The sensation of shooting pain between the ribs on the side will cause concern in any person. The first thing that comes under suspicion is the heart. But a disease such as intercostal neuralgia has a similar localization. To correctly diagnose pathology, it is important to know its causes and symptoms. What is included in the complex of treatment and prevention, read on.
What is intercostal neuralgia?
Neuralgia of the intercostal nerves is pain of a different nature that occurs due to various etiological factors. It is more often observed in adult men and women over 30-35 years of age. Symptoms of neuralgia may appear suddenly on one or both sides of the chest, along one or more intercostal nerves. The disease has an ICD code - M.79.2.
To understand what intercostal neuralgia is, you should understand the anatomical features of the thoracic nerves. There are 12 pairs in total. Each intercostal nerve contains motor, sensory and sympathetic fibers. It originates from the anterior roots of the spinal cord of the thoracic spine, passes along the lower edge of each rib, reaching the sternum. The parietal pleura covers the nerve fibers on top.
Thoracic nerves transmit impulses to the skin, the musculo-ligamentous apparatus of the chest and the anterior wall of the abdomen, partly the pleura and peritoneum, and the mammary glands. Sensitive fibers of neighboring nerve trunks actively interact with each other, creating cross innervation.
How to distinguish intercostal neuralgia from heart disease?
If neuralgia has acute symptoms in the thoracic region on the left side, differential diagnosis with heart disease must be carried out. You should not look for the cause of the pain syndrome on your own. Thoracalgia on the left side should always be a reason to consult a doctor.
Heart pain and symptoms of intercostal neuralgia on the left have distinctive features:
| Intercostal acute neuralgia on the left: typical symptoms | Cardiovascular diseases: characteristic manifestations |
| The pain intensifies with forced breathing, coughing, sneezing, laughing, physical exertion and movement, but does not change with fast walking and excitement. | The pain does not change its intensity with a deep breath or muscle tension, but intensifies with cardio exercise (fast walking, running, climbing stairs). |
| Chest neuralgia is not relieved by taking nitroglycerin | With angina pectoris, the pain attack goes away within 3-5 minutes after using nitroglycerin. With myocardial infarction, severe pain cannot be relieved with medications. In this case, you should immediately call an ambulance. |
| Normal pulse and blood pressure are determined | Changes in heart rate and blood pressure |
| Pain increases with palpation of the ribs and spaces between them | The intensity of pain does not change when palpating the intercostal spaces |
| Painful symptoms on the left “go” along the nerve or are encircling in nature | Pain is localized behind the sternum or in the projection of the heart |
Symptoms of intercostal neuralgia on the left and right should also be differentiated from other diseases (pleurisy, pneumonia, thoracic aortic aneurysm, pericarditis, acute pancreatitis and others). If there is severe pain in the chest, only a doctor can determine exactly what it is - neuralgia or another pathology.
Causes of intercostal neuralgia and risk factors
Intercostal neuralgia can develop for a variety of reasons. Among them are:
- injuries to the thoracic nerves, chest and spine;
- surgical interventions, long-term immobilization of a person in a certain position;
- poisoning with chemicals, prolonged use of medications;
- congenital developmental anomalies, hereditary diseases;
- infectious processes (shingles, tuberculosis, brucellosis and others);
- some neurological diseases, such as radiculitis and multiple sclerosis;
- diseases of the spine (osteochondrosis, deforming spondylosis, herniated intervertebral discs);
- compression of nerve branches in the bone-connective sheaths, for example, in the presence of scar changes, benign or malignant neoplasms;
- immunodeficiency (HIV infection, cancer, etc.);
- allergic reactions;
- diabetes;
- various metabolic disorders in nervous tissue and its hypoxia;
- lack of B vitamins in the body;
- alcohol abuse;
- osteoporosis;
- pathology of nearby anatomical structures (aorta, lungs, pleura);
- various systemic diseases (atherosclerosis, rheumatism, anemia, thyrotoxicosis, etc.).
More often, chest neuralgia appears due to several causes. Therefore, it is typical for older patients with vascular, degenerative and metabolic disorders. Sometimes symptoms of neuralgia appear after excessive physical activity, sudden movements or prolonged stay in one position. They can also occur after hypothermia or severe stress.
More often, intercostal neuralgia is observed on the left or right; less often, there is a bilateral lesion. In most cases, the pathogenesis is based on muscle spasm, leading to compression of nerve fibers. Pain occurs in response to nerve damage.
In children, signs of intercostal neuralgia are rare. When they appear, parents should definitely show the child to the doctor, as this may be a signal of the presence of a serious pathology. The doctor will determine the possible causes and explain how to cure intercostal neuralgia in this case.
Treatment of pain between the shoulder blades
In the vast majority of cases, conservative therapy is initially prescribed. It is especially effective when intervening during the pathological process in the early stages and allows you to completely eliminate the changes that have arisen. Only if severe complications develop, the patient is immediately referred for consultation to a neurosurgeon, since in case of sequestered intervertebral hernia, severe curvature of the spine or advanced spondylosis, the patient’s condition can only be improved through surgery. Therefore, it is important to consult a doctor as soon as possible if pain occurs between the shoulder blades.
Conservative therapy is always comprehensive and involves taking measures to improve the patient’s well-being, as well as eliminating the cause of discomfort. Its main components are:
- drug therapy;
- osteopathy;
- manual therapy;
- massage;
- physiotherapy (phonophoresis, carboxytherapy, ozone therapy, RF current pressure therapy);
- individual sessions with a rehabilitation doctor.
To increase the effectiveness of treatment, neurologists recommend that patients reconsider their habits and lifestyle, in particular:
- normalize weight (but strict diets and excessive physical activity are unacceptable; a transition to a balanced diet and moderate physical activity is recommended);
- refuse to lift and carry heavy objects, grueling workouts in the gym;
- workers in “sedentary” professions should increase their level of physical activity, do a warm-up every hour, and walk more;
- buy an orthopedic mattress and pillow;
- introduce into your daily diet foods rich in vitamins and minerals (fresh fruits and vegetables, dairy products, etc.).
Regular swimming has a very positive effect on the condition of the spine and the body as a whole. Usually visiting the pool 2-3 times a week is enough.
Drug therapy
The main goals of drug therapy are to eliminate pain between the shoulder blades, inflammation and activate the body's recovery processes. For these purposes, patients are prescribed:
- NSAIDs are non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, widely used both to relieve various types of inflammatory processes and to eliminate pain;
- corticosteroids are drugs that have a powerful anti-inflammatory effect and are prescribed to patients with severe inflammatory processes that cannot be eliminated with NSAIDs;
- muscle relaxants - medications that help eliminate muscle spasms caused by pain of vertebrogenic origin;
- chondroprotectors are drugs used in the initial stages of degenerative processes in the intervertebral discs and help restore their elasticity and strength. To prevent diseases of the musculoskeletal system, we recommend to our patients the most effective drug Mermaids Marine Collagen;
- B vitamins – agents used to improve nerve conduction and improve the functioning of internal organs;
- vitamin D is a remedy responsible for the condition of bone tissue, as well as for higher brain functions, such as memory, attention, speech.
If the patient has detected pathologies of the heart, gastrointestinal tract and others, additional treatment is prescribed, which involves the use of antibiotics, proton pump inhibitors, antihypertensives or other drugs.
Manual therapy
Manual therapy can be called the basis of the treatment of spinal diseases. It should not be confused with therapeutic massage. If the latter only allows you to improve the condition of soft tissues and activate blood circulation, then manual therapy involves the direct impact of a specialist’s hands on the spine.
Thanks to the use of certain techniques of manipulation, mobilization, post-isometric relaxation, osteopathy and especially the Gritsenko technique, it is possible not only to restore the correct position of the vertebrae and the straightness of the spinal column, but also to increase the distance between them to the optimal value. Due to this, the pressure on the intervertebral discs sharply decreases, which creates optimal conditions for their regeneration. Also, a chiropractor can eliminate the pressure of various anatomical structures on the spinal roots, due to which the radicular syndrome is overcome, i.e. pain in the hands, sensory disturbances, a feeling of numbness go away, and the functioning of the pelvic organs also normalizes. There are no general standards of treatment in our clinic; an individual approach is applied to each patient.
In addition, manual therapy allows you to eliminate functional blocks and muscle spasms, which has a beneficial effect on a person’s mobility and well-being. Since normalization of muscle tone reduces pain between the shoulder blades, improves tissue trophism and transmission of nerve impulses. The manual effect itself, as well as with therapeutic massage, has a beneficial effect on the quality of blood circulation. Thanks to this, all tissues receive the maximum of the substances they need, subject to the correct diet and taking medications prescribed by a doctor, which contributes to their speedy recovery.
An additional “bonus” of manual therapy carried out according to the Gritsenko method is strengthening the immune system and enhancing the body’s adaptive abilities. Patients may notice the first improvements in well-being after the first session. But to obtain the maximum possible, and most importantly, lasting result, you need to undergo a full course of treatment, the duration of which is selected individually.
Physiotherapy
Physiotherapeutic procedures are prescribed outside the acute period of the disease. With their help, you can potentiate the effect of other therapeutic measures, as well as achieve analgesic, anti-inflammatory, reparative, antispasmodic effects, as well as improve microcirculation in tissues.
Often, for spinal pathologies, courses are indicated:
- electrophoresis;
- traction therapy;
- laser therapy;
- ultrasound therapy;
- UHF, etc.
Exercise therapy
Exercise therapy is an essential component of the treatment of almost any disease. It involves daily performance of a set of exercises individually developed by a rehabilitation doctor that will help normalize muscle tone, activate blood circulation and increase the flexibility of the spine.
It is important not to use the complexes presented on the Internet, but to contact a specialist who will individually develop a training program for a specific patient. In this case, it will take into account not only the peculiarities of the condition of the spine, but also the age of the patient, any concomitant diseases he has, as well as the level of physical fitness, which will allow achieving the maximum effect from the exercises and eliminating the possibility of harm to the person.
The first classes are recommended to be carried out under the supervision of a doctor. This is necessary so that the patient can fully master the technique of performing each exercise and perform it correctly in the future at home. During exercise, it is important to avoid any sudden movements and overexertion, and if pain occurs, you should immediately contact your doctor.
Thus, pain between the shoulder blades may indicate the development of serious diseases. Therefore, when it appears, you should not hesitate to contact a specialist, otherwise the disease can lead to complications of various types, including disability. If you start treatment right away, you can almost always quickly achieve complete recovery of the body and eliminate the pain syndrome, along with the causes that cause it.
0 0 votes
Article rating
Forms of the disease
Chest neuralgia can be primary (an independent pathology) and secondary (a symptom of another disease). There are also radicular and reflex forms of the disease. In the first case, symptoms of intercostal neuralgia on the left and right arise due to irritation of the spinal roots. The second type of pathology occurs due to a negative effect on peripheral receptors.
In addition, clinicians distinguish the following types of thoracic neuralgia:
- musculoskeletal;
- vertebrogenic;
- spicy;
- chronic;
- right-sided;
- left-handed;
- psychogenic;
- during pregnancy.
Intercostal neuralgia of a certain type has its own characteristic symptoms and treatment features.
Symptoms
Symptoms of spinal root impingement are similar to those of degenerative spinal diseases. To accurately determine the pathology, the help of instrumental analysis methods and additional research will be required. The main symptoms of the disease include:
- If the sciatic nerve is pinched, there is a burning sensation and pain at the site of the pathological process (lower back), numbness of the lower extremities and a tingling feeling. In advanced cases, there is disruption of the internal organs of the pelvis, spasm of muscle tissue and pain radiating to the rectum.
- With chest compression - pain radiating to the upper extremities, intercostal neuralgia, pain in the heart, shortness of breath and difficulty breathing. Intercostal neuralgia is observed in the patient on a constant basis, due to which the patient cannot sleep, breathe and eat normally.
- If the cervical region is affected, severe headaches, spasms of the neck muscles, increased pain when turning the head and sleep disturbances. When the patient’s head remains in one position for a long time, and then tilts sharply, the person experiences darkening of the eyes. You can read more about pinched nerves in the cervical spine in this article.
As soon as the first symptoms of pathogenesis appear, the patient should go to the hospital. In the absence of characteristic signs and timely treatment, a simple pinching can develop into inflammation of the nerve endings of the spine.
No ads 1
Symptoms of neuralgia on the right and left
Any neuralgia, including intercostal neuralgia, is primarily pain. Painful sensations can be of a different nature (aching, dull, sharp, piercing, burning) and have different intensity. Sometimes the pain is so severe that it forces a person to take a forced position and sharply limit physical activity. Intercostal neuralgia, which has pronounced symptoms, is described by patients as a lumbago or electric current discharge running from the spine to the sternum.
Thoracalgia often begins gradually, with a tingling sensation in the intercostal spaces, then acquires pronounced intensity. Less often it occurs suddenly. The pain can radiate to the scapula, epigastric area, heart, arm and lower back. Sometimes it takes on an encircling character. It intensifies with changes in body position, movements, coughing and deep breathing.
As a rule, painful attacks are constantly repeated, lasting from a few seconds to 2-3 minutes. Therefore, treatment of acute intercostal neuralgia on the right and left, first of all, always begins with the elimination of pain.
In addition to thoracalgia, a person may be bothered by characteristic local signs caused by the influence of sympathetic, sensory and motor nerve fibers. Intercostal neuralgia, depending on the damage to a particular nerve, will have characteristic symptoms on the right, left or both sides of the chest:
- impaired sensitivity, crawling sensation, numbness, tingling;
- muscle twitching;
- increased sweating;
- change in skin color.
If chest neuralgia appears against the background of a herpes infection, it may be accompanied by skin rashes. The latter appear 2-4 days after the onset of thoracalgia. Elements of the rash are located on the skin of the intercostal space in the form of small pink spots, which then turn into vesicles and then into crusts. Subsequently, traces of pigmentation may remain on the skin.
Types of pain between the shoulder blades
The nature of the pain can say a lot about the reasons for its occurrence. The pain between the shoulder blades is most often aching, pulling. Therefore, they rarely force people to immediately seek medical help, which leads to the progression of existing diseases. They recur regularly and can persist for quite a long time, which indicates a chronic course of the pathology.
Acute pain in the upper back occurs quite rarely. They appear suddenly, quickly intensify and then gradually disappear. They are the ones who most often bring patients to the doctor. Although chronic mild pain is an equally compelling reason to consult a specialist.
Often the appearance and intensification of pain is facilitated by:
- physical exercise;
- prolonged maintenance of a static position, including prolonged sitting or standing;
- sleeping in an awkward position.
Pain between the shoulder blades can also be burning, which requires making an appointment with a doctor as quickly as possible, and in some situations, receiving emergency medical care.
Initially, pain between the shoulder blades can eventually begin to radiate to the neck, arms and shoulders. This is often accompanied by a feeling of numbness, goosebumps or other sensory disturbances, as well as limited mobility of the arms and body or disturbances in the functioning of internal organs, i.e. the development of radicular syndrome.
It is a consequence of compression of the spinal roots by intervertebral discs, vertebral bodies, their processes or other anatomical structures. In this case, the localization of discomfort directly depends on the level at which spinal motion segment the compressed spinal root is located. If the nerves localized at the level of the first thoracic vertebra are pinched, sensory disturbances will be observed on the inner surface of the forearm, shoulder, and also in the armpit. And with compression of the nerves located at the level of the last, 11-12th vertebra of the thoracic spine, the development of pelvic organ dysfunction is possible, which may be accompanied by disturbance or loss of control over urination and defecation.
Diagnosis of intercostal neuralgia
Make an appointment Shpigel Anna Yakovlevna Neurologist, massage therapist 33 years of experience. The specialist receives: - newborn children and schoolchildren - adults - athletes Reviews from patients Consultation from 3000 rubles.
Acute intercostal neuralgia is a reason to contact a competent, qualified neurologist. Since symptoms in adults with damage to the thoracic nerves can be disguised as other diseases, the patient must undergo a comprehensive examination to exclude possible pathology. The doctor must conduct a survey and examination.
The person’s posture is noteworthy when he leans towards the healthy side, so as not to provoke a painful attack. Palpation of the chest reveals pain. Trigger points are identified at the lower edge of the rib, where the affected nerve passes. If neuralgia affects several nerve branches, which often happens, this leads to a decrease or complete loss of sensitivity in the corresponding area of the body.
First of all, the doctor must distinguish the symptoms of intercostal neuralgia on the left from cardiovascular pathology. For this purpose, the patient undergoes an ECG. If indicated, a cardiologist is consulted. In order to correctly diagnose and treat intercostal neuralgia, the doctor also excludes diseases of the respiratory system, digestive tract, musculoskeletal system, infectious processes and other diseases. He may prescribe a number of additional tests (laboratory tests, x-ray of the lungs, ultrasound of the abdominal organs, MRI of the spine, etc.).
Thoracic neuralgia is an indication for electroneurography. This method allows you to determine the condition of nerve fibers by assessing their structure and functionality.
Chest neuralgia can be a manifestation of benign and malignant tumors. It is often the first symptom of a herniated disc and degenerative changes in the spine. Therefore, early identification of its causes is considered an important task for the neurologist and the patient.
Causes
The spinal cord is an organ of the central nervous system. It is located in the spinal canal, on one side formed by the vertebral bodies together with the cartilaginous layers separating them (intervertebral discs), and on the other by the bony processes of the vertebrae. Thus, nature took care of protecting such a delicate and important organ for human life as the spinal cord.
The vertebral processes connect at several points, thereby forming natural openings called foraminal openings, through which the nerve roots extending from the spinal cord exit. They are large nerve fibers. As they move away from the spinal cord, they branch more and more into smaller fibers and reach all organs and parts of the human body, ensuring the transmission of appropriate signals to them that regulate their functioning.
Each spinal root is formed by sensory and motor nerve fibers. The first ones depart from the spinal cord from the side of the vertebral processes, i.e., closer to the back of the body and are therefore called posterior. The motor roots are located almost adjacent to the vertebral bodies and intervertebral discs and are called anterior. Thus, from their names it is clear that the anterior roots are responsible for motor capabilities and are responsible for muscle contraction, while the posterior ones transmit signals to receptors that must respond to the action of various kinds of irritating factors: touch, rough blows, etc.
As already mentioned, the spinal roots exit on both sides of the spine through natural openings formed by the arches and processes of the vertebrae. Therefore, any changes in the condition of the spine and the surrounding soft tissues can affect the condition of such important nerves and lead to the development of radicular syndrome.
The bulk of cases of radiculopathy occur in diseases accompanied by degenerative changes or inflammatory processes in the spine and surrounding tissues. In the latter case, it is provoked by a reflex muscle spasm that occurs in response to pain, or swelling of the soft tissues.
The most common causes of radicular syndrome are:
- osteochondrosis;
- protrusion and intervertebral hernia;
- spondylosis;
- spondyloarthrosis;
- spondylolisthesis;
- traumatic injury to the spine;
- infectious diseases of the spine;
- neoplasms.
The significant “rejuvenation” of radicular syndrome is largely due to changes in the lifestyle of modern people for the worse. It is excess weight, a sedentary lifestyle, bad habits, stress and lack of habit of maintaining posture that become the main reasons for the development of the above diseases, which in turn cause the occurrence of radiculopathy. All of them contribute to poor circulation, which becomes a “trigger” for the occurrence of degenerative changes in the cartilage tissue of the intervertebral discs and the development of corresponding pathologies.
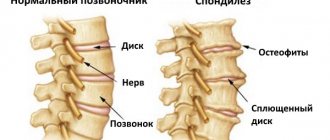
Osteochondrosis
Osteochondrosis is a chronic disease in which there is a gradual destruction of the intervertebral discs against the background of degenerative-dystrophic changes occurring in them, i.e., the cartilage located between the vertebral bodies, acting as shock absorbers and ensuring the flexibility of the spine. They gradually become thinner and lose their natural elasticity. This leads to the fact that the bodies of neighboring vertebrae come closer together, and the diameter of the foraminal openings decreases, which can result in pinching of the spinal roots.
Protrusions and intervertebral hernias
Protrusions and hernias are one of the consequences of osteochondrosis, accompanied by deformation of the shape of the intervertebral disc and its protrusion. Initially, a protrusion is formed. This means that the disc is already deformed, but its outer shell (annulus fibrosus) still retains its integrity. If untreated, it ruptures in the most vulnerable place, which leads to the loss of internal contents (nucleus pulposus) into the spinal canal or the area from the front of the spine, i.e. the formation of a full-fledged intervertebral hernia.
Both protrusion and hernia can compress the spinal roots, either just one of them or both at once. This directly determines on which side neurological disorders will be observed. Large hernias and sequestered ones, that is, separated from the intervertebral disc, can also compress the spinal cord itself, which is fraught with serious complications. If the sequester begins to move along the spinal canal, this will be accompanied by the appearance of signs of damage to those nerve roots to the level of which it descends. If it reaches the lumbosacral region and the large bundle of nerves located there, called the cauda equina, it can lead to paresis and paralysis of the lower extremities.
Spondylosis
Spondylosis is another complication of osteochondrosis, in which the intervertebral discs wear out and become so thin that the vertebrae come together to a critically close distance. Against this background, their deformation occurs, which is accompanied by the formation of bone outgrowths called osteophytes on their edges. Over time, adjacent vertebral bodies can firmly fuse together, which leads to severe pinching of the spinal roots.
Spondyloarthrosis
This disease means the destruction of the facet joints, i.e., the place where the processes of the vertebrae meet. It involves damage to all elements of the joint, including its capsule, ligaments, surfaces and even periarticular muscles. This may also be accompanied by the formation of osteophytes and pinched nerve roots.
Spondylolisthesis
Spondylolisthesis is a pathology of the spine in which the body of one or more vertebrae is displaced relative to the underlying one by a certain distance. Since this disrupts the spinal axis and displaces all the anatomical structures in this area, this leads to compression of the spinal cord roots or even the spinal cord itself.
Traumatic injuries
Spinal injuries are far from uncommon. Strong blows, falls from heights, road traffic accidents and other factors can lead to vertebral subluxations, fragmentation and compression fractures, which is almost always accompanied by the development of radicular syndrome.
Infectious diseases
From the point of view of the occurrence of radiculopathy, the greatest danger is posed by syphilitic and tuberculosis infections, as well as osteomyelitis and nonspecific bacterial meningitis. In such cases, damage to the nerves by pathogenic viruses and bacteria may occur, which will lead to their inflammation.
Neoplasms
The spine and spinal cord, just like other organs, can be subject to the formation of benign and malignant tumors. In addition, with oncological diseases of other organs, metastases can separate from the maternal tumor, which, through the bloodstream, enter the tissues surrounding the spine and can also provoke pinching of the nerve roots and the occurrence of corresponding symptoms.
One of the very common benign tumors of the spine is hemangioma. Many people are already born with such a vascular neoplasm located in the vertebral body, or acquire it with age. It is not dangerous, but it significantly increases the risk of spinal compression fracture.
How to treat intercostal neuralgia?
Treatment of any neuralgia, including intercostal neuralgia, is aimed at eliminating the clinical manifestations and causes of the disease. Therapy includes a whole range of activities. If a patient is diagnosed with neuralgia, you can find out how to treat it from the specialists of our clinic. The doctor will select the optimal therapeutic course, taking into account the characteristics of the disease and the individual characteristics of the person.
As a rule, intercostal neuralgia requires long-term treatment and further measures to prevent painful attacks. The doctor prescribes specific methods of therapy, determines the duration of each course, and gives his recommendations on lifestyle and regimen. The treatment plan may include:
- painkillers;
- etiotropic therapy aimed at combating the underlying disease;
- anti-inflammatory drugs;
- neurotropic drugs;
- physiotherapy;
- osteopathy;
- massage;
- Exercise therapy.
The doctor always chooses how to treat neuralgia, based on the clinical picture, the stage of the process, the results of diagnostic examinations and the individual characteristics of the patient.
Treatment of radicular syndrome
Treatment for each patient is selected individually depending on what disease caused the development of radicular syndrome. In the absence of a serious threat to the health and life of the patient, for example, sequestration of an intervertebral hernia or other severe complications, they initially try to relieve the nerves from compression using conservative methods. In such situations, in accordance with the diagnosis, patients may be prescribed:
- drug therapy, which consists in the use of NSAIDs in the form of injections, tablets, ointments or suppositories, chondroprotectants, muscle relaxants, vitamins (if the radicular syndrome is infectious, the use of antibiotics, antiviral and other agents is indicated);
- manual therapy, which helps eliminate functional blocks, normalize muscle tone, and most importantly, restore the normal position of the vertebrae and release compressed spinal roots;
- physiotherapy, which increases the effectiveness of other measures taken to treat radicular syndrome;
- Exercise therapy, which is an obligatory component of treatment and is necessary to improve blood circulation, strengthen muscles and prevent their atrophy.
In case of very severe pain, patients can undergo blockades of the corresponding spinal motion segment. They do not have a therapeutic effect, but are able to eliminate pain of any severity in a matter of minutes.
But conservative therapy does not always bring positive changes in the patient’s well-being. If the patient’s condition does not improve within 3 months after its onset, he will be indicated for appropriate surgery. Also, surgical intervention may be prescribed immediately if:
- large intervertebral hernias;
- sequestered hernias;
- dangerous tumors of the spine or surrounding tissues;
- spondylolisthesis and some other pathologies.
In each case, the method of surgical intervention is selected individually, based not only on what pathology was detected, but also on its severity. For example, for small intervertebral hernias, percutaneous surgery techniques can be used, in particular cold plasma nucleoplasty or hydroplasty. For larger intervertebral disc defects, endoscopic surgery or microdiscectomy is indicated. For large hernias, the only way out of the situation is microdiscectomy or open discectomy with stabilization with a metal structure. If the patient is diagnosed with spondylolisthesis, it will be possible to eliminate the radicular syndrome only by implanting special fixing titanium plates, etc.
Thus, the appearance of symptoms of radicular syndrome or radiculopathy is a reason to immediately contact a neurologist, conduct an appropriate examination and begin treatment. But even if there are indications for surgery, you should not be afraid of it. Modern spinal surgery techniques are highly effective, and they are much safer than non-intervention and the inevitable addition of complications and subsequent disability.
Is osteopathy effective for intercostal neuralgia?
The causes of neuralgia in the rib area can be different. However, in many cases, a pinched nerve is caused by the consequences of various injuries a person has received in the past. The capabilities of fine diagnostics using hands make it possible to identify and eliminate these disorders, which leads to the elimination of compression of the nerve and the restoration of its normal blood supply. As a result, inflammation and its integral companion – pain – go away. Osteopathy shows high effectiveness in the treatment of both unilateral and bilateral intercostal neuralgia.
Possible complications and consequences
Any neuralgia, in particular intercostal neuralgia, that does not respond to treatment, may be a sign of a serious illness. Most of the complications that arise with thoracalgia are precisely a manifestation of the underlying pathology, which worsens against the background of constant pain.
Chest neuralgia itself, with a long-term severe course, can provoke the development of a hypertensive crisis or an attack of angina (less often, myocardial infarction). Severe, constant pain affects a person’s physical and mental state in different ways. Often severe symptoms of intercostal neuralgia on the left or right significantly complicate the patient’s life. He sleeps poorly, is nervous, cannot move normally and do his usual work.
Pain in the intercostal spaces does not allow the patient to perform full breathing movements, which leads to a decrease in oxygen supply to the body and the development of hypoxia. Sometimes neuralgia is accompanied by such debilitating pain that it contributes to emotional exhaustion, and this is a serious complication, since this condition causes depression.
Neuralgia during pregnancy
If intercostal neuralgia appears in a pregnant woman, how to diagnose it and how to treat it is decided by a neurologist together with a gynecologist. Therapy is selected taking into account possible negative effects on the fetus. Self-medication in this situation is considered unacceptable, as this can have a negative impact on the health of the expectant mother and child.
To prevent chest neuralgia from appearing during pregnancy, it is advisable to follow preventive measures. If a woman has previously had attacks of thoracalgia, then at the stage of preconception preparation she should visit a neurologist and osteopath. The doctor will conduct a diagnosis, and then the neurologist will give a number of recommendations on how to treat intercostal neuralgia. An osteopath will identify possible causes of neuralgia and conduct a treatment session aimed at eliminating them.
Forecast and prevention of intercostal neuralgia
In most patients, intercostal neuralgia can be completely cured. If thoracalgia occurs against the background of a herpetic infection, relapses are possible.
If adequate treatment of neuralgia does not bring the desired result, a more “deep” diagnosis is carried out to search for the possible cause of this condition. First of all, spinal hernias, benign and malignant tumors are excluded.
To prevent neuralgia of the intercostal branches from recurring, and its symptoms in adults to manifest themselves less painfully, doctors recommend the following preventive measures:
- follow the canons of a healthy lifestyle: give the body adequate physical activity, eat right, actively relax in the fresh air, give up bad habits, etc.;
- maintain normal functioning of the immune system;
- monitor posture and spinal health;
- promptly treat chronic diseases and infectious processes;
- if possible, visit the pool and harden yourself;
- undergo preventive examinations on time;
- undergo regular scheduled examinations by an osteopath approximately once every six months.
If a person has previously had thoracic neuralgia, he should not be overcooled, be in a draft, expose the body to excessive physical stress, perform sudden movements or remain in an uncomfortable position for a long time. In addition, it is necessary to eliminate or minimize as much as possible stress and any unfavorable factors that can cause symptoms of intercostal neuralgia on the left, right or both sides.
Did you like the article? Add the site to your browser bookmarks
How to prevent a pinched nerve?
When the pain has passed and the disease has receded, you cannot relax. If pinching occurs, it may happen again. To avoid relapse, you must adhere to the following recommendations:
- Try not to overeat. It is better to eat more often, but in smaller portions. Otherwise, the load on the vertebrae will increase.
- It is advisable, if the slightest opportunity arises, to try to relax in sanatoriums and resorts located by the sea.
- Of course, you won’t be able to completely give up carrying heavy bags. But the weight should be lifted correctly, periodically changing the shoulder.
- When work involves a predominantly sedentary lifestyle, breaks are a must. You can do gymnastics or just walk back and forth.
- The chest must be kept warm. Clothes should be chosen only according to the weather.
It is recommended to do light gymnastic exercises in the morning or evening.