively, taking into account the symptoms. Therapeutic measures include medication, physical therapy, diet, healthy lifestyle, and, if necessary, orthopedics or surgery. Treatment for jaw arthrosis can take a long time, but the prognosis is positive. All procedures and medications are prescribed by a doctor who closely monitors the dynamics of the disease.
The doctor determines what lifestyle the patient leads, then prescribes medications and selects a diet. And when the first results appear, the patient is referred for health procedures.
Medication
For medicinal purposes, pain-relieving gels, ointments or tablets are used. Drugs used include: NSAIDs, corticosteroids, opiates and adjuvants, muscle relaxants, hypnotic anxiolytics and antidepressants.
At the first therapeutic stage, NSAIDs (Ibuprofen, Ketanov, Paracetamol, Etoricoxib, Diclofenac and Ketorol) are prescribed. This is a wide group of drugs with great analgesic, antipyretic and anti-inflammatory activity. However, long-term treatment with NSAIDs is not recommended due to the side effects they can cause (especially at the gastrointestinal level).
When prescribing medications, the doctor must take into account the characteristics of the patient’s gastrointestinal tract when prescribing drugs that reduce the acidity of gastric juice (Omeprazole, Lansoprazole).
For more severe inflammatory symptoms, corticosteroids are recommended. They are effective when administered orally and by iontophoresis. But repeated injection of corticoids can induce chondrocyte apoptosis and accelerate degenerative changes. Therefore, an alternative is hyaluronic acid injections. They are as effective as corticosteroids but do not cause degenerative bone changes.
In arthralgia and myalgia, muscle relaxants are used as analgesics, especially when the opening of the mandible (lower jaw) is limited. Other adjuvants in the treatment of chronic pain in the jaw joint are a group of antidepressants. Tricyclic antidepressants (Amitriptyline) reduce pain, combat insomnia and anxiety. Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors are used with caution because they have many side effects and can lead to stretching of the masticatory muscles, exacerbating muscle pain.
Opioid therapy is indicated for moderate to severe chronic pain that is not relieved by traditional analgesics, including Codeine, Tramadol, Morphine, Fentanyl. However, it is important to become familiar with the contraindications that arise from the use of opiates.
To restore cartilage tissue, chondroprotectors (Teraflex, Chondrolon, Chondroitin sulfate, hyaluronic acid) may be required. Vitamin complexes (Ascorbic acid, Cholecalciferol) and calcium preparations (Calcium-D3-Nycomed Forte, Kalcemin) are an important part of the drug treatment of arthrosis of the jaw joint.
All drugs used in the treatment of TMJ arthrosis must be prescribed by a doctor. It is important to continue the course of treatment and not interrupt it immediately after the first symptoms disappear.
Physiotherapy
Physical therapy medicine can be effective for patients with limited jaw mobility and pain. Mandibular exercises are often the only treatment needed. They include relaxation, rotation, stretching. Stretching along with local cold and heat is very effective in reducing pain and improving mobility. Such exercises are effective when performed regularly as they reduce jaw clenching.
If exercises are ineffective or increase pain, there are other physical techniques that can be used:
- magnetic therapy;
- electrophoresis with potassium iodide and novocaine (exposure to weak electric current);
- massage;
- laser therapy;
- warming with bile;
- ultraviolet irradiation;
- galvanotherapy;
- exposure to ultrasound or microwaves;
- paraffin therapy;
- infrared irradiation;
- ozokerite therapy.
In the short term, these procedures can reduce jaw pain and increase your range of motion so you can continue doing facial exercises.
Anton Epifanov on the effectiveness of physiotherapy:
Diet and lifestyle
Dietary recommendations are of great importance in the treatment of TMJ arthrosis. The food taken by the patient must contain carbohydrates, proteins (for the restoration of cartilage tissue) and B vitamins (for the growth of bone tissue). Its preferred consistency is mushy, since in this form it will not create a load on the jaw joint. Therefore, the diet includes cereals, purees, soups, eggs, grated fruits and vegetables, juices and milk. The meat can be ground and served in the form of puree, soufflé, cutlets or meatballs.
It is necessary to completely exclude coffee, strong tea, alcohol, carbonated sweet drinks, chocolate, chewing gum, smoked foods, whole pieces of meat, spicy and hard-to-chew foods from the daily menu, as they can increase tension in the jaw and increase pain.
In addition to diet, the patient should adhere to a healthy lifestyle. During treatment, it is necessary to give up smoking and alcohol, avoid stress, maintain a sleep-wake schedule, and get enough rest. It is important to reduce the load on the joint, which can be achieved by combating certain habits (chewing gum, biting nails, opening your mouth too wide when yawning).
Basic therapy methods
In the treatment of arthrosis of the temporomandibular joint, an integrated approach is practiced with mandatory consideration of the severity of symptoms. The patient is advised to reduce the load on the affected joint. To do this, you need to talk less and exclude solid foods from your diet that require chewing for a long time. Preference should be given to pureed soups, porridges, products made from minced meat or fish. Doctors recommend drinking plenty of fluids to speed up metabolism and regeneration of muscles, ligaments, and soft tissue tendons.
Soft food.
Drug treatment
No drugs have yet been synthesized to restore damaged cartilage tissue. Taking medications is indicated to eliminate pain and prevent further spread of recurrent pathology. The use of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) in tablets, capsules, and dragees helps improve the patient’s well-being. The most therapeutically effective drugs are Diclofenac, Meloxicam, Ketorolac, Nimesulide, Ibuprofen. They not only eliminate pain, but also relieve inflammation and have an antiexudative and antipyretic effect. NSAIDs are not prescribed to patients with ulcers and hyperacid gastritis, since their use increases the production of caustic gastric juice. To prevent damage to the gastrointestinal mucosa, proton pump inhibitors with omeprazole, pantoprazole, and esomeprazole are simultaneously prescribed.
Glucocorticosteroids will help eliminate severe pain, especially when accompanied by an inflammatory process:
- Triamcinolone;
- Kenalog;
- Hydrocortisone;
- Prednisolone;
- Diprospan;
- Dexamethasone.
They can be used in three ways - orally, by introducing injection solutions directly into the joint cavity, or during the physical procedure of iontophoresis. The principle of operation of the latter is the migration of charged ions under the influence of a small direct current. Hormonal drugs are not used for the treatment of arthrosis of the TMJ for a long time, as they reduce the density of bone tissue.
The use of chondroprotectors allows you to stop the spread of pathological changes in tissues:
- Structum;
- Teraflex;
- Arthro-Active;
- Dons;
- complexes of chondroitin and glucosamine.
Muscle relaxants (drugs that eliminate increased muscle tone) may be included in the therapeutic regimen: Mydocalm, Baklosan, Sirdalud, especially when limiting mouth opening. The localization of the pathology often causes depression or psycho-emotional instability in patients, especially females. Therefore, the treatment regimen is supplemented with tricyclic antidepressants, tranquilizers, and sedatives. Opioid analgesics (Morphine, Tramal, Tramadol) are rarely prescribed, only when the patient complains of severe pain. Since they are characterized by the rapid formation of addiction, the course of treatment lasts no more than 5-7 days.
Non-drug treatment
In the treatment of arthrosis of the TMJ, physiotherapy is mandatory. They help improve blood supply to the affected joint with nutrients and oxygen, accelerate metabolic processes and tissue regeneration. Most often, patients are recommended 5-10 sessions of electrophoresis, UHF therapy, laser therapy, magnetic therapy, and phonophoresis. The dentist writes a referral to visit a physical therapy doctor, under whose supervision the patient performs mandibular exercises. They are designed to eliminate stiffness of the lower jaw and relieve pain. Often such therapeutic exercises become the most effective method of treatment. What other methods are used in therapy:
- orthopedic treatment to distribute the load on all joints and their structures. Wearing mouthguards, braces, dentures, sling-shaped bandages, and grinding of teeth are practiced;
- surgical intervention. During the operation, the joint can be removed, the head of the lower jaw can be removed or transplanted, and an implant can be installed.
Temporomandibular joint prosthesis.
Therapy with folk remedies will cause you to seek medical help at that stage of the disease when only surgery can solve the problem. Compresses, infusions, honey and propolis are unable to prevent the destruction of hyaline cartilage. The sooner treatment is started, the greater the person’s chances for a full recovery.
Orthopedic treatment
The essence of this therapy is to create the same load on all jaw joints. In case of malocclusion, mouth guards, braces, plates, crowns and dentures are used in treatment. In some cases, the patient is fitted with a sling-shaped bandage, which limits the mobility of the joint and prevents possible sudden opening/closing of the jaw. You have to wear such a bandage from 2 to 10 days, depending on the degree of damage to the joint.
Operation
Surgery is indicated when other treatment methods have failed. The indication for surgery is persistent pain in the joint associated with specific structural changes. The essence of the method is to remove the joint or intra-articular disc, remove or transplant the head of the mandible, or install a graft. What kind of surgery is necessary for the patient can only be decided by the attending physician. But a transplant is the most effective method of treating pathology, since it replaces a damaged joint.
The postoperative rehabilitation period also includes medication, physiotherapy, psychological treatment, a certain diet and lifestyle.
Treatment
Effective treatment of TMJ osteoarthritis requires an integrated approach.
In particular:
- taking medications;
- physiotherapeutic procedures to relieve symptoms.
Drug treatment
- The patient is prescribed non-steroidal drugs and anti-inflammatory drugs. In case of serious violations, the treatment protocol includes chondoprotectors that have a restorative effect.
- To relieve acute pain, potent analgesics are prescribed in various forms.
- In combination, the patient is recommended to install orthopedic structures (braces, mouth guards).
- It is recommended to limit your intake of solid foods.
Physiotherapeutic manipulations
- Ultrasound procedures.
- Laser therapy.
- Impact of dynamic currents.
- Electrophoresis.
- Microwave.
Surgery
If conservative methods do not bring the expected result, the patient is prescribed surgery. As a rule, surgical elimination of the problem is indicated only in complex cases when strong medications are ineffective. The operation is performed as an emergency if there is a purulent focus in the joint.
Instead of a conclusion
Statistics show that every third resident of the country has one or another joint pathology. Limitation of motor functions can lead to general complications, such as disruption of the metabolic and endocrine systems, hernias, limited mobility, etc. The earlier treatment is started, the higher the likelihood of recovery.
After successful treatment, a period of remission begins. The patient needs to remember that TMJ osteoarthritis is a chronic disease, so after the therapeutic course it is important to follow a diet and listen to the state of the body. Even minor infections can cause an exacerbation of the disease.
Folk remedies
With the permission of a doctor, non-traditional methods of treating arthrosis of the jaw joint can be used. There are both simple and complex traditional medicines to prepare. For example, warming with salt or sand is a great way to cope with pain. They need to be warmed up, poured into a textile bag and applied to the affected jaw for 1.5-2 hours until completely cooled. Another simple recipe is to use raw egg whites. At night, apply it to the entire jaw and the area behind the ears.
Among the more labor-intensive, but also more effective folk remedies, the following can be distinguished:
Drops based on celandine
- Mix crushed and squeezed celandine through cheesecloth with honey in a 1:1 ratio.
- When the honey is completely dissolved, the medicine is ready.
- Place 1 drop in each nostril before bedtime. In the first few days, this treatment may cause discomfort, but over time the effect will be noticeable.
Solution for compresses
- Mix 5 g of the following components: rhizomes of elecampane, burdock and horseradish, leaves and flowers of mint, St. John's wort, lemon balm, celandine, calendula, eucalyptus, plantain, juniper fruits.
- Grind the raw materials and pour in hot corn oil.
- After cooling, the solution is freed from all solid ingredients.
- Add 5 g of bee bread and propolis to the resulting liquid.
- Infuse the medicine in a warm place for about 20 minutes.
- At this time, mix 100 g of gum turpentine with 15-20 g of gum rosin.
- After 20 minutes, mix both solutions.
- Use the resulting mixture as compresses at night.
Prevention
Prevention of arthrosis of the jaw joint involves the fulfillment of several conditions:
- proper and balanced nutrition;
- increased motor activity of the whole body;
- getting rid of bad habits;
- oral hygiene;
- Regular visits to the dentist and increased attention to your bite.
Until recently, arthrosis of the temporomandibular joint was considered a disease of older people, but in current conditions it is increasingly possible to meet young people with this diagnosis. Every year the number of patients suffering from this pathology increases. The reasons are poor nutrition, environmental conditions, a sedentary lifestyle and reluctance to go to the doctor when the first symptoms appear.
Delayed contact with a doctor contributes to the transition of the disease to the last stage. Its treatment may require a multidisciplinary team that includes a dentist, oral surgeon, physical therapist, psychologist, and other specialists.
Diagnosis, treatment and prognosis
| Click to sign up for a FREE consultation |
Diagnosis of the disease includes a number of radiological, clinical, and functional methods. When visiting a doctor, the oral cavity will be examined, complaints will be collected, and the existing range of motion will be determined. The examination also uses a diagnostic jaw model.
X-rays can detect pronounced signs of the disease; CT scans can identify early signs, which is important for timely treatment. In addition, consultations with an orthodontist, endocrinologist, rheumatologist and other related specialists will be scheduled. Among the prescribed studies are rheography, arthrophonography, axiography, and gnathography.
After receiving the diagnostic results, the patient will be prescribed physiotherapeutic, orthodontic, therapeutic and other procedures. During the entire treatment period, it is necessary to follow a gentle diet, which will help reduce the load on the joint. In addition, heavy loads on the jaws, including speaking and chewing, are eliminated.
At the initial stage, factors that lead to joint overload are eliminated to relieve pain, NSAIDs are used in the form of ointments and tablets. In later stages, measures such as removal of the articular head or disc and subsequent installation of a graft are indicated.
A favorable prognosis can be given only in case of timely treatment of the disease, rational prosthetics, normalization of the bite, and elimination of concomitant diseases. At an advanced stage, it will not be possible to completely restore lost functions without surgery. But even after a successful operation, regular follow-up with a dentist is recommended.