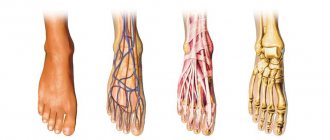
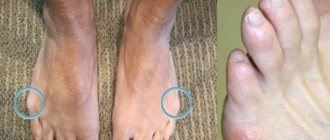
Deformation of the “bones” of the big toes is one of the common problems that affects the fair sex. In men, this disease occurs only in 2% of cases. This disease not only disfigures the foot and forces women to forget about dress shoes, but also causes pain, inflammation, suppuration, and calluses.
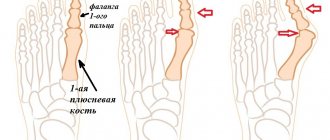
“Bumps” on the feet appear as deformities due to deviation of the first toe. The more the first finger deviates towards the small ones, the stronger the deformity becomes, and the “bumps” become painful and the limitation of movements in the joint progresses. Hallux valgus is a term that involves the outward and inward deviation of the first toe.
Peculiarities
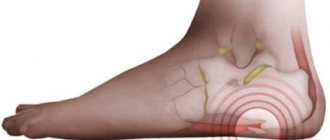
When there is a painful bulge on the outside of the foot at the base of the little toe, podiatrists diagnose Taylor's deformity, or "tailor's disease." For the first time, a detailed description and diagnosis was carried out by the American specialist H. Davis in 1949, noting complete identity with the development of Hallux Valgus.
An inflamed area forms on the lateral surface of the head of the little finger bone, causing the finger to deviate inward. The pain can radiate to the lateral part of the foot and provoke inflammation of the ligaments, bone and cartilage tissue. Characteristics:
- the forefoot expands, the angle between the 4th and 5th toes increases;
- the little finger takes on the shape of an arc; with the varus subtype, it can overlap the ring finger in a cruciform manner;
- a “bone” is formed on the outside.
For a long time, the pathology develops asymptomatically. The foot gradually increases in volume due to a growth, an increase in the fourth intermetatarsal angle. Conservative treatment eliminates the disease only at the initial stage. In most cases, surgery is performed using different methods.
Causes
The disease is not common, but is not a rare pathology. In most cases, orthopedists associate the appearance of a painful growth with genetic predisposition and hereditary risk factors. In many patients, the formation is observed on both legs at the same time.
When diagnosing the causes of Taylor deformity, they are conventionally divided into several types:
- Post-traumatic. The growth forms after a fracture, improper fusion of bones, against the background of frequent subluxations and dislocations.
- Structural. The reasons are associated with an abnormal disorder during the intrauterine formation of the arch of the foot. Genetically weak ligaments do not hold the fingers in the correct position when walking or running. Pathological redistribution of the load provokes expansion of the anterior section and its deformation.
- Functional. Congenital or acquired gait features in which the main load is on the outer part. The problem is exacerbated by wearing tight or narrow shoes.
The fifth metatarsal bone is often deformed due to congenital clubfoot, a pathological absence of small bones in the little toe area. In response to increased load, the bone head grows and changes in the structure of cartilage tissue occur.
The main factors that increase the risk of developing the disease:
- osteoporosis;
- rickets;
- inflammatory diseases of the joints;
- excess weight;
- abnormal structure of the foot;
- lack of physical activity, sedentary lifestyle;
- systemic connective tissue diseases;
- disruption of collagen production in the body.
The formation of growths is caused by the abnormal structure of the little finger, including the hammer-shaped or dumbbell-shaped bones. At risk are people with a history of cerebral palsy, Lederhosen contracture and meningitis.
An external cause of deformation can be wearing tight shoes with narrow toes and high heels. Such shoes connect the toes, incorrectly redistribute the load on the foot, provoke a fanning of the metatarsal bones, and deform the head.
What is hygroma?
If the tendon joints or joints of the foot are injured, under no circumstances should it be left unattended. In places where there is a tear, serious pathological changes often begin, connective tissue cells degenerate, and a tendon cyst is formed, which is called a “hygroma.”
Although the hygroma seems quite rigid to the touch, it is actually hollow inside. The shell is a cartilaginous capsule containing a thick yellowish mass. Hygroma cells divide, which explains its gradual increase in size.
Symptoms and signs
At the initial stage, the formation at the fifth finger is almost invisible. As you grow, the following symptoms are observed:
- throbbing pain, burning and discomfort, which intensifies when walking or active movements;
- aching pain in a resting position;
- problems when choosing shoes due to widening of the foot;
- painful callus at the base of the little finger;
- swelling;
- skin redness;
- the appearance of corns.
Anatomical changes in the structure of the foot lead to severe pain, forcing a person to change his gait. Often the joint acquires a hammer-shaped shape, the little finger extends onto the fourth finger,
Hygroma of the foot in a child
A bump on the instep of a child’s leg is a rare occurrence. Most often it occurs due to improperly selected shoes. To avoid such trouble in the future, try to prevent your child’s shoes from being too small, stinging his toes, or rubbing against calluses. Watch the size carefully, do not let children wear what they have outgrown. The foot in such shoes bends and deforms unnaturally. The situation is further aggravated by the fact that the child’s bones and veins are fragile, and it won’t be difficult to damage them, but it may not be possible to restore them.
Also, hygroma on the instep of the foot can appear in child athletes who put a lot of stress on their legs. The health of such children must be monitored especially carefully.
Indications for surgery
At the initial stage, conservative therapy helps to reduce the load on the affected joint and reduce pain. But you can completely get rid of the deformity only with the help of surgery. Among the main indications for resection:
- persistent calluses that develop into purulent wounds, ulcers that threaten sepsis, necrosis of the skin;
- loss of elasticity of the ligamentous apparatus, inability to bend or straighten the little finger;
- loss of support on the foot, which makes it difficult for a person to stand or walk;
- frequent relapses of purulent bursitis;
- loss of sensitivity due to damage to nerve endings.
Taylor's deformity leads to decreased quality of life. Pain limits mobility and leads to disability at a young age. A persistent inflammatory process provokes the destruction of cartilage plates and accelerates the development of osteoarthritis.
The main indication for surgical removal of a bone growth is the results of radiography. When receiving the image, the orthopedist measures the angle between the 4th and 5th fingers and the size of the head of the joint. The choice of tactics may be influenced by the severity of the deformity, the presence of flat feet or club feet in the patient, the development of bursitis and other inflammatory processes.
Stages of hallux valgus deformity of the big toe
Traumatologists and orthopedists at the Komarova Clinic identify several stages of deformation:
- First stage: displacement no more than 20 degrees. There are no unpleasant sensations, only aesthetic inconvenience.
- Second stage: displacement of 20-30 degrees. When walking for a long time, pain appears.
- Third stage: displacement of 30-50 degrees. The bunion prevents you from walking, it hurts, and it becomes difficult to find comfortable shoes.
- Stage four: displacement greater than 50 degrees. Constant pain and ongoing inflammation bring suffering even at rest. The deformity begins to affect other phalanges of the fingers.
Features during operations
The mechanism of development of Taylor's pathology or tailor's disease largely mirrors the pathogenesis of hallux valgus in Hallux Valgus. this allows surgeons to use identical treatment and surgical techniques.
The purpose of surgical intervention is to restore the biomechanical connections in the forefoot, improve the condition of the ligamentous apparatus, and eliminate the aesthetic defect. It is necessary to remove the valgus deformity of the fifth metatarsal bone and return the parabola of the little finger to its natural position.
The first practices of surgical treatment of a diseased leg bone
At the beginning, the operations to treat the diseased bone were terrible. The orthopedic surgeon simply removed the protruding part of the bone. After a while, the disease appeared again, and in a more acute form, and the pain became even stronger.
The next step in treatment was the Wreden operation, which was named after the man who created it - the famous Russian surgeon R.R. Harmful. The patient experienced less pain during this operation. The method involves completely removing the inflamed metatarsal bone on the big toe. As a result, the big toe ceases to be connected to the foot and is supported only by soft tissues. Oddly enough, when everything heals, people feel relatively well, the pain goes away, and the ability to walk and lead a normal life returns. This practice still exists today. It would seem that there is no need to further develop the treatment of a diseased bone, but medicine continued to progress.
Advantages of minimally invasive techniques
With early treatment, in 80% of cases, surgeons prescribe low-traumatic foot surgeries. The work is carried out through small incisions or pinhole punctures. Advantages of the methods:
- allow you to correct complex deformities in one procedure;
- give predictable results;
- You can operate on two feet at the same time;
- with the percutaneous technique, the patient can stand on his feet and move freely from the first day;
- no plaster cast or crutches are required.
Minimally invasive operations are highly specialized and are performed by highly qualified orthopedic surgeons using a special technical base.
Surgeries for Taylor deformity take from 25 minutes to an hour and can be performed on both legs simultaneously. In most cases, there is no significant blood loss, which shortens the rehabilitation period.
Removing a bump on the leg using traditional methods
to remove a bump on your leg using folk remedies . However, it is permissible to resort to such a technique only if an examination has been carried out and no oncological neoplasm, severe inflammatory processes, or damage to neighboring tissues have been detected.
If a “bone” appears on your toes or foot, you can use the following folk methods:
| Compress with clay | To prepare a medicinal compress you will need: · blue clay – 50 g; · iodine – 5 drops; alcohol infusion of chamomile. Pour chamomile infusion into the clay in a deep container. Add the infusion gradually to form a thick, creamy mass. After this, add iodine and mix vigorously. Apply the mixture to the leg in the area where the bump appears, wrap it in film or a plastic bag, and wrap it with a bandage on top. Keep the compress overnight, and in the morning wash your foot with soapy water. Repeat the procedure daily. This method perfectly eliminates pain, relieves inflammation, and over time allows you to reduce/completely remove the bump on the leg. |
| Compress with iodine and aspirin | Required components: · iodine – a whole small bottle; · aspirin – 6 tablets. Grind the tablets to a powder, pour the iodine into a bowl, combine both components and mix. Apply the compress for 1.5 hours. A burning sensation may occur. If it is not strong, you need to endure it. If severe discomfort occurs, you can add crushed aloe or Kalanchoe leaves to the mixture. In this case, the procedure time increases to 3 hours. The compress relieves swelling, eliminates pain, and allows you to reduce the size of the lump. |
| Compress with medical bile | Medical bile can be purchased at a pharmacy. Moisten a sterile bandage thoroughly with the undiluted mixture and apply to the area of the bump. Keep the compress throughout the night, repeat the procedure daily. Medical bile is a powerful pain reliever. In addition, it improves lymph outflow, normalizes blood circulation, and has a resolving effect. According to expert reviews, daily compresses with bile allow salt deposits to dissolve, the lump gradually disappears, and the foot acquires its previous correct structure. |
| Salt bath | To prepare a therapeutic bath you need: · sea or coarse table salt – 100 g; · hot water – 3 l. Pour salt into a bowl of hot water. Stir and wait until the water cools to a comfortable temperature. Place your feet in the basin and hold until the water becomes cool. Wipe your feet dry with a terry towel, do an intense foot massage, and put on warm socks. Salt baths perfectly relieve swelling, eliminate pain symptoms, improve lymph flow, which helps reduce the size of the lump. |
| Potato peel bath | Required: · potatoes – 1 kg; · hot water – 4 l. Peel the potatoes. Place the peelings in a saucepan with water (3 l), put on fire, and bring to a boil. Remove from heat, pour into a bowl, add another liter of hot water. Wait until the water reaches a temperature that is comfortable for your feet. The duration of the procedure is until the solution cools completely. Baths with potato peels will improve the condition of the skin of the legs, eliminate inflammatory processes, strengthen damaged ligaments and tendons, and accelerate the outflow of lymph. |
| Egg ointment | An unusual but very effective method for eliminating bumps on the foot. You need to put a whole raw egg in a glass and fill it with acetic acid. Wait until the eggshell has completely dissolved. After this, pour 15 ml of liquid turpentine into a glass. To obtain a thick mixture, add pork fat. Apply the resulting mass to the area of the cone twice a day. This recipe, when used regularly, will help you quickly get rid of the “bone” on your leg. |
If a bump on the leg is detected at an early stage, traditional methods will help not only relieve unpleasant symptoms, but will also allow you to get rid of the painful growth over time. To improve the therapeutic effect, it is recommended to combine the presented recipes with daily massage.
Main types of operations
If Taylor's pathology is diagnosed, doctors offer the following options for surgical removal of the painful defect:
- distal osteotomies (for types 1 and 2 of the disease);
- osteotomies at the level of the bone diaphysis (with type 2 or 3);
- operations in the proximal part for severe deformities of the 4th and 5th types.
In the latter case, the most popular and effective are: distal transverse osteotomy of the fifth metatarsal according to the method of Hohmann, Wilson, Mitchel, Helal and distal chevron osteotomy.
Some specialists prefer percutaneous distal osteotomy (Austin operation or CHEVRON), which aligns the axis of the foot. The technique is indicated for the formation of hammertoes and does not require intervention on the ligamentous apparatus.
In most cases, soft tissue surgery is additionally performed. Special plastic surgery involves excision of part of the damaged capsule, which remains in a stretched position after removal of the bone exostosis. The surgeon transposes the tendon from the main phalanx of the toe to the metatarsal head to hold it in the correct position.
Classic exostosis removal
At the initial stage, a minimally invasive technique is recommended, in which the surgeon makes punctures at the base of the finger. Using a special thin drill, it grinds down and removes bone growth and corrects the shape of the head, making it more natural.
On the inside of the foot, a thin triangular cut is made through a second puncture in the body of the metatarsal bone. The head is lowered into the formed recess, the finger takes the correct position relative to the longitudinal axis. The punctures are closed with intradermal sutures, a corrective bandage is applied to the foot and tightly fixed during dressing.
Operation by SERI
A minimally invasive method is recommended for stages 1 and 2 of Taylor's disease. During the procedure, a small incision is made on the outside of the foot, through which the surgeon removes up to a third of the head of the bone. After reducing the deformed area, the finger is fixed in its natural position using short-length metal knitting needles. In this case, the specialist does not touch the tendons, which reduces the recovery and healing time of the wound.
A characteristic feature of the operation using the SERI method is that the work is performed through an incision no more than 2-4 cm long. The wires hold the head of the bone in the correct position. The muscle frame is gradually formed. After complete healing and rehabilitation, the metal rods can be removed.
CHEVRON
Chevron osteotomy has been used to correct deformities since 1962. The operation allows you to reduce the angular dimensions and bring the 4th and 5th metatarsal bones closer together, reconstructing their anatomical position. An incision of no more than 3-4 cm is required.
Main stages:
- the surgeon cuts the skin on the foot under the damaged metatarsophalangeal joint;
- expands the joint capsule and injured ligaments, excises fibers that have shrunk due to deformation;
- after compression of the operated ligaments, the angle between the 4th and 5th bones decreases, the cause of the pathology is eliminated;
- the doctor makes an additional incision on the side of the foot and removes the bone tumor;
- moves the head of the bone, fixes the little finger with a titanium bolt or staples.
At the last stage of the operation, fluoroscopy of the foot is performed: the surgeon needs to make sure that the metatarsal bones are correctly positioned. The bolts must remain in the leg for at least 3 months.
Scarf osteotomy
For moderate and severe forms of deformity with an angle of up to 40°, scarf osteotomy is used. It allows you to eliminate the strong rotation of the little toe relative to the foot and the longitudinal axis. Advantages of the technique:
- allows the doctor to shift and rotate bone fragments to achieve optimal connection and correct position;
- if necessary, it is easy to shorten the metatarsal bone or lengthen it in case of a congenital anomaly or lack of longitudinal size;
- you can move the fragment up or down to correct the load when walking and reduce the risk of relapse;
- the surgeon can simultaneously correct the valgus deformity at the base of the big toe, which often complicates the course of Taylor syndrome.
During a Scarf osteotomy, the surgeon makes a thin incision on the side of the foot and divides the metatarsal bone in a zigzag (Z-shape) pattern, completely separating the head. Using a titanium bolt, it strengthens it in the anatomically correct position, while simultaneously adjusting the length and angle between the fingers.
During the operation, the tendons are additionally strengthened and, if necessary, cut and shortened. This increases the flexibility of the fibers and helps keep the bone in the anatomically correct position. All manipulations are performed under general anesthesia.
Weil's operation
With severe flat feet, patients often develop hammertoe and claw-like curvature of the 4th toe. The combination with curvature and cruciform overlap of the little finger leads to partial loss of support and gait disturbance.
Bayle's operation is performed under conduction or spinal anesthesia. For additional correction of hallux valgus, general anesthesia is recommended. During manipulations, the surgeon shortens the metatarsal bones of the deformed fingers, restoring their correct direction relative to the longitudinal axis. This allows you to change the load when walking and eliminate hypertonicity of the extensor apparatus.
Open angle osteotomy
It is performed from the inside, preserving bone tissue. During manipulation, part of the metatarsal bone is not shortened, but lengthened. Recommended for congenital pathologies and deformities associated with arthrosis. For plastic surgery, a fragment of pseudoexostosis is used, which is secured with titanium knitting needles and bolts. The technique is used to a limited extent and is often combined with other methods of treating Taylor syndrome.
Oblique diaphyseal rotational osteotomy
Indicated at an intermetatarsal angle of 12°. The surgeon removes the plantar surface of the head of the little finger bone at the bottom. The technique is used as a last resort in the absence of effectiveness from other methods of treating tailor's foot. Contraindicated in case of poor blood supply to the lower extremity, does not exclude repeated deformation.
Postoperative measures
- You should not put any weight on your leg for some time after surgery. Keep it quiet often to ensure successful healing.
- If necessary, take care of the postoperative suture at the site of excision of the hygroma. The doctor will tell you all the necessary information.
- Follow all medical recommendations. You may be prescribed a complex of vitamins and minerals to strengthen bones and tissues.
- Try to eliminate the unfavorable factor that led to the lump. Change your shoes to more comfortable ones, do your work more carefully, otherwise the hygroma will appear again.
Preparing for surgery
In most cases, manipulations are performed under spinal anesthesia. To exclude complications and develop a surgical plan, the patient is prescribed the following preparatory procedures:
- radiography of the foot in two projections;
- blood chemistry;
- coagulogram;
- tests for sexually transmitted diseases, HIV, hepatitis C;
- Ultrasound of the lower extremities;
- X-ray of the chest and respiratory organs.
For chronic diseases of the cardiovascular and endocrine systems, additional consultation and examination by specialized doctors is required.
We diagnose correctly
In order for the diagnosis to be made correctly and treatment to be prescribed in a timely manner, it is necessary to accurately determine the nature of the origin of the lump on the instep of the leg. For this, the following medical diagnostic methods are used:
- Ultrasound. Using this method, you can determine where the tumor is located and what size it is.
- X-ray. Allows you to accurately determine the location of the lump and prescribe further treatment. Intraosseous damage or joint injuries are clearly visible on x-rays.
- Magnetic resonance or computed tomography. Used in particularly serious cases where internal damage cannot be seen using the two previous methods.
- Diagnostic puncture. The most accurate way to determine the nature of a neoplasm. To do this, the internal contents of the cone are taken for examination with a special needle. Using a puncture, the benign quality of the lump is determined.
Only a doctor can prescribe one or another diagnostic method for you, based on the results of an external examination.
Rehabilitation period after surgery
On the first day, the patient is recommended to remain in the clinic under the supervision of a surgeon. The patient is fitted with special orthoses - Baruk boots, which, when walking, relieve the load from the forefoot and toes on the heel. These shoes must be worn for at least 6 weeks. In a difficult situation, you can additionally rely on crutches and limit physical activity.
After surgery, for 2 weeks it is recommended:
- bed rest;
- place a pillow or cushion under your feet to stimulate the outflow of excess fluid;
- for severe pain, apply cold compresses for 30 minutes up to 4 times a day.
To reduce pain, the doctor selects medications individually and calculates the dosage for home use. Swelling begins to decrease on the 3rd–5th day after surgery. After 14 days, it is recommended to visit the surgeon again to remove the skin sutures.
After 6 weeks, the patient is sent for a repeat x-ray. With pronounced positive dynamics and the absence of contraindications, walking without corrective orthoses with a load on the toes is allowed.
In some older patients, swelling may persist for a long time, which is associated with decreased tone of the veins of the extremities. In such a situation, lymphotropic therapy and contrast foot baths are prescribed.
Expert advice
- Attempts to open or pierce a hygroma on your own, in the hope that the contents will come out and it will resolve, are strictly prohibited. This will not happen, you will only harm your health and make the situation worse.
- On the injured area of the foot, use special soft inserts when wearing shoes. If the hygroma causes severe inconvenience, you can try special orthopedic shoes.
- Folk remedies should be used only in addition to the main one. And do not forget about the need to consult a specialist. Don't self-medicate!
Contraindications for surgery
Absolute or temporary restrictions for performing an osteotomy on the foot are:
- osteoporosis and reduced bone tissue regeneration;
- exacerbation of rheumatoid arthritis;
- obesity 3-4 degrees;
- acute stage of infectious diseases.
Minimally invasive surgeries are allowed for varicose veins and joint bursitis.
Taylor syndrome leads to the formation of a painful growth at the base of the little finger, swelling, and calluses. New methods of surgical treatment can relieve the patient of complications and restore lightness to his gait.