Intervertebral hernia is a protrusion of an intervertebral disc. In normal condition, the intervertebral disc is a shock-absorbing pad between the vertebrae, flattened on both sides, which is held in place by the spinal ligaments. Due to age-related changes, injuries and chronic diseases, the disc tissue can become thinner, the ligaments can weaken, which leads to a bulging disc.
Intervertebral hernia, regardless of its form, is manifested by the following symptoms:
- back pain that gets worse with exercise;
- a feeling of tension in individual back muscles;
- muscle weakness;
- disturbance of urination and defecation;
- dizziness and headaches;
- numbness of the fingertips or individual areas on the arms and legs.
In the absence of proper treatment, the hernia passes from one stage to another, increasing in size, which can ultimately lead to disability and the need for surgical intervention.
Spinal hernia - Symptoms
A herniated disc can significantly ruin the happy life of every person. Spinal hernia not only causes pain and discomfort, but is also a dangerous disease for health and life! It is possible to determine the signs of an intervertebral hernia at the initial stage of development of a spinal hernia. However, there are certain difficulties in diagnosis, because many of its symptoms are similar to those of other ailments.
Specific symptoms that you should definitely pay attention to:
- stiffness of the spine when moving in the morning;
- numbness of the limbs;
- dull pain in the spine that occurs when standing up;
- deterioration of posture;
- lethargy in the muscles.
Indirect symptoms
- impotence;
- urinary disturbance;
- menstrual irregularities;
- constipation;
- urinary disturbance.
Spinal hernia: pain characteristics
- As a rule, pain is concentrated in the spine. Its appearance is due to the fact that the nerve root compresses the protruding spinal disc, pressing it against the spinal column.
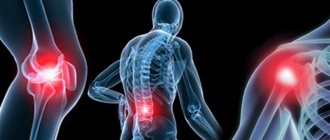
- Depending on the location, pain can be felt in the chest, arms, shoulders, legs, back of the head, rectum, and even in the perineum.
- Mostly, unpleasant sensations appear during movements: bending or bending.
- Often pain in the spine makes itself felt in the morning due to the fact that the disc remains in the same position for a long time.
- It is important to pay attention to the area where pain is concentrated, because... in the case of a herniated disc, it appears in only one part of the body.
How to determine the shape of an intervertebral hernia based on the type of numbness? Symptoms of hernias of different parts
- If the hernia is lumbar, then its main manifestations are pain in the buttocks on the outside of the leg.
- If a nerve is pinched in the sacral region, the discomfort is less pronounced. However, the calves and feet lose their sensitivity. In addition, numbness may appear in the buttocks, lower back and legs.
- Headaches occur with chest and neck pathologies. In this case, the unpleasant sensations intensify when turning and tilting the head. In addition, you should not forget about such signs of intervertebral hernia as dizziness, attention and memory disorders. Intervertebral hernia is accompanied by chest pain, which often radiates to the arm. Also, the patient may experience uncomfortable feelings while turning the body. Tingling sensations are felt between the shoulder blades and in the hypochondrium. These symptoms are often confused with signs of cardiovascular disease.
Characteristic symptoms of intervertebral hernia
If you cannot independently distinguish between the signs of a herniated disc and other ailments, then you should pay attention to the complex symptoms. How does intervertebral hernia manifest itself? So, this disease is characterized by:
- increased feeling of discomfort during movements (even during coughing, chewing and bowel movements);
- less pain when standing, sitting or lying down.
These symptoms of a hernia should be followed in order not to confuse the disease with myositis, intercostal neurology, and heart ailments.
Symptoms
A hernia is very easily identified - an atypical bulge appears in the area where it formed. When pressing on it, a person feels discomfort and pain. Additional symptoms include nausea, discomfort, and pain with certain movements. The symptoms of the disease depend on where exactly this pathology appeared. A vertebral hernia manifests itself especially pronouncedly. Due to the fact that the nerve endings are pinched, patients note numbness in the fingertips, tingling and other unpleasant symptoms. At the same time, the mobility of the spine significantly worsens. For example, straightening up without the help of others becomes very difficult.
How to deal with intervertebral hernia, and most importantly, get rid of all its painful symptoms?
There are two methods: surgical and non-surgical. Our clinic practices a non-surgical method that includes an integrated approach. Our specialists will prove to you that intervertebral hernia is a nuisance that anyone can overcome, enjoying a happy, comfortable and healthy life! We believe that non-surgical full restoration of a spinal hernia (in most cases this is possible) is effective only with an integrated approach. Our center uses comprehensive treatment for spinal hernia with an individual approach. The medical center’s specialists use the entire arsenal of tools that can cure spinal hernias in our patients, restoring their joy of life and ability to work. We try to save our patients time and money, and we do this without compromising the quality of their hernia treatment. A herniated disc is one of the most complex diseases of the spine, but there are means and methods to combat this disease.
Diagnostics
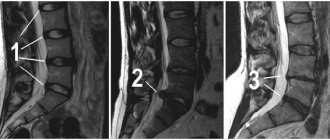
Making a diagnosis begins with an initial examination by a specialist. He determines the presence of a problem, and then prescribes the most appropriate examination in this case. Most often, this is an ultrasound, thanks to which it is possible to establish the size of the pathology, its neglect and concomitant pathologies. If the disease is localized in the spine, then an X-ray or CT scan is prescribed - all the features of the anatomy of the bones are clearly visible in the pictures. But if it is necessary to visualize soft tissues, then computed tomography is combined with myelography. The most universal and informative method of examination for any hernia is MRI, which clearly shows both soft and bone tissues.
Photodynamic therapy
PDT is a unique technique that requires the use of low-intensity laser radiation with a specific wavelength and photosensitizers (drugs that are sensitive to light) that have the ability to selectively accumulate in pathologically altered cells and tissues (sclerosation, dysplasia, tumor, etc.) which are destroyed during treatment and are deleted. During laser irradiation, a photodynamic reaction occurs; the catalyst for this reaction is singlet oxygen; healthy cells do not react to this reaction. The advantage of PDT is safety; there is no toxic effect of the drug. Even 1-2 PDT procedures create conditions conducive to reducing the size of the vertebral hernia with future decompression of soft tissues.
Types of hernia
The classification of hernias is determined by organs and location. In this regard, hernias are distinguished:
- muscular,
- on the diaphragm
- inguinal,
- umbilical,
- vertebrates,
- sternal, etc.
The most dangerous are vertebral types - they represent a displacement of the disc with subsequent trauma to the fibrous ring. Vertebral hernias, in turn, are divided into several types depending on the location of the problem: lumbar or cervical, intervertebral.
Magnetic pulse stimulation
MIS uses a powerful magnetic stimulator up to 4 Tesla. Short-term magnetic pulses and a high-intensity electromagnetic field easily penetrate and affect deep nerve centers, the spinal cord, and peripheral nerves that are inaccessible to other methods of stimulation. The number of positive results of the new method - photodynamic removal of herniated intervertebral discs - has clearly increased. A spinal hernia is a complicated form of disc protrusion; only timely consultation with a doctor will help you prevent the occurrence of a spinal hernia. You can find out more here From protrusion to spinal hernia.
Treatment methods for intervertebral hernia in Scandinavia
In most cases, our doctors are able to cure patients without surgery using the following methods.
- Massage of the back and neck-collar area.
- Physiotherapy.
- Physiotherapy, including acupuncture.
- Drug therapy with muscle relaxants to reduce muscle tension.
- Injection techniques, various types of drug blockades.
In advanced cases, the doctor may prescribe removal of the hernia. Our clinic is equipped with endoscopic devices, which allows us to perform operations through a puncture in the skin, that is, as efficiently, quickly and painlessly as possible.
Hospital treatment in comfort
More details
Benefits of treatment from professional doctors
There are several reasons why it is best to trust experienced specialists, namely:
- Before starting treatment, the patient must be carefully examined to obtain as much information as possible about the condition of the intervertebral hernia. In particular, data on the localization of the protrusion, its features and size are important.
- The treatment program is drawn up based on the information obtained during the examination and the personal wishes of the patient. The doctor thinks through the treatment plan in such a way that the patient can attend procedures without compromising his usual lifestyle.
- Treatment is carried out using modern equipment. Experienced doctors who have undergone special training are introducing more and more innovative techniques.
- Experienced doctors use only an integrated approach in treatment. Experienced specialists at the Vlasov Medical Center will ensure that intervertebral hernia stops bothering you.
Which doctor treats hernia
Usually, visiting just one specialist is not enough. The patient has to undergo a full examination in order not only to identify the hernia and all its features, but also to establish the reasons why it occurred, as well as to determine possible complications.
Depending on the factors that provoked them, different specialists treat hernias.
- Therapist. This is the first doctor you should contact if unusual symptoms appear. The specialist’s task is to make an approximate diagnosis and prescribe the necessary examinations. After this, the therapist refers you to a more specialized specialist.
- Vertebrologist. The most likely doctor who will carry out treatment in the future. This doctor specializes in problems related to spinal health. So a consultation with him will be needed if a hernia of this part of the body is detected. The vertebrologist finds out the features of the deviation, the reasons due to which it appeared, prescribes additional examinations and tests, and on the basis of this prescribes treatment.
- Neuropathologist. Usually works in tandem with a vertebrologist. He is involved in treatment if a vertebral hernia is accompanied by pinched nerves and impaired spinal circulation. Its task is to prevent disturbances in the functioning of the spinal cord and, if any have already appeared, to eliminate them. It will also help determine the cause of the vertebral hernia.
- Traumatologist. Included in treatment if the hernia is the result of an injury. The goal of this doctor is to determine how serious the injuries are and to identify whether there are other, as yet hidden, consequences of the traumatic injury.
- Osteopath. It will help if the hernia is small and not advanced. The methods used by this specialist usually do not involve long-term drug treatment or dangerous surgery. Most often, he prescribes an individual course of physical therapy. The effectiveness of the technique in 35% of cases allows you to do without surgical intervention. In addition, this is the best way to avoid recurrence of the hernia and strengthen the skeletal muscles.
- Surgeon. Usually this doctor is prescribed if surgical treatment is required. Only in rare cases does a specialist allow you to do without it. Surgery is required if a nerve is pinched, the location of the vertebrae has changed, or the spinal cord tissue has become inflamed. Everything is accompanied by unbearable pain and can lead to serious consequences, including disability. Therefore, the help of a surgeon in such a course of the disease is simply irreplaceable.
Which specialist the patient ends up with depends, first of all, on the advanced stage of the disease. It is advisable not to delay visiting a doctor and make an appointment at the first signs of pathology. Then, most likely, it will be possible to manage with the help of a local therapist.
Advantages of endoscopic removal of cervical disc herniation
Why, when faced with a choice, is it better to undergo endoscopic surgery to remove a hernia in the cervical spine?
- There is no need to additionally install a fixing interbody cage or implant.
- The mobility of the operated segment of the spine will be completely preserved.
- The integrity of the intervertebral disc itself is preserved (no need to perform a disectomy).
- The development of adjacent segment syndrome is excluded.
- There is no risk of damage to nerve endings, blood vessels and muscle fibers.
- High controllability.
- Good cosmetic effect (no noticeable scars, which can be especially important for patients with an individual tendency to keloid and hypertrophic skin scars).
Features of removal of a hernia of the cervical spine
Cervical hernias are less common than lumbar hernias and are more difficult to remove. Firstly, this part of the spine is highly mobile. Secondly, the aesthetic consequences of surgery are more difficult to hide. Thirdly, the architecture of the cervical spine is penetrated by a network of fine nerve plexuses and vessels that supply the spinal cord and brain, and the vertebrae themselves are smaller than in the thoracic or lumbosacral segment. The cost of error or inaccuracy when performing such an operation is high. In this regard, preference is given to endoscopic spinal surgery to remove a hernia. However, such an operation is unfortunately not always possible. For example, in the presence of osteophytes in the cervical spine, significant canal stenosis, which are detected by CT (computed tomography) results, there is a risk of destabilization of the spinal segment in the future. Therefore, in this case, a microsurgical operation with the installation of an implant or a fixing interbody cage may be more appropriate. The choice of one or another method for removing a hernia of the cervical spine is also influenced by the localization of the pathology and the type of surgical approach that is possible in this case, as well as the size and specificity of the hernial formation.
How is the operation for endoscopic removal of a cervical hernia performed?
The neurosurgeon makes a small (7 mm) incision in the back of the neck. Under X-ray control, a working port is installed in the wound, into which an endoscope with a diameter of 6 mm is inserted, equipped with micro-forceps, a micro-camera, light and flushing channels. The hernia is removed under detailed visual control. During the intervention, the neurosurgeon carefully moves apart the adjacent muscles, ligaments and soft tissue fibers without injuring them. To gain access to the spinal canal and decompress the spinal root, a small foraminotomy (widening of the intervertebral foramen) is performed. After endoscopic removal of a cervical hernia, that is, cleansing the spinal canal, the pain goes away immediately. The neurosurgeon applies a single suture, which is removed after 10 days. Mobility returns the same day. The duration of hospitalization is 1 day, after which the doctor discharges the patient from the clinic home with simple recommendations for recovery. Recovery is comfortable, so within a month the patient can return to work and normal life.
Intervertebral hernia in the lower back. Treatment during an exacerbation. What to do?
If there is a sequestered disc herniation that compresses the root, the patient experiences severe pain, there are signs of sensory impairment, weakness in the leg, and non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs are powerless, then the neurosurgeon is clearly inclined to surgical treatment. The effect of the operation is comparable to the effect of an extracted tooth - relief occurs immediately after surgery.
When the pain does not radiate to the leg, but only bothers the back, then most often we are dealing with spondyloarthrosis.
In this situation, it is possible to be conservative, i.e. without surgery. It includes taking NSAIDs, bed rest, wearing orthoses, physiotherapy, massage and even manual therapy (with a skillful approach), various types of therapeutic blockades. Methods of denervation of the causative facet joints are also used - radiofrequency denervation of the facets.
Outside of an exacerbation, the patient must develop a motor behavioral stereotype for himself, go to the pool, get a massage, do fitness, and normalize weight.