Arthrosis is just one of many joint pathologies. Very often it is accompanied by other chronic diseases, such as chondromatosis. In this disease, the cells of the synovial membrane are gradually replaced by cartilage cells, which is why the disease is often called “synovial chondromatosis”, or “coral joint”. Why is such a diagnosis dangerous and why is it often accompanied by osteoarthritis?
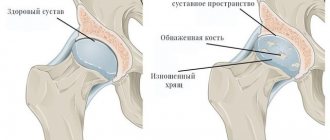
The symptoms of arthrosis and chondromatosis are very similar
Mechanism of disease development
At a certain point, the synovial membrane cells in the joint are partially replaced by cartilage cells. The latter form certain figures resembling balls and increase in size. Over time, they penetrate into the joint cavity and remain there, moving freely inside. The surface of the “balls” ossifies and becomes covered with layers of lime. Many folds and villi form on the synovial membrane - all this prevents the joint from functioning fully.
Most often, in 42% of cases, chondromatosis affects the knee joint
Etiology of the disease
For the first time, the presence of loose bodies inside the joint, which normally should not be there, was described in 1865 by the surgeon Munro. It was he who discovered the little body in the ankle joint, observed the patient and compiled the most detailed description of what was happening at that time. The name osteochondritis dissecans corpuscles was received in 1888 from another doctor who observed them in the knee joint.
Today, it is still not possible to accurately determine the origin of the disease. The disease often develops as a result of injury. However, there are patients who do not have traumatic injuries to the ankle, but there are pathological bodies.
The medial edge of the talus is primarily damaged by frequent, repetitive trauma. Various endocrinological disorders, the formation of microemoles, and growth characteristics of the body can play a role.
The trochlea area of the talus is also damaged mainly due to trauma. This occurs, for example, with supination, which must be combined with internal rotation and forced flexion.
Involvement of the medial trochlea of the talus is also possible with external rotation.
How to recognize chondromatosis: symptoms
The symptoms of the disease are not very obvious: a person may think that he needs treatment for arthrosis, osteoarthritis or arthritis. The joint begins to hurt and increases in size, the temperature of the skin around it rises against the background of the inflammatory process, movements are limited.
When the cartilaginous body enters the joint cavity, a sharp pain is felt. Until the pathological fragment leaves the lumen of the joint capsule, movements are completely blocked, and then restored in full. If such moments occur frequently, the cartilage is injured and secondary osteoarthritis develops.
Chondromatosis leads to wasting of the muscles around the joint
Reasons for activating processes
Due to the peculiarities of the development of pathology, it is almost impossible to determine the exact causes of its occurrence.
There is an assumption that a congenital pathological process is formed as a result of a violation of the embryonic differentiation of articular tissues.
The acquired form is usually associated with external causes that have a negative impact and disrupt metabolic processes within the tissues of the joint.
Additionally, it is noted that joint injuries of various sizes, as well as excessive loads and previous infections can act as a risk factor.
Diagnostics
Most often, if chondromatosis is suspected, radiography is prescribed in frontal, lateral and other projections. In addition to shadows from the cartilaginous bodies, the image will show changes characteristic of secondary osteoarthritis - bone growths and narrowing of the joint space. To clarify the diagnosis, you may need (at the choice of an orthopedist):
- CT;
- Ultrasound;
- arthrography;
- MRI;
- thermography;
- arthroscopy (performed simultaneously and for therapeutic purposes).
With the above symptoms, it is very important to distinguish chondromatosis from other joint diseases with similar symptoms. This may be primary osteoarthritis, neurogenic osteoarthropathy, Koenig's disease, or primary bone neoplasm. Depending on the diagnosis, treatment tactics will be developed.
What is arthroscopy and how can it help diagnose joint diseases?
60-75% of people with chondromatosis are men aged 20-60 years
Features of the clinical picture
Symptoms of the disease have similar features in both children and adult patients. Initially, when the pathology is just emerging, a person does not pay attention to slight changes in his well-being.
The progression of the disease initially leads to the appearance of unpleasant sensations in the ankle joint. They intensify when walking, with sudden movements, if you take an uncomfortable position. Initially, the discomfort subsides at rest, but as osteochondritis dissecans progresses, their duration and intensity increases, and they begin to bother you even with minimal or no exercise. In some cases, swelling of the affected joint is noted, and pain appears when trying to palpate the problem area.
The necrotic area of bone tissue is gradually separated from the main bone mass. Such particles are called “joint mice.” After the separation occurs, the person will begin to complain of a crunching sound when moving, a feeling as if the joint is “stuck” in the middle of some action.
Some patients develop joint blockage due to the presence of articular mice. In this case, the joint “jams” and the ability to move in any direction is lost. All this is accompanied by an acute pain attack that is difficult to ignore.
Treatment of chondromatosis
If it is confirmed, the only way to get rid of the pathology is through surgery - through arthrotomy or arthroscopy. During the operation, the doctor removes “articular mice” - parts of the cartilage that have broken off, as well as damaged areas of the synovium. Sometimes it is so damaged that it needs to be completely removed.
If, against the background of chondromatosis, treatment of secondary osteoarthritis with pronounced symptoms is necessary, the patient is often recommended to undergo endoprosthesis replacement of the affected joint or arthroplasty. If arthrosis has developed for another reason, it can be dealt with by intra-articular injections of Noltrex, a synovial fluid substitute. The presence of “articular mice” in the cavity, unfortunately, does not allow choosing this effective minimally invasive method.
Joint surgery for chondromatosis often ends in synovitis - inflammation
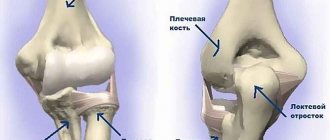
Anatomy of the ankle joint
The ankle joint is formed by the connection of three bones.
The talus bone is placed in the so-called fork, which is formed by the fibula and tibia bones on top. Below the talus lies the calcaneus, and together they form the subtalar joint. Ligaments are tough bands that connect bones together. The lateral complex of ligaments on the outside of the ankle joint is represented by three ligaments: the anterior talofibular ligament, the calcaneofibular ligament, and the posterior talofibular ligament. An ankle ligament rupture or inversion injury (internal dislocation) of the ankle most often involves damage to the anterior talofibular and calcaneofibular ligaments.
The implant is installed in the intervertebral space in a folded state (in the form of a rod with a diameter of 5 mm) using a special device. It also allows, after installation, to pull out the metal segments - teeth - from the rod. Two implants are installed in one intervertebral space.
The anterior talofibular ligament performs several functions:
- keeps the ankle and talus from moving anteriorly
- Provides both anteroposterior and lateral ankle stability
- limits foot flexion and inversion
- prevents internal rotation of the talus
The calcaneofibular ligament has the following functions:
- keeps the ankle joint from moving inward
- limits foot inversion
- prevents excessive extension of the foot
- prevents internal rotation of the talus
The posterior talofibular ligament is the strongest of the three lateral ligaments. This ligament is almost entirely surrounded by synovial membrane. Functions of the posterior talofibular ligament:
- prevents foot extension
- limits rear movement
- limits external rotation of the talus
- short fibers of the ligament inhibit excessive adduction of the foot
The deltoid ligament is located on the inner side in a triangular shape. The deltoid ligament plays a large role in stabilizing the ankle joint. The deltoid ligament performs the following functions:
- inhibits excessive eversion (turning outward) movements of the foot
- inhibits flexion, pronation and external rotation of the foot
- prevents valgus (outward) tilt of the talus
Procedure (operation) for sanitation arthroscopy of the ankle joint.
Recovery period
As after treatment of arthrosis, in the recovery period it is important to follow the doctor’s recommendations and undergo the necessary physical procedures. The scheme is similar: laser therapy, compresses, warming up, exercise therapy, special exercises on simulators to develop joint mobility and restore blood circulation. The goal of all measures is to enhance the production of natural synovial fluid, which will cover the cartilage and will fully perform shock-absorbing functions.
In general, after surgery, the prognosis for recovery is favorable. But in isolated cases, benign formations still turn into malignant ones. Only a doctor can detect the cause and make an accurate diagnosis in order to prevent complications, because the symptoms of joint diseases are very similar.
Joint pain and limited mobility are a good reason to consult a specialist without experimenting with home recipes for treating arthrosis or arthritis. Some will benefit from a planned course of Noltrex intra-articular injections, while others will have to agree to surgery if the diagnosis of chondromatosis is confirmed. Trust an experienced orthopedist and don’t wait for the disease to progress!
Current classification
There are several criteria by which the classification of chondromatosis is formed. First of all, this is the type of pathology by which they determine:
- congenital - heads the category of true articular dysplasia and progresses with the formation of tumors;
- postnatal – benign or malignant (chondroma/chondrosarcoma, respectively).
The second criterion for classification is the form:
- stable - occurs with a small number of formed bodies (single or multiple), after which their formation slows down greatly or stops altogether;
- progressive – the development process is accompanied by the continuous formation of tumors (the number is not limited);
- rare.
Prevention
Preventive measures to prevent the occurrence of the disease or reduce the likelihood of its complications include:
- balanced diet;
- systematic performance of gymnastic exercises;
- rejection of bad habits;
- eliminating the possibility of hypothermia;
- control of optimal body weight indicators;
- timely treatment of various types of diseases;
- systematic preventive medical examinations.
A long course of degenerative-dystrophic processes without proper treatment can lead to the development of lameness and disability of the patient.
Remember, maintaining a healthy lifestyle, adjusting your daily diet and systematically visiting your doctor is the key to effective prevention of the development of the disease.
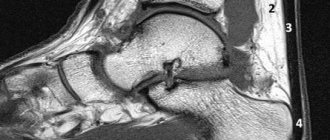
Degree of damage to the cartilage of the talus
Treatment methods
Conservative treatment
- orthopedic mode - unloading of the ankle joint using orthopedic products (crutches)
- To relieve swelling and reduce pain, the use of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, a course of physiotherapy, and physical therapy are prescribed
- intra-articular injection of hyaluronic acid preparations
- intra-articular injection of platelet-rich plasma (make an active link with the transition to)
- SVF – therapy (make an active link with a transition to)