Ankylosis
- This is an absolute loss of joint mobility. In most cases, it develops against the background of previous injuries or progressive diseases; congenital cases can occur extremely rarely. Pathology can occur in various parts of the musculoskeletal system (MSA) of the human body, including the temporomandibular system.
The main symptom of ankylosis is loss of functionality of the musculoskeletal system.
With fibrous fusion, pain is observed, which intensifies significantly when testing loads and attempting to perform movements.
Diagnosis and the final diagnosis are carried out based on the results of a visual examination, as well as data obtained as a result of primarily x-ray examination.
Treatment of ankylosis is predominantly radical. It is possible to fix the limb in the most advantageous position for the patient. Restoration of mobility is achieved through plastic surgery or prosthetics in combination with medication and physiotherapeutic treatment.
General information
Ankylosis is a serious consequence of various types of injuries or diseases of the joints. Pathology can develop at any age, however, it is most progressive in middle or old age.
According to medical practice, ankylosis of the lower extremities is much more common than the upper extremities. Up to 50% of all diagnosed cases are due to pathologies in the knee.
Considering the features of the clinical manifestation, the closest attention should be paid to lesions of larger joints, as well as diseases of the musculoskeletal system, accompanied by ankylosing spondylitis.
General overview
According to research results, pathologies associated with dysfunction of the TMJ occur in patients of all age groups. Ankylosis, one of the forms of the disease associated with insufficient development of the mandibular region, is diagnosed mainly in men, and, due to its specificity, can be detected in the early stages of formation. A joint defect is associated with a violation of the aesthetic appearance, as a result of which patients consult a doctor at the first sign of a problem.
A characteristic symptom of ankylosis is the inability to fully open the oral cavity to perform basic functions, be it eating or articulation. As the pathology progresses, the limitation of mobility becomes more and more noticeable, which forces patients to limit themselves in the choice of food and ready-made meals, and also creates problems when communicating with other people. In addition, the manifestation of pathology at an early age entails deformation of the facial skeleton, accompanied by a violation of the shape of the bite and defects in the development of the dentition.
Causes of ankylosis
The development of pathology has certain prerequisites and is most often caused by tissue fusion or activation of inflammatory processes, as well as the characteristics of recovery processes after injury.
According to numerous studies and best practices of domestic and foreign doctors, it is customary to identify the following causes of ankylosis:
- previous infectious arthritis - negative pathogenesis can cause fusion of bone ends;
- rheumatic diseases - pathologies involving joint tissues and causing inflammatory processes, as well as the scar formations that follow them, provoke loss of mobility;
- various groups of osteoarthritis - degenerative type lesions provoke structural changes, which causes the formation of bone growths that limit or provoke loss of the ability to perform movements;
- previous injuries - serious fractures and various types of dislocations that occur in the background significantly increase the risk of developing pathology, especially in the presence of infection;
- restriction of movements - immobilization or, in other words, a prolonged lack of the required level of mobility of the musculoskeletal region leads to a shortening of muscle movements, forming certain changes. Soft tissue structures grow together, which leads to various types of pathologies.
Ankylosis in children
Since bone tissue is in the active growth phase at a young age, bone ankylosis predominates in children. They often become the result of purulent inflammatory processes, birth and other types of traumatic injuries (fractures, dislocations). In the absence of correct and timely treatment, complications develop that affect not only the damaged joint, but also other structures - shortening and curvature of the limbs, malocclusion, etc. (as active growth and maturation of tissues continues).
A common childhood pathology is ankylosis of the temporomandibular joint.
Pathogenesis of the disease
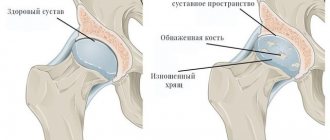
It is the cartilage that creates comfort and optimal conditions for free movement, ensuring the sliding of the surfaces that form the joint, the mobility of which is achieved exclusively due to the natural properties of the synovial membrane and, of course, the tissues adjacent to it.
The development of the pathology in question involves a violation of one or several links responsible for the mobility of the musculoskeletal system.
The most common sign of ankylosis is considered to be complete or partial loss of cartilage with the provoked fusion of joint surfaces and the proliferation of fibrous formations. In rare cases, cartilage fusion is observed.
Symptoms
Parents should be wary of the fact that their child’s baby teeth are not falling out. It is fused to the bone and cannot easily separate from the alveoli, as is normal. If the pathology is not detected and treated in a timely manner, the child’s jaw begins to develop incorrectly. The diseased tooth is located lower than the others, and the neighboring teeth are placed at an angle in relation to it. Problems with bite occur.
Another scenario is also possible. The baby tooth does not erupt completely and is delayed in its development. Because of this, the permanent tooth also cannot develop, and after the milk tooth falls out, it becomes fused with the jaw. This is how ankylosis of permanent teeth occurs. The final diagnosis is made after analyzing the results of a computed tomography scan.
Good to know. The service life of ankylosed teeth is completely different. They can last for decades or fall out, thinning out the dentition.
Classification of ankylosis
In modern medicine, it is customary to distinguish several types of ankylosis:
- fibrous ankylosis – development is typical in conditions of prolonged lack of movement, as well as the course of non-purulent chronic processes. With this type, the key sign of ankylosis is the connection of bones with fibrous tissue. The results of the X-ray examination suggest a slight deformity, but at the same time, they note the preservation of the joint space. Functional capabilities are largely lost, leaving only the ability to perform minor movements of small amplitude;
- bone ankylosis – formed after purulent arthritis or intra-articular fracture. The bones fuse into a single mass, which makes it impossible to determine the joint space on X-ray films;
- cartilaginous ankylosis - detected mainly at a young age. The formation is caused mainly by arthrogryposis. The key features are loss of mobility, as well as disruption of the configuration of the ends of the articular bones, which is clearly visible on the x-ray.
Treatment of nonunions, defects and false joints of bones
In most cases, bone restoration after a fracture occurs in normal or normal time, rarely in a shorter time. Much more often, the time for fusion is extended, although the fusion process itself proceeds normally and is not disturbed by anything.
Fractures with delayed healing include those in which, after the usual period of time sufficient for healing of the fracture, the ends of the fragments are not connected by a mechanically stable bone callus; clinically, some very limited mobility of the fragments at the level of the fracture is determined.
X-ray examination shows
- lack of bone fusion of fragments, their ends may be separate or small cavities are visible on them,
- the ends of the fragments have a sclerotic border,
- the medullary canal is not closed by a bone plate.
In all cases, first of all, one must strive to find out whether there are objectively ascertainable local or general causes that slow down or may slow down the process of fusion. In this case, it is necessary to take into account the different healing periods of fractures, which depend on their type, location, age of the patient, etc. It is known that different bones are restored in different periods. Fractures of the same bone at different levels also heal unequally quickly.
A thorough clinical analysis usually makes it possible to establish objective reasons delaying bone union, e.g.
- displacement of fragments,
- a small diastasis or gap between them,
- infection,
- sequestration,
- incorrect or insufficient immobilization, etc.
Elimination of these causes inhibiting fusion, creation of favorable conditions and, above all, good and continuous immobilization lead to normalization of the fusion process and the formation of callus.
The term persistently nonunion fracture, or pseudarthrosis, should be used only when, after a period sufficient for the formation of bone fusion, persistent abnormal mobility resulting from a disruption in the process of callus formation is clinically determined at the site of the former fracture.
Clinical and radiological data allow us to conclude that fusion of the fragments is impossible without appropriate intervention. A non-union fracture is clinically characterized by mobility of the fragments.
X-ray reveals that the periosteal callus did not fill the defect between the ends of the fragments and did not connect them with a bridge. Excess callus formed along the edges of the fragments becomes dense, the medullary canal of the ends of the fragments is closed by a compact layer of bone substance. In some cases, the ends of the fragments are rounded, sclerosed and become dense, in others, on the contrary, the ends are reabsorbed, they become sparse and rounded. The recovery process has completely stopped.
To heal pseudarthrosis (without a bone defect), it is enough to induce mesenchymal proliferation at the site of the damaged bone by mechanical and chemical means (tissue decay products), to ensure stable long-term immobilization of the fragments, after which, as a rule, the fragments grow together with callus. Emphasizing the diversity of pathogenetic factors and putting forward the concept of the role of developing limb diseases in the pathogenesis of pseudarthrosis, it should be noted that the principles of treatment of pseudarthrosis (i.e., fractures with persistent nonunion) and fractures with delayed union are nevertheless the same.
The basic principles of treatment of pseudarthrosis and fractures with delayed healing boil down to the following: creating conditions for restoring reparative regeneration in the area of the pseudarthrosis and fusion of fragments.
This is achieved
- ensuring complete immobility of fragments,
- bringing their ends together
- identifying and eliminating factors inhibiting fusion.
Symptoms of ankylosis
The symptomatic picture is formed individually and depends on the form and stage of the existing disease. It is worth noting that a general clinical picture is still identified, which is observed to some extent in most patients.
In connection with the above, it is worth paying special attention to such general symptoms of ankylosis as:
- pain caused by tension in the muscle frame, as well as their persistence due to a localized pathological process;
- stiffness, manifested mainly in the first hours after waking up from a night's rest (in the initial stages it goes away within half an hour, as it progresses, a longer period is required);
- mild swelling or noticeable swelling;
- local change in skin color (redness), accompanied by an increase in temperature;
- noticeable deformation (exclusively in the later stages), expressed in an increase in the size of the joint and the acquisition of uneven outlines.
It is also necessary to note the existence of a group of specific symptoms of ankylosis, which include:
- severe pain and swaying of the joint joint affected by the disease (with the development of the fibrous form);
- loss of the ability to move, accompanied by pain and severe discomfort (in the bone form).
Coalitions of the bones of the foot
Please see the relevant section of our website for information regarding what you may encounter after surgery.
You must understand that the following is only an approximate rehabilitation plan, while each patient’s recovery process is different. This information is intended to help you understand the essence of your condition, treatment and rehabilitation options. The time frames we have given are only a minimum, and when deciding in favor of surgical treatment, you should keep in mind that in your case the healing and rehabilitation process may take longer.
Early postoperative period
All operations for osteoarthritis of the subtalar joint are performed under general anesthesia.
After resection of the tarsal coalition
After surgery, the foot and ankle joint will be fixed with a posterior plaster splint while the surgical wounds heal.
Postoperative immobilization
Do not remove the splint until the next dressing change, which will take place 2-3 weeks after surgery.
You should not put any weight on your limb for approximately 2-3 weeks after surgery. Before you are discharged home, you will be advised by a physiotherapist, who will include: will tell you how to use crutches correctly.
In the first 2 weeks after surgery, try to elevate your foot and keep it in that position 95% of the time.
Elevated foot position
Most people certainly don't have a functional bed at home like the one in this photo. However, the same effect can be achieved on a regular bed or sofa by placing a pillow under your foot. You should not put your feet in an elevated position when you are sitting on a chair. And once again we advise you to stay at home for the first two weeks.
To minimize the risk of infection, keep your feet dry and cool. Avoid excess humidity and heat. When showering, wear a sealed bag over your foot.
In order to prevent venous thrombosis, regularly perform movements in the foot and ankle joint. Drink enough fluids. If you have risk factors for thrombosis, be sure to tell your doctor about this; if necessary, he can prescribe you anticoagulants.
Subtalar/triarticular arthrodesis addendum
You will spend the first night after surgery in the clinic, and the next day we will repeat antibiotic prophylaxis. Your foot and ankle will be immobilized in a rigid splint for 6 weeks after surgery, and you will not be able to put any weight on your limb for at least this period.
Two weeks after surgery
You will be examined by your doctor and your dressing will be changed. You will be allowed to drive for a short time, but only if your left leg has been operated on and your car has an automatic transmission. If the right leg has been operated on, we recommend driving no earlier than 6-8 weeks after the operation.
After resection of the tarsal coalition
If the healing process is going well, by this time your swelling and bleeding will have largely disappeared, but some swelling may persist for up to 3-4 months after surgery. If the wounds have completely healed, then we will tell you how to properly massage the tissues in the intervention area. Measures aimed at reducing the sensitivity of the scar begin only after the wound has completely healed. For this purpose, you can use a massage cream (for example, E45), which should be rubbed into the scar area and around it. You can expose the surgical area to moisture and take a shower only after the wounds have completely healed.
You will be advised to wear special orthopedic shoes for approximately 4 weeks.
At this stage we may refer you to the rehabilitation department. And this is the earliest time you can return to your job.
Subtalar/triarticular arthrodesis addendum
At this stage, if post-operative swelling has largely subsided, we will allow you to lower your foot down more often, but we recommend that you still keep it flat most of the time if possible. The ankle joint will be immobilized with a rigid bandage for another 4-6 weeks. Loading during this period is still prohibited. You can take short walks outside as long as your pain and swelling allow.
Six weeks after surgery
After resection of the tarsal coalition
Significant reduction in the severity of swelling and pain. You will be able to start wearing normal shoes (as swelling will allow), but we recommend wearing hard-soled shoes during this time. Over the next 3-6 months, you will undergo physical therapy classes, which will allow you to achieve the most optimal result of the surgical intervention.
Subtalar/triarticular arthrodesis addendum
If the healing process is going well, by this time your swelling and bleeding will have largely disappeared, but some swelling may persist for up to 4-6 months after surgery.
Depending on the results of the x-ray control, you will be advised to use an orthopedic boot that allows the possibility of weight bearing on the operated foot, or immobilization will continue and weight bearing will continue to be excluded.
If the results of X-ray control are satisfactory and postoperative wounds have completely healed, massage of the soft tissues in the surgical area and desensitization of the scar will be recommended.
Measures aimed at reducing the sensitivity of the scar begin only after the wound has completely healed. For this purpose, you can use a massage cream (for example, E45), which should be rubbed into the scar area and around it. You can expose the surgical area to moisture and take a shower only after the wounds have completely healed.
Three months after surgery
After resection of the tarsal coalition
If you are satisfied with the result, then this is your last visit to the doctor.
After subtalar/triarticular arthrodesis
Control radiography, which should show signs of consolidation. You will be able to start wearing normal shoes (as swelling will allow), but we recommend wearing hard-soled shoes during this time. Over the next 3-6 months, you will undergo physical therapy classes, which will allow you to achieve the most optimal result of the surgical intervention.
Current diagnostic methods for ankylosis
If you notice the presence of a number of signs or symptoms of ankylosis, you should immediately seek the help of a treating specialist.
Before diagnosing and starting treatment for the disease, you should understand which doctor to contact. Of course, it is recommended to visit a therapist who will collect anamnesis and recognize the existing disease. After an initial superficial diagnosis, a patient with ankylosis is referred to a traumatologist, orthopedist or surgeon.
As for diagnosis by highly specialized specialists, the first stage is a visual examination. Determining swelling or redness of the surrounding tissues, as well as changes in the shape of the joint and the degree of reduction in the range of available movements provide an opportunity to assess the patient’s condition and tell a lot about the existing disease, for example, the features of its course, the degree of progression and, of course, the prospects for recovery.
In order to accurately make a diagnosis and determine the type of illness, the patient is referred to instrumental diagnostic methods, which include radiography, MRI and CT.
Diagnosis of joint ankylosis
Diagnosis of joint ankylosis begins with a consultation with a surgeon or traumatologist. The patient's medical history is assessed, the range of motion in the affected joint is determined, and the further necessary plan for examination and treatment of identified ankylosis of the joint is formed.
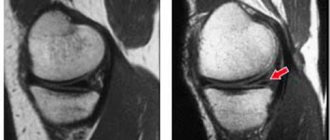
MRI of the knee joint in the sagittal plane (ligaments, meniscus, articular cartilage) with ankylosis.
Of the hardware methods for diagnosing joint ankylosis, a doctor can prescribe and carry out:
- CT joint (computed tomography)
- Joint MRI (magnetic resonance imaging)
- radiography of the joint (arthrography)
Treatment of ankylosis
Like any other disease of the musculoskeletal system, treatment of ankylosis involves a combination of available methods. It is worth noting that due to a number of features of the pathogenesis of the disease, drug therapy is used primarily to eliminate the etiological factor, as well as relieve pain. Despite the variety of therapeutic methods, surgical intervention remains the only advantageous and most effective solution.
Conservative treatment of ankylosis
Conservative therapy is used in the treatment of fibrous type ankylosis. In order to eliminate pain, physiotherapeutic procedures are used such as:
- mud baths;
- electrophoresis using painkillers;
- therapeutic exercises and massage;
- Spa treatment.
Surgical intervention for the treatment of ankylosis
In a situation where conservative therapy is not able to give the desired results or attempts to use it are obviously pointless, the time comes to make more radical decisions, namely, preparation for surgical intervention.
In order to eliminate bone tissue fusion, one of the following operations can be used:
- redressing – forced stretching of tissues with subsequent restoration of their anatomical position;
- osteotomy - a deliberate fracture of the joints in order to restore the natural connection of the articular ends;
- arthroplasty – isolating excess bone formations formed during the progression of pathology, using a spacer made of artificial material that ensures free movement of articular elements;
- endoprosthetics.
There is a list of contraindications to surgical intervention, including the active development of the inflammatory process in the periarticular tissues.
Drug treatment of ankylosis
Drug treatment is mandatory when performing operations of varying complexity.
In order to relieve inflammation before or after surgery, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) are used. If inflammation is observed before surgery, then surgical manipulations will become possible only after 6-8 months after the inflammation has resolved.
For fibrous types of the disease, treatment uses analgesics to relieve pain.
It is also worth noting that after the surgical intervention, in order to achieve the most effective result, medications from the group of chondroprotectors are prescribed, which help accelerate regeneration. Artracam is considered to be one of the most effective drugs of this type.
IMPORTANT! determination of the list of medications, as well as the dosage and duration of their use should be determined exclusively by the attending physician.
Ankylosis is the fusion of the bones of a joint. Do not let the joint become ankylotic!
Our doctors
Meet our specialists
Work experience 30 years Status Orthopedic traumatologist Qualification Doctor of the highest category
Donskoy E.O. Chief physician of the medical center "MEDICUS". Graduated from the First St. Petersburg State Medical University named after Academician I.P. Pavlov.
Work experience 12 years Status Vascular surgeon Qualification Doctor of the highest category
Nikitina O.A. Graduated from St. Petersburg State Medical University named after academician I.P. Pavlov. She completed an internship at the City Hospital of St. Great Martyr George.
Work experience 5 years Status Therapist Qualification Doctor
Nigai E.Yu. Works as a general practitioner at the Medical Center "Medicus". Conducts initial consultations with patients with various concomitant pathologies.
Work experience over 30 years Status Therapist Qualification Therapist
Danilchenko A.V. Conducts initial consultations with patients with various concomitant pathologies. Works as a therapist at the Medical Center "Medicus"
Work experience 15 years Status Orthopedic traumatologist Qualification Doctor of the highest category
Malofeev V.A. He is fluent in all the necessary methods of diagnosing and treating orthopedic pathologies and successfully restores patients.
Work experience over 30 years Status Nurse Qualification Nurse
Pugacheva O.N. Graduated from Leningrad Medical School. Works as a nurse.
Work experience 10 years Status Physiotherapy nurse Qualification Highest category
Murzakova A.Z. In 1981 she graduated from the Ufa Medical School. In 2012 - “Center for Advanced Training of Specialists No. 1”. Specialty: physiotherapy.
Work experience over 20 years Status Chiropractor Qualification Highest category
Azimov O.A. Specializes in the treatment of diseases of the joints and spine, rehabilitation after injuries and fractures. Works as a chiropractor at the Medical Center MEDICUS.
Work experience 4 years Status Nurse Qualification Junior nurse
Semenyuk E.B. Graduated from St. Petersburg Medical College No. 2. Works as a nurse at the Medical Center MEDICUS.
Work experience 30 years Status Nurse Qualification Highest qualification
Gadzhieva L.A. Graduated from Leningrad Medical School. Works as a senior nurse at the Medical Center MEDICUS.
What is the cause?
These can be joint fractures, arthritis, arthrosis, open wounds. Especially if such pathologies are accompanied by a long process of suppuration. Chronic infections can also cause this pathology. And infectious arthritis is considered perhaps the most common cause of ankylosis.
Staying in a cast for a long time can also cause ankylosis of the joints.
What are the signs to determine that ankylosis is developing?
The early stage of the pathology is characterized by poor joint mobility; at an advanced stage, its immobility occurs. With bone ankylosis there is no pain. With fibrotic pain syndrome can be observed if the joint retains the ability to rock.
Results of our patients BEFORE and AFTER treatment
Evgenia Semenovna, 67 years old.
Arthrosis of the knee, stage 3, was sent for joint replacement surgery. With the help of plasma, I coped with arthrosis in 3 sessions. Refused the cane. Avoided surgery. There is no pain, the cartilage and joint capsule have been restored. The duration of treatment is a week.
Pavel Ivanovich, 73 years old
Periarthrosis of the shoulder joint stage 2. I was treated by chiropractors, with leeches and needles - it didn’t help. The plasma caused the regeneration of lost tissue. Full mobility returned, chronic pain of 15 years went away. The treatment period is 10 days.
Natalya Igorevna, 59 years old
Osteochondrosis complicated by hernia formation. Excruciating back pain was relieved in one session. Neurological manifestations - goose bumps in the legs, numbness in the lower leg - disappeared after the second procedure. Course - 2 weeks.
Taisiya Romanovna, 82 years old
Arthrosis of the hip joint stage 3. The operation was refused due to his age and heavy weight. Plasmacytopheresis restored the joint capsule, restoration of articular cartilage and joint lubricating fluid production occurred. Course - 7 days.
Roman Stepanovich, 73 years old
Headaches, cervical osteochodrosis and vertebral hernias. As a result of treatment, headaches disappeared and pain in the cervical spine decreased. The pictures show restoration of the paravertebral tissues, reduction of the hernia.
How to reliably identify ankylosis?
In most cases, radiography is sufficient. However, there is a danger of mistaking ankylosis for contracture. If necessary, and for a more detailed examination, magnetic resonance and computed tomography are used. This is a more accurate diagnosis.
Diagnostic methods
Magnetic resonance imaging
The most effective and accessible research method, presenting information in 3D volume. MRI images are a clear illustration of what is currently happening with the patient’s spine, joints or other structures.
X-ray examination
A method for quickly assessing the condition of internal structures by obtaining an image using x-rays passed through an object. Fast, inexpensive, informative.
ULTRASOUND DIAGNOSTICS
Study of the body using ultrasonic waves. The ability to evaluate organs in motion. Passing through structures of different densities, ultrasound is reflected from them - this gives a picture of the state at the time of the study.
Biochemical analysis
This is a blood test. Show me your tests and the doctor will tell you who you are. This is the fastest and most accurate way to find out everything about the biochemical processes occurring in the patient’s body. Inexpensive, fast, effective.
Electrocardiogram (ECG)
Electrocardiography is the study of the electrical activity of the heart. For measurements, special electrodes are applied, the cardiograph records changes in the work of the heart and displays them in the form of a cardiogram.
How to treat ankylosis?
The main direction is to restore mobility, which means removing swelling and inflammation and eliminating pain, if any. Methods for helping with ankylosis are different; physiotherapeutic techniques, such as electrophoresis, UHF and others, are considered effective. In any case, the doctor has the final say. The MEDICUS clinic offers a full range of assistance for joint diseases, and if your joint needs help, sign up for the online registration using the registration form from the website or by calling 986-66-36.
Treatment methods
Joint reconstruction
1 procedure per course FREE!
Introduction of organic serum with hyaluronic acid into the joint capsule. As a result, cartilage reconstruction occurs Read more…
Neuroprotective therapy
Discount -10%! Only 3 days!
Neuroprotectors are new generation drugs that can restore the conduction of impulses in nerve tissues. Read more…
Plasmacytopheresis
1 procedure for the course is FREE!
Treatment and healing of cartilage with growth factors. Restoration of joint tissue with purified platelet blood. Read more…
Transdermal therapy
Discount -25%! Only 3 days!
The introduction of titanium glycerosolvate into a diseased joint is a unique method of drug delivery without surgery or painful injections. Read more…
Ultraphonophoresis
Discount -25%! Only 3 days!
This is an innovative way to administer medications using ultrasound, which has the unique ability to loosen tissue. Read more…
EHF therapy
Discount -25%! Only 3 days!
This is a promising method of physiotherapy with a great future. In life, waves of this range do not reach the ground, being dispersed in the atmosphere. The device generates these waves itself. Read more…
Infusion therapy
Combinations of drugs for drip administration through a vein. High digestibility and rapid achievement of therapeutic action make infusion therapy Read more…
Blockade
1 procedure for the course is FREE!
A joint or spinal block is a way to quickly help a joint or back. In case of acute pain, the blockade helps to quickly relieve pain and help locally Read more…
Introduction of chondroprotectors
"HONDRO" in Latin means "cartilage" and that says it all. Injection of cartilage cells into damaged segments of the spine Read more...
Autohemotherapy
Treatment using the patient's autologous blood cells. Blood is administered intramuscularly, which provokes the body to intensify the fight against chronic infection, suppuration and trophic ulcers, the immune system is strengthened and effectively resists new infections. Read more…
Laser treatment
Infrared healing with a wavelength of 0.8-0.9 microns affects the internal source of the problem. This relieves inflammation, swelling and pain in the joint. Degenerative processes in the joint fade away as metabolic processes inside the joint accelerate many times. Read more…
Peloid therapy
Nutrition and growth of cartilage cells using peloid dressings. The base comes from Lake Sivash, where mud with a high concentration of Dunaliela Salina microalgae, which is rich in beta-carotene, is extracted.
Why is ankylosis dangerous?
Complications of the pathology include respiratory failure, changes in the position of internal organs and disruption of their functions, skeletal deformation and, in some cases, complete disability.
Prognosis and probable complications of ankylosis
Ankylosis has a rather unfavorable prognosis. In most cases, the disease can only be overcome through surgical treatment.
Regardless of the success of the method used, the pathology is prone to reappearance (subject to partial prosthetics and simpler operations).
Full restoration of the motor function of the joint is extremely difficult to achieve, even with complete replacement of the affected tissues, because the surrounding muscle frame atrophies as the disease progresses.
Basic methods of surgical correction of TMJ ankylosis
If the patient has underdevelopment of the jaw, then at the first stage the surgeon lengthens the body of the lower jaw to normalize the position of the tongue and unblock the upper respiratory tract, eliminating hypoxia. This procedure is performed either by osteotomy, reconstruction of the lower jaw, or by the distraction method using an external or intraoral apparatus. At the second stage of treatment, a false joint is formed as close as possible to the real joint or plastic surgery of the temporomandibular joint is performed with a preserved, artificial or natural joint.
After surgical correction, the jaw is pulled forward and down, the fragments are separated by 2-3 cm, the bone is covered with metal or plastic caps, and soft tissue is formed.
Methods for preventing ankylosis
You can prevent the possibility of loss of functionality of joint joints at any age if you follow a number of medical recommendations, which include:
- timely contact a traumatologist if injury is suspected;
- proper treatment of acquired injuries of various parts of the musculoskeletal system, subject to the condition of preventing their prolonged immobility;
- systematic performance of gymnastic exercises and dosing of physical activity.
Remember that prevention is the best cure for any disease, even the most difficult to treat.
Have you been diagnosed with ankylosis? Do not despair, because a serious attitude to the recommendations of the attending physician, combined with modern medical technologies, can significantly improve the quality of life for various musculoskeletal diseases.
Pathogenesis and basic information
Ankylosis often develops against the background of autoimmune arthritis, but is less common after injury. It can appear in both young and middle age. Congenital ankylosis is very rare. The lower extremities, according to statistics, are more often subject to active ossification. With injuries, ankylosis of the knee usually occurs, and with ankylosing spondylitis, the spine is affected, starting with the iliosacral joints.
What is ankylosis
Pathogenesis is associated with the growth of bone tissue around the joint, which limits its movement. The phenomenon is similar to arthrosis, but the growths are not similar in structure to osteophytes. If inflammation continues for too long, the body, trying to “protect” the joint from destruction, begins to cover it with bone tissue. This restorative reaction underlies the formation of ankylosing spondylitis, which most often affects men aged 20 to 40 years.
Childhood TMJ ankylosis and its causes
The cause of the development of ankylosis of the TMJ in childhood may be the penetration of infection into the blood of a newborn, which is why ulcers appear in the bones and joints. Ankylosis can also be a consequence of injury, fracture of the condylar process and dislocation of the lower jaw. The joint cavity fills with blood, and hemarthrosis begins. In such a case, it is difficult for the child to eat, and a general delay in the development of the body may occur.
Orthodontists and oral and maxillofacial surgery specialists are involved in eliminating this disease. As a result of ankylosis, the lower jaw may remain underdeveloped and the bite may be disrupted, which doctors have to correct.
Doctors lengthen the damaged lower jaw and restore its mobility. At the same time, the bite is adjusted. After taking these measures, the facial skeleton will receive conditions for normal development and growth, full breathing will be restored, normal speech and the ability to chew food will return.
Main symptoms
Before approaching treatment, it is important to find out what symptoms accompany this disease.
The main symptom of the disease is problems with motor activity in movable joints.
With bone and fibrous ankylosis, there is no pain when walking. Discomfort in the hip joint occurs with incomplete ankylosis.
Varieties
According to the nature of the lesions, ankylosis is of the following types:
- Bone is characterized by immobility due to the connection of the articular ends. In this case, there is no joint space.
- The fibrous appearance occurs when scar adhesions appear between the joints.
- The extra-articular type is characterized by bony connections outside the joint.
It is worth noting the different types of contractures:
- Painful pain occurs with high muscle tone.
- Muscular ones are formed due to degenerative changes in the muscles.
- Cicatricial lesions occur when scars form from muscles, skin, and subcutaneous tissue.
- Primary traumatic ones appear with reflex muscle tension during an impulse to tissue damage.
- Osseous are associated with bone damage.
- Joint joints occur due to degenerative changes in tissues.
Ankylosis develops gradually. At first, significant pain and stiffness in the joints may appear in the morning.
The joint swells and becomes very hot to the touch. Then the pain decreases, and the joint becomes deformed.
Diagnosis and treatment methods
The difficulty of identifying pathology is determined by the anatomical specificity of the joint structure, as well as the polyetiological nature of the disease. It is important not only to identify the presence of arthrosis, but also to determine the cause of its occurrence. Diagnostic methods include:
- Conducting an initial visual inspection;
- Instrumental examinations of the oral cavity;
- X-ray and computed tomography;
- Collection of samples for laboratory research.
The treatment plan is drawn up based on the results obtained during the formation of the clinical picture, and may include drug treatment, physical therapy (including electrophoresis), orthopedic treatment, as well as surgery.
During the treatment period, it is recommended to establish a dietary regimen that reduces the overall load on the jaw joint. As part of dental intervention, the causes that influence the formation of excess jaw pressure are eliminated, including bite defects and dentition anomalies.